2025 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part VIII
A city’s infrastructure has a large impact on its community. Part VIII of the 2025 Study Architecture Student Showcase features projects that reimagine infrastructure in innovative ways. With interconnectedness at the forefront, these designs re-envision highways, commuter routes, and hybrid energy sources. Each project presents a design solution that increases accessibility, promotes connection, and makes a positive difference in its respective community.
Scroll down for a closer look at these outstanding projects!
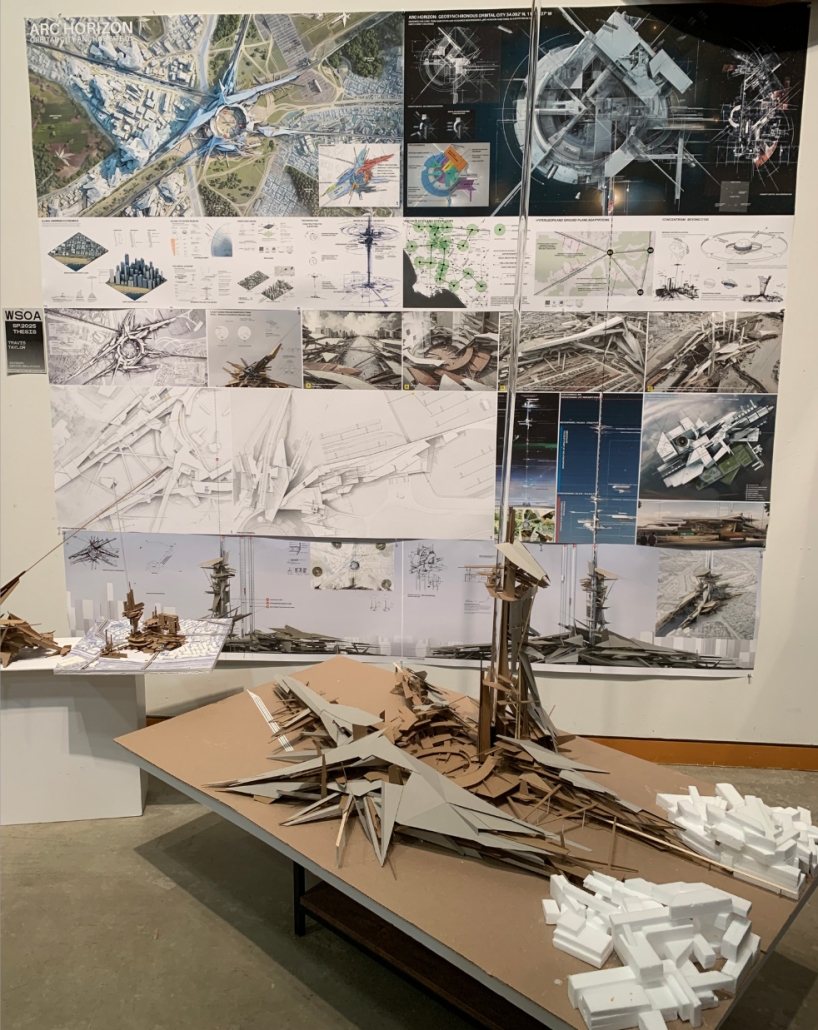
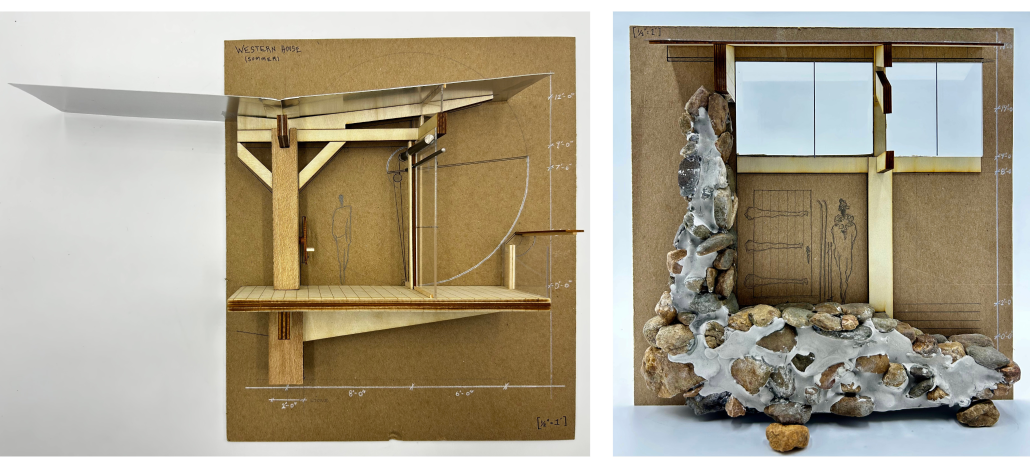
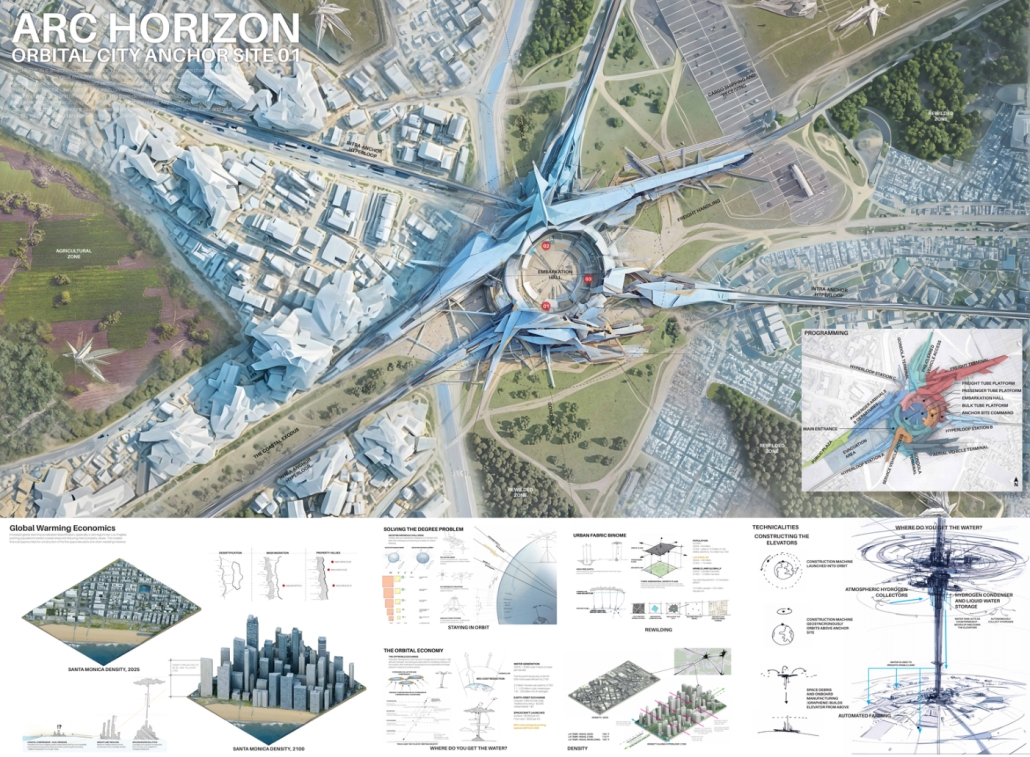
ARC HORIZON: Anchoring Humankind’s Future in the Orbital Era by Travis Colton Taylor, B.Arch ’25
Woodbury University | Advisor: Gerard Smulevich
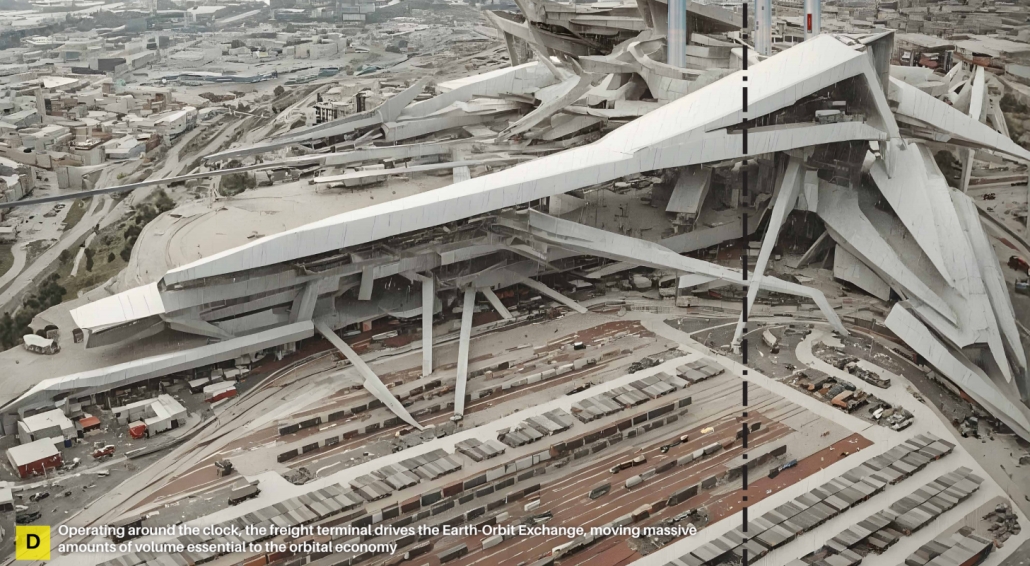
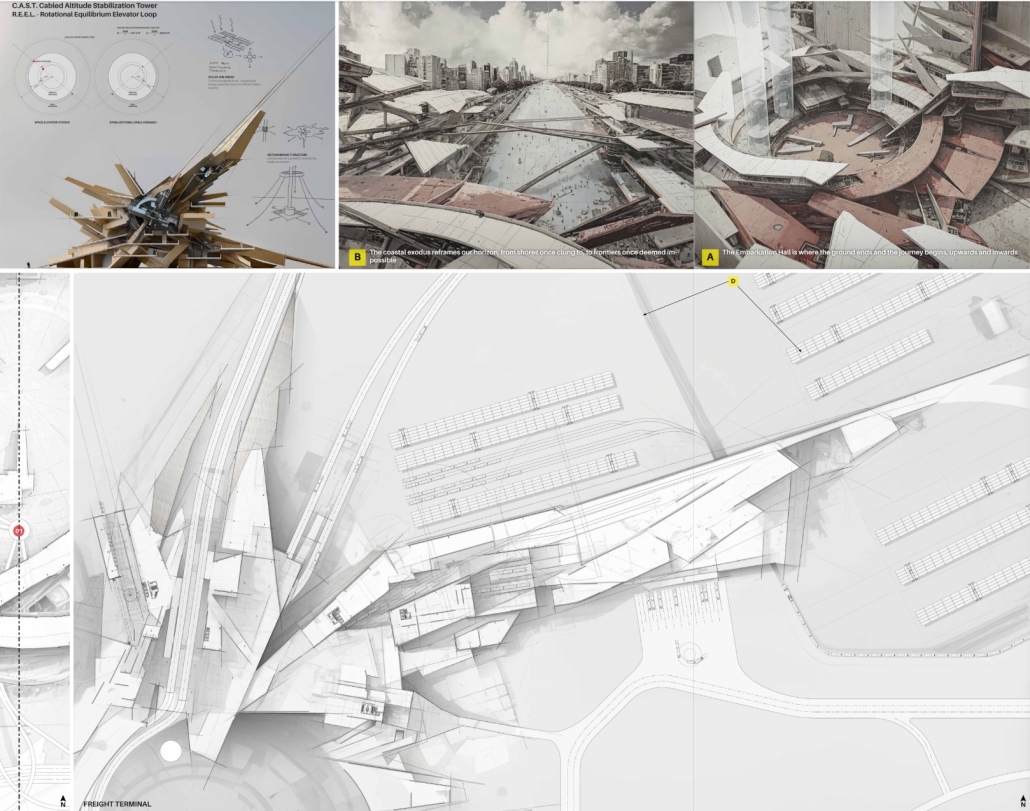
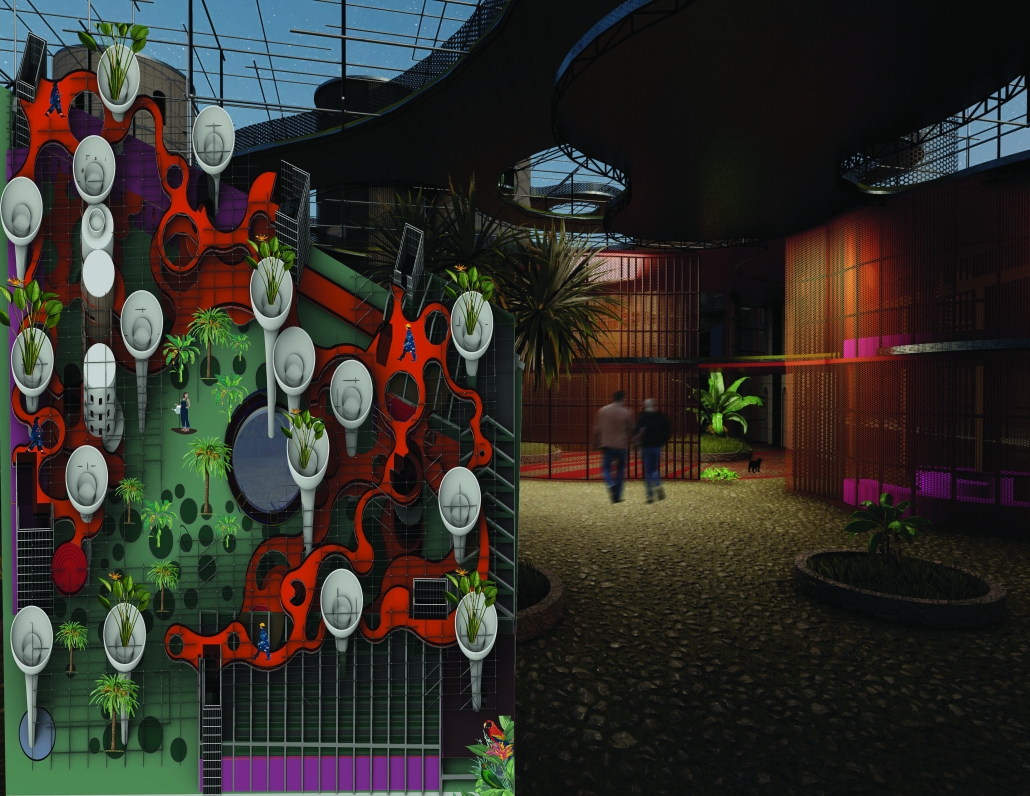
“Arc Horizon” is an architectural redefinition of urban fabric in response to climate change, resource scarcity, and technological evolution. Faced with desertification, migration, and the weaknesses in traditional cities, humanity shifts toward vertical urbanism and orbital expansion. Anchor site mega-structures and orbital cities form a new interconnected system, enabling rewilding on the surface, autonomous mobility, and off-world industry. This three-dimensional urban fabric transcends terrestrial limits, catalyzing a regenerative, symbiotic relationship with the planet. As the orbital economy supplants geopolitics, humanity transitions to an interplanetary species, one that thrives across Earth and orbit, united through innovation and stewardship of the planet.
This project received the Architecture Degree Project Design Excellence Award.
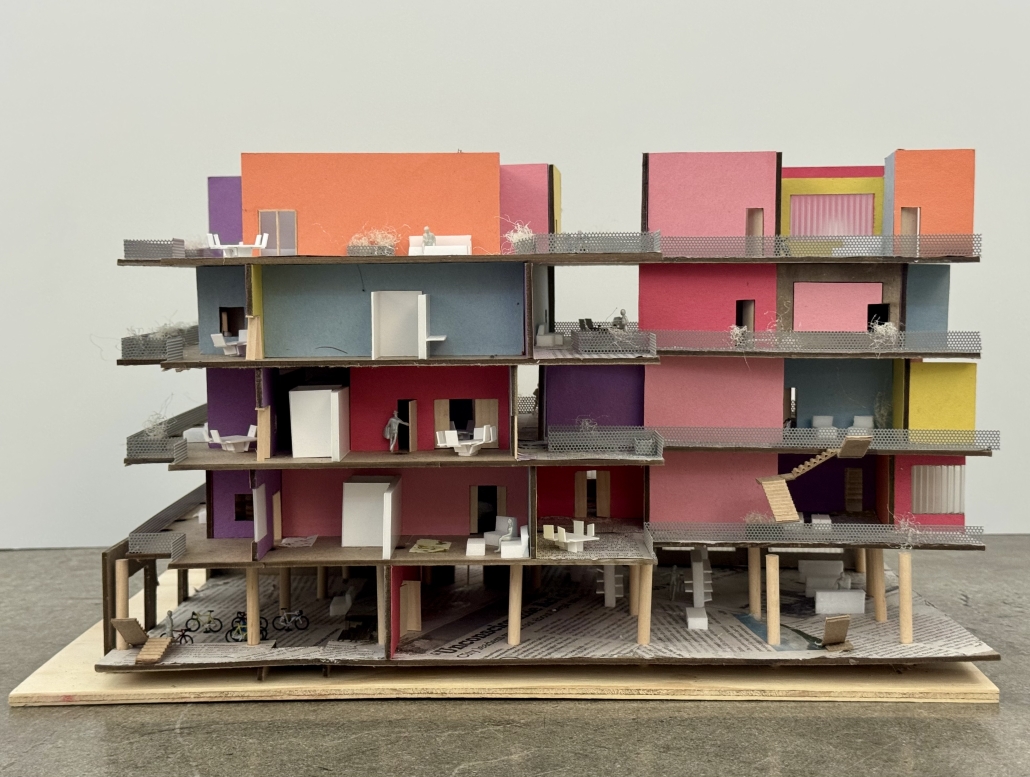
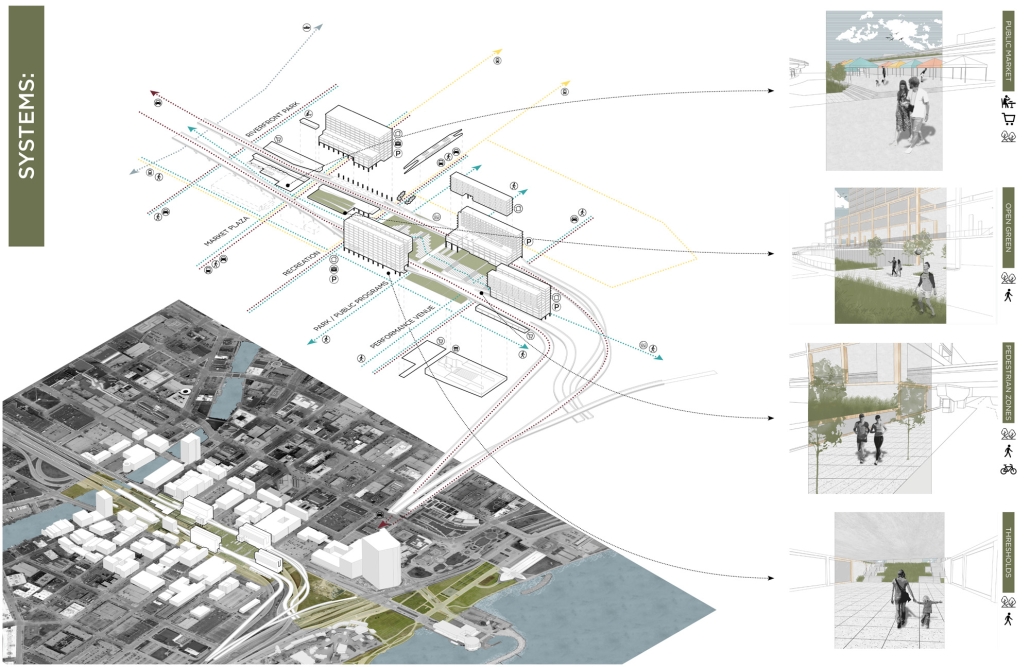
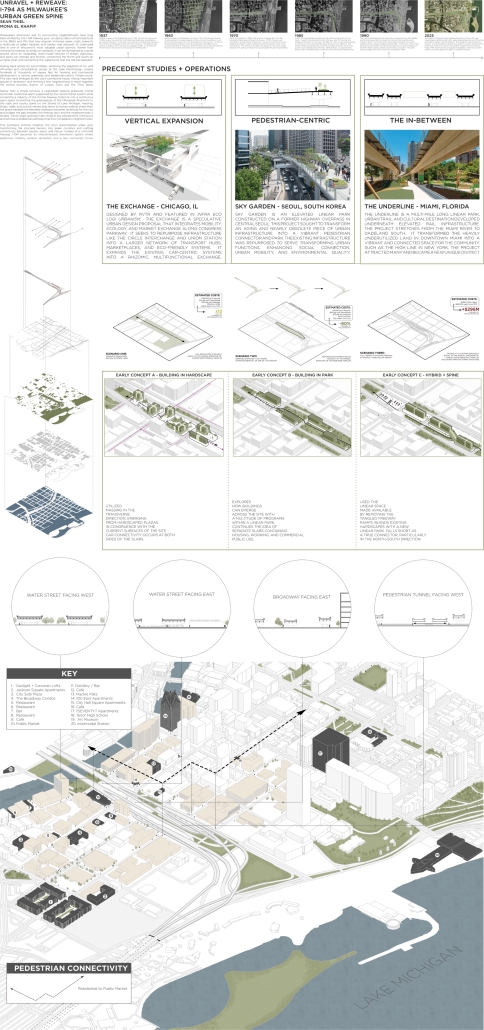
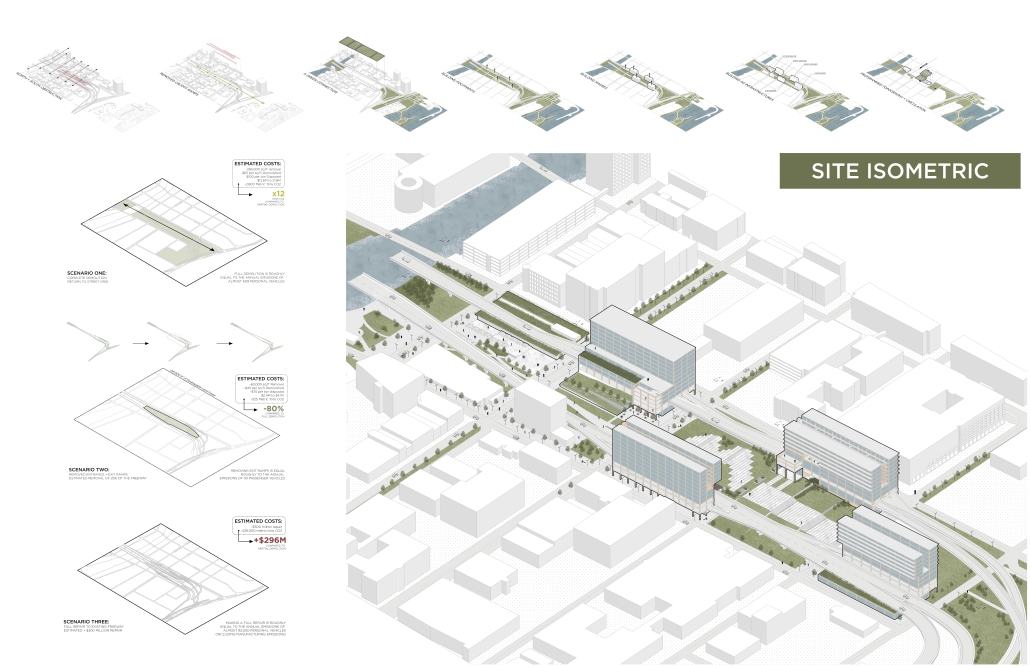
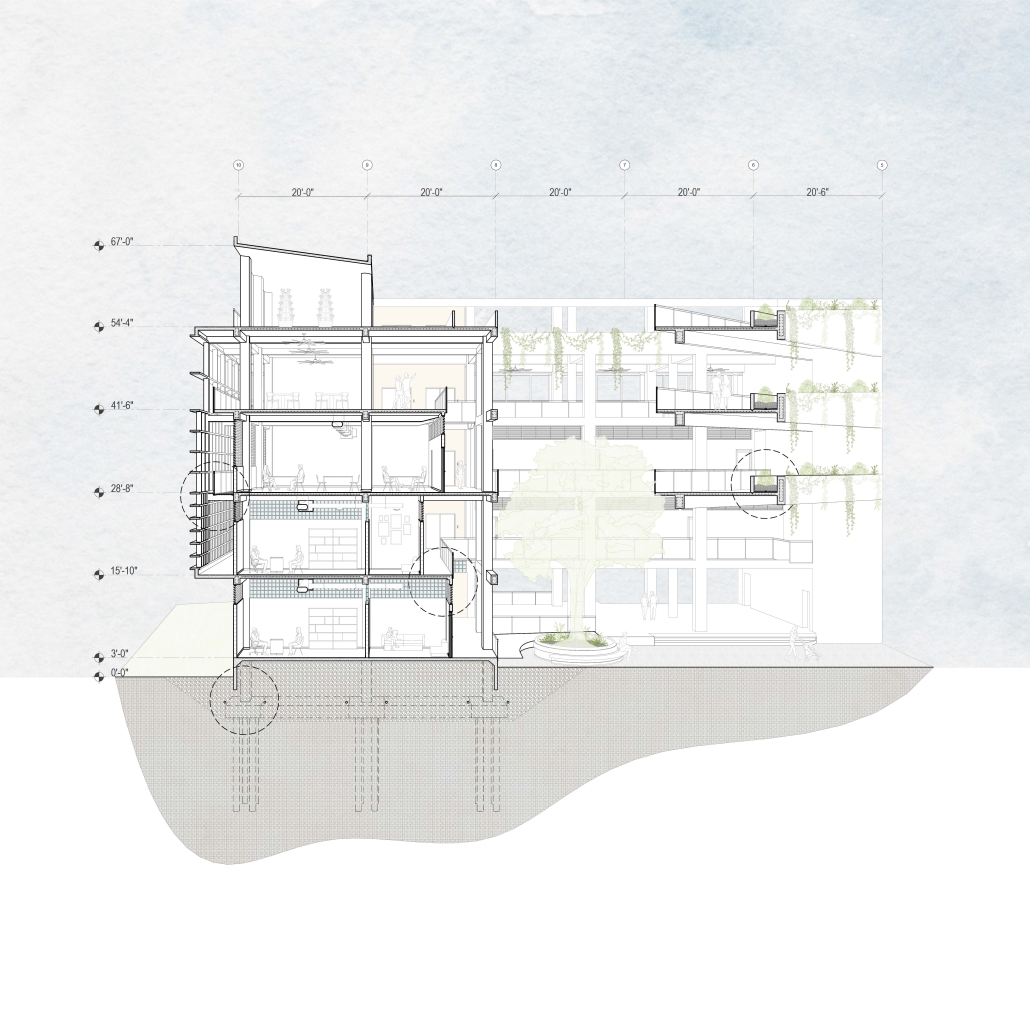
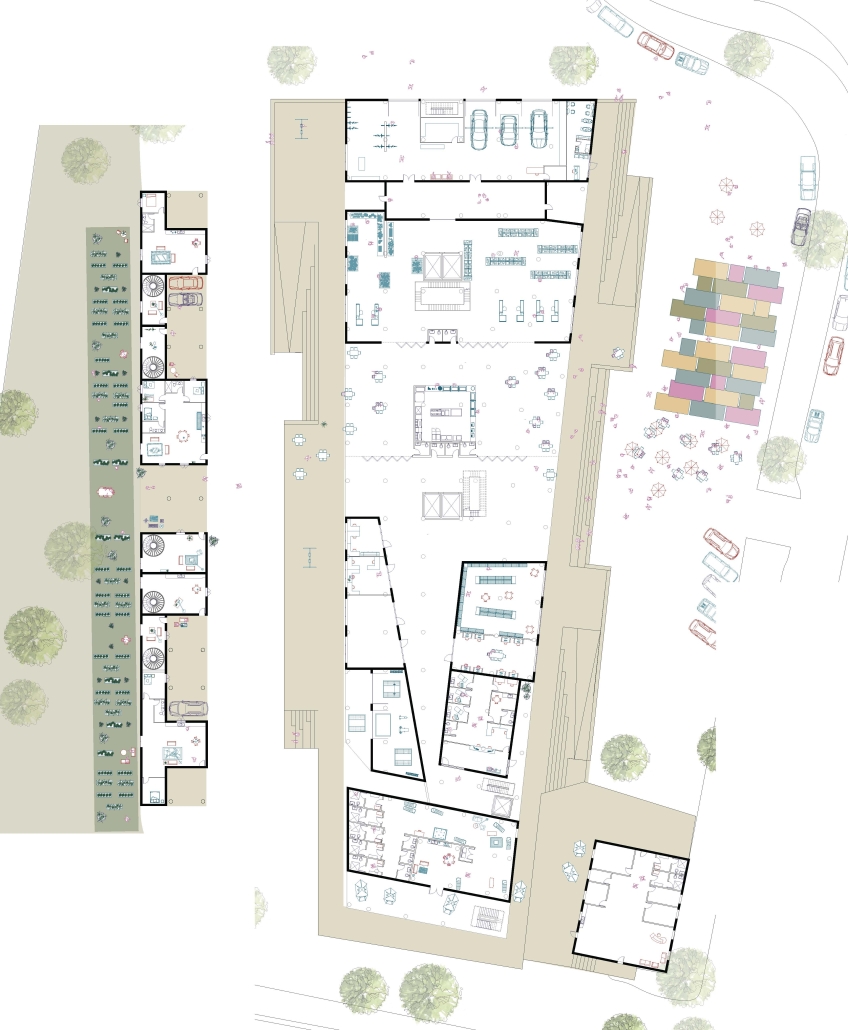
UNRAVEL & REWEAVE: I-794 AS MILWAUKEE’S URBAN GREEN SPINE by Sean Thiel, B.S. in Architecture ‘25
University of Virginia | Advisor: Mona El Khafif
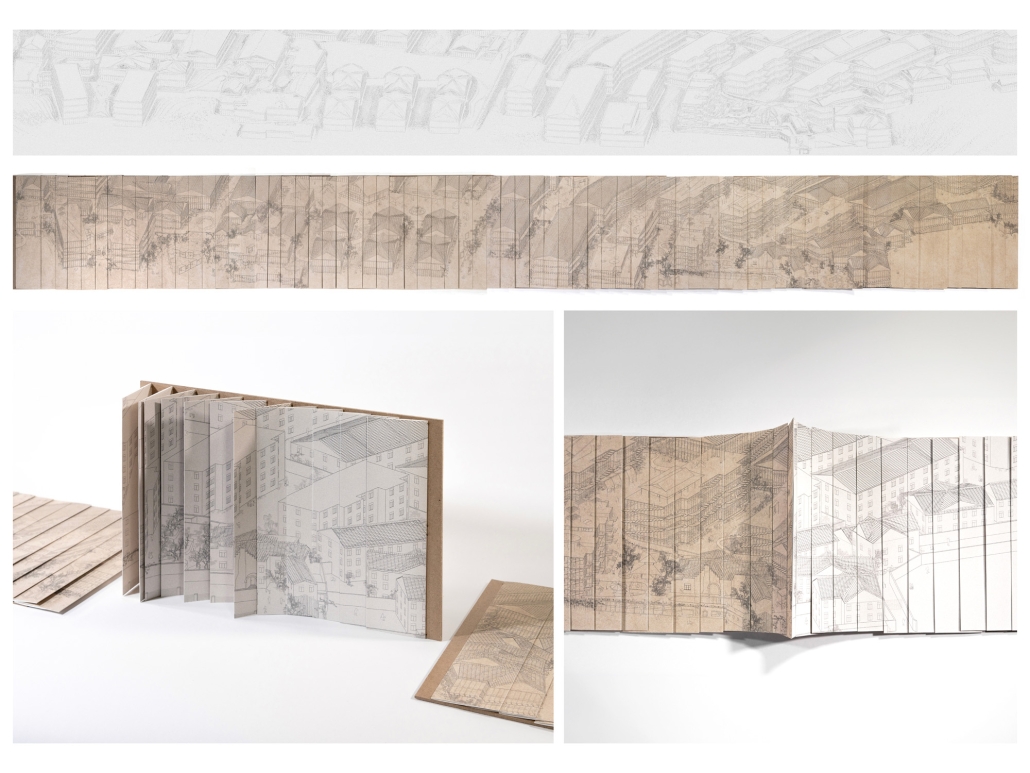
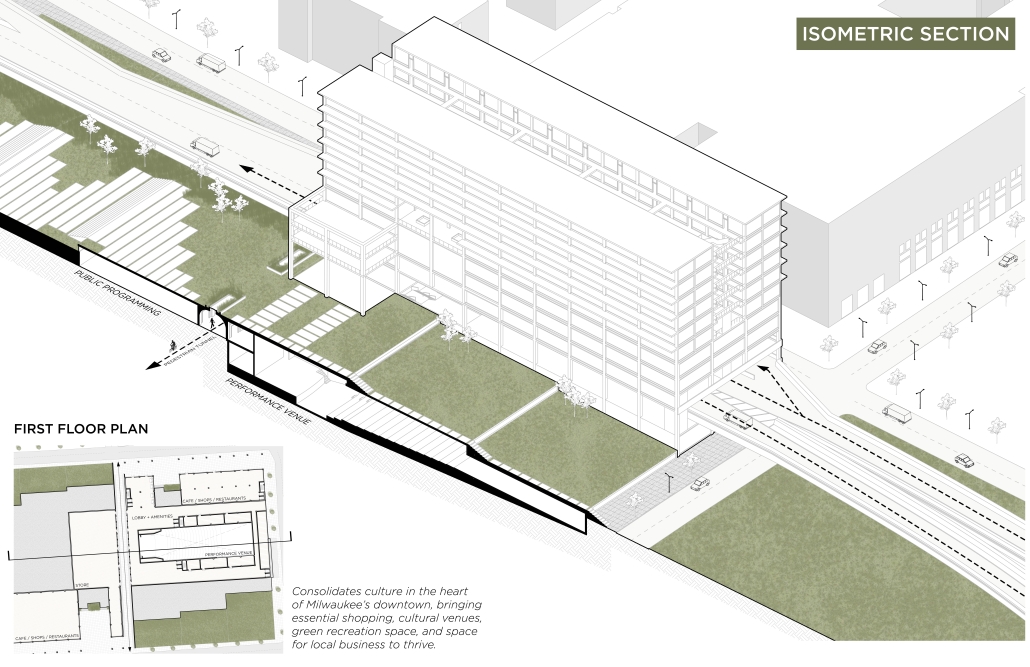
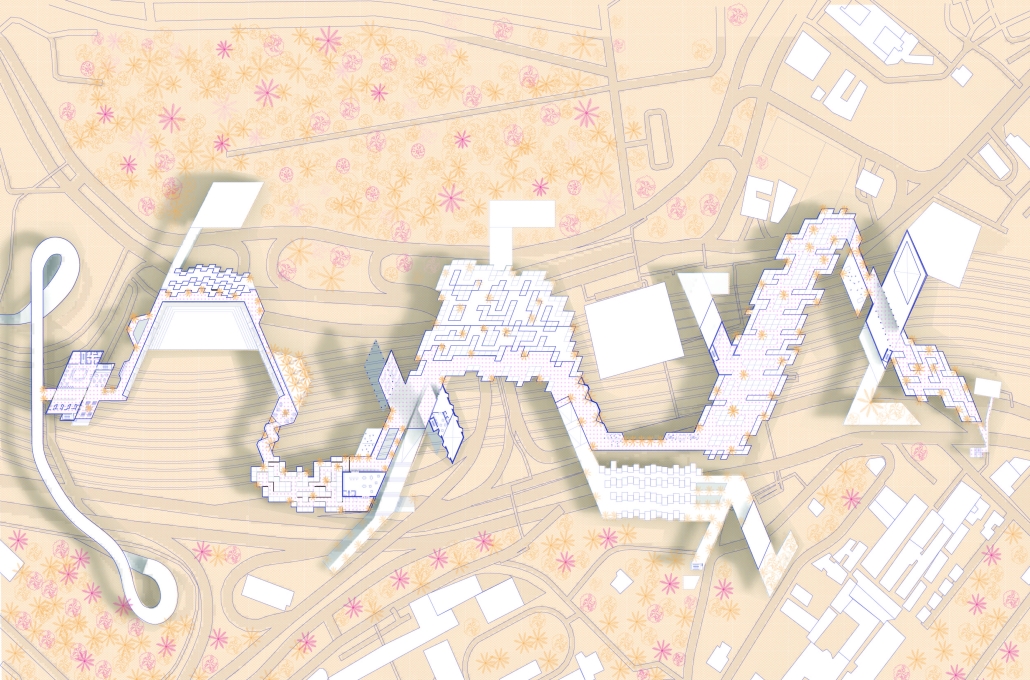
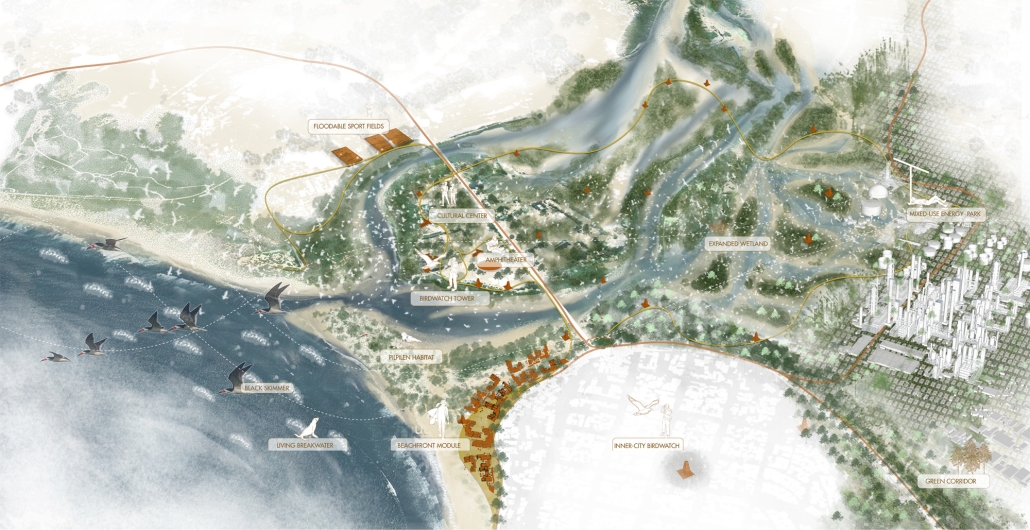
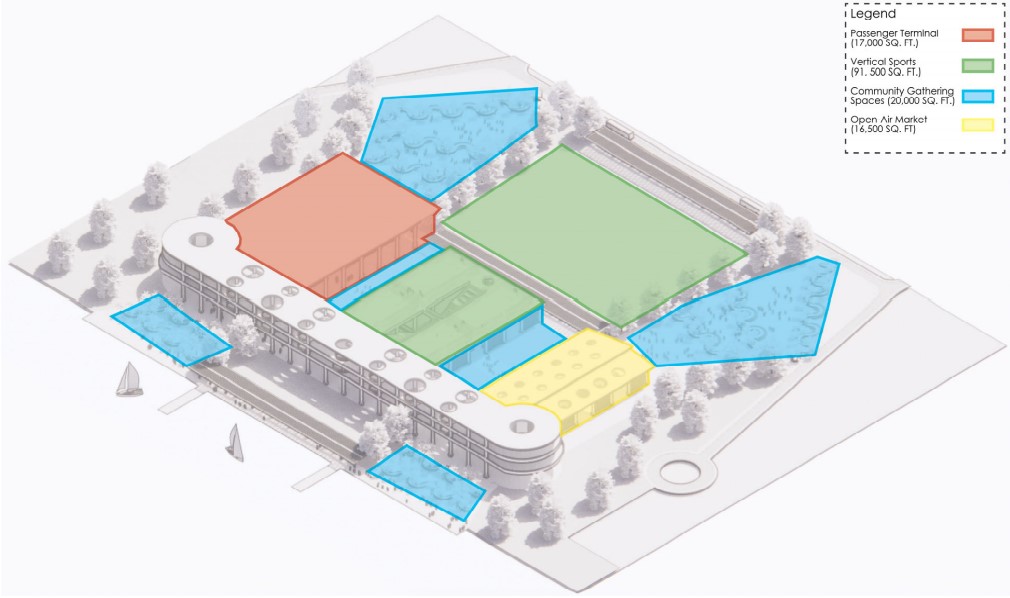
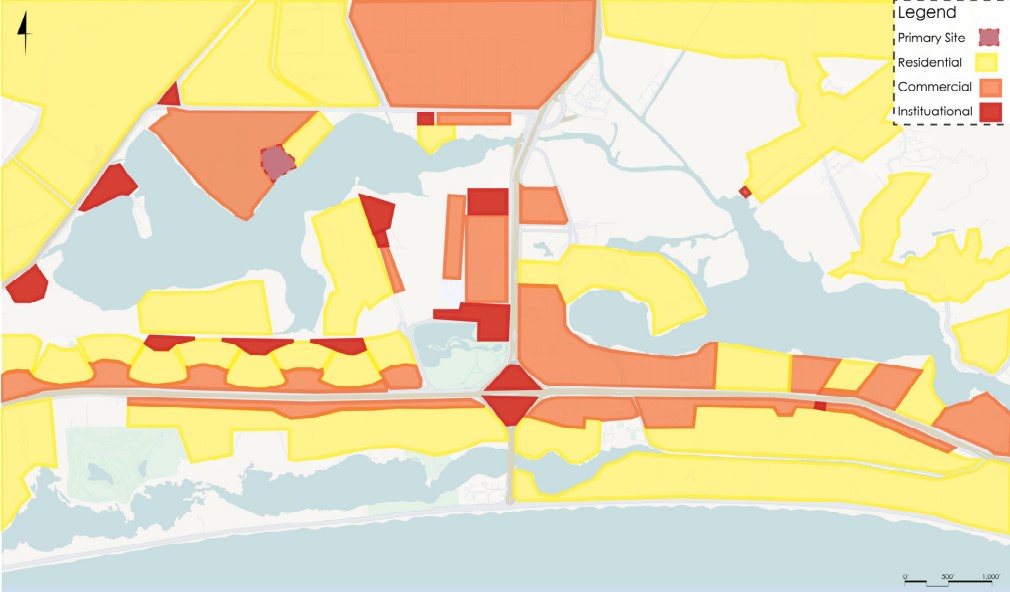
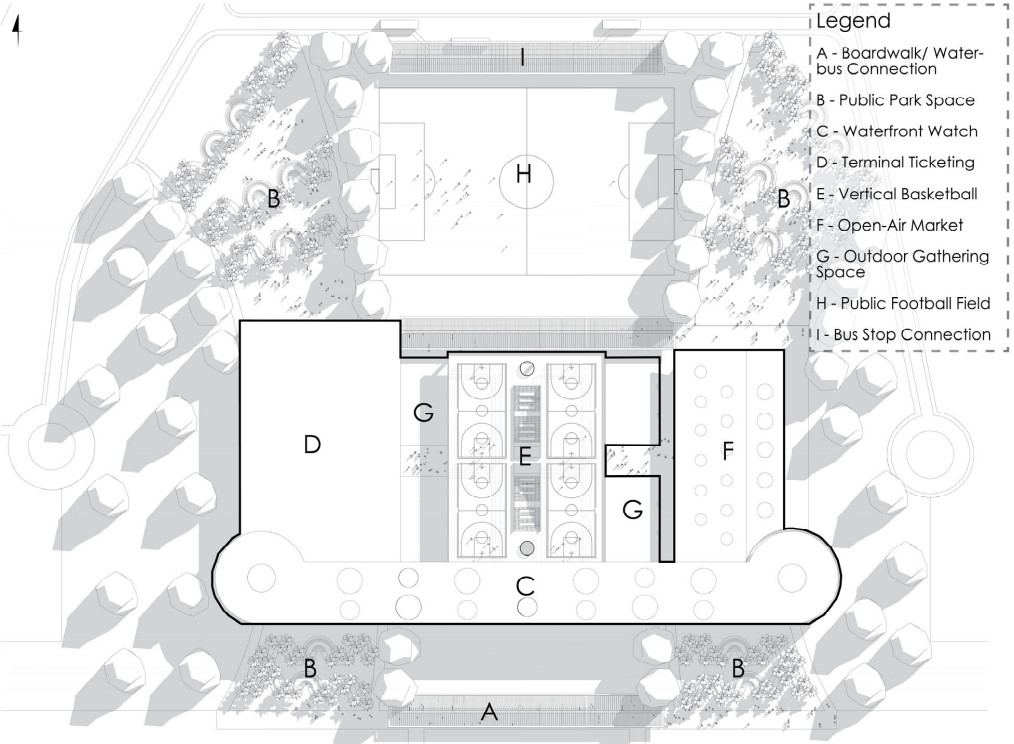
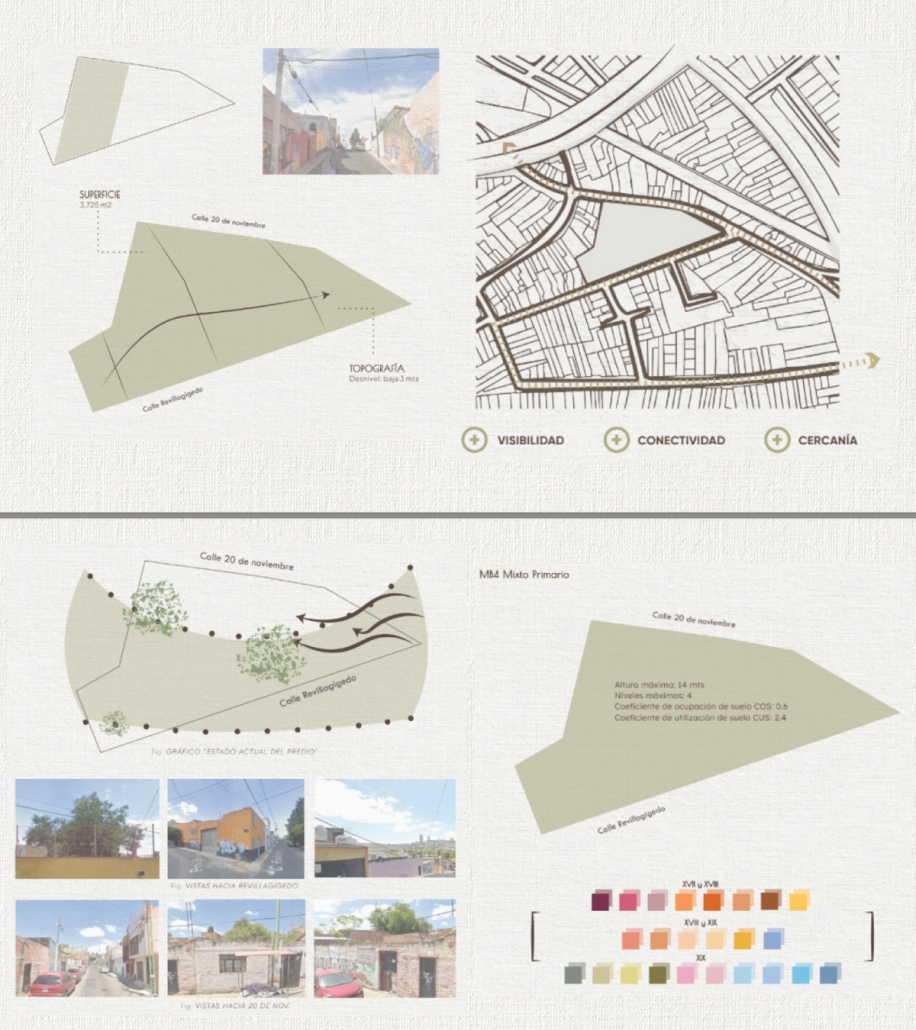
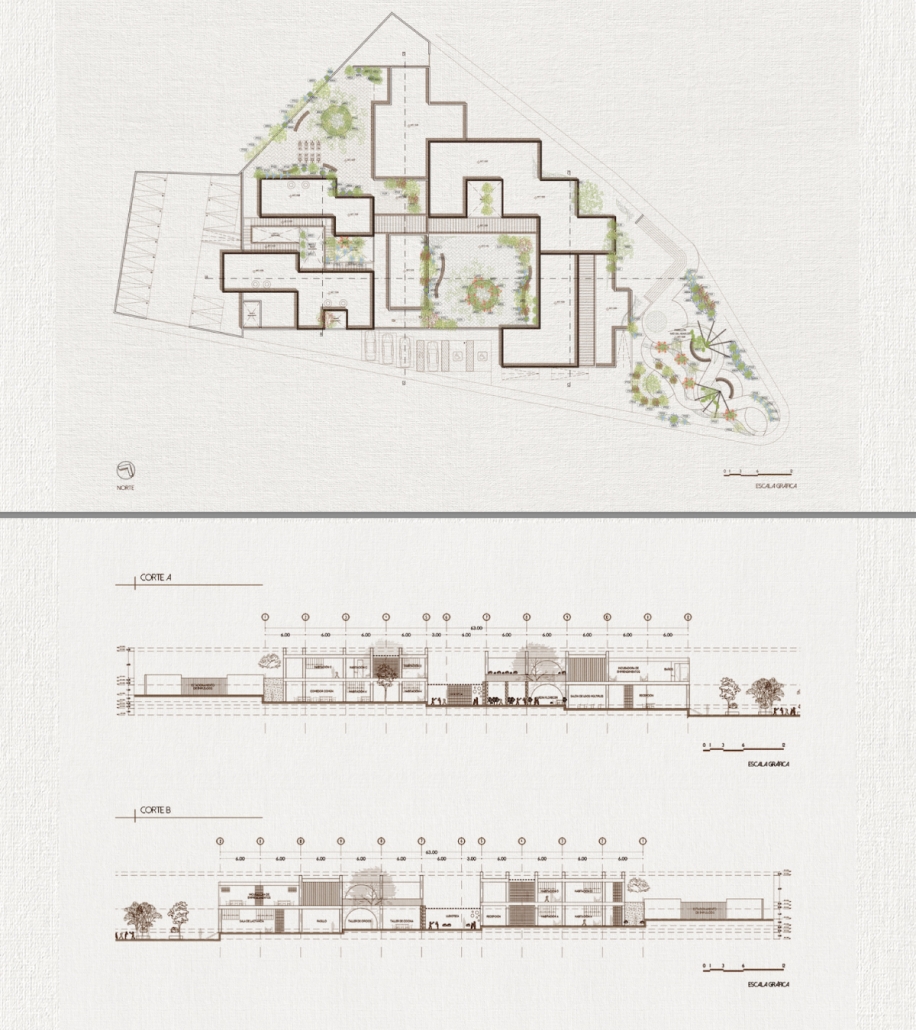
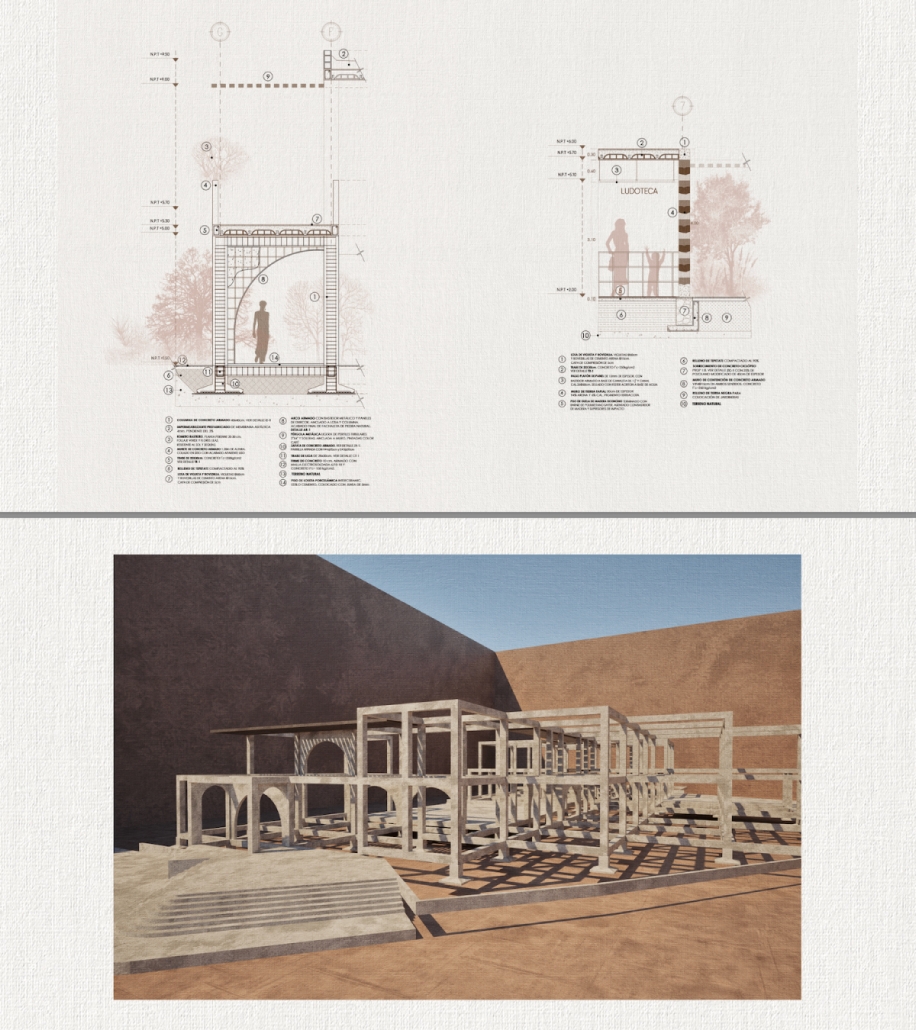
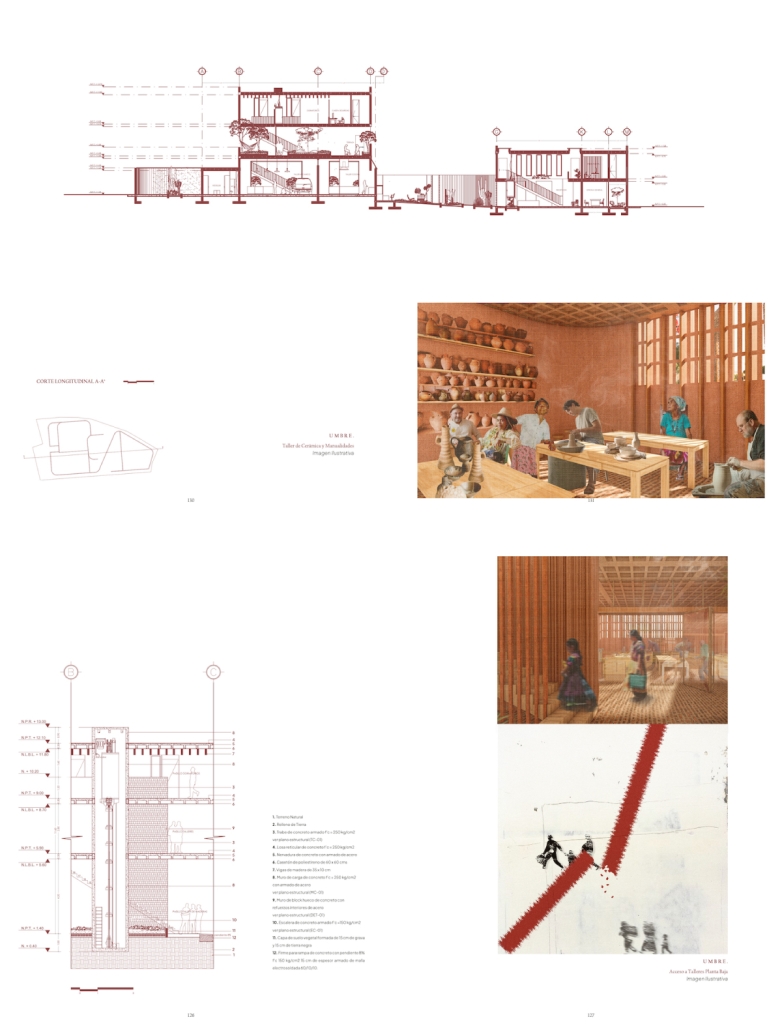
Milwaukee’s downtown and its surrounding neighborhoods have long been divided by the I‑794 freeway spur– an aging band of concrete built in the 1960s and ‘70s that now requires immense repair costs, poses a multitude of safety hazards, and leaves vast amounts of underused land in one of Wisconsin’s most valuable urban districts. Rather than viewing the freeway simply as an obstacle, it can be reimagined as a spine around which an integrated, multi‑modal network of streets, pathways, programs, and parks can emerge and flourish, connecting the North and South on a higher level, and connecting the waterfronts that the site lies between.
Scaling back access for automobiles— removing the “spaghetti” of on‑ and off‑ramps and consolidating access eastward at the Lake Interchange —reveals hundreds of thousands of square feet for housing and commercial development, a central greenway, and pedestrian-centric infrastructure. This new land emerges as the city’s connective tissue, linking important spaces of recreation and forming a new neighborhood to stitch together the central business district of Juneau Town and the Third Ward.
Rather than a simple removal, a negotiated balance preserves critical commuter routes that aren’t supported by the current transit system while converting a majority of the former freeway footprint into a continuous open space connecting the greenspaces of the Milwaukee Riverfront to the state and county parks on the Shores of Lake Michigan. Housing, shops, cafés, and cultural venues step down to human scale at street level; the space beneath the elevated roadways becomes reclaimed for the city and bridges the gap between the freeway spur and the neighborhoods it divides. These new buildings integrate parking garages that are directly accessible from the I-794 overpass, allowing vehicles to enter and exit without encroaching on street-level activity. This approach helps relegate car traffic away from pedestrian spaces, promoting a vibrant street life and encouraging ‘park-and-walk’ rather than driving directly to one’s destination. Transit stops and bike hubs nestle at key intersections, linking bus and rail lines to pedestrian pathways that flow seamlessly into adjacent neighborhoods.
This symbiosis stitches together the city’s disconnected urban grid, transforming the concrete barriers into green corridors and crafting connectivity between people, place, and nature. Instead of a unimodal freeway, I‑794 becomes an interconnected downtown system where pedestrian mobility, outdoor recreation, and a new community thrive.
Instagram: @sean.thiel, @smt_arch, @monaelkhafif
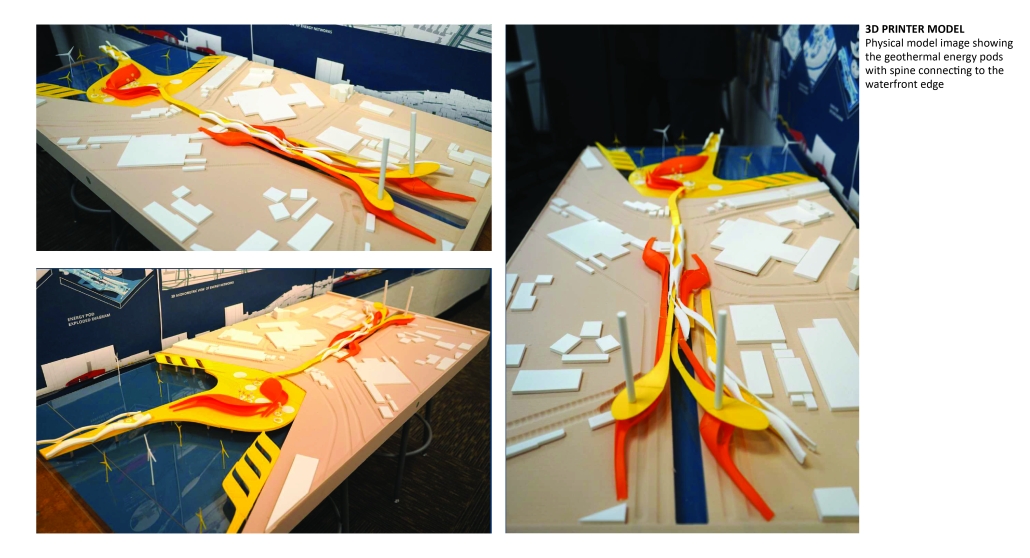
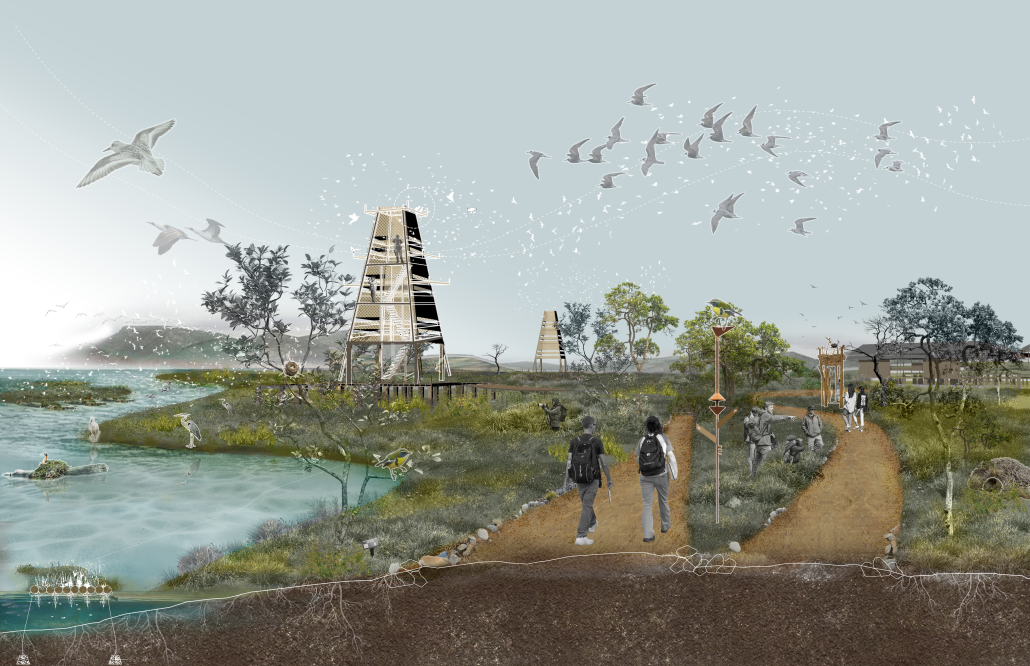
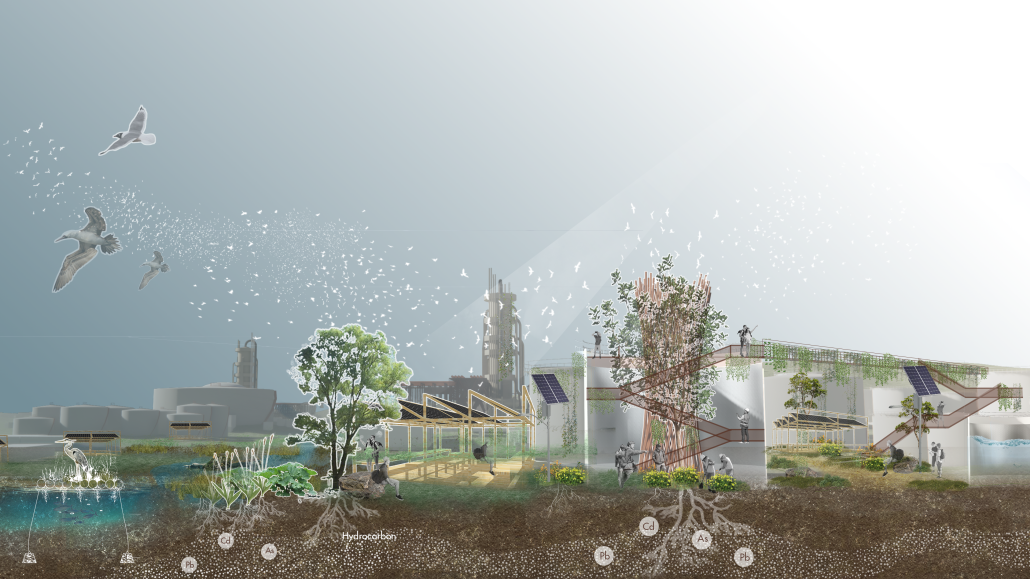
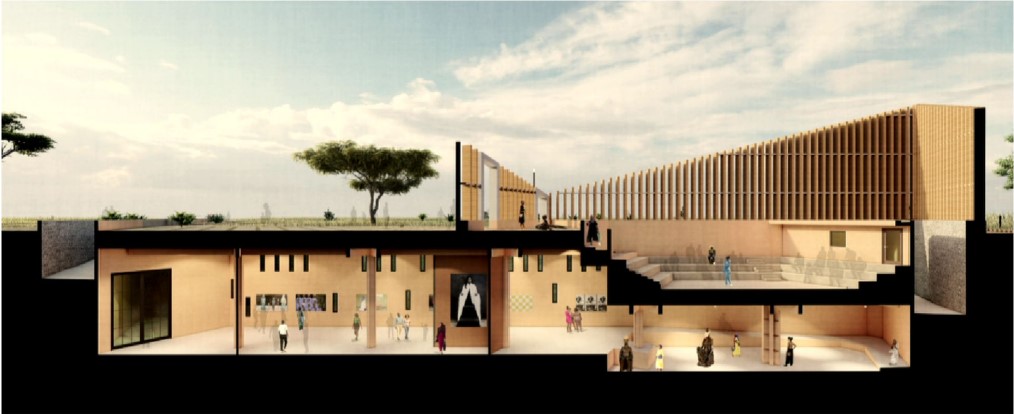
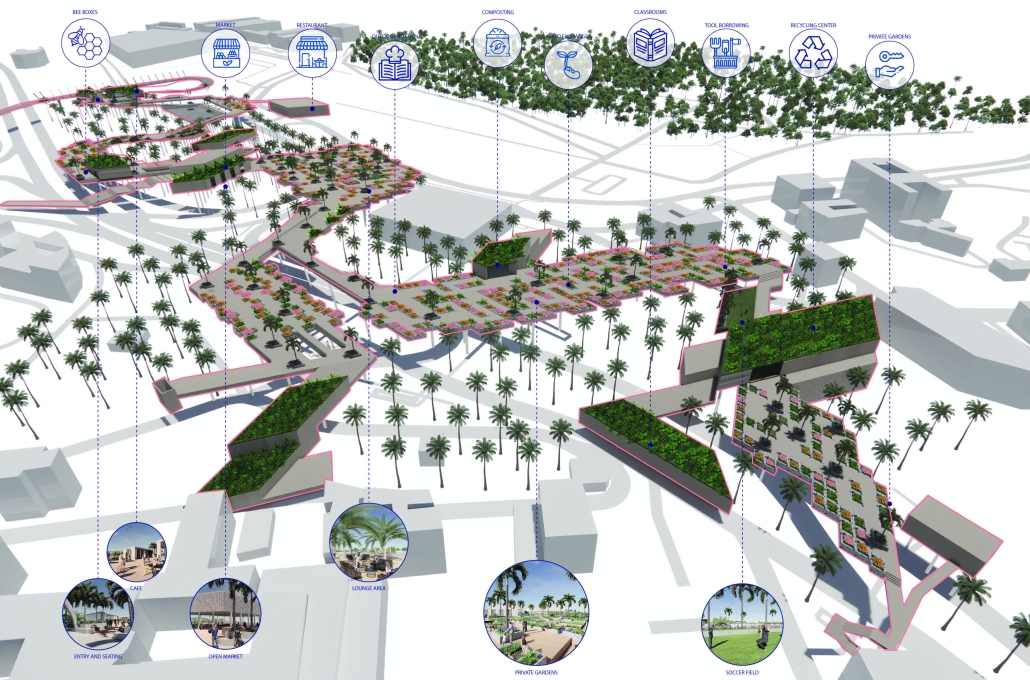
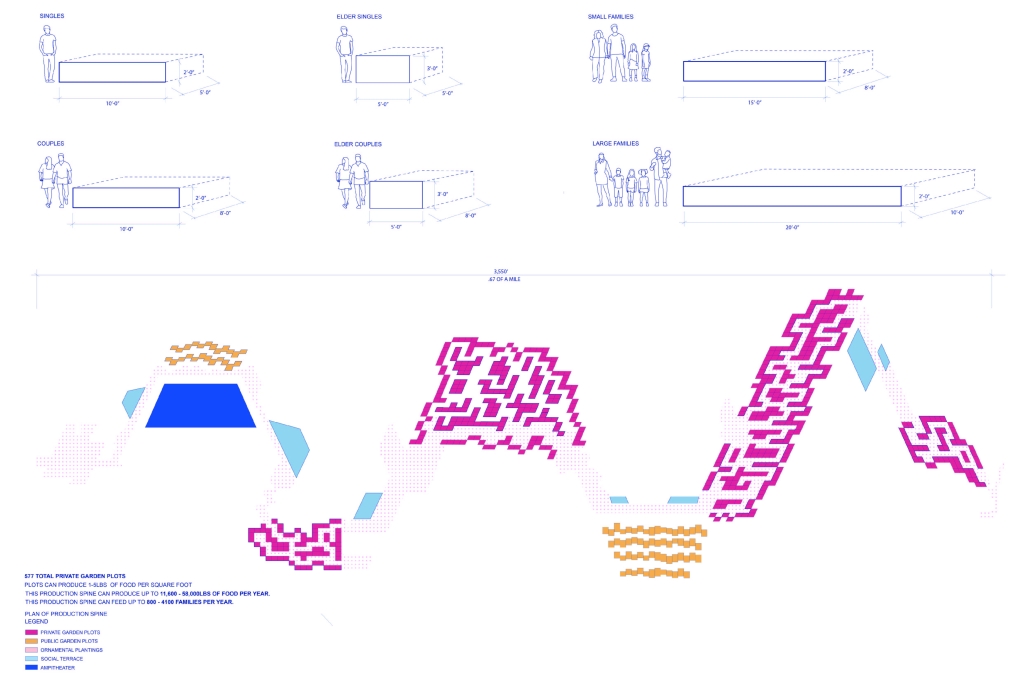
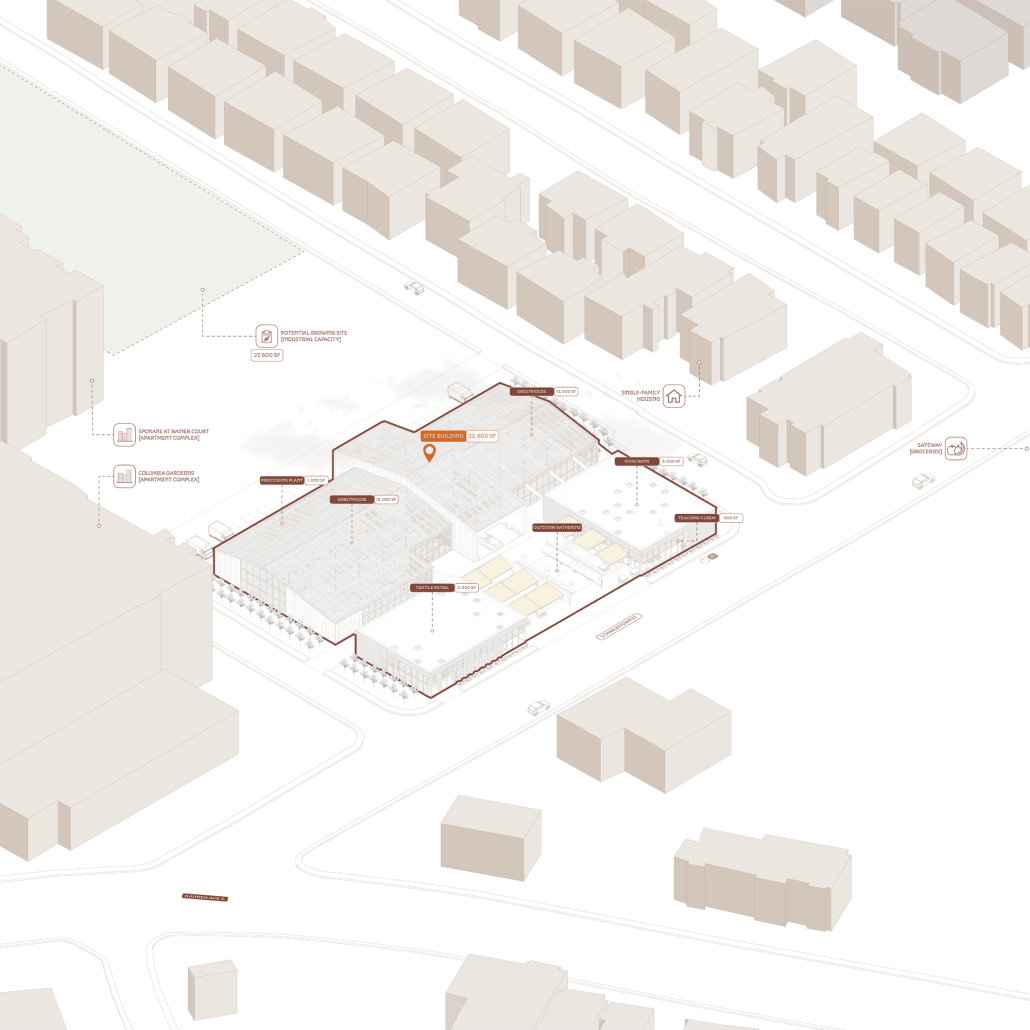
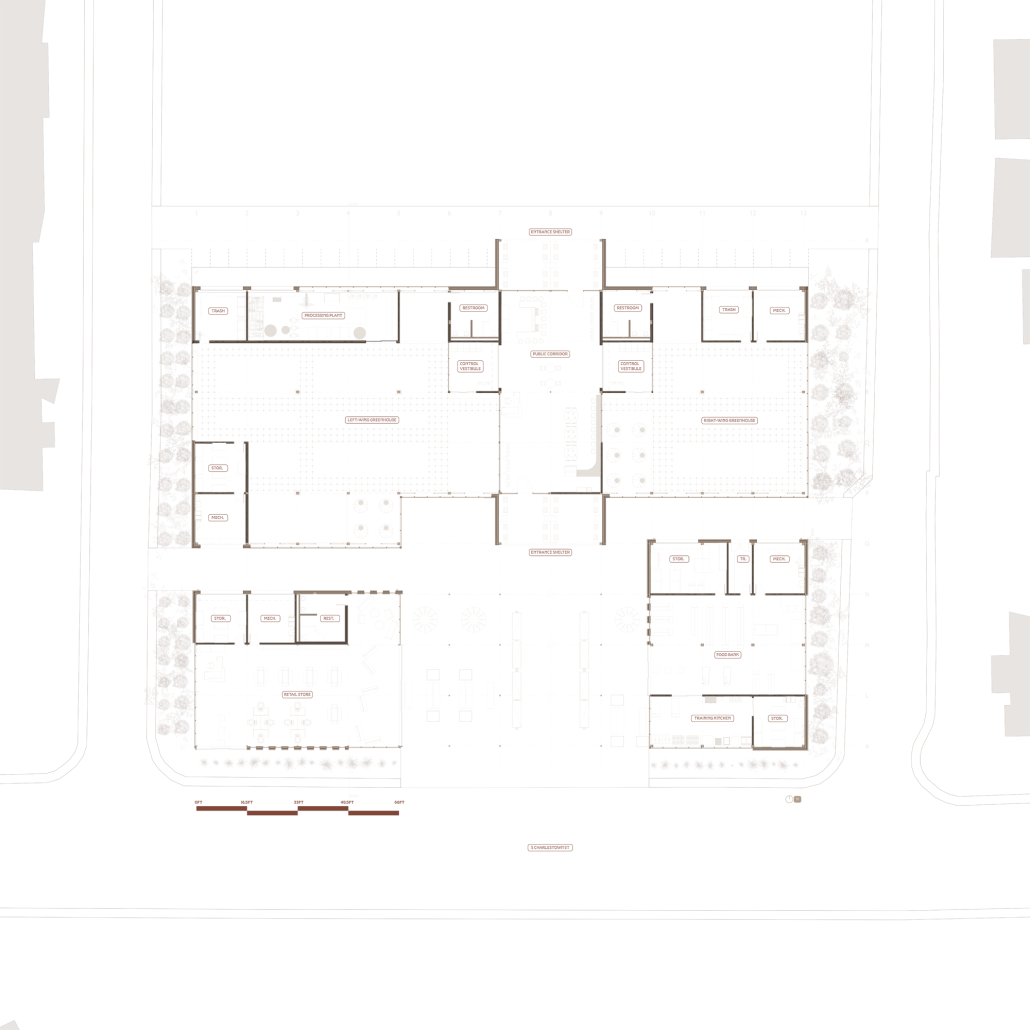
Energy Networks: Stitching Infrastructure through Land & Water by Neha Mudu & Sarvesh Joshi, M.Arch ’25
New York Institute of Technology | Advisors: Marcella Del Signore & Evan Shieh
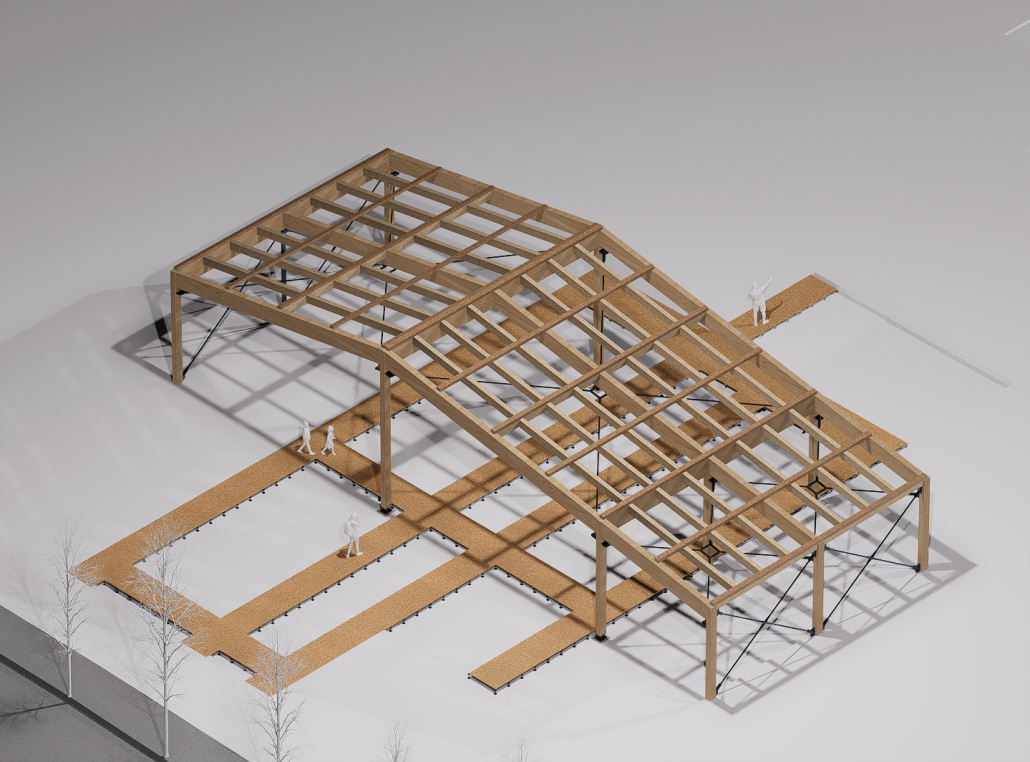
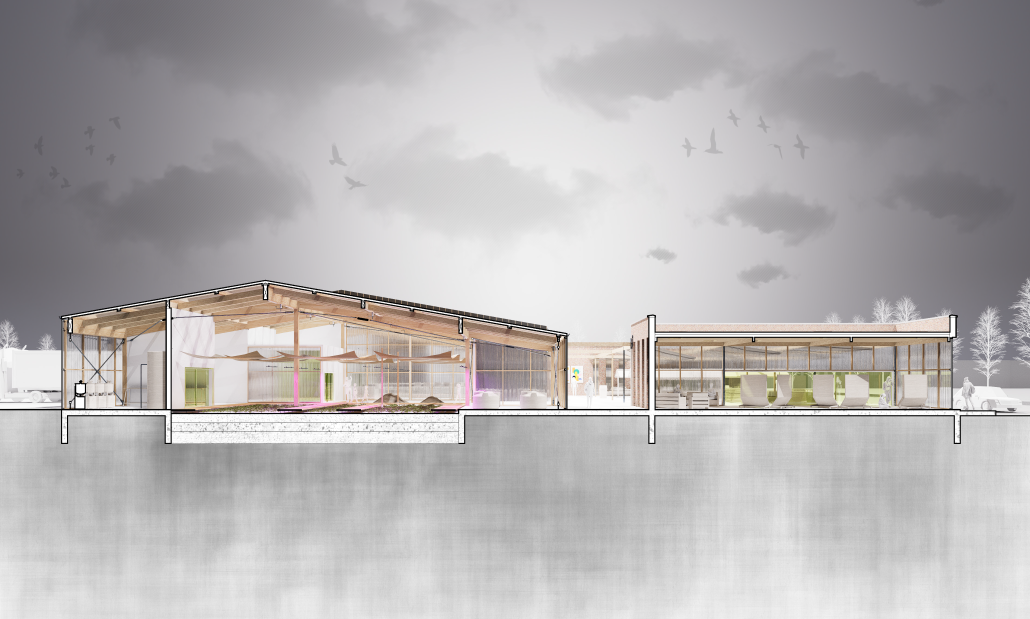
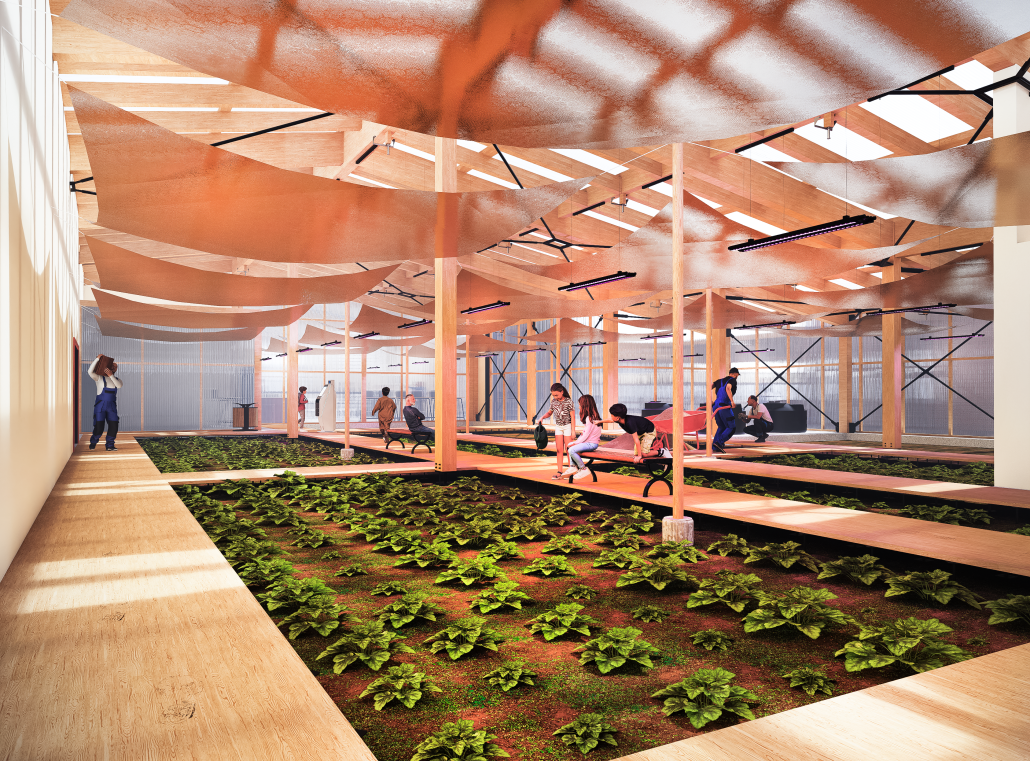
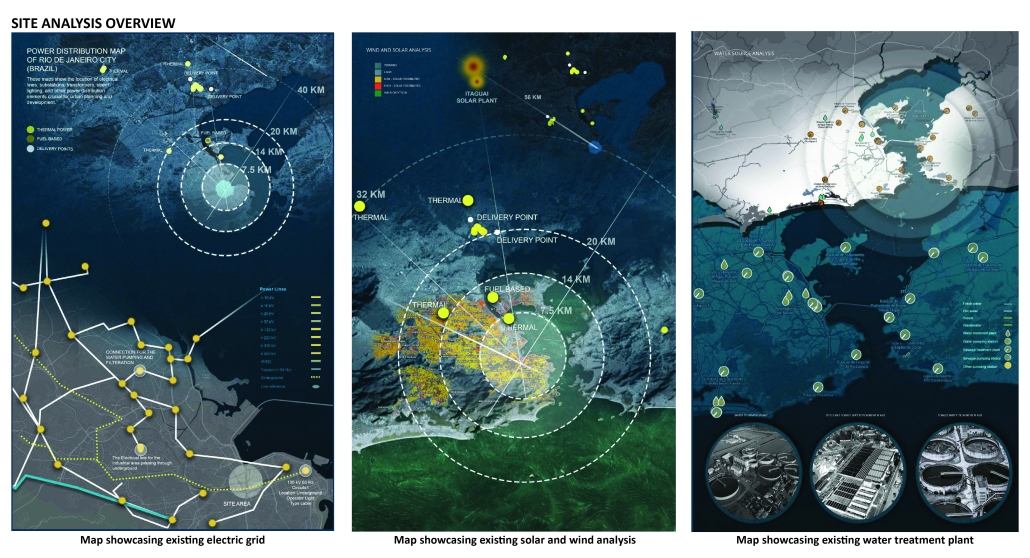
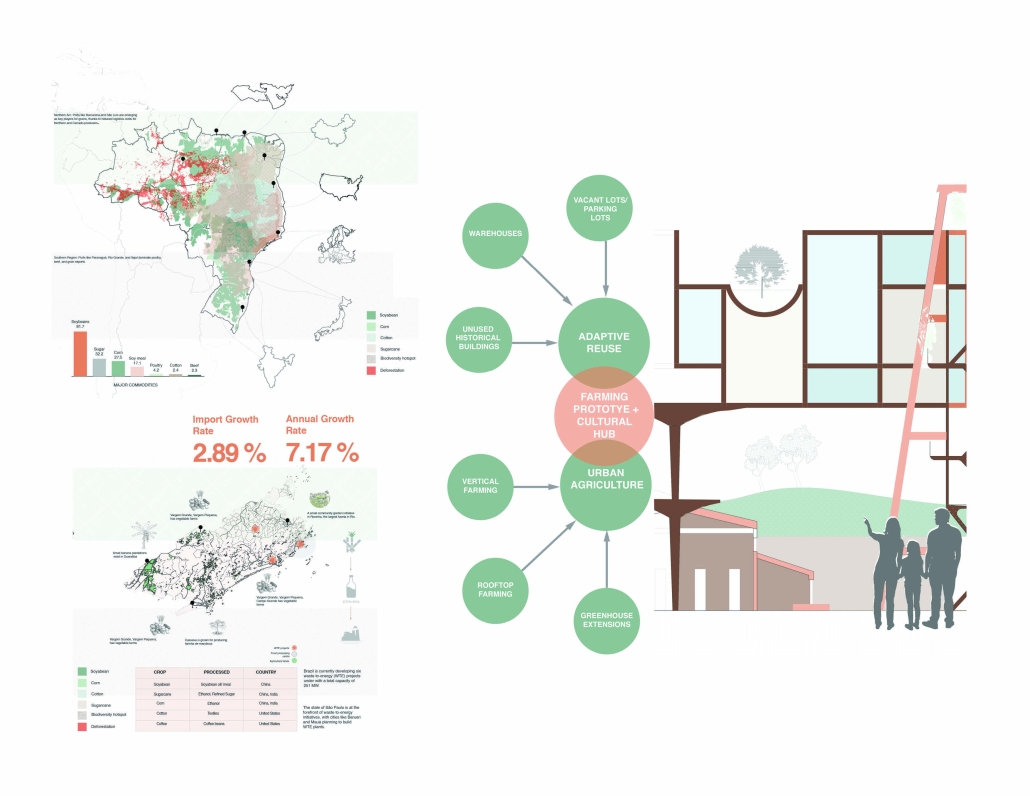
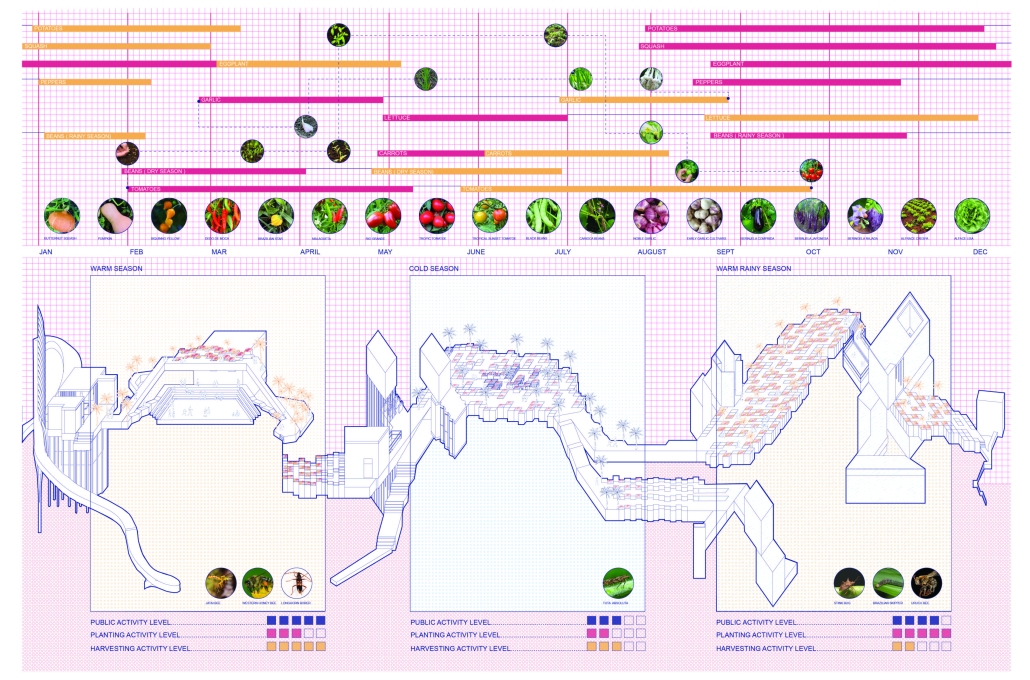
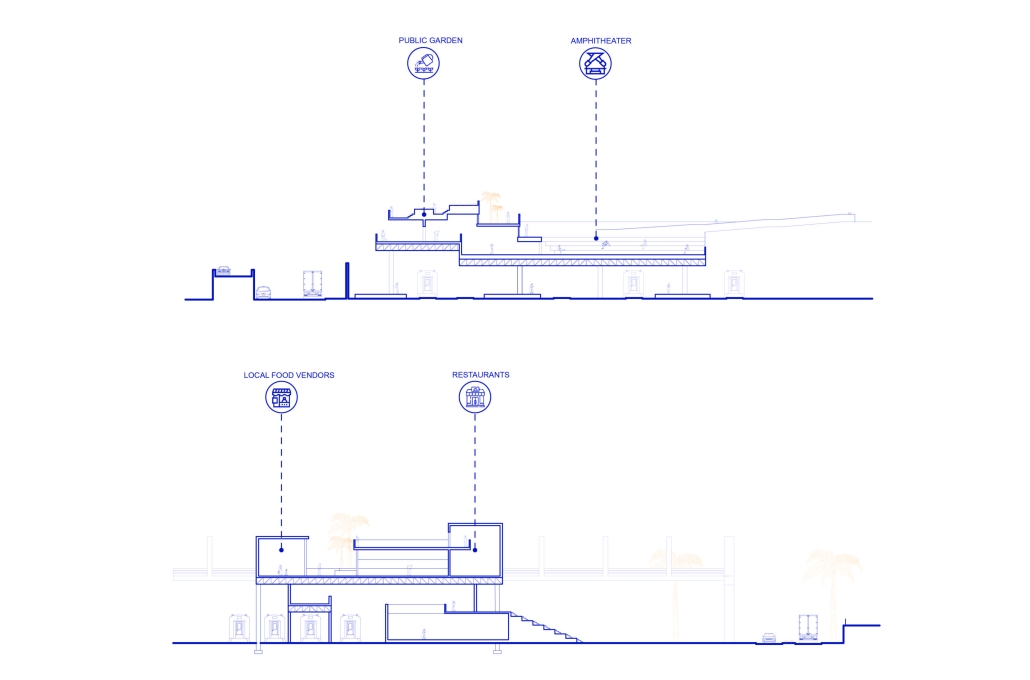
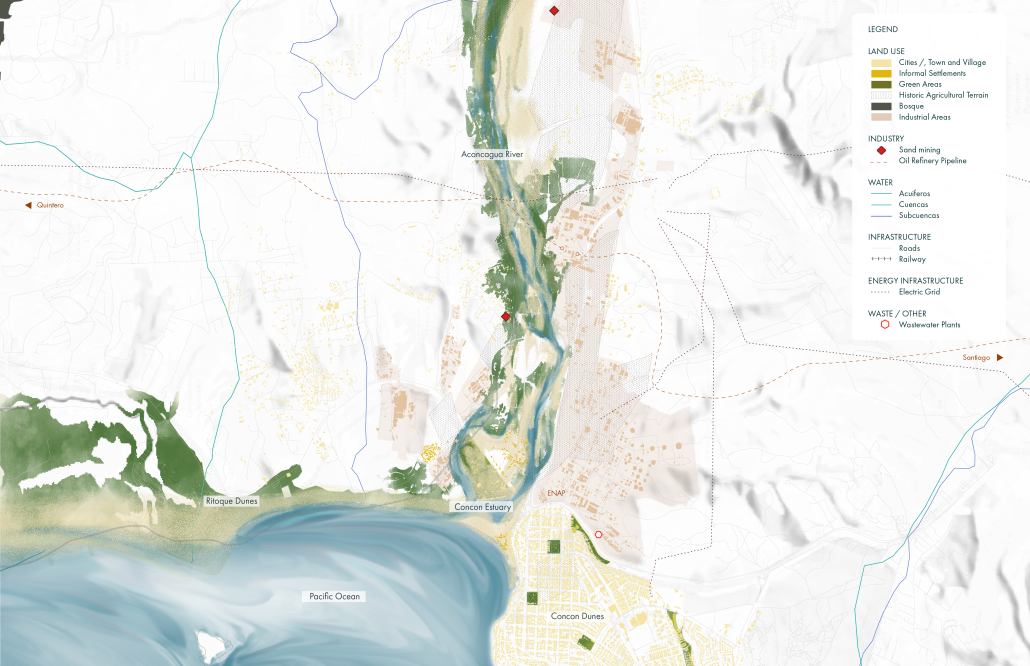
[This] proposal envisions a renewable energy power plant designed to act as a resilient backup system for Rio de Janeiro’s industrial zones, addressing the city’s recurring power outages while supporting long-term sustainable urban development. The design responds not only to the functional need for energy resilience but also to the environmental and social challenges faced by rapidly urbanizing coastal cities.
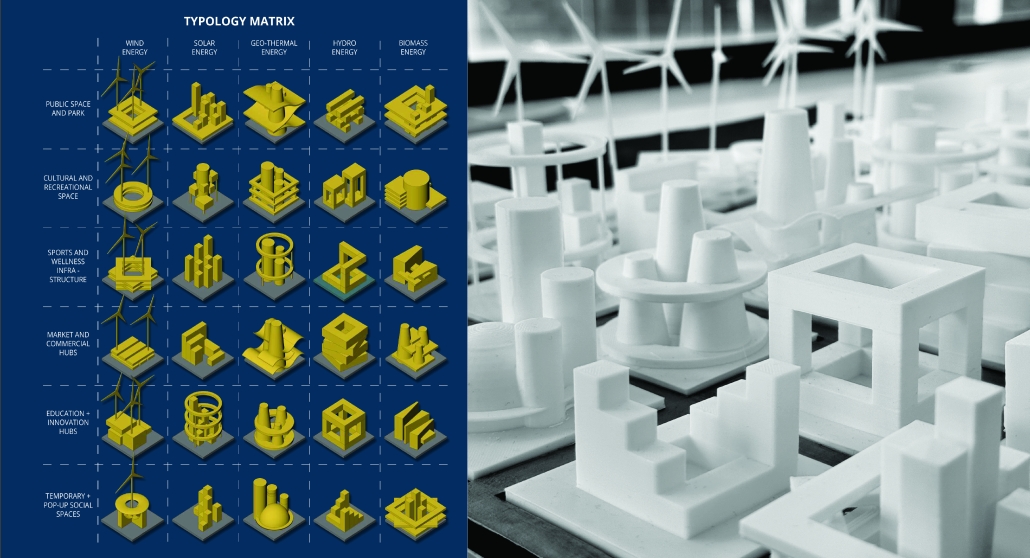
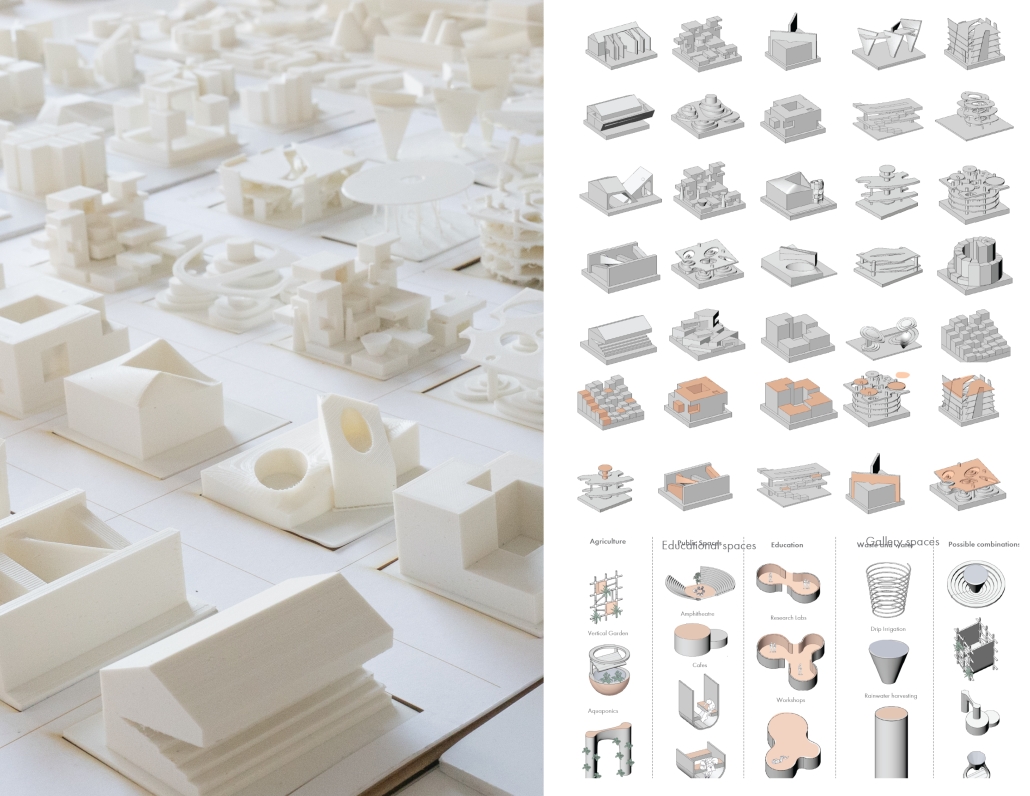
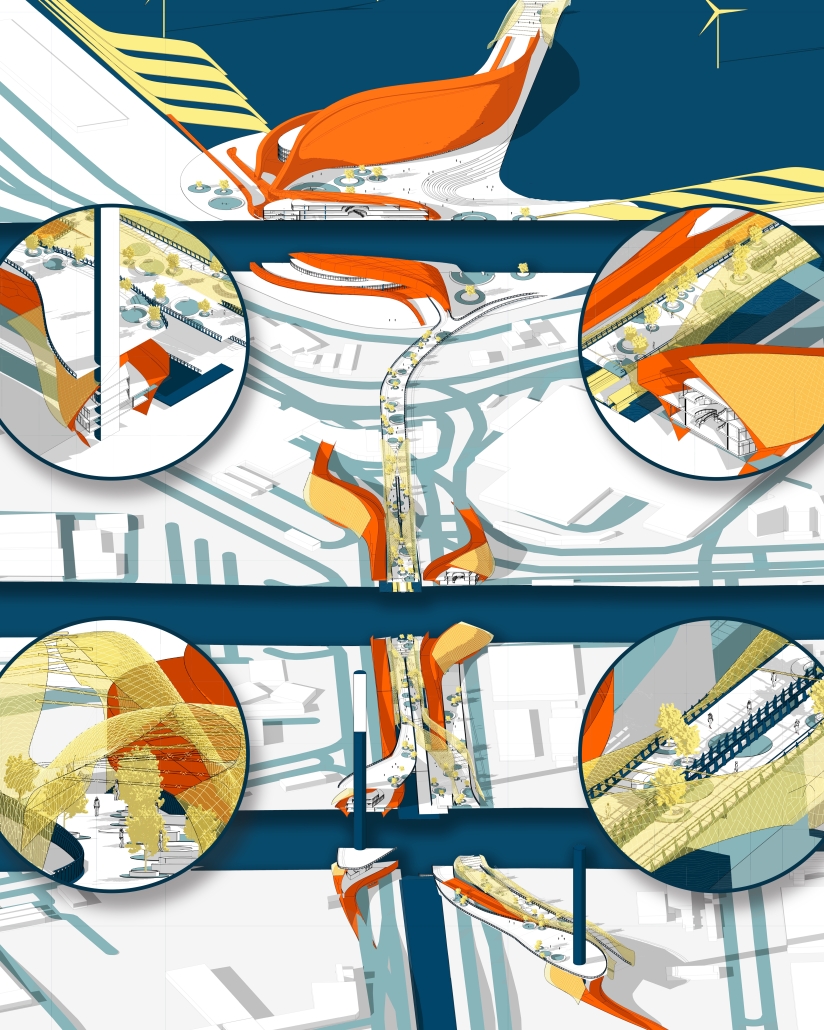
At the heart of the project is a hybrid energy infrastructure that integrates four key renewable sources — hydroelectric, geothermal, solar, and wind. These systems are carefully sited and layered across the landscape, forming a continuous network that blends with both the urban and natural context. The infrastructure is not hidden away, but exposed and celebrated, functioning as both a power-generating engine and a public experience.
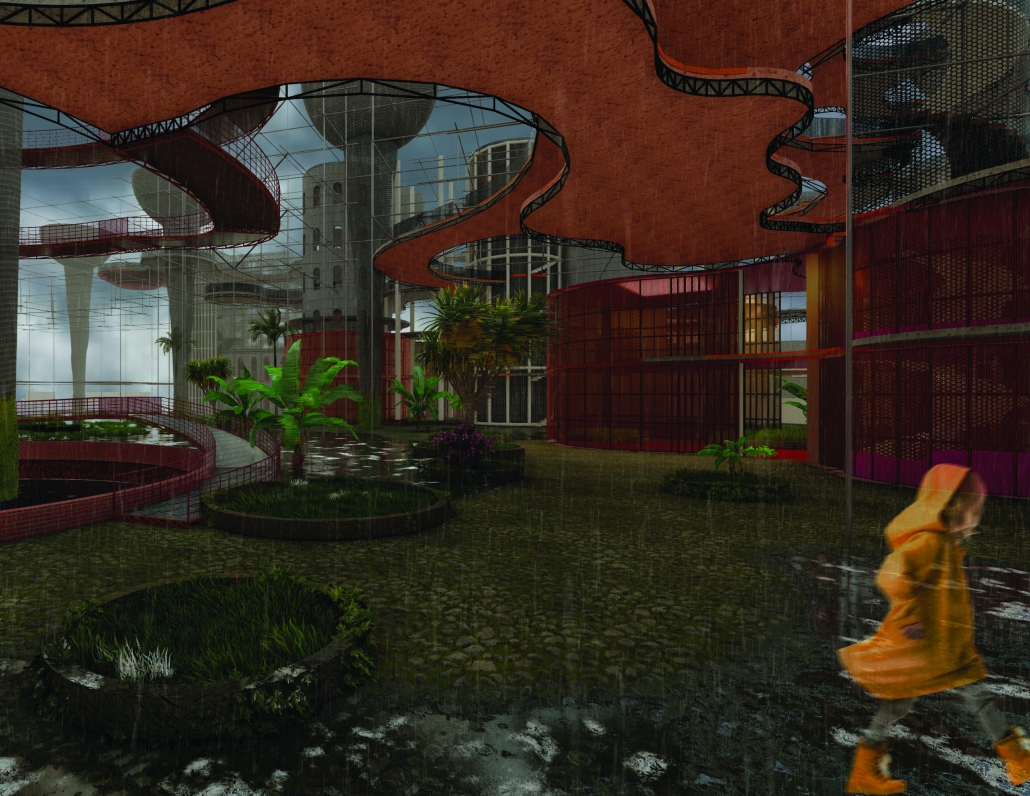
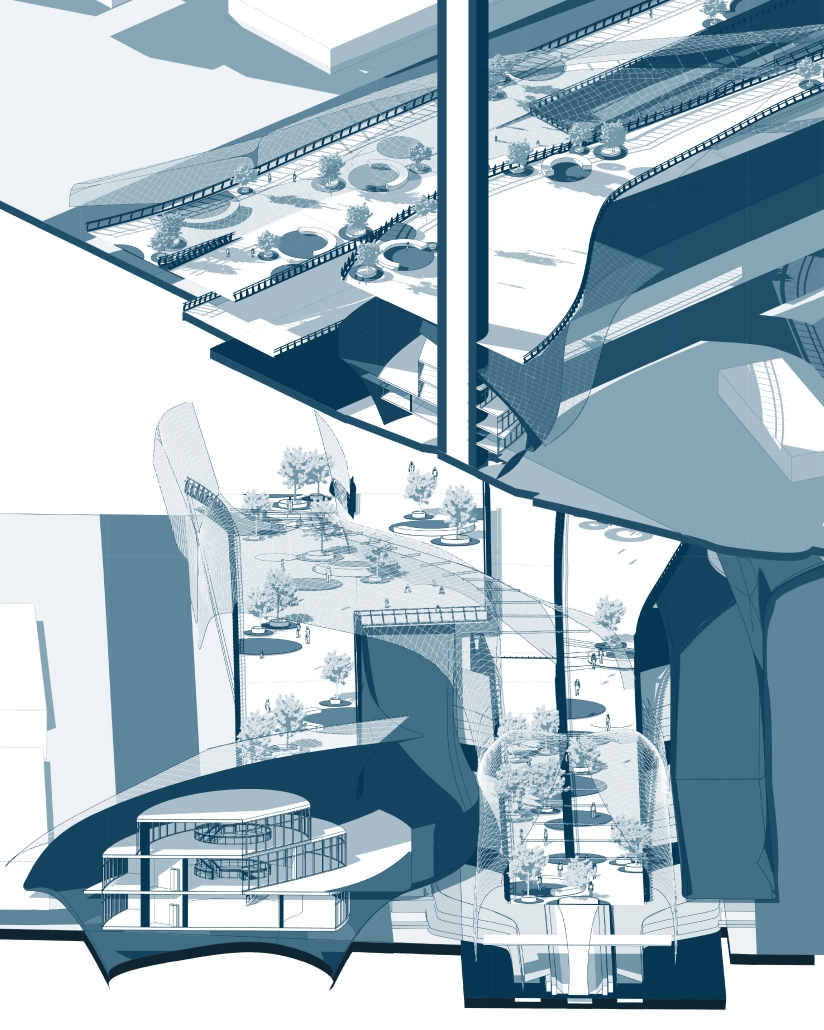
A central feature of the project is a spine-like elevated pedestrian walkway. This linear path connects the energy-producing nodes across the site, guiding movement and interaction while educating the public about sustainable energy systems. The walkway is embedded with piezoelectric panels that convert foot traffic into electricity, symbolizing how everyday public activity can contribute to a collective energy future.
Along this spine, key programmatic zones unfold — including educational centres, community spaces, research pods, and waterfront public areas. The project becomes more than a utility; it transforms into a civic landscape where infrastructure, technology, and people converge.
By treating renewable energy infrastructure as a public asset, this proposal aims to blur the boundaries between utility and urban experience. It supports energy independence, encourages public engagement, and creates a resilient framework that can adapt to future environmental and social needs.
This project was featured in the NYC X DESIGN Presentation Showcase.
Instagram: @nehamudu, @sarveshjoshi2697, @ev07, @marcelladelsi
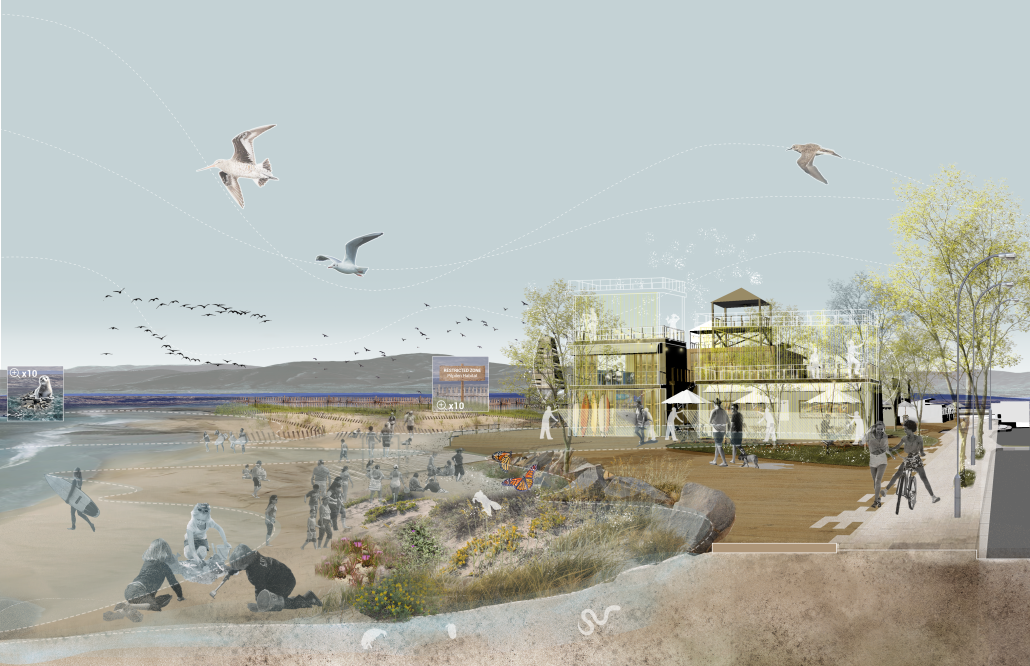
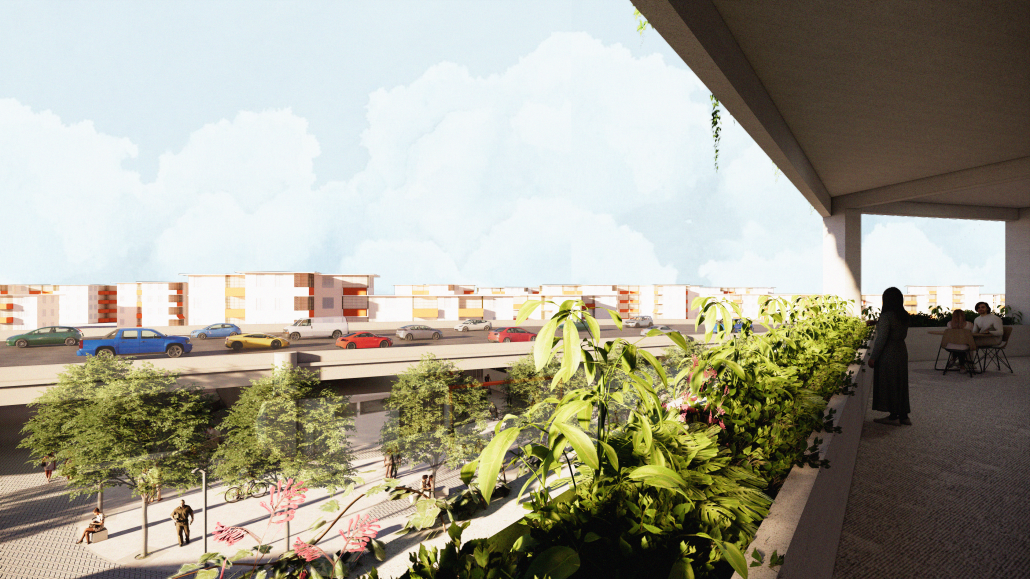
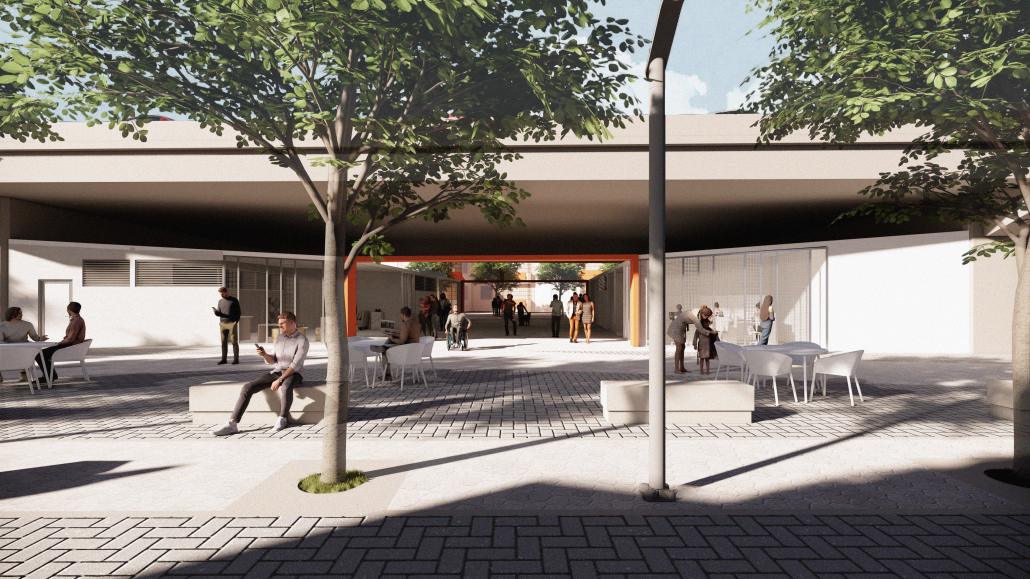
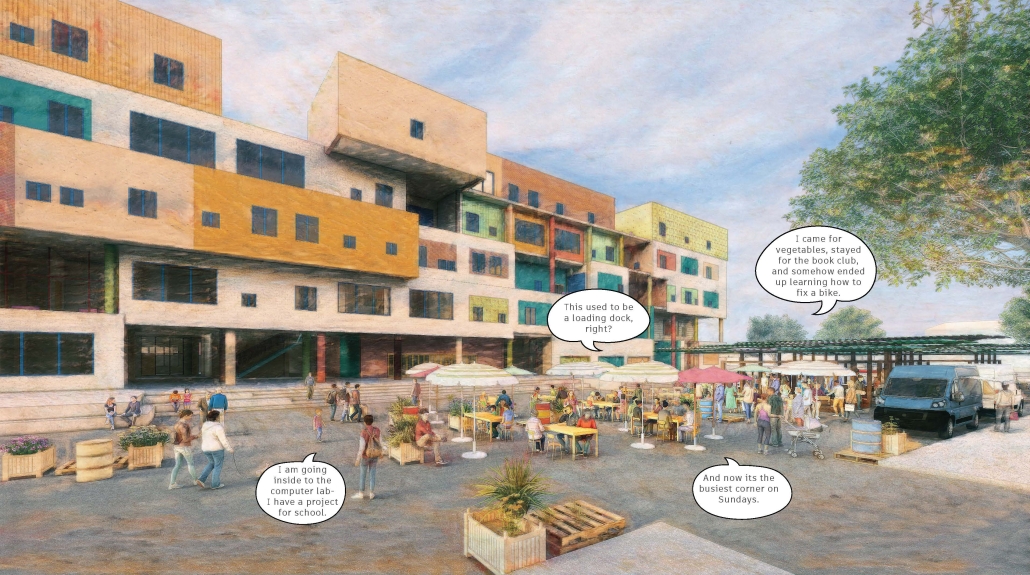
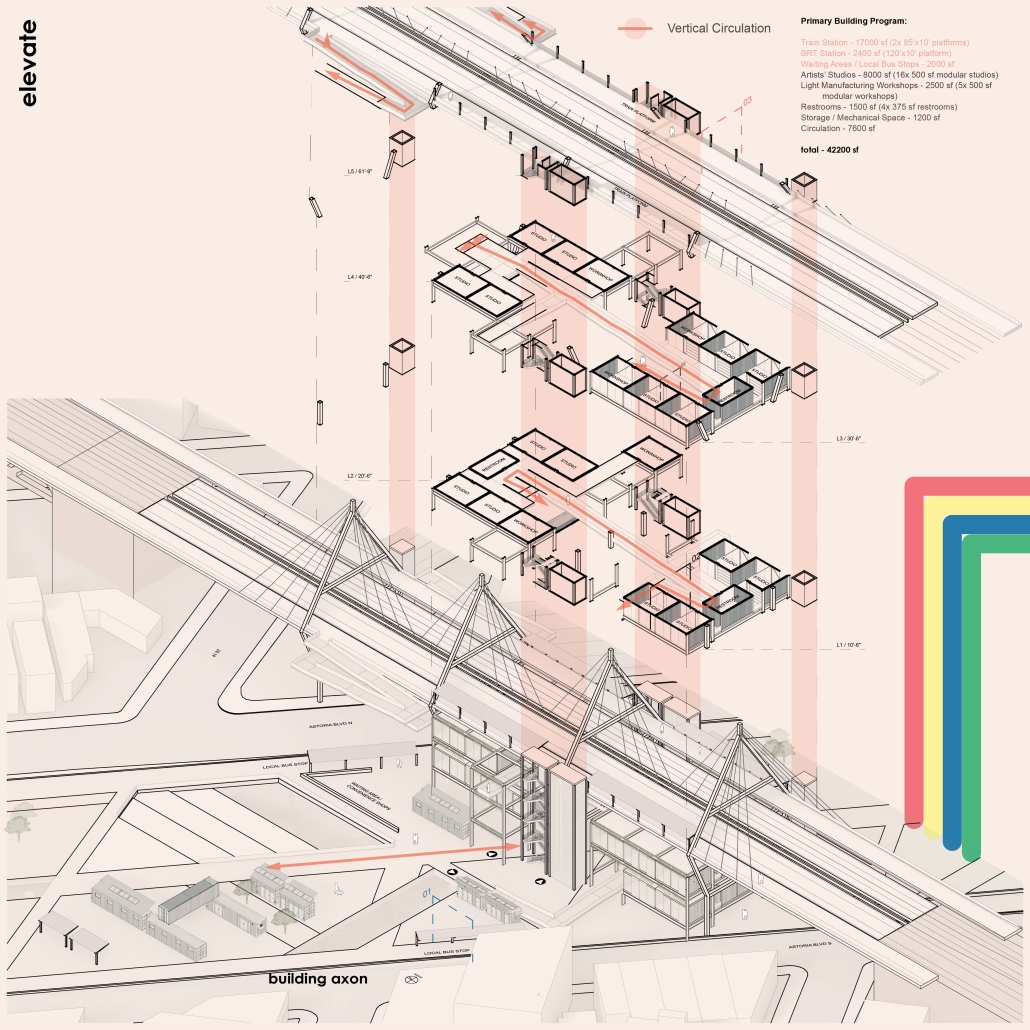
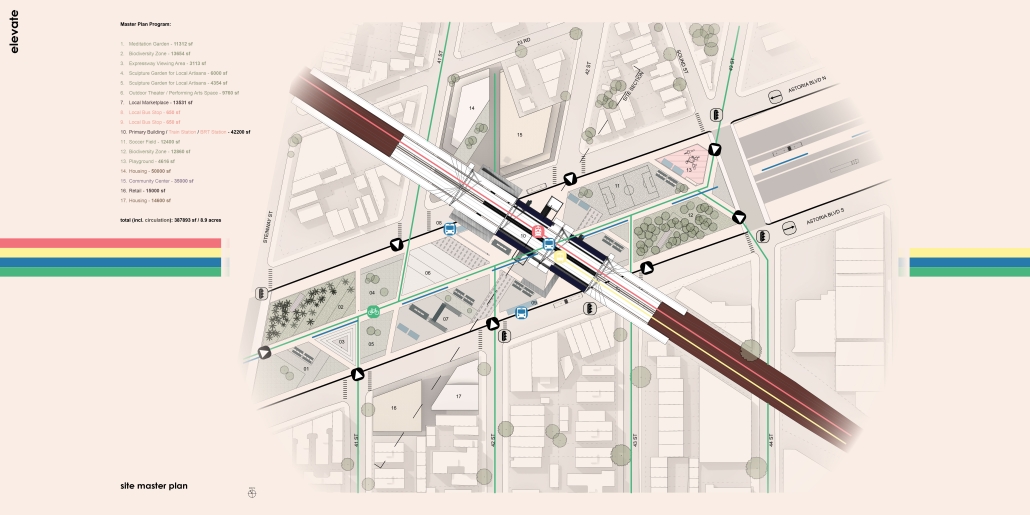
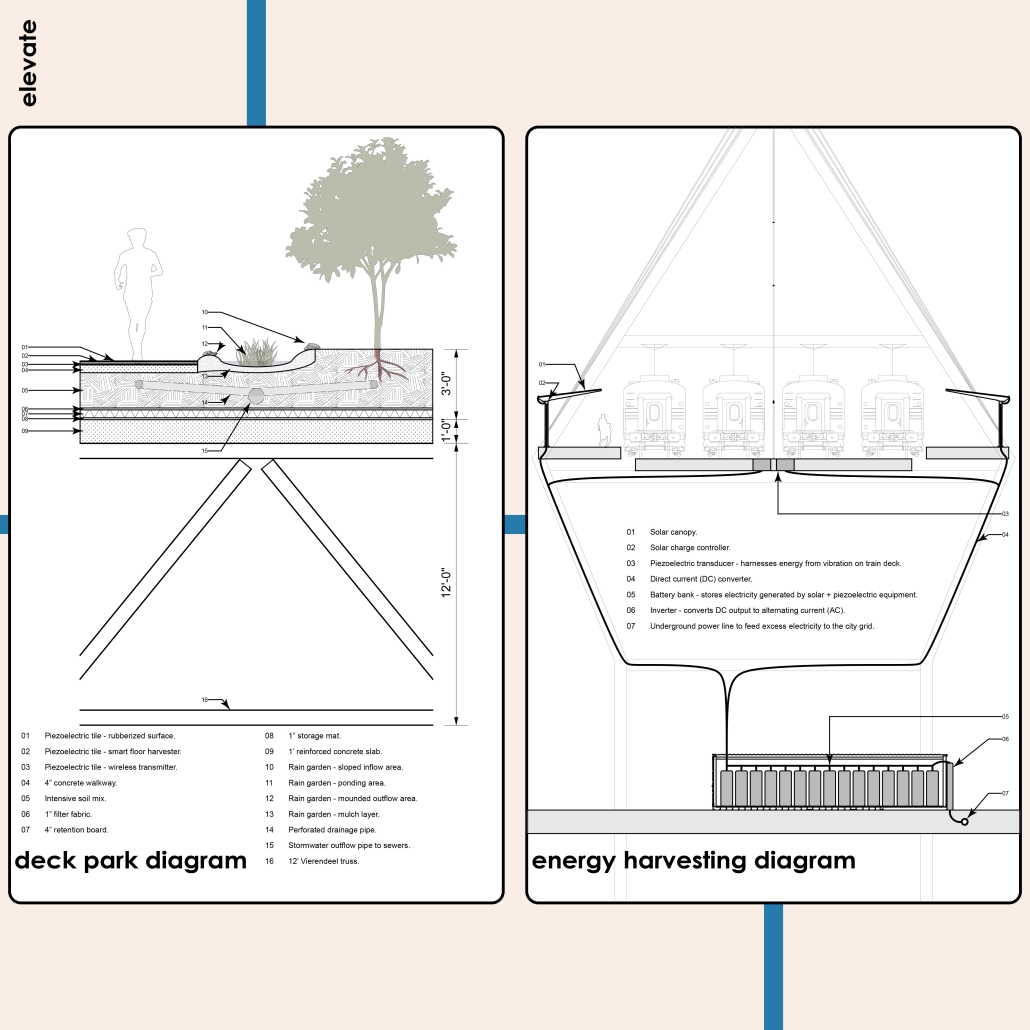
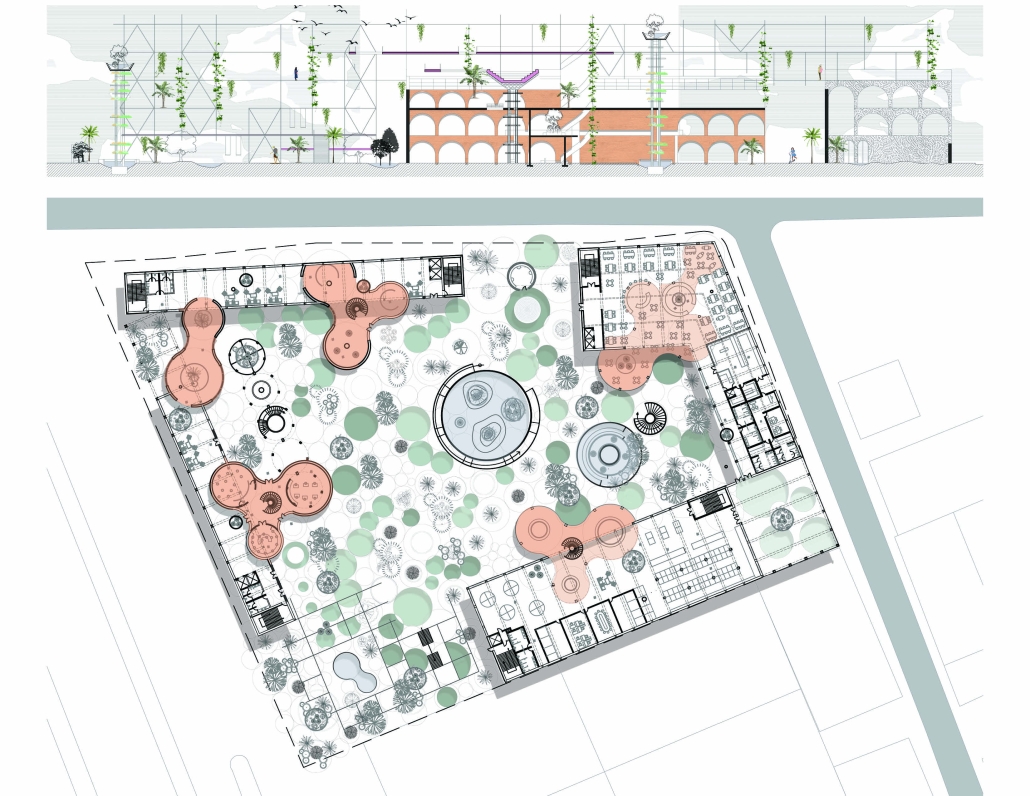
ELEVATE: Rethinking Urban Mobility Infrastructure by Luke Stefanchik, B.Arch ’25
New York Institute of Technology | Advisor: Farzana Gandhi
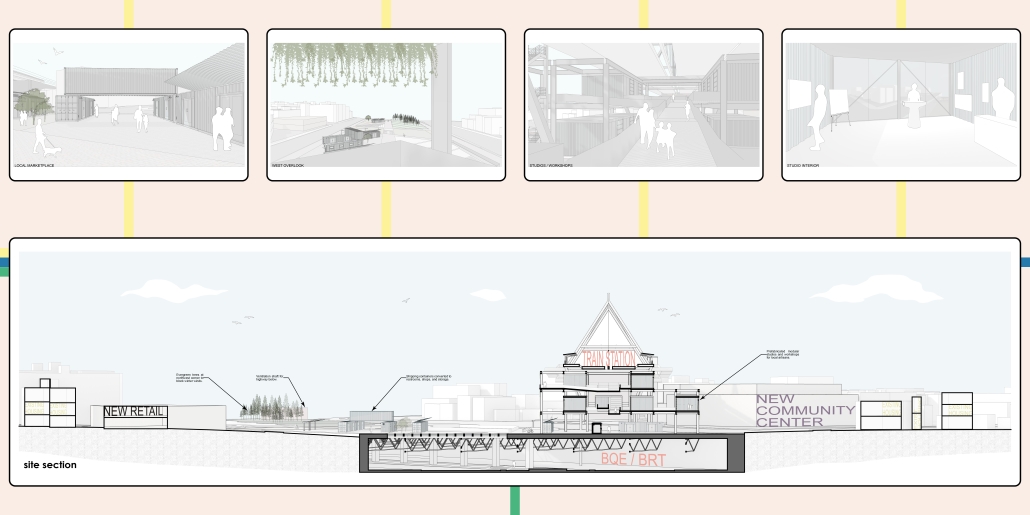
Cities around the world are removing or decking over their highways in favor of linear parks and boulevards. Is this enough to repair decades of damage caused by highways and car-centric infrastructure? We need to develop a new typology that weaves public transit with community services and adaptive reuse, and bridges the divide created by highways. New public transit projects in NYC and innovations in architecture and infrastructure provide an opportunity to rethink the city’s existing transit corridors. [This project redevelops] the intersection of the sunken Brooklyn-Queens Expressway with the elevated Hell Gate rail bridge along Astoria Boulevard between Steinway Street and 43rd Street in Queens. This is a densely-populated and diverse area that lacks recreation and community spaces, and was split in half by the highway.
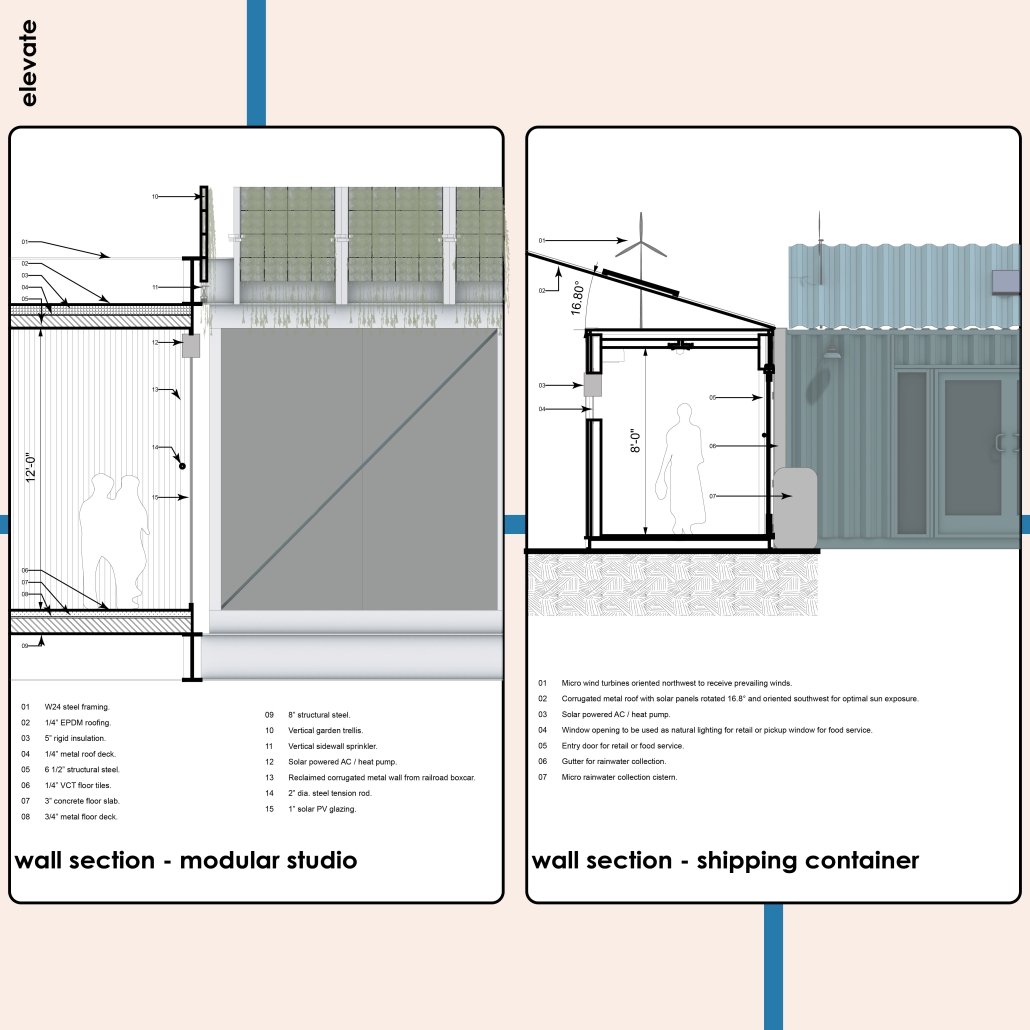
Right now, two different projects plan to make use of the railway — Metro-North’s Penn Station Access and MTA’s Interborough Express — which is currently only used by Amtrak and freight trains. Merging these projects creates an opportunity to develop this new typology. I am proposing to add two bus rapid transit lanes to the BQE for the M60 bus to LaGuardia Airport. At street level, the expressway will be decked over to create a park with exhibition and performance spaces for local artists. A section of the bridge will be torn down and rebuilt with modern, lightweight materials to support a new train station for the Metro-North, Amtrak, and Interborough Express. The space under the bridge will house prefabricated, modular workshops for local artisans to create and sell their work. Sustainable aspects incorporated into the project include hanging vegetation, solar canopies, and retrofitted shipping containers in the park. This hub will bridge the divide created by the expressway and serve as a catalyst for future transit design.
This project received the Dean’s Award for Excellence in Architecture and was featured during the 2025 NYIT Symposium of University Research and Creative Expression (SOURCE) and the 2025 NYCxDesign Festival.
Instagram: @luke.js, @fg_architecture
The SVX Pavilion: EL Salvador At Expo 2030 by Elaine Bonilla-Villatoro, B.Sc. in Architecture ’25
University of the District of Columbia | Advisor: Golnar Ahmadi
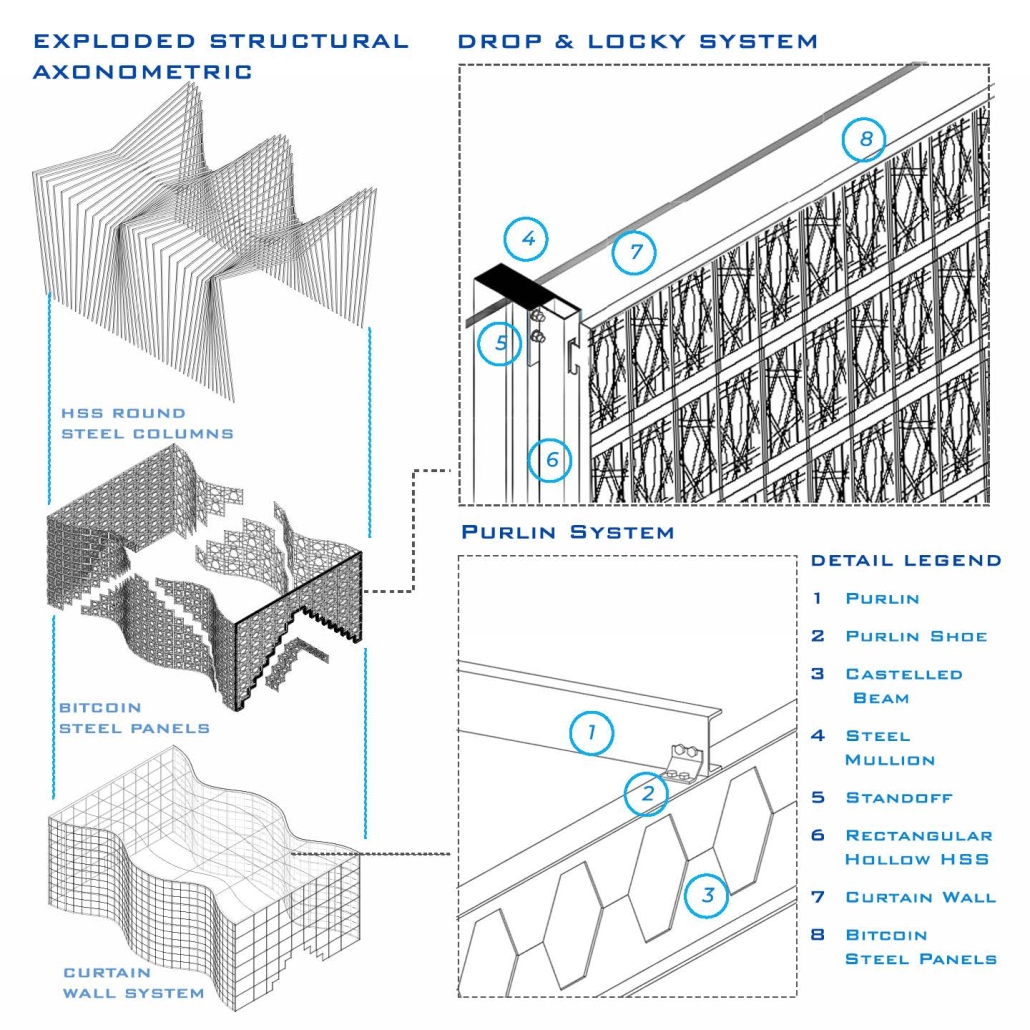
The SVX Pavilion, designed for Expo 2030 in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, symbolizes El Salvador’s bold leap into a digital and sustainable future. Rooted in an expressive steel structure, the pavilion expresses a national identity through architectural elements, merging cultural roots with the country’s adoption of Bitcoin as a legal tender, which makes it the first nation to do so.
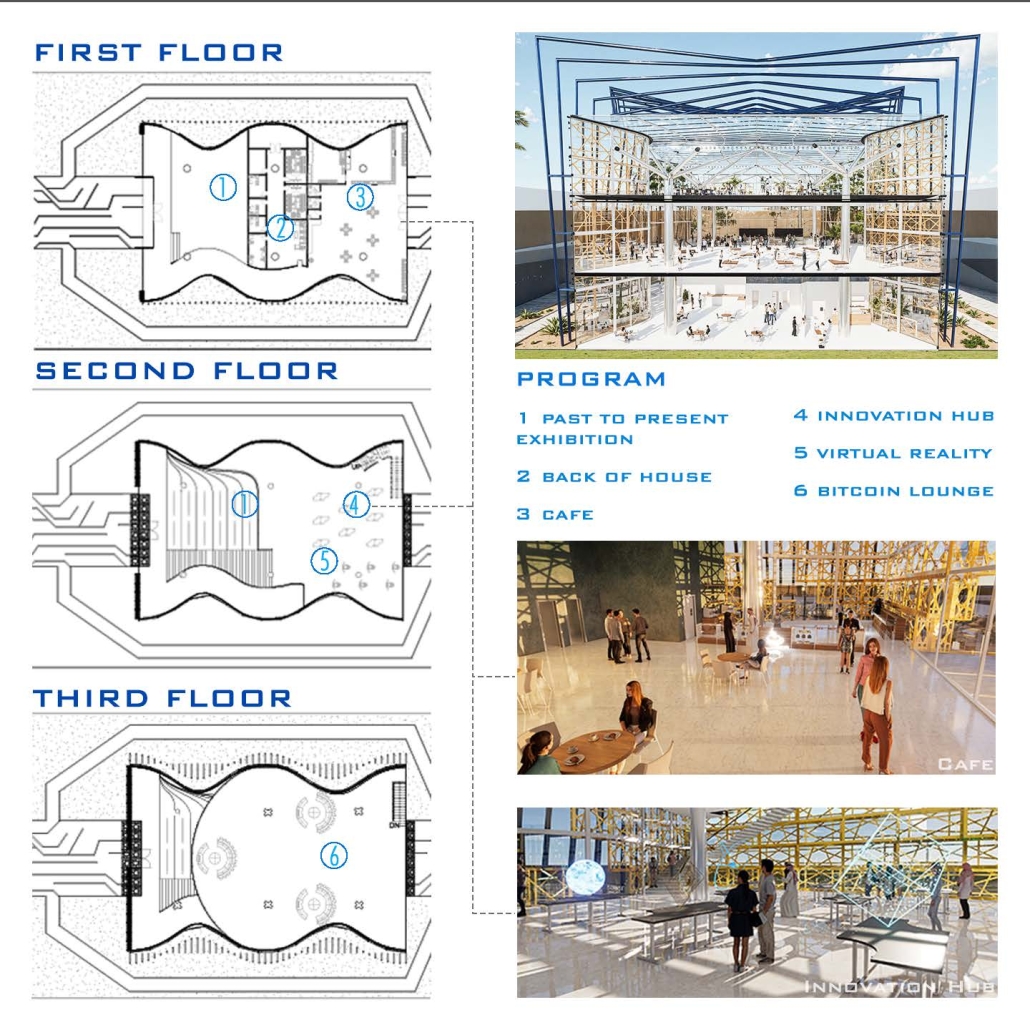
Inspired by the Ceiba tree, the pavilion features branching rolled steel columns that rise continuously from the ground floor to the roof and support a canopy and the glazed roof, which allows the spaces to be filtered with desert light. These structural columns shape the main circulation spaces and frame key exhibition zones while representing strength and interconnectedness, a metaphor for El Salvador’s digital network. A golden perforated panel facade references blockchain technology’s traditional craft and digital mesh, creating a visual connection between the past and future.
At its core, the SVX Pavilion includes the Bitcoin Lounge and Innovation Hub, with holographic displays representing El Salvador’s digital economy. These spaces offer a platform for education, interaction, and diplomacy while inviting global visitors to reflect on how emerging technologies shape sovereign futures and redefine national narratives.
Surrounding the pavilion, the “Digital Forest Garden” combines native Salvadoran plants that can adapt to Riyadh’s desert climate. This makes the futuristic structure belong in nature and promotes ecological resilience. The landscape is a metaphor for sustainable adaptation and a thermal buffer that enhances passive climate control.
Steel is not only the structural core of the SVX Pavilion but also a symbol of strength, modularity, and meaningful possibilities. Its use enables rapid fabrication and bold sculptural identity, which supports the project’s narrative of innovation and transformation. The SVX Pavilion is more than a national exhibition. It is a statement of El Salvador’s emerging role in the global dialogue on technology and sovereignty.
Instagram: @golnarahmadi
Stay tuned for Part IX!