2023 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part XXVII
Welcome to Part XXVII of the Study Architecture Student Showcase! Today’s featured work focuses on the care of elderly populations. From dementia care centers to a multi-use facility that promotes multi-generational encounters, each design and thesis looks at various methodologies to promote optimal well-being for the elderly.
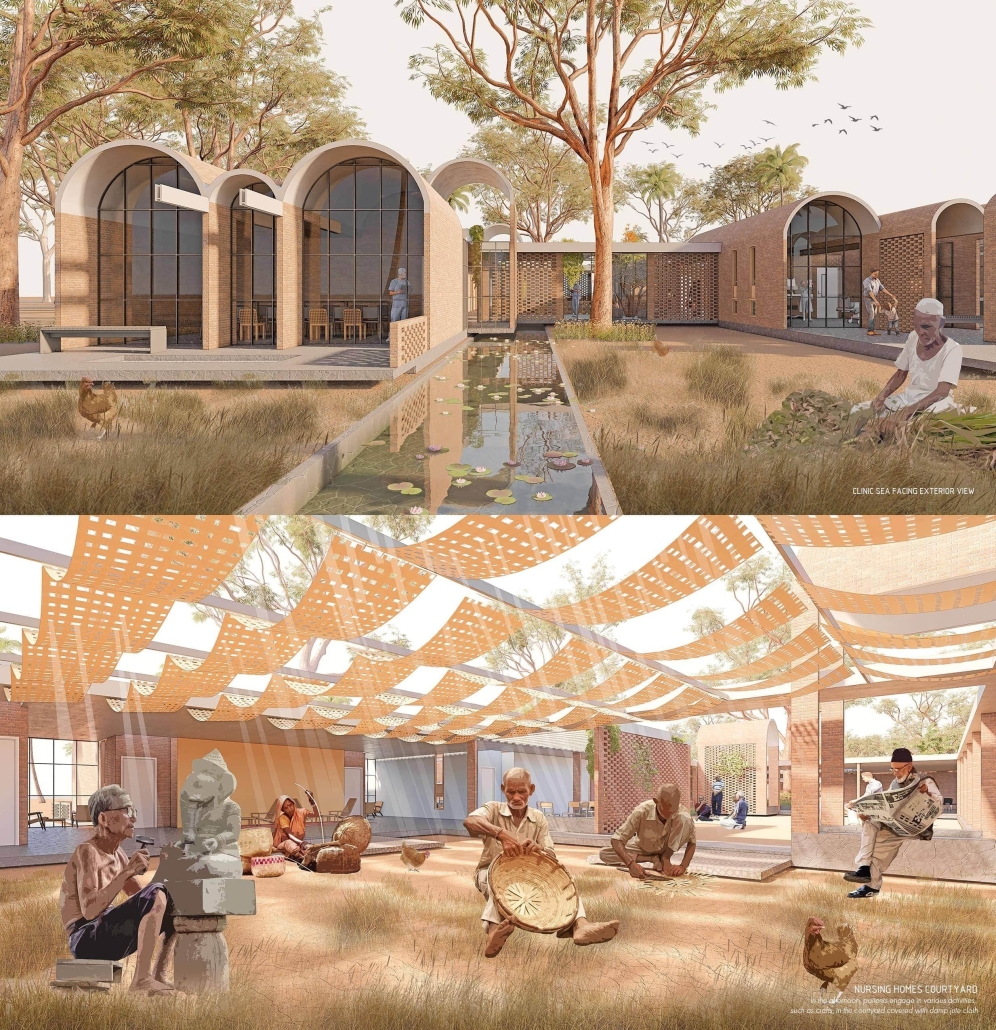
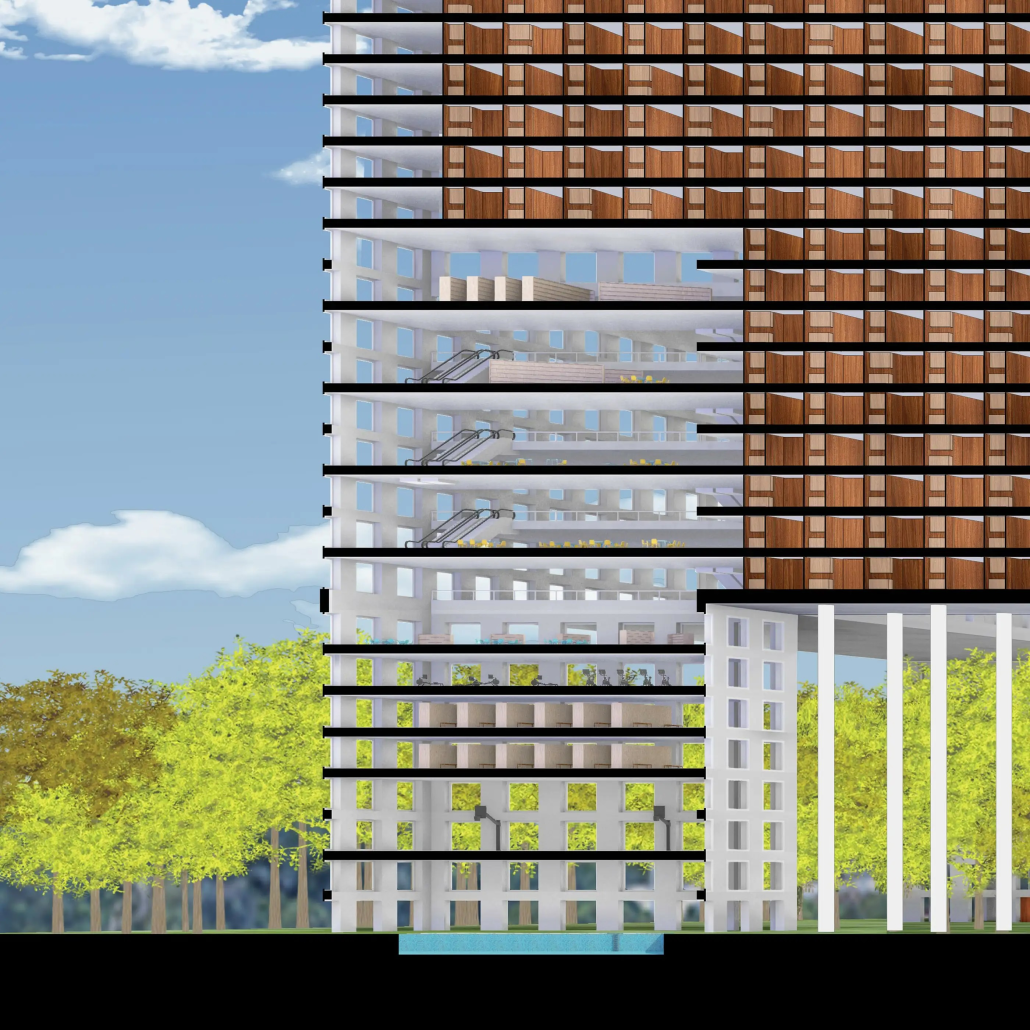
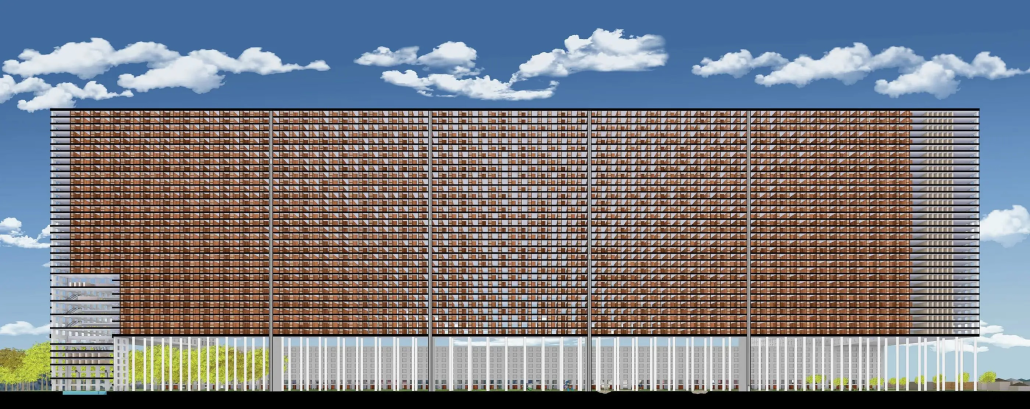
Design to Heal – Dementia Care Center in Goa, India by Surbhi Subhash Ghodke, M.Arch ‘23
University of Utah, School of Architecture | Advisor: Anne Mooney, FAIA, NCARB, LEED AP
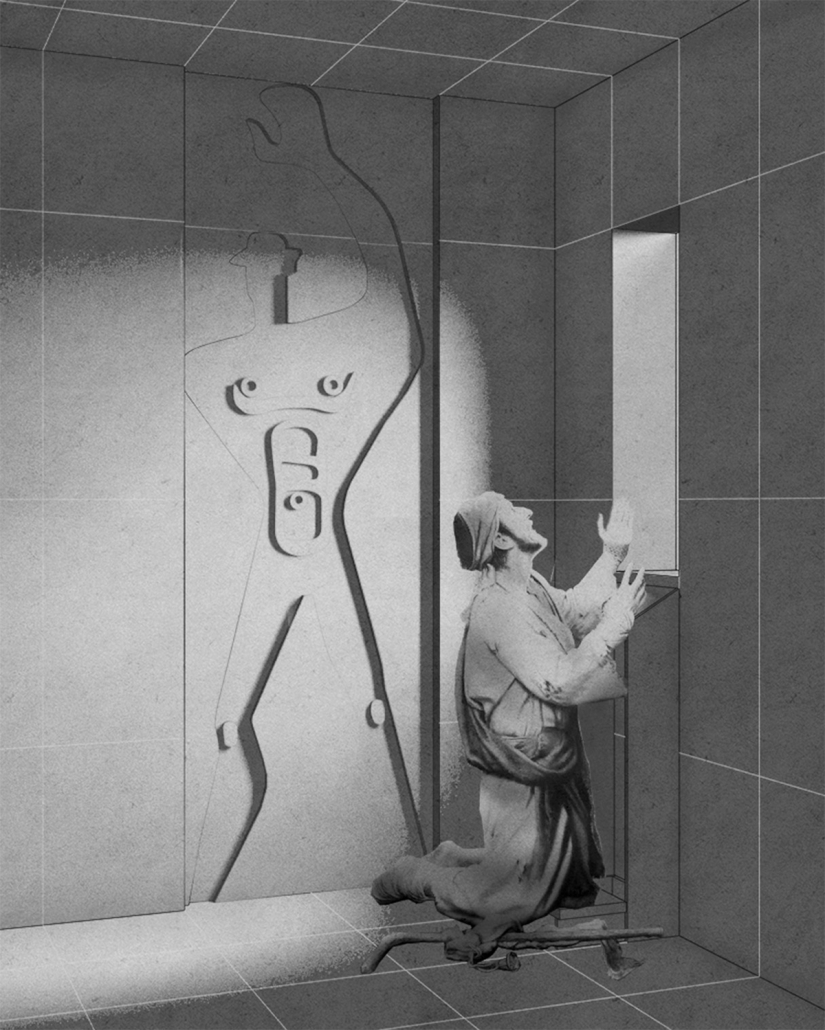
Dementia is a growing concern in India, affecting a significant number of older adults. To address this issue, a dementia care center is being designed in Goa, India. The center aims to provide a holistic environment that promotes the well-being and spiritual needs of individuals with dementia.
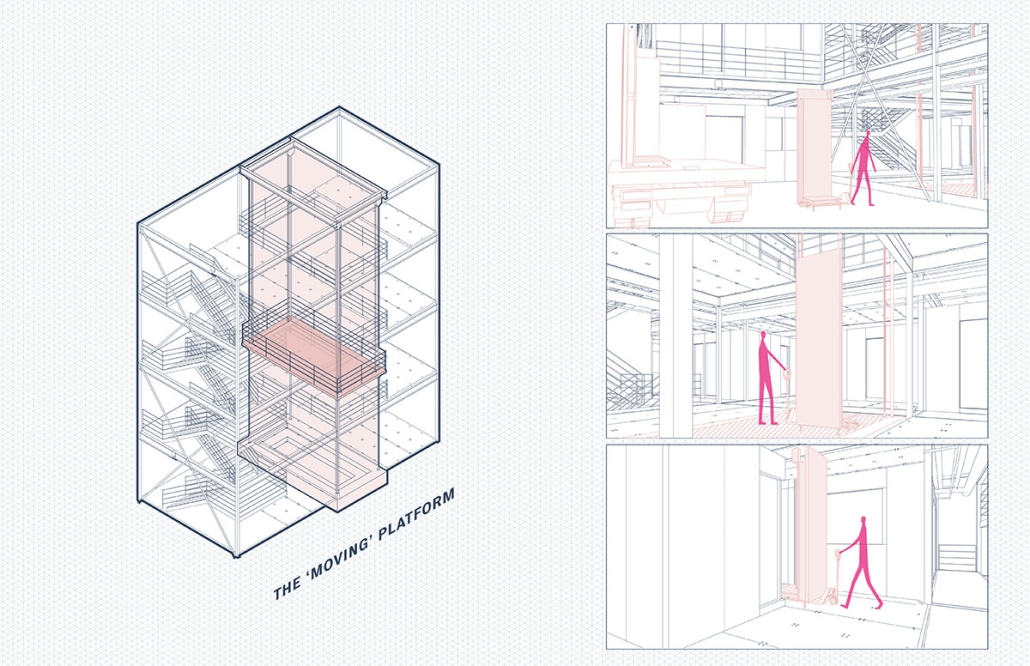
The design prioritizes wayfinding and natural light usage, acknowledging the challenges faced by patients transitioning from private homes to shared living spaces. The center creates a sense of belonging by incorporating familiar spaces and a friendly atmosphere.
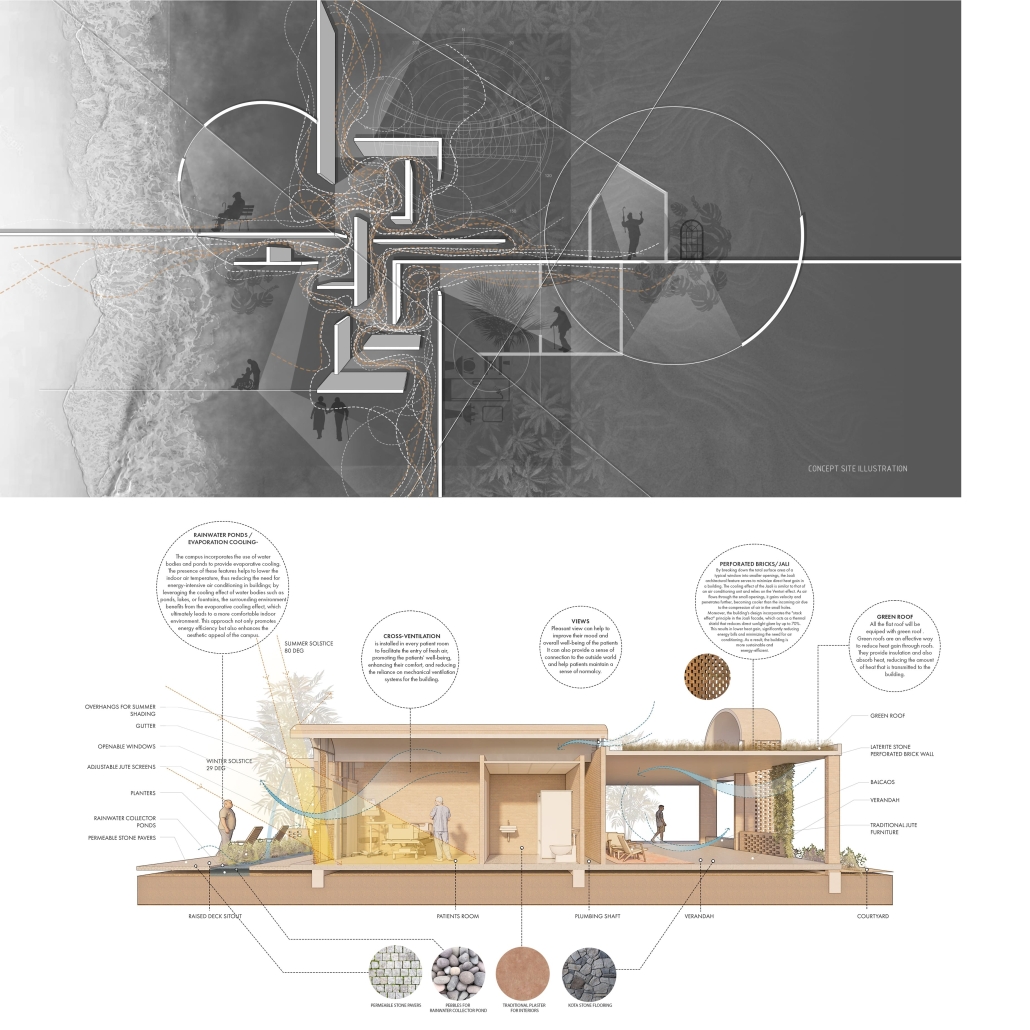
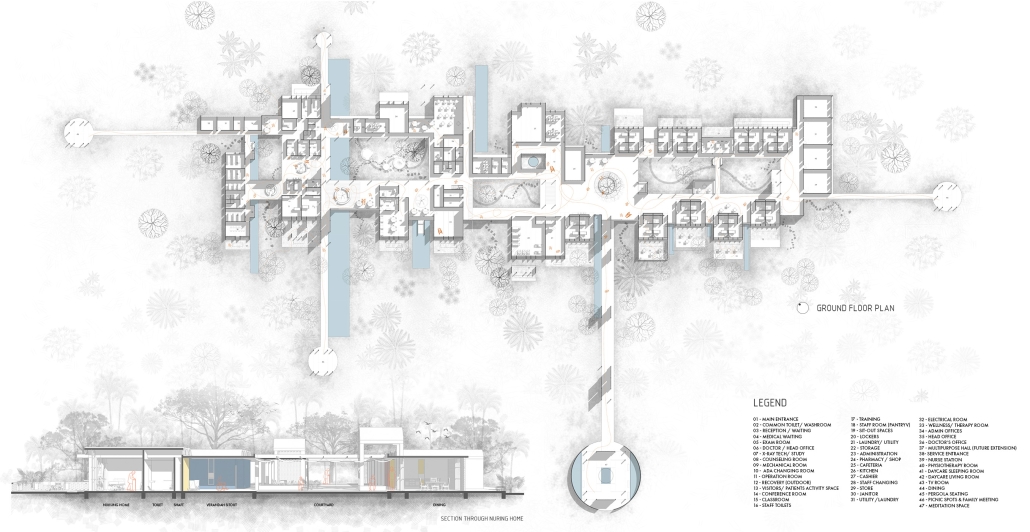
Inspired by traditional Indian architectural elements, the campus design draws from the Wada architecture of Maharashtra. Verandahs, patios, jali (perforated screens), and multiple courtyards are utilized to enhance air circulation and maximize daylight. The design fosters a sense of community, resembling a close-knit village with rooms placed along courtyards.
The care center features multiple purposeful courtyards accessed through narrow paths, encouraging patients to explore and engage with their surroundings. Varying levels of visual access aid wayfinding and social engagement. Colors, textures, and patterns are used as visual cues to differentiate areas and rooms.
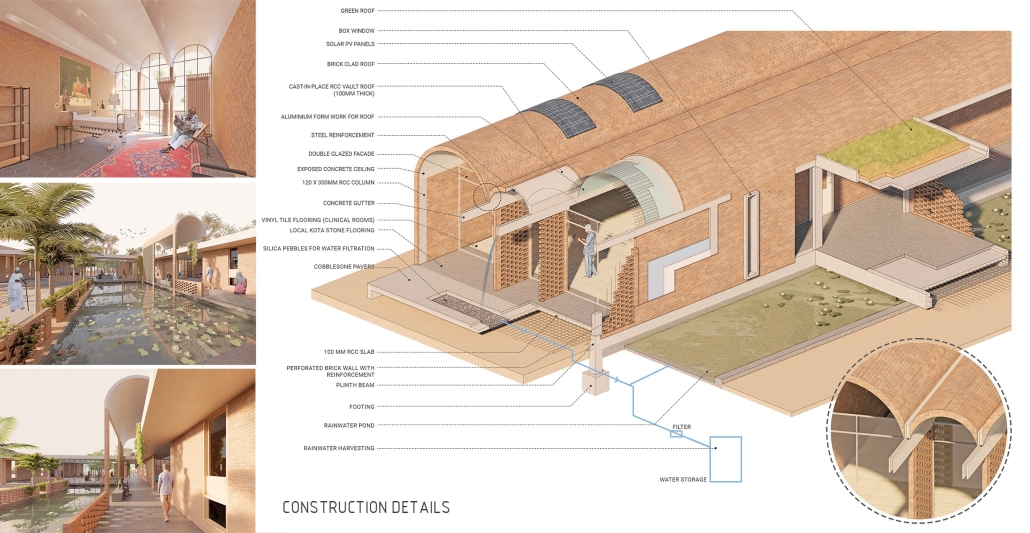
Given the tropical climate in Goa, the campus incorporates large overhangs, circular cutouts for plantations, and water bodies to provide shade and maintain a cool environment. Perforated brick facades offer privacy while allowing natural light and cool breezes to flow into the campus.
To add an element of playfulness, the roof design includes roofs of varying heights and shapes. Daylight integration through skylights and effective rainwater drainage systems are incorporated, with rainwater collected for lotus plantations and gardens on the campus.
The campus design utilizes local materials such as red laterite bricks and stone, aligning with the vernacular architecture of rural Goa and respecting the surrounding context.
Overall, the design of the dementia care center in Goa aims to create a people-centered environment that addresses the physical, spiritual, and emotional needs of individuals with dementia.
This project received the 2023 ARCC KING STUDENT MEDAL for innovation, integrity, and scholarship in architectural research.
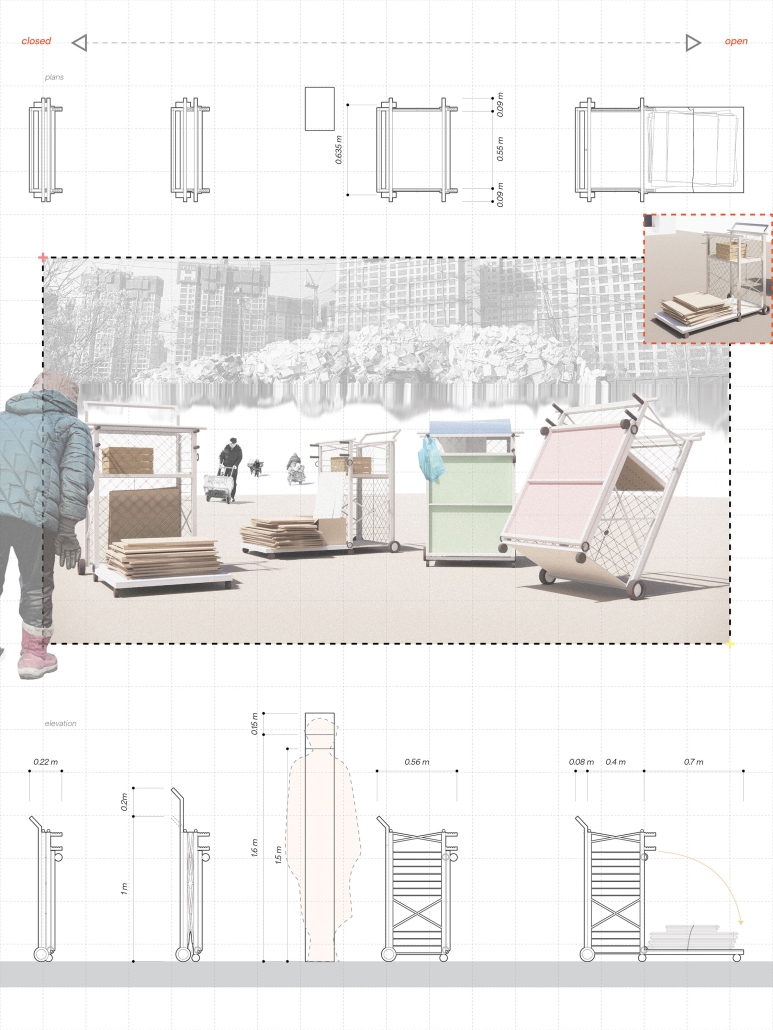
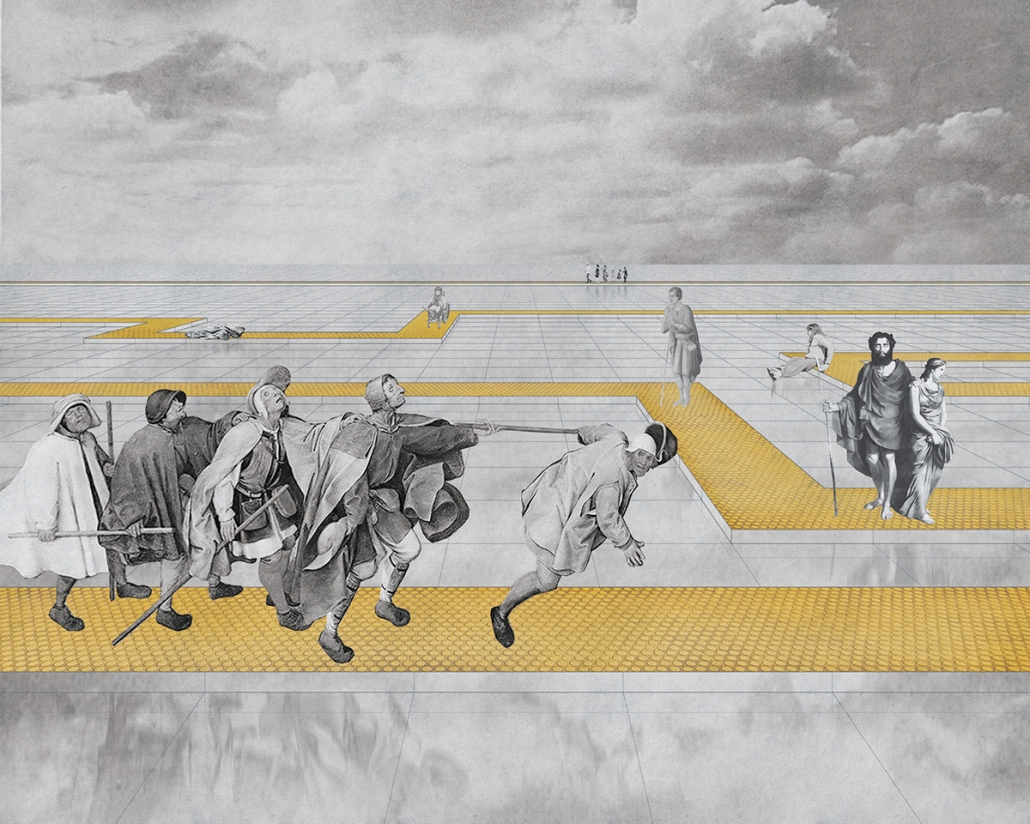
Lending a Hand to Guryong Village: Agency, Community, and Shared Economies by Jonathan Chung, M.Arch ‘23
Carleton University | Advisor: Jerry Hacker
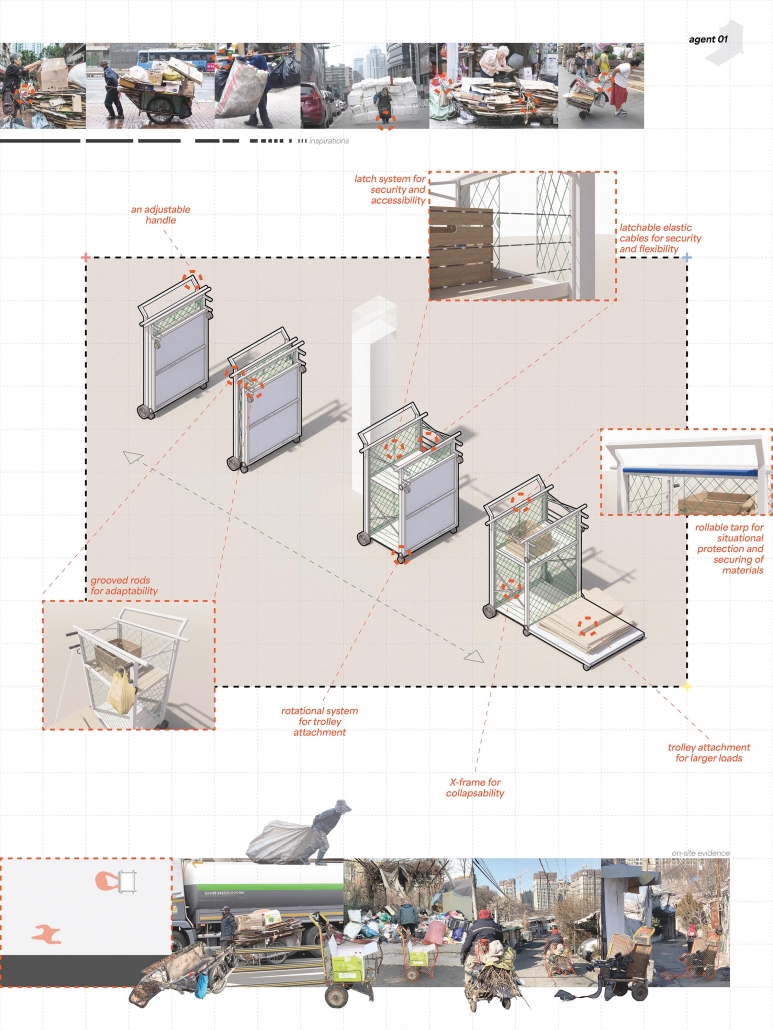
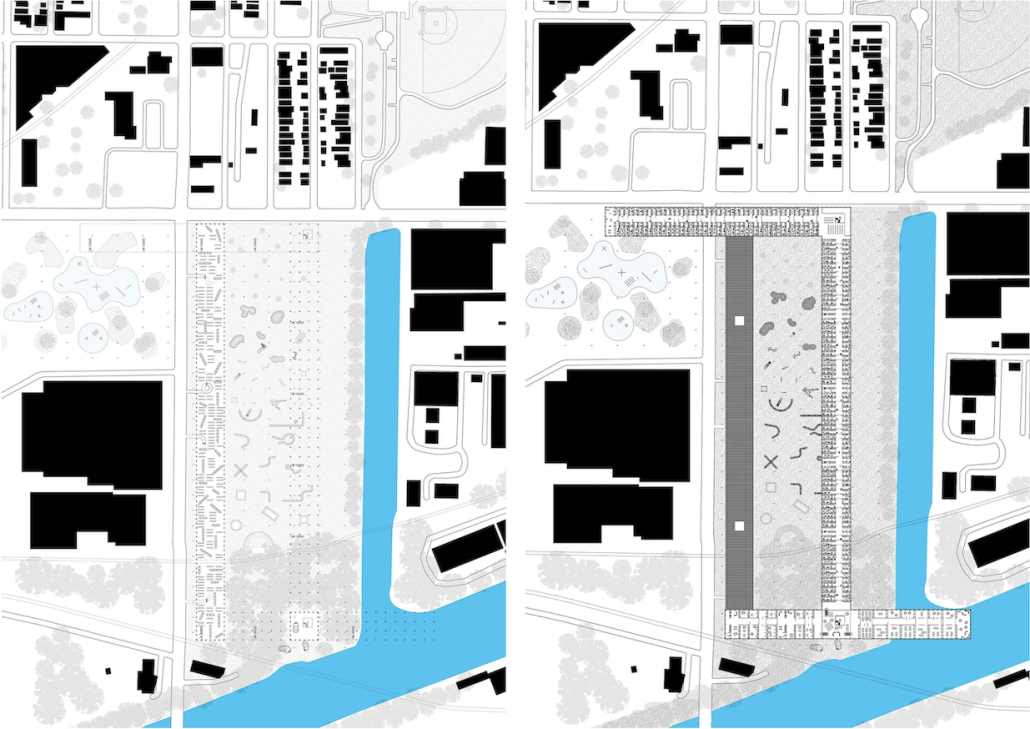
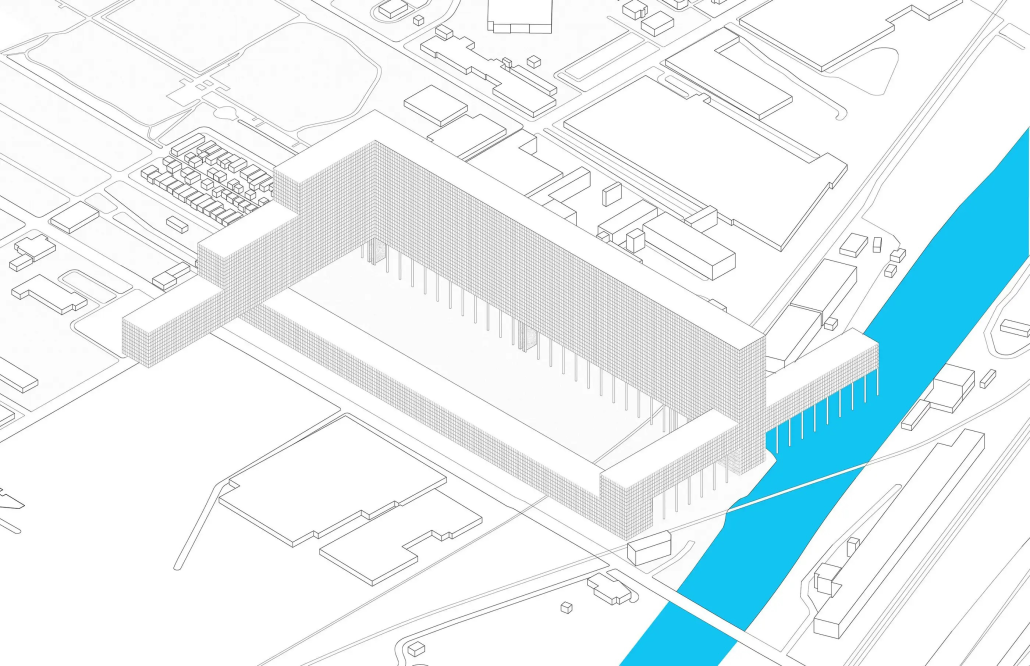
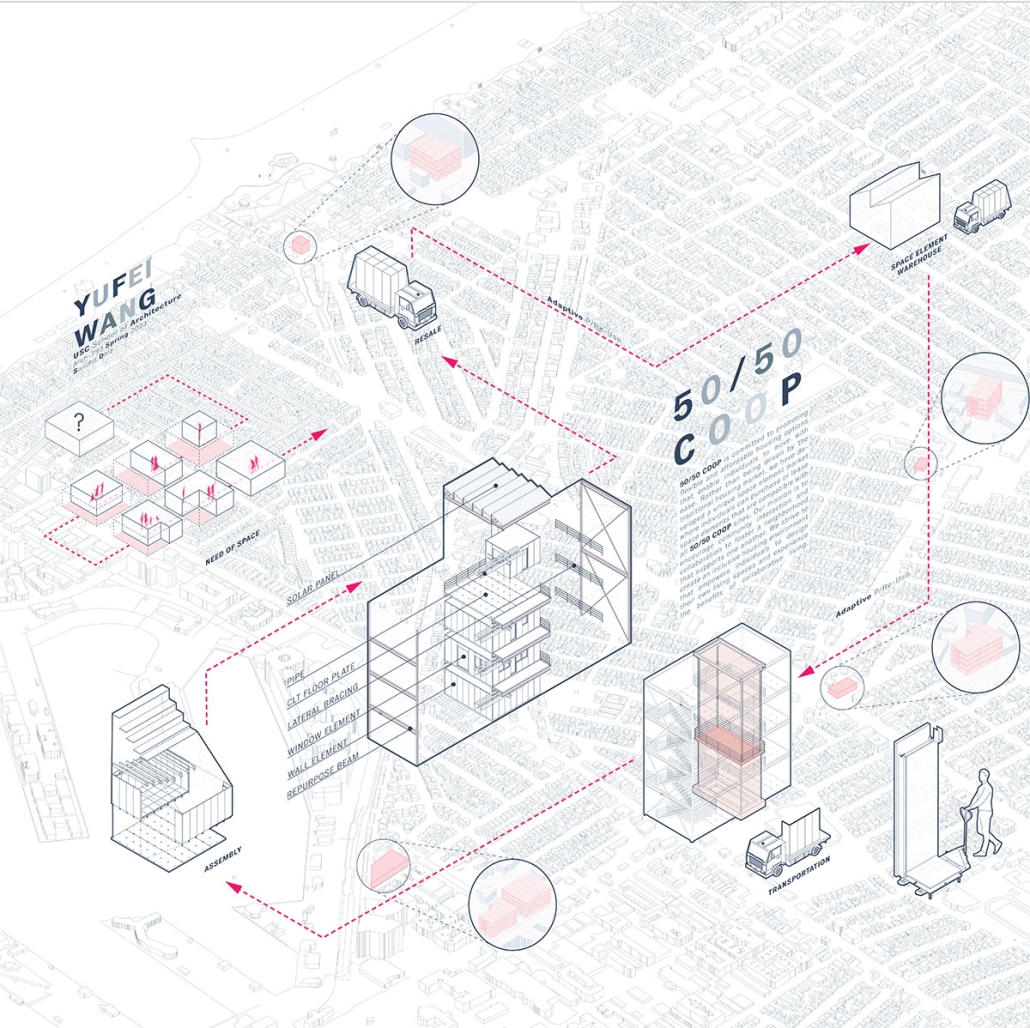
Using Guryong village (a self-built community in Seoul, South Korea) as the site of investigation, this thesis explores the spatial relationships and architectures of care between the state and the city’s ignored and most vulnerable citizens. Recognizing the residents’ progress in self-creation and self-provision, the question of interest is what degree of aid should be provided for the waste economy to further enhance community and quality of life for those in the village. To date, Guryong village has been subject to debate over land ownership and government provisions; however, this thesis endeavors to explore the role, active and creative users hold in lending a hand to normalizing waste collection and making it more accessible. Research methodologies include literature and media reviews, on-site experience, analytical drawing, and research through design. As a result, this thesis proposes a singular infrastructural framework of three agents of support at three different scales intended to further the agency and community of those in Guryong village: an agent for travel, for storage, and for collection and resource. Specifically, these infrastructures augment the existing self-created economy of waste transformation led by the elderly of the village and South Korea. Therefore, using architecture’s potential to create broader citizen and urban dialogue, this work strives to help build a better understanding of the value and state of self-actualized spaces and their communities, and to reflect on the impact of community on an individual, city, country, and the world.
This project received the Boraks Prize.
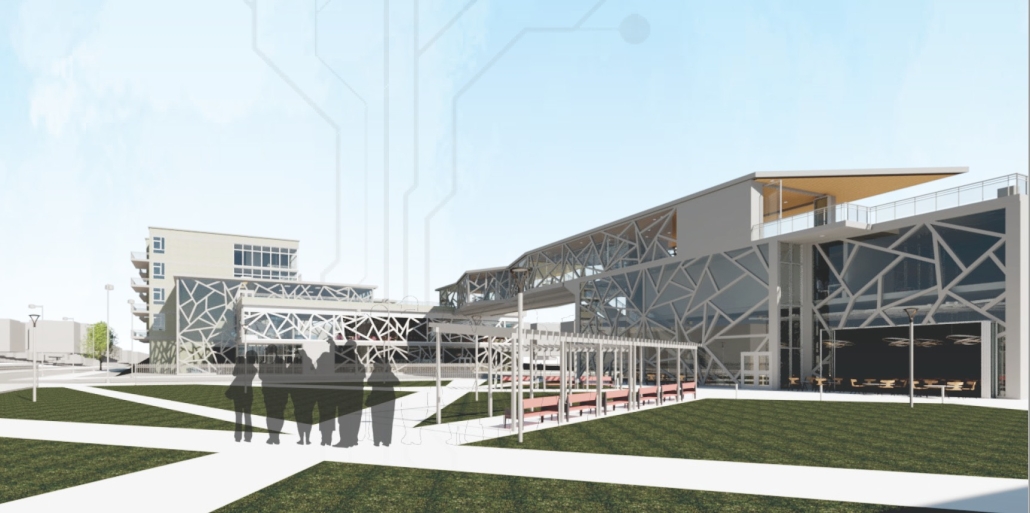
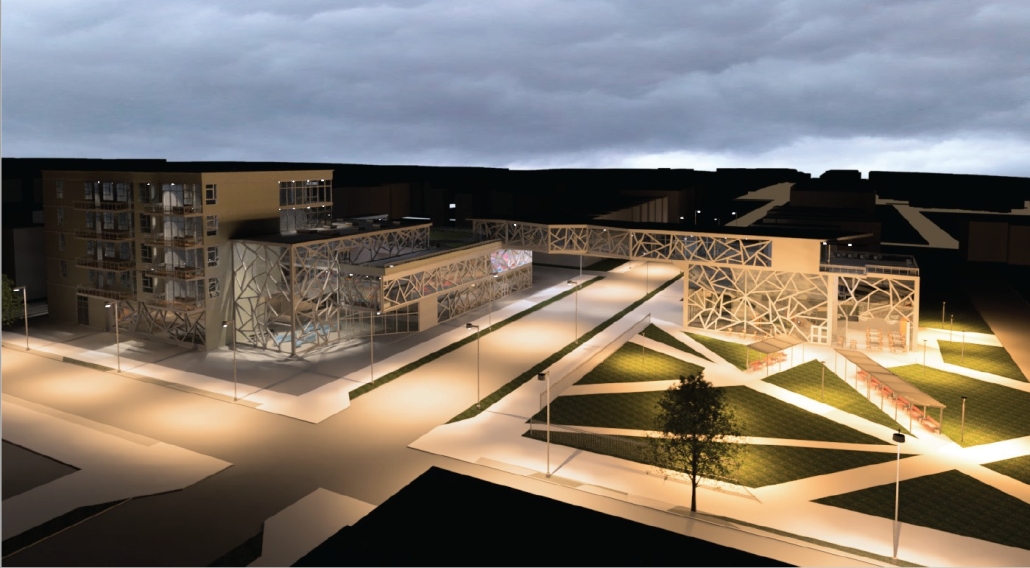
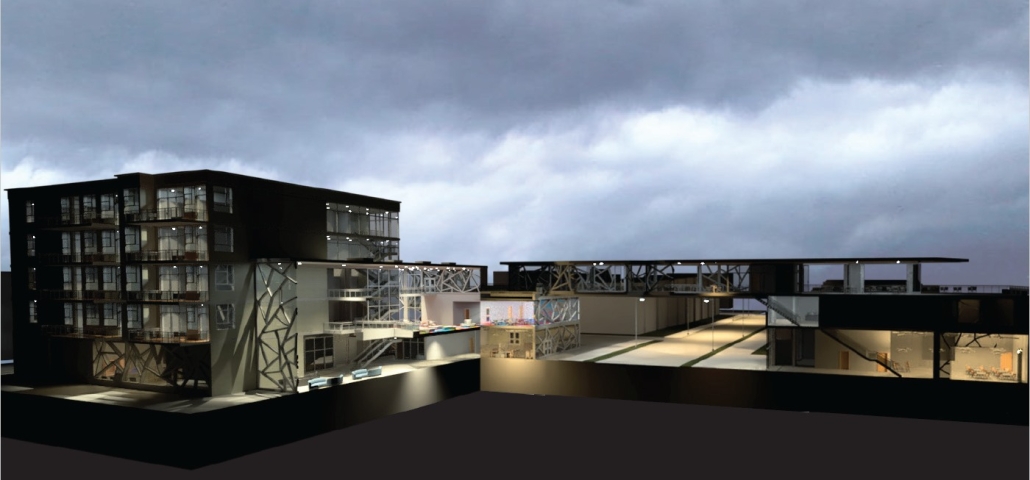
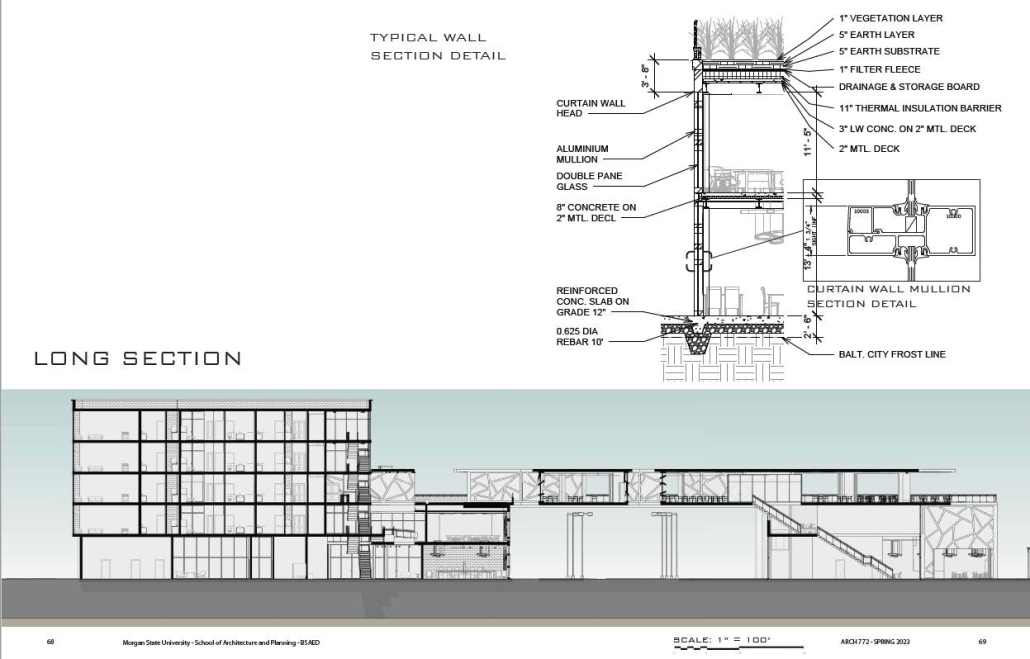
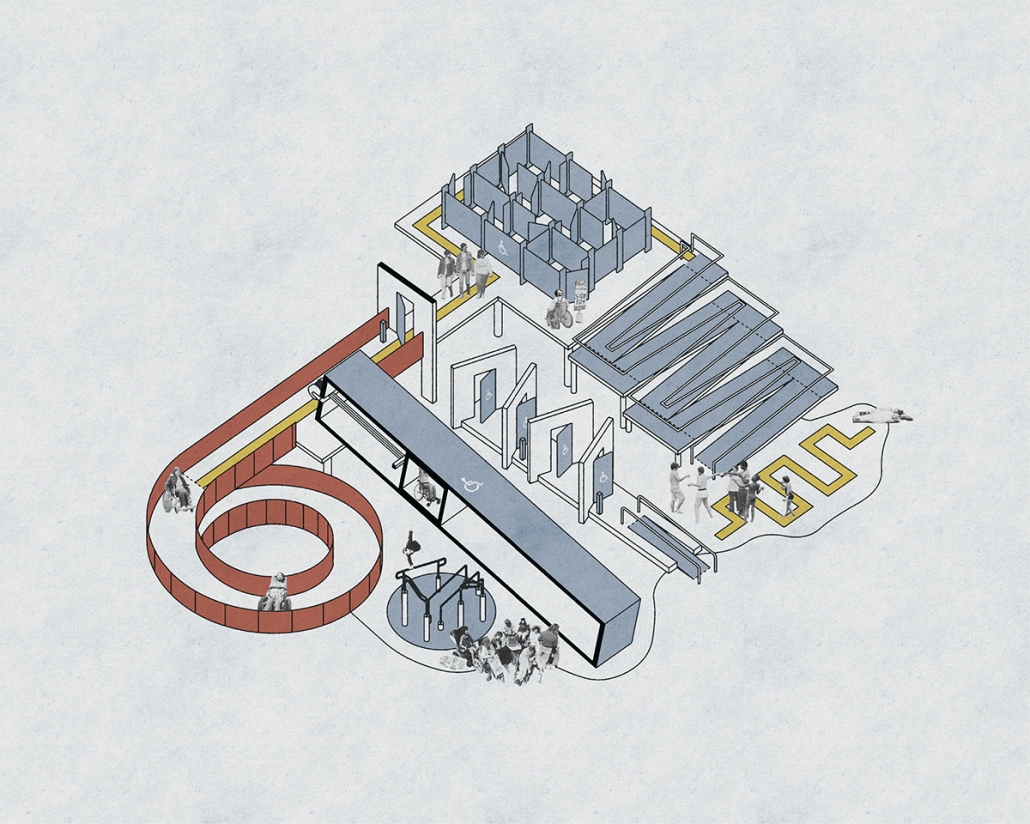
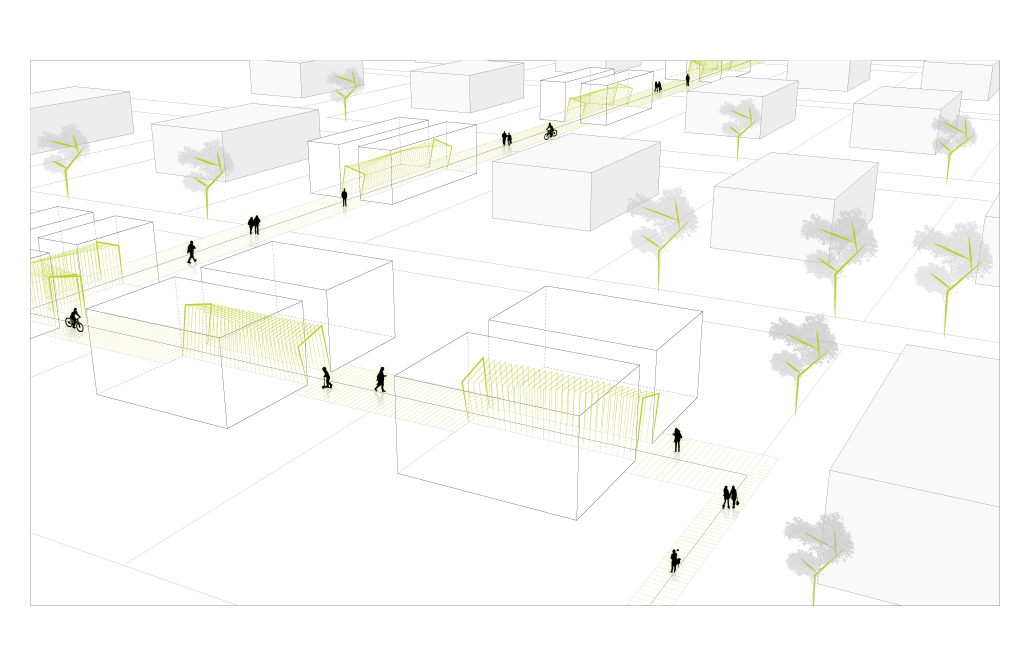
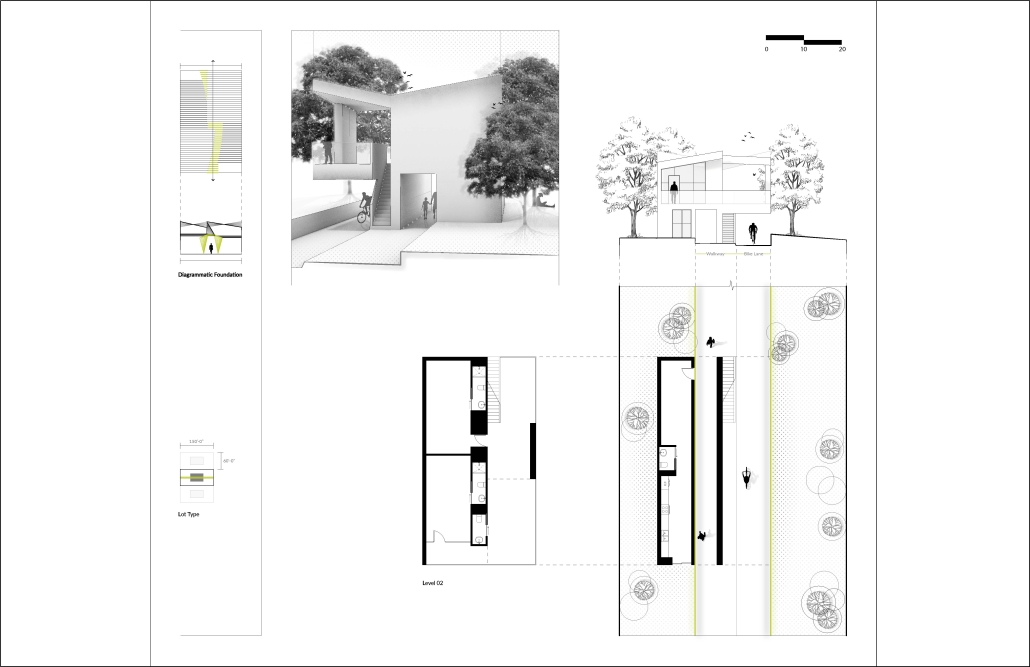
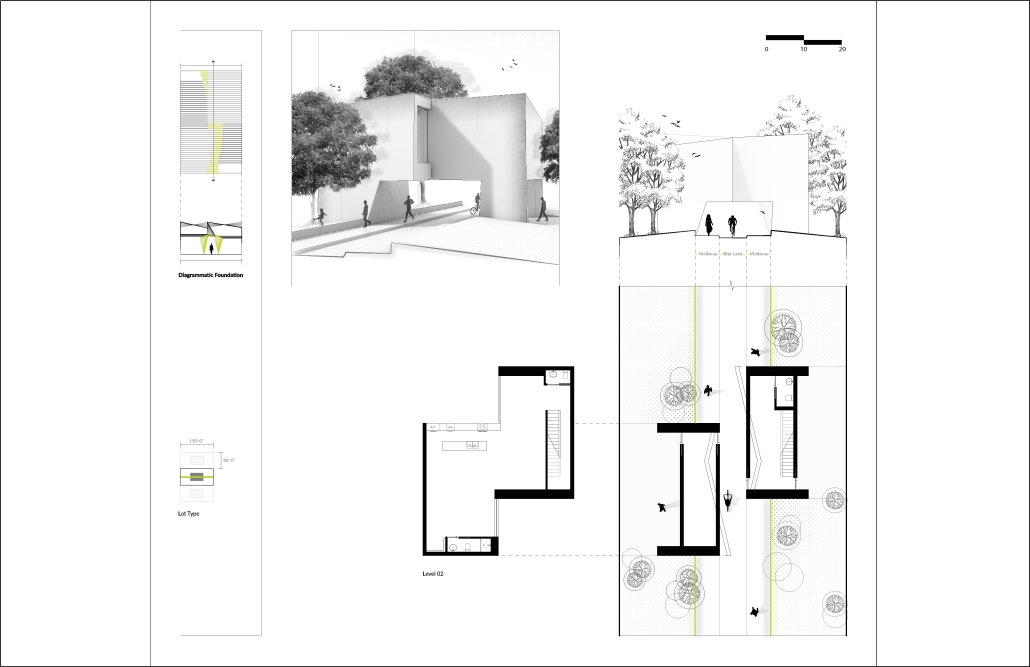
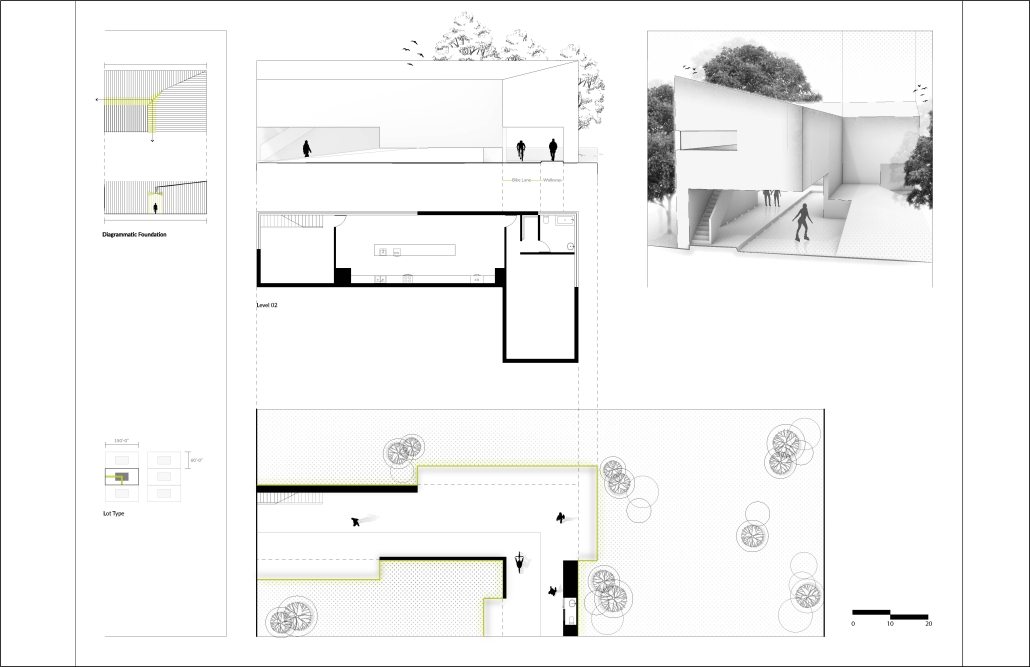
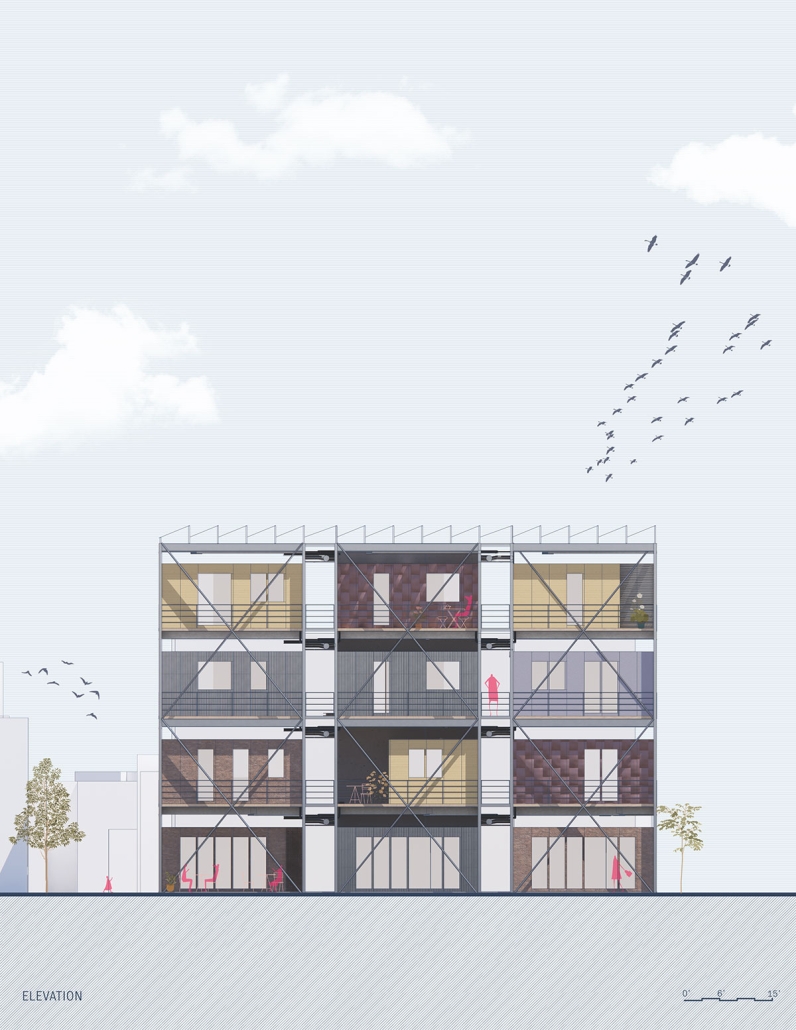
(RE)GENERATION MULTI-GENERATIONAL HOUSING & DAY CENTER by Devin Simmons, M.Arch ‘23
Morgan State University, School of Architecture & Planning | Advisor: Carlos A. Reimers
The elderly are isolated in our American cities, and suffer depression and the looming thought of the endpoint of their lives drawing near. Conventional independent and assisted living facilities may be good buildings, but they usually serve only the function of housing, shelter, and health. Where is the life of it though? Residents interact with their care providers and others their age. The youth exuberates life and enjoyment, none of that is present in these facilities. The vision for this project is not only to integrate generations together, but to provide the elderly with the motivation to embrace life instead of feeling isolated and stressed about the end. A building that has multiple uses to integrate multi-generational encounters.
This project won the Best Thesis Award
Instagram: @reimerscarlos
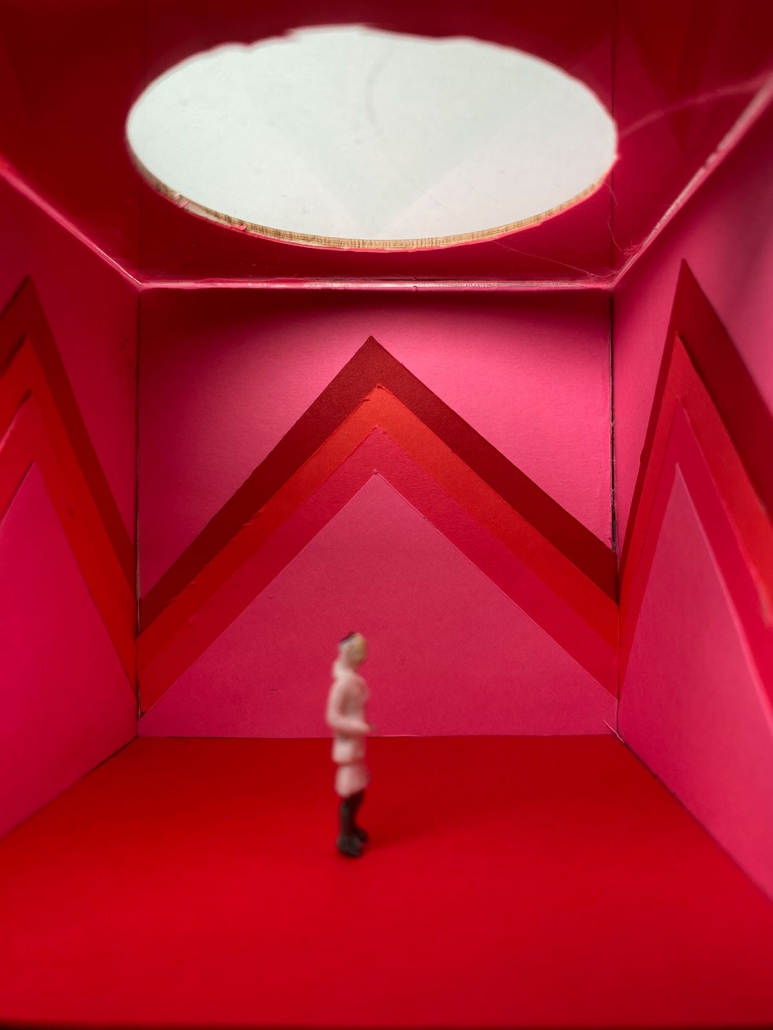
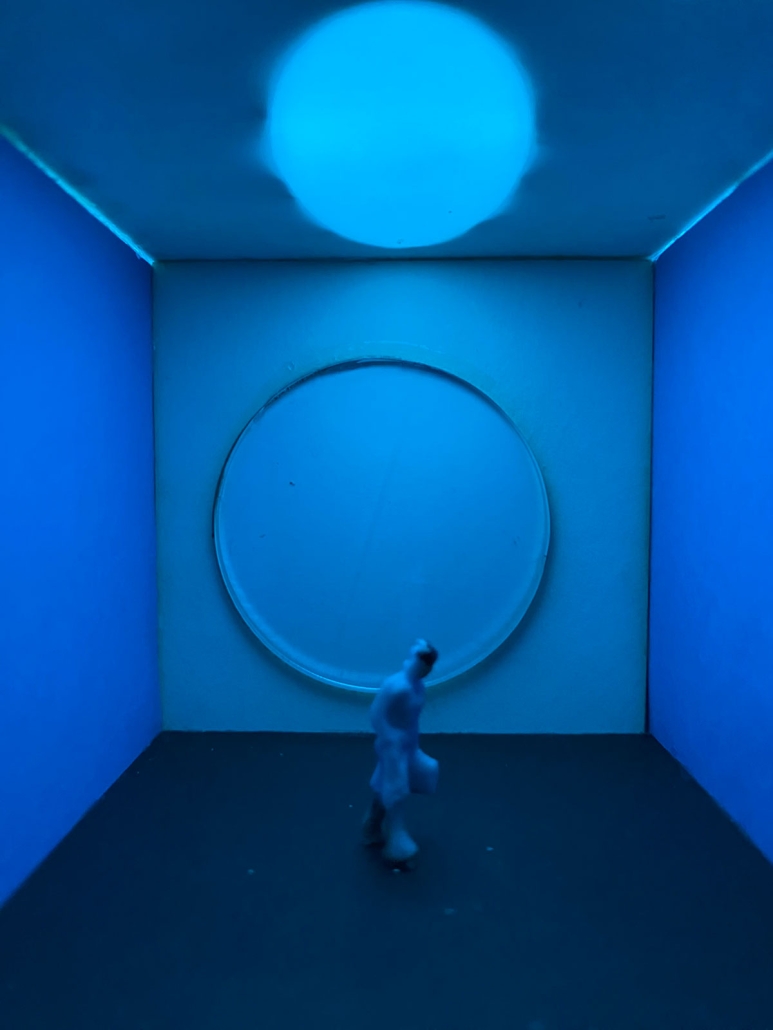
Bedlam by Leka Mpigi, M.Arch ‘23
University of Southern California | Advisor: John Southern
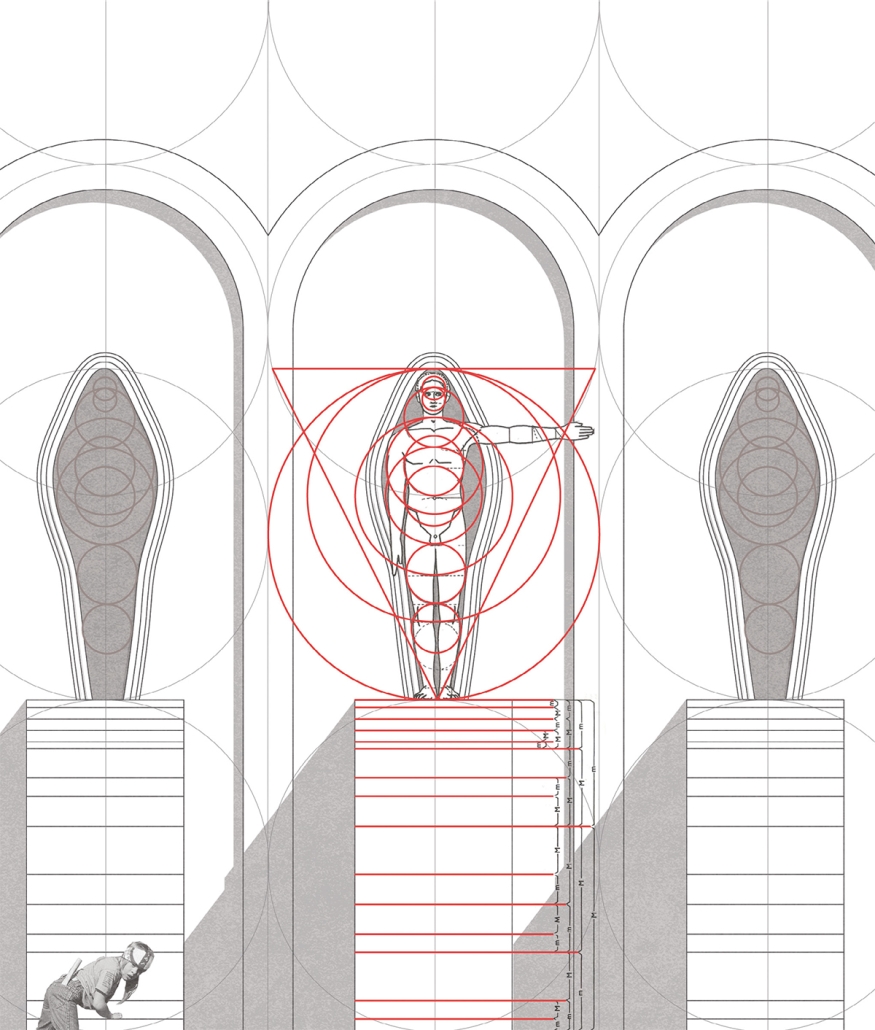
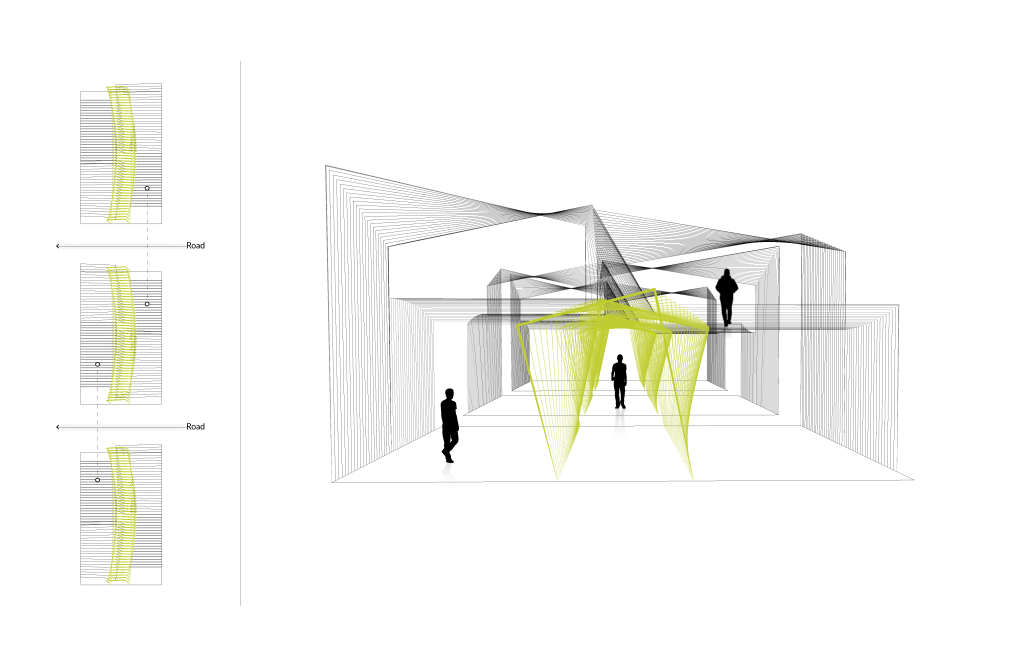
Architecture can play a more vital role in the built environment that goes beyond urban organization and aesthetic value. Statistics show that as humans regardless of character, belief, and ability, are most affected by the spaces we inhabit in comparison to any other mortal factors. Exploring collage with the intent to explore design elements such as color, light and mass presents us with the potential to optimize the spaces we create, not just visually, but also functionally. Functionality is no longer defined only through the narrow lens of practicality and usefulness as humans have evolved, looking inward toward the importance of features that aid, not just physical ability, but also mental stability and growth. It is important that architecture in all sectors perseveres to not only try to follow but also lead this conversation. Designing to accommodate human behavior such as eating, bathing, and sleeping have been explored on thorough levels being that the focus group only includes a small percentage of people with all abilities intact. However, limiting ourselves to this scale of exploration sells us short not just as a profession but as members of the global community at large. Theories of the appropriate manipulation of color, light and mass have been studied to be able to produce the highest quality of space that not only guarantees overall wellness but also longevity and potentially by 2040 a greater population of people living more cognitively over 65 years old.
The age group most affected by all concepts discussed above is the elderly 55+ population and to critically analyze the claims I have made above; I have decided to narrow down my research to members of this community with cognitive impairments such as dementia. This thesis will reevaluate the current living conditions on a local scale here in Los Angeles but will arguably be effective also in other cities and possibly countries, keeping in mind that culture and tradition do play a vital role in the connections people have to design elements such as color and light. The remodeling of a curated sample of already existing nursing homes will create room for critical evaluation showing how these spaces can be optimized for patients with certain formal architectural and interior design edits. I predict that this experiment will not only create care homes that are more visually and aesthetically pleasing but also potential optimal wellness environments proven to slow or in rare cases even reverse the decline of people with dementia over time. The ideal space in this experiment will have the following characteristics: negotiability (obstacle-free), familiarity and sensory stimulation (ways to trigger memory and recall). On this foundation, I will also introduce researched elements such as color coding, friendly mass (non-triggering forms) and light therapy to enhance set sample space. It is important to note that these experiments are amenable to and require implantation and validation. However these prototypes are based on research, many observations of case studies, and interviews with facility directors with their opinions occasionally taken into play due to their years of onsite hands-on experiences.
This project received a USC Master of Architecture Distinction in Directed Design Research
See you in the next installment of the Student Showcase!