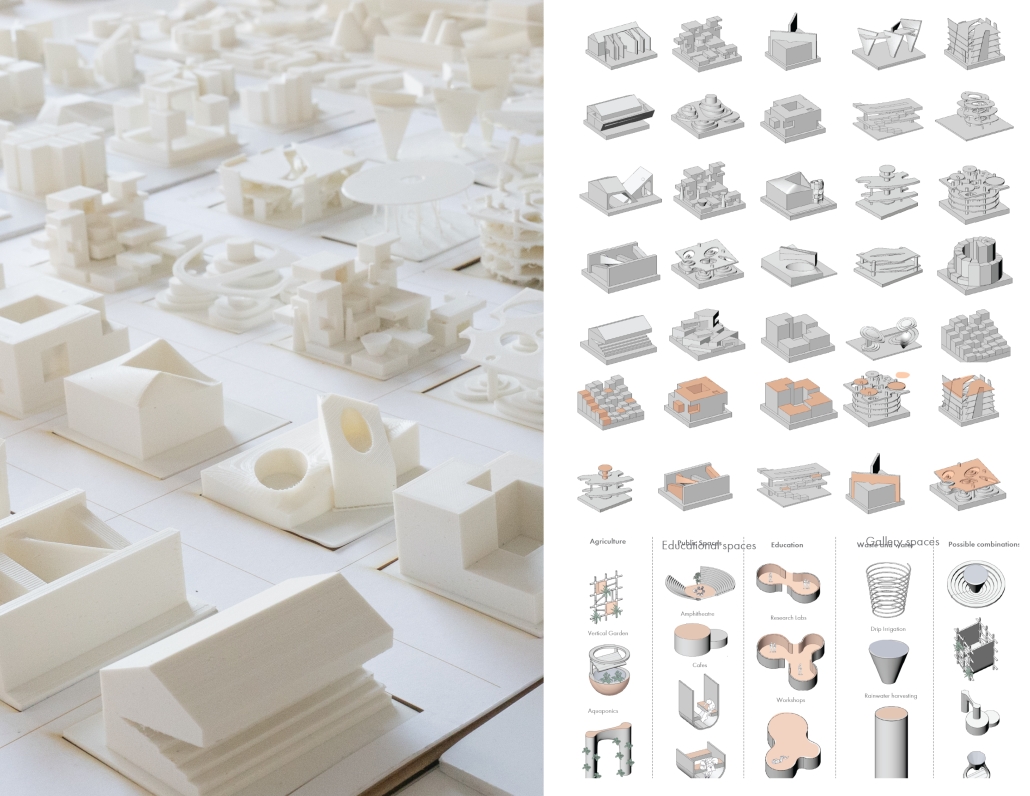
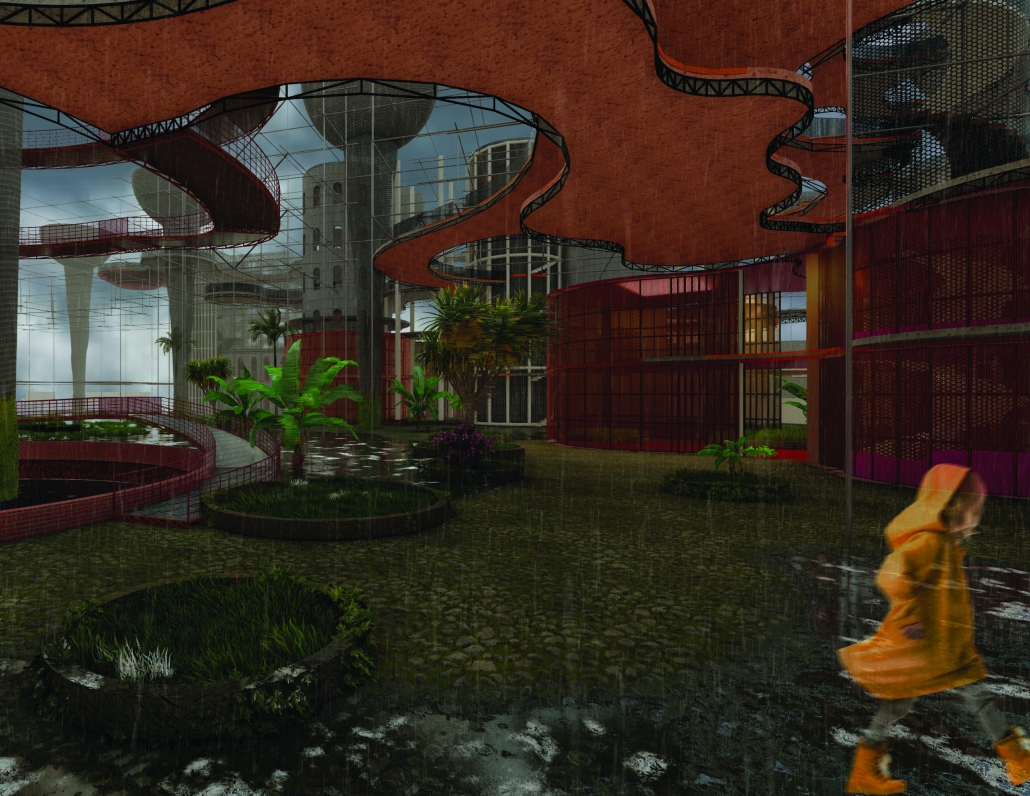
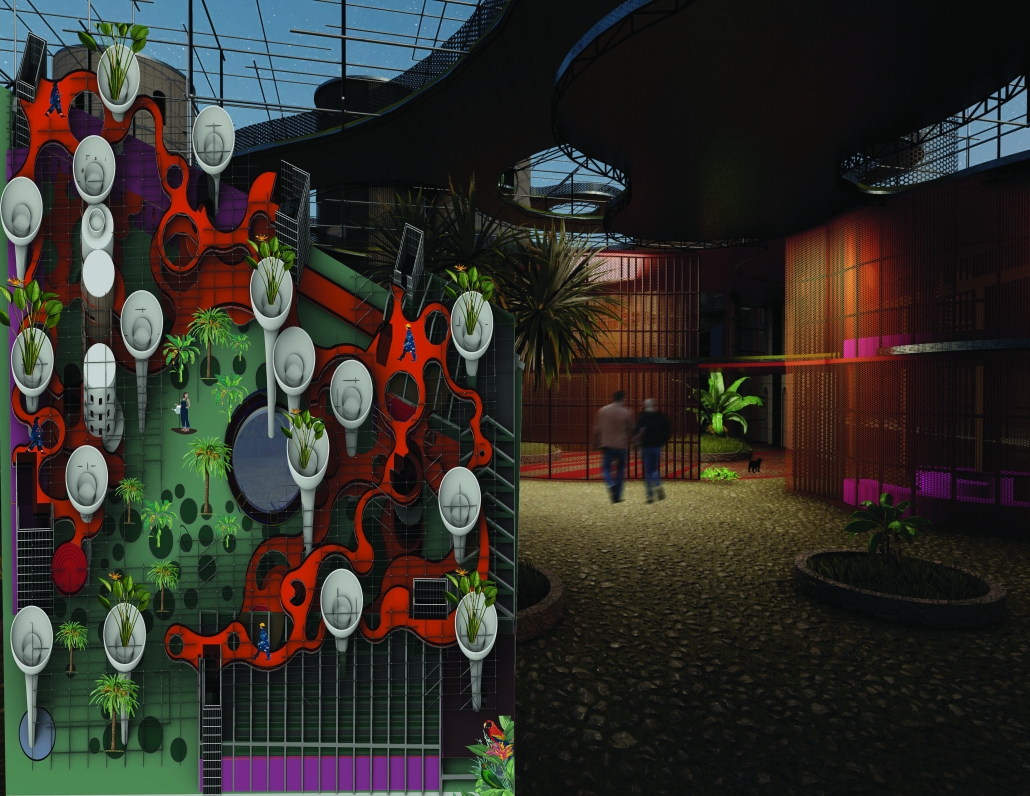
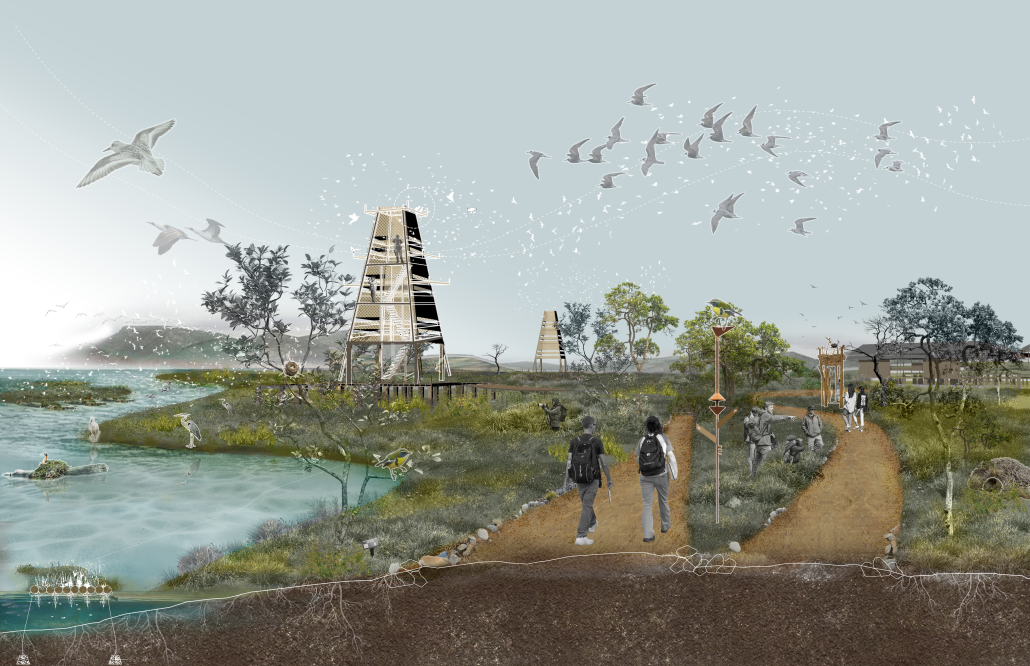
2025 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part VI
Today’s installment of the 2025 Student Showcase highlights projects with a focus on landscape and agriculture. Part VI features student work that takes place in diverse settings, including New Mexico, Brazil, Chile, Alaska, and more. Each project utilizes architecture as a tool to promote sustainability, social equity, and community resilience.
Scroll down for a closer look at these outstanding student projects!
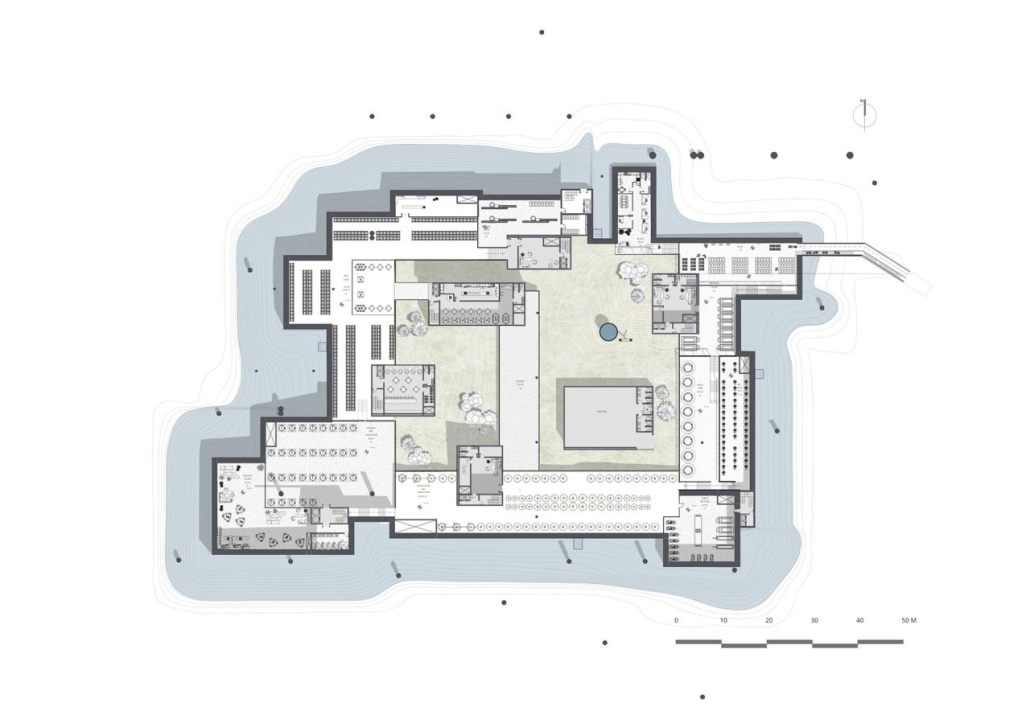
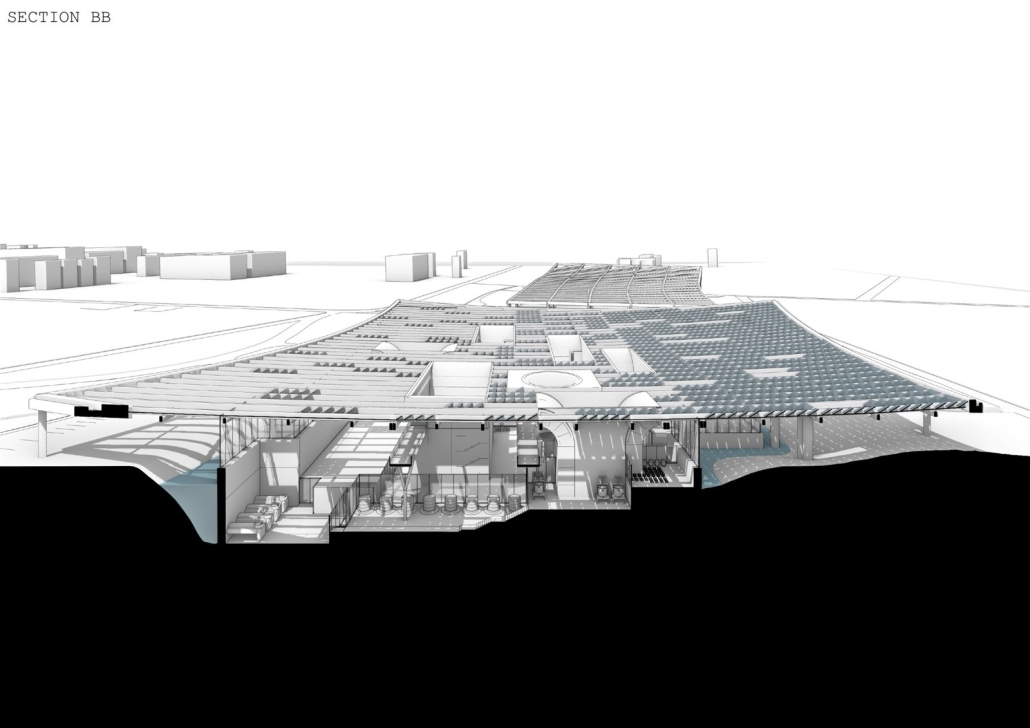
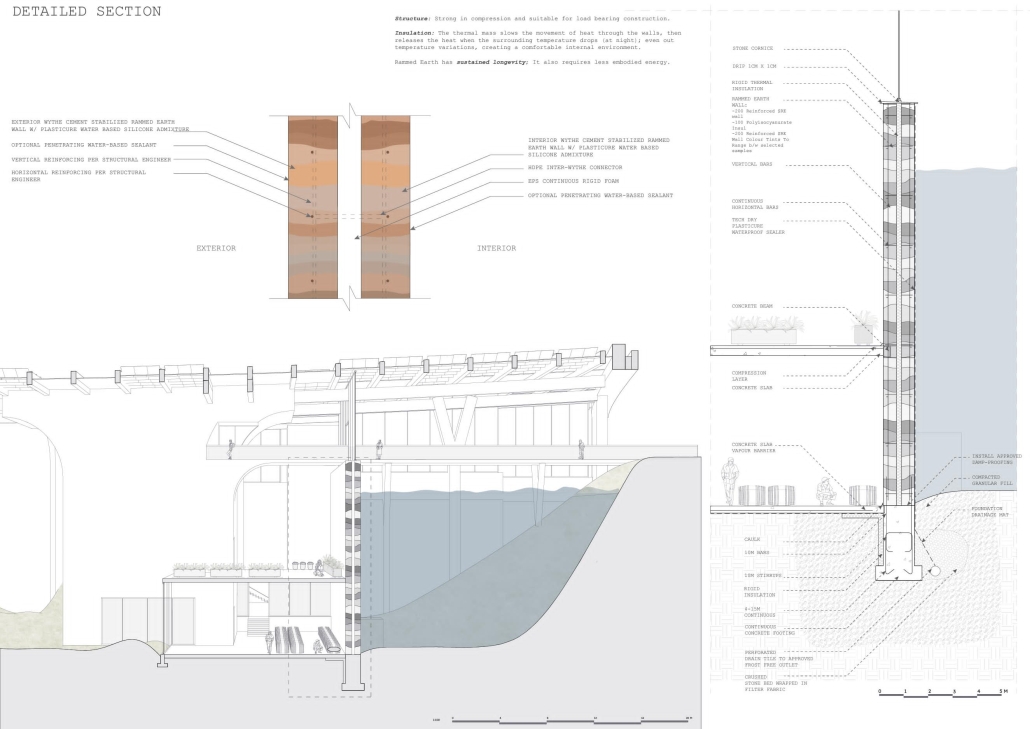
The Agrarian City by Aneesha Muthuraj & Rajni Kathiriya, M.Arch ‘25
New York Institute of Technology | Advisors: Marcella del Signore & Evan Shieh
In a time when urban centers face growing food insecurity and rural traditions risk being forgotten, architecture has the potential to bridge the gap between cultural heritage and contemporary urban challenges.
This project began with two key questions:
- How can architecture reconnect Brazil’s deep agrarian identity with its current urban food insecurity?
- And how can we transform abandoned structures into systems that grow food, share knowledge, and empower local communities?
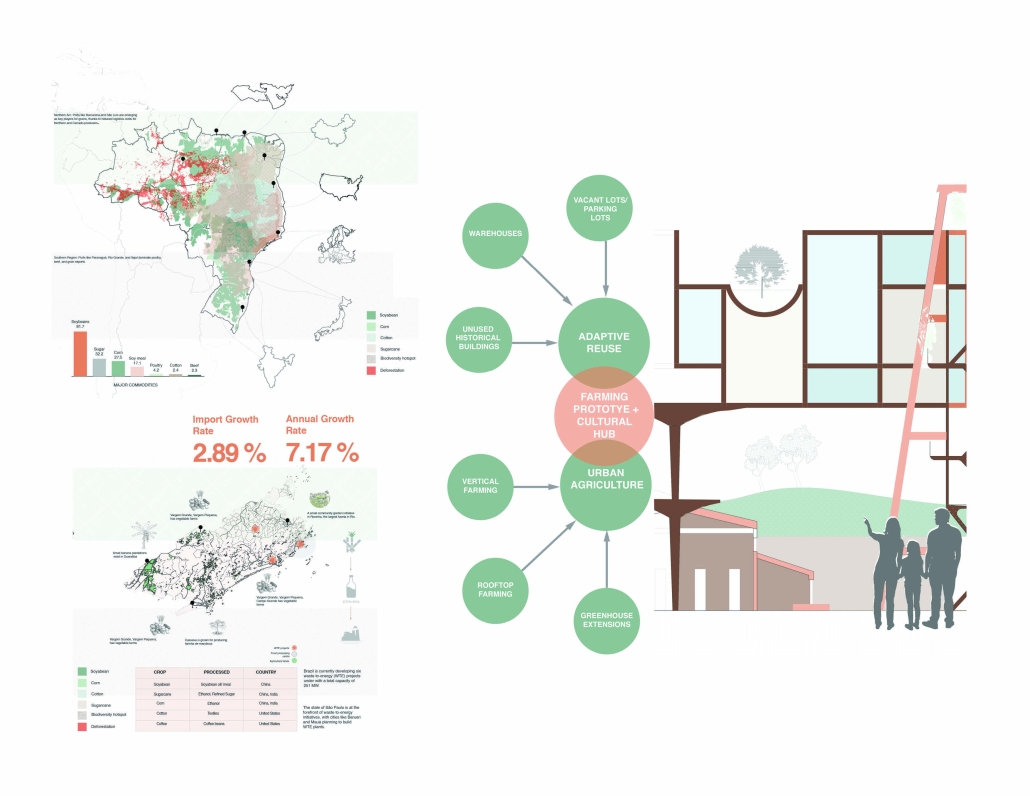
From these questions, “The Agrarian City” was born, a design framework that proposes scaffolding systems and modular toolkit insertions to retrofit unused buildings into vertical teaching farms. These structures not only produce food but also serve as platforms for education, skill-building, and community gathering.
Our pilot site in São Cristóvão, Rio de Janeiro, is rooted in the principles of adaptive reuse, seasonal crop planning, and integrated spatial systems that blur the lines between agriculture, learning, and public life. By treating architecture as an evolving, regenerative system rather than a static form, the project aims to demonstrate how the built environment can support ecological restoration, food justice, and social empowerment. At its core, The Agrarian City is about growing, reusing, and educating, rethinking the role of architecture as a living system that cultivates resilience and belonging within the urban fabric.
Instagram: @aneesha_muthuraj, @ev07, @marcelladelsi
Nuclear Landscapes of New Mexico by Amanda Champion, Master of Landscape Architecture (MLA)’25
University of New Mexico | Advisors: Catherine Page Harris, Chris Wilson, Nora Wendl & Dr. Myrriah Gomez
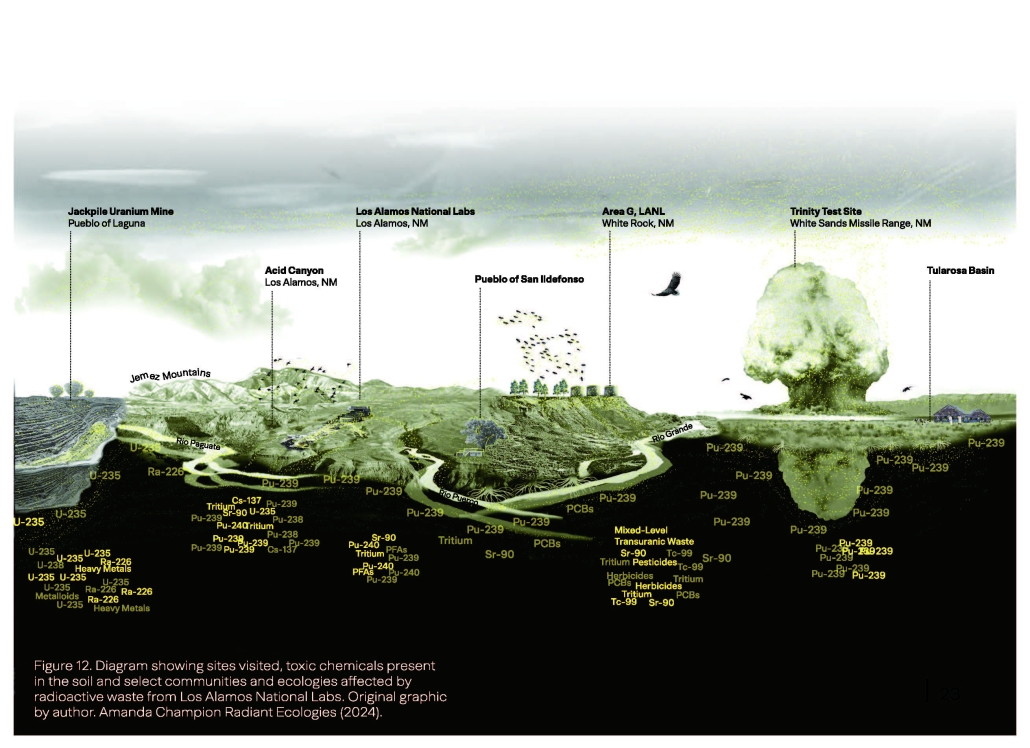
Champion (MLA 2025) investigated Acid Canyon, Los Alamos, NM, through her master’s project, making visible water moving plutonium through public recreational landscapes into the Rio Grande. Champion wrote, “The landscapes of nuclear sites, both historic and contemporary, are designed spaces that tell specific stories about the societies we live in. Whether highly visible industrial infrastructure or naturalistic spaces touched by the invisible yet toxic hand of radiation, these landscapes are woven into the fabric of the New Mexican landscape … Many of these landscapes are unknown due to the intentional secrecy of the federal government around the nuclear weapons industry.”
This project received a master’s distinction.
Instagram: @a_man_dog, @cph_landart
Roots and Rails by Alyssa Ascani, Naomi Metzger & Siraphat Sukarom, M.Arch ’25
New York Institute of Technology | Advisors: Marcella Del Signore & Evan Shieh
“Roots and Rails” is a design thesis focused on reimagining food distribution infrastructure in Brazil at a micro scale, specifically in the São Cristóvão neighborhood of Rio de Janeiro. The project addresses issues of food insecurity, infrastructure inequality, and community disconnection, proposing a local food network.
Brazil is a major exporter of agricultural goods, but simultaneously imports rising amounts of processed food. In neighborhoods like São Cristóvão, this results in food deserts and traffic congestion from export-driven transport. Mapping studies revealed that large portions of the population live beyond walkable distances to grocery stores, especially in dense areas like favelas.
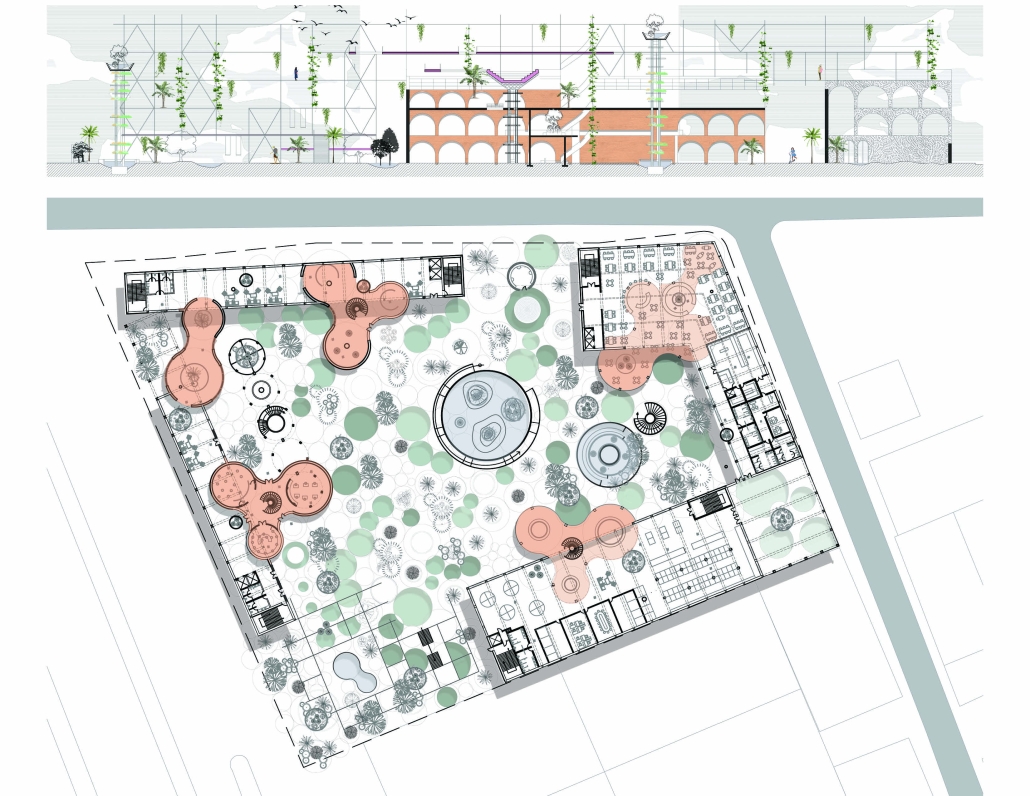
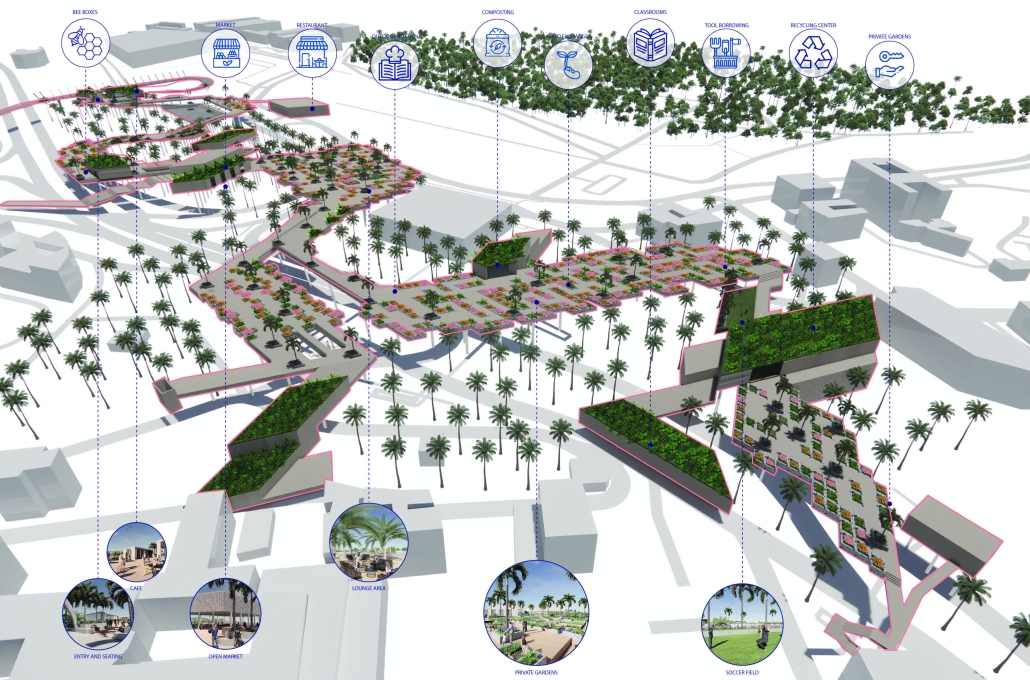
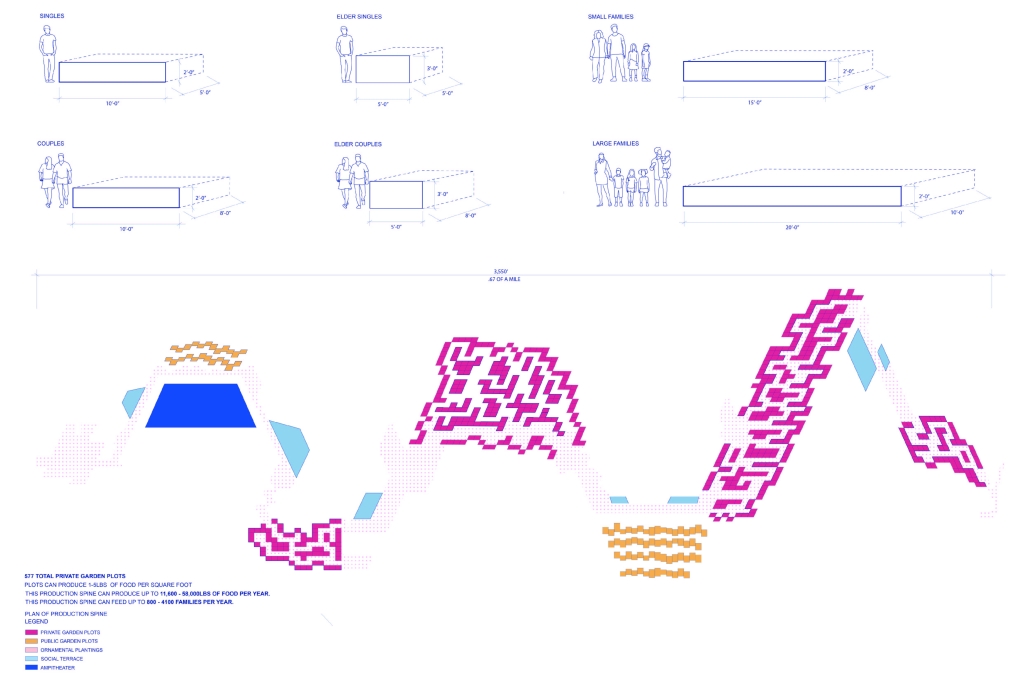
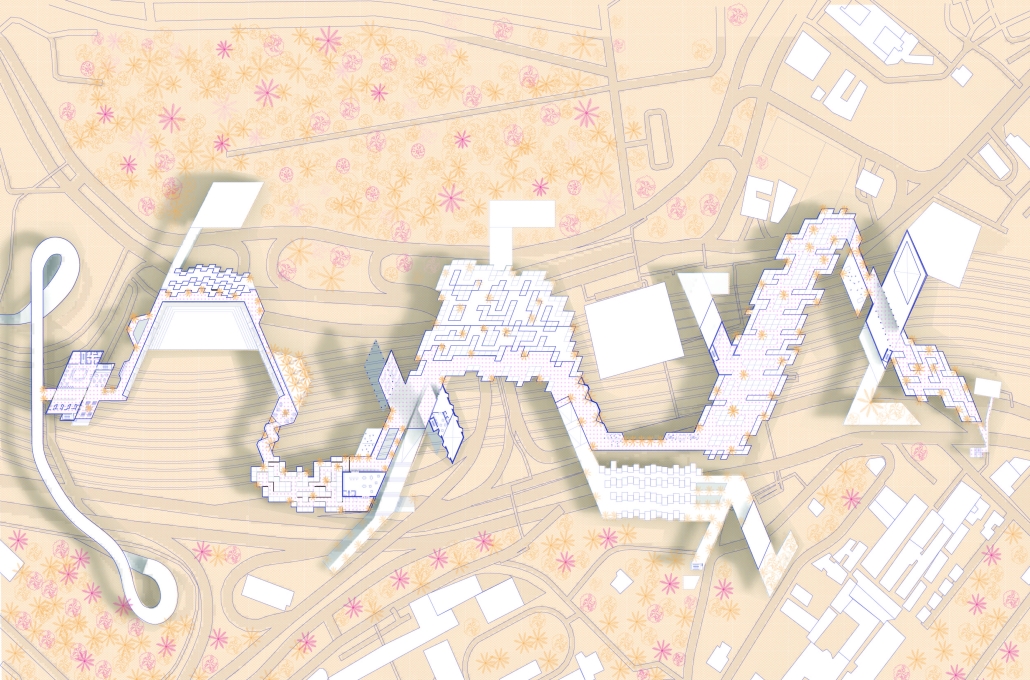
Our solution transforms underutilized land and divides urban infrastructure, specifically the railway corridor, into a linear public food system. We identified three vacant or unproductive sites along the railway and connected them with a continuous “spine” built above the tracks. This elevated path hosts production, consumption, exchange, and celebration programs, forming the core of a new community-based food network.
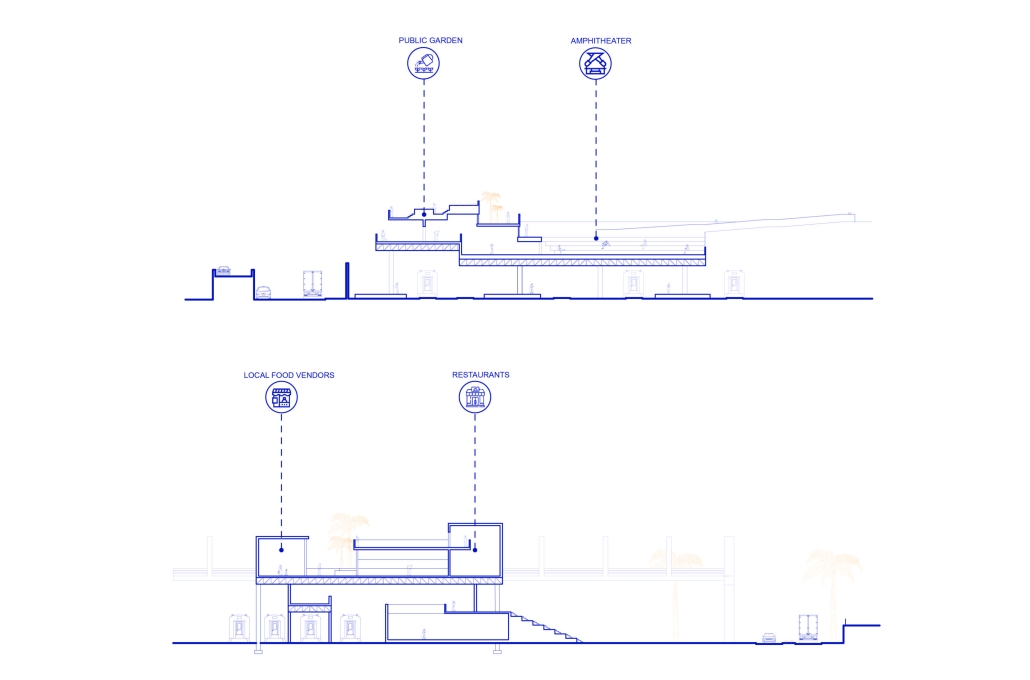
The spine includes community gardens, open markets, dining areas, and public spaces. It is accessible via existing pedestrian bridges and integrates with surrounding neighborhoods, connecting local businesses, bars, restaurants, and homes. The spine’s design allows programs to “bleed” into adjacent areas, transitioning from large-scale infrastructure to neighborhood-scale interventions.
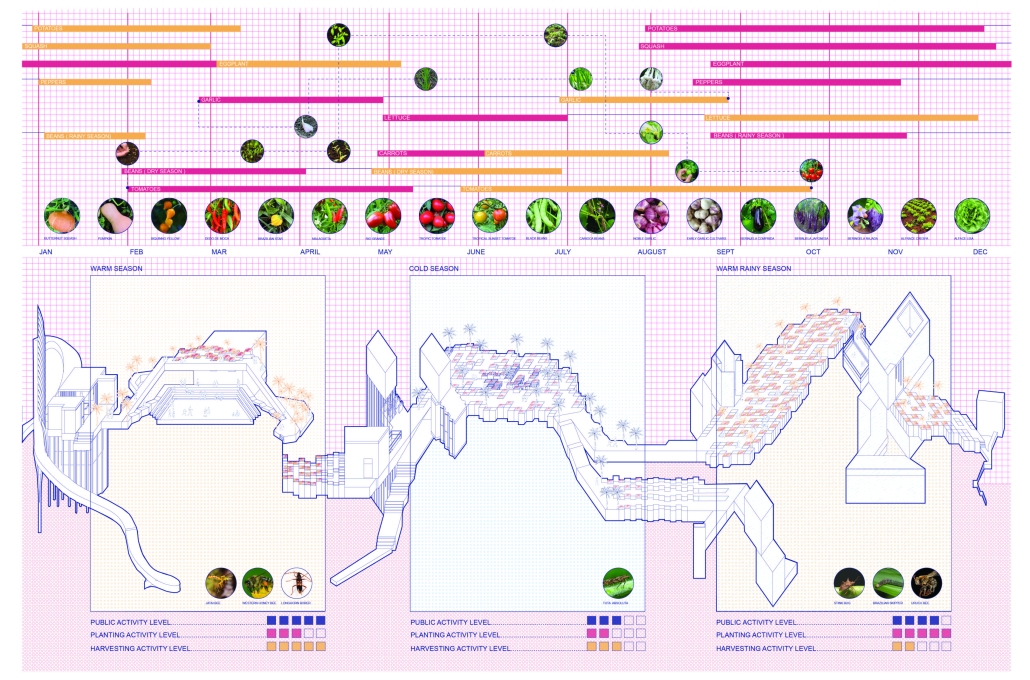
Gardens are divided into private, communal, and market plots, with varied sizes to serve individuals, families, and elders. These plots supply fresh produce to local vendors and cafes located along the spine, and excess goods can be distributed via the adjacent railway. Additional elements include amphitheaters, educational classrooms, seed exchange hubs, and compost stations.
A management team oversees garden plot rentals, market operations, and waste management. Organic waste is collected, composted, and returned as fertilizer, creating a sustainable loop that reduces pollution and supports local agriculture.
Roots and Rails reclaim neglected infrastructure to serve the local community, transforming a divisive element of the city into a unifying, productive space. The project not only tackles food insecurity but also fosters local economies, environmental sustainability, and community resilience through thoughtful urban design
Instagram: @ascaniarchitecture, @naomilewinter, @pattapsp, @ev07, @marcelladelsi
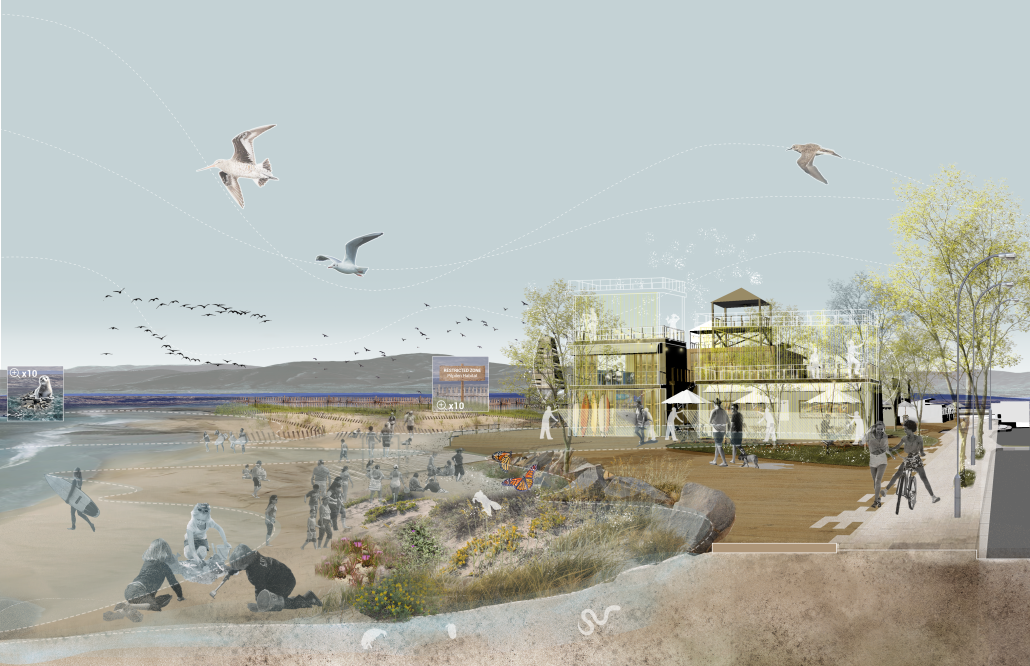
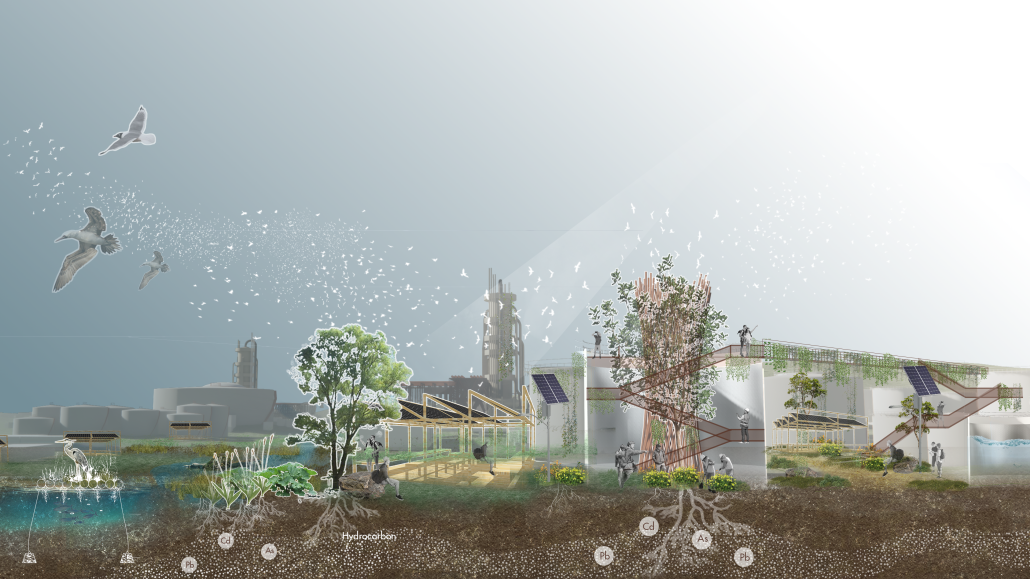
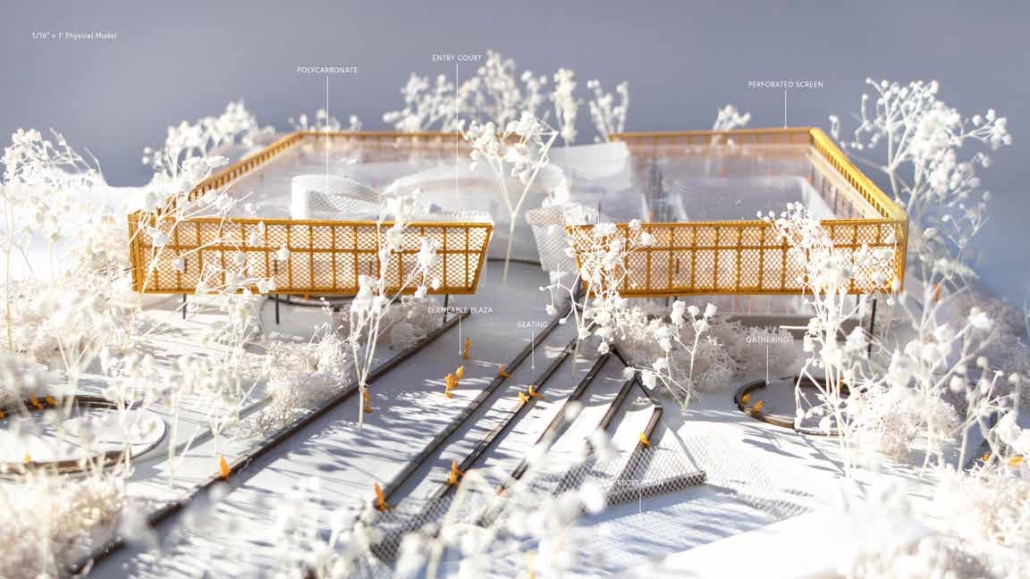
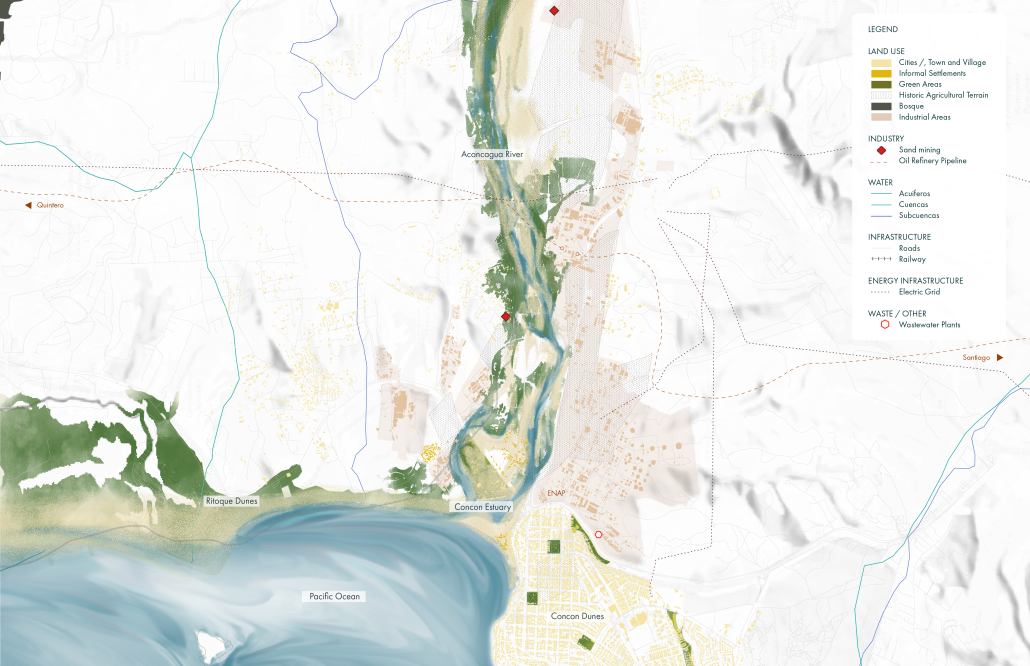
Reimagining Concon Estuary: Reclaiming Concon With Community-Led Catalysts by Mutita (Maeve) Ouk, Vicky Sindac Gomez, Daisy Castro & Qingyi (Eva) Gan, M.S. Architecture and Urban Design (MSAUD) ’25
Columbia University | Advisors: Kate Orff, Geeta Mehta, Sebastian Delpino, Gabriel Vergara, Emanuel Admassu & Lucas Coelho Netto
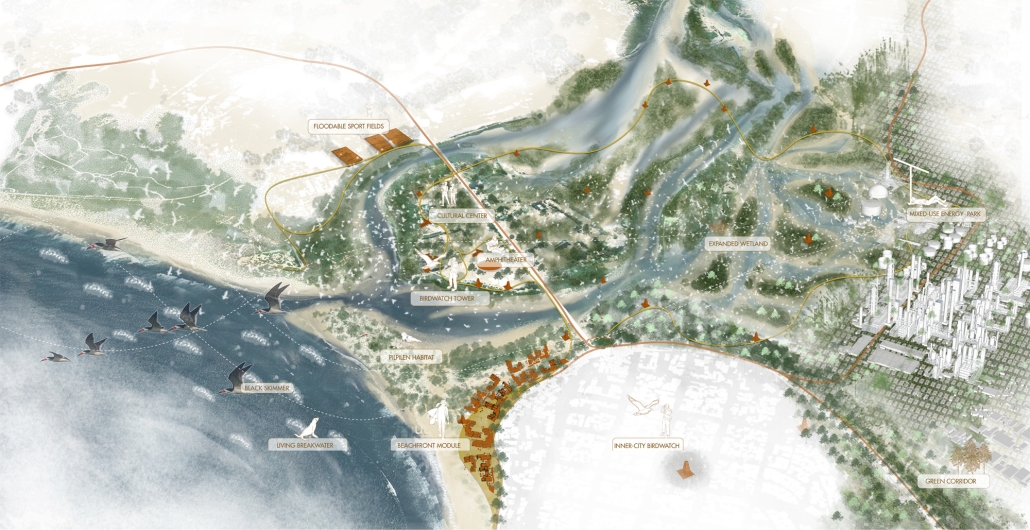
What if the Concon Estuary and the surrounding wetland ecosystem were restored to enhance the well-being of local flora, fauna, and community?
The Concon Estuary, located in the coastal region of Valparaiso, Chile, is a vital transitional zone between the Aconcagua River and the Pacific Ocean. It boasts rich biodiversity and a dynamic landscape that constantly changes throughout the days, seasons, and years– where river meanders, ocean tides fluctuate, sediment flows, and birds are free to come and go. However, human activities, including urban development, pollution from the ENAP oil refinery, the Asfalcom cement factory, sand mining, waste dumping, and unregulated recreational activities, have placed significant pressure on the ecosystem. This constant resource extraction and exploitation has led to more frequent and intense storm surges, increased flood risks due to rising sea levels, habitat loss, saltwater intrusion, shifting river course, and unregulated activities.
ENAP, the primary polluter, contributes little to the local economy. Locals rely on small businesses along the beach that are poorly constructed and are exposed to flood risks due to the abrupt transition between the coastline and the urban area. Given Chile’s policy goals of replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy and the risk of sea level rise, we envision a future where ENAP is gradually phased out, paving the way for sustainable energy sources. Throughout this transition, the existing industrial structures and operations will be integrated into the design process to mitigate pollution and environmental impacts. Additionally, sand mining will be banned to facilitate the regeneration of the wetland ecosystem and restore its natural space. This will also create new job opportunities, supporting a more resilient and sustainable way of life for the community.
Instagram: @mutita.ouk.arch, @vsg.arch, @dyc_urbdesign, @gsapp_aud, @mehtageeta999, @gabrielvergarag, @sdelpino_arq, @eadmassu, @lucascoelhonetto
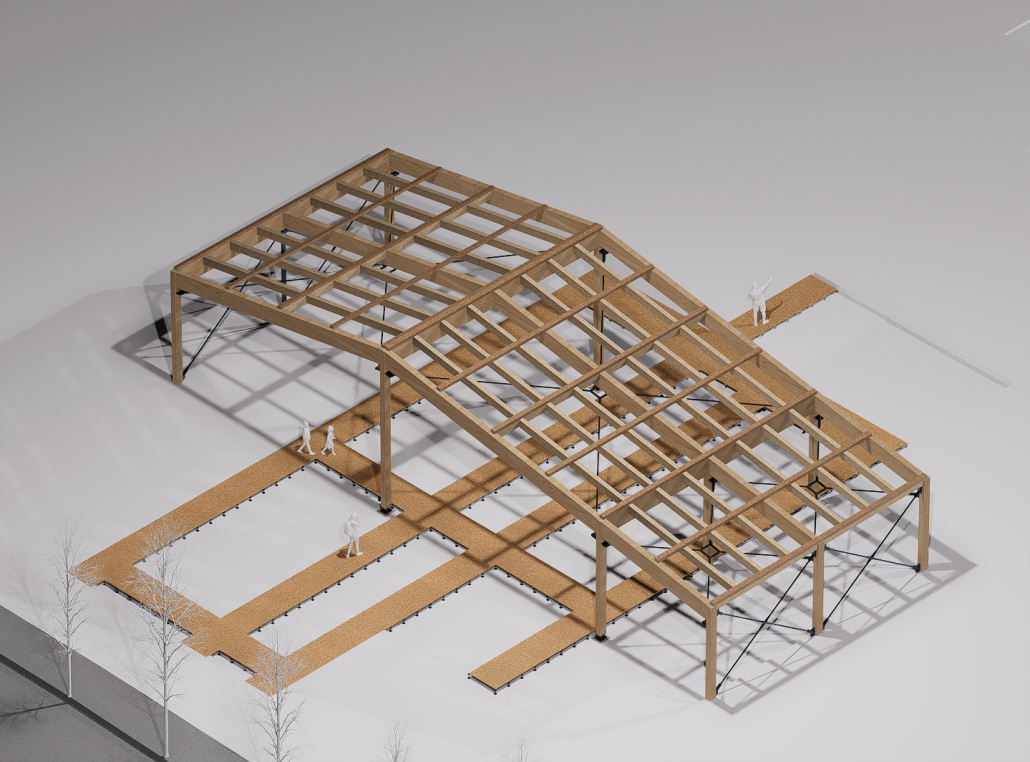
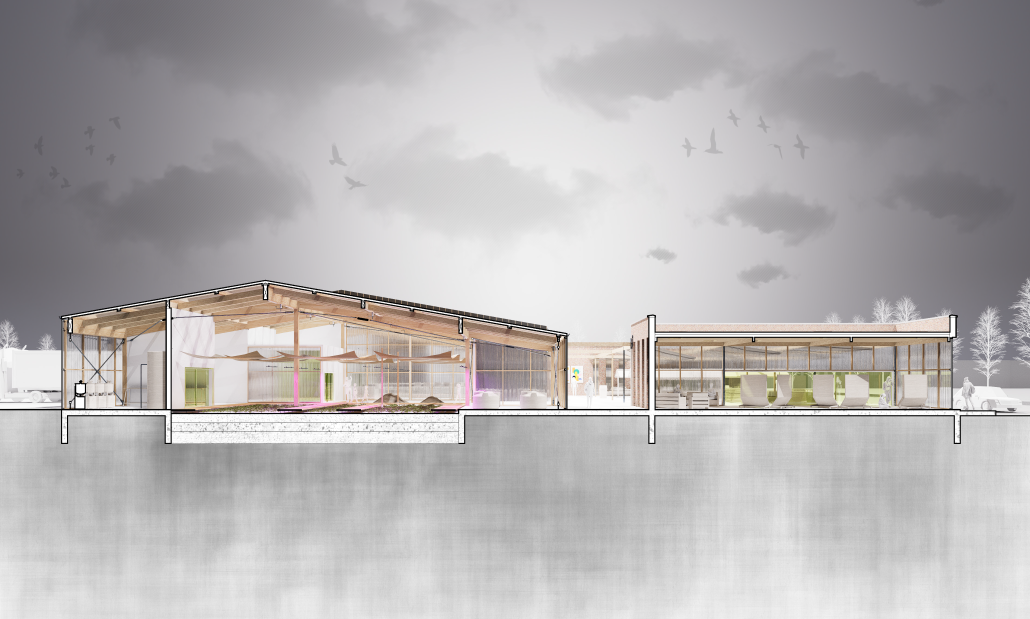
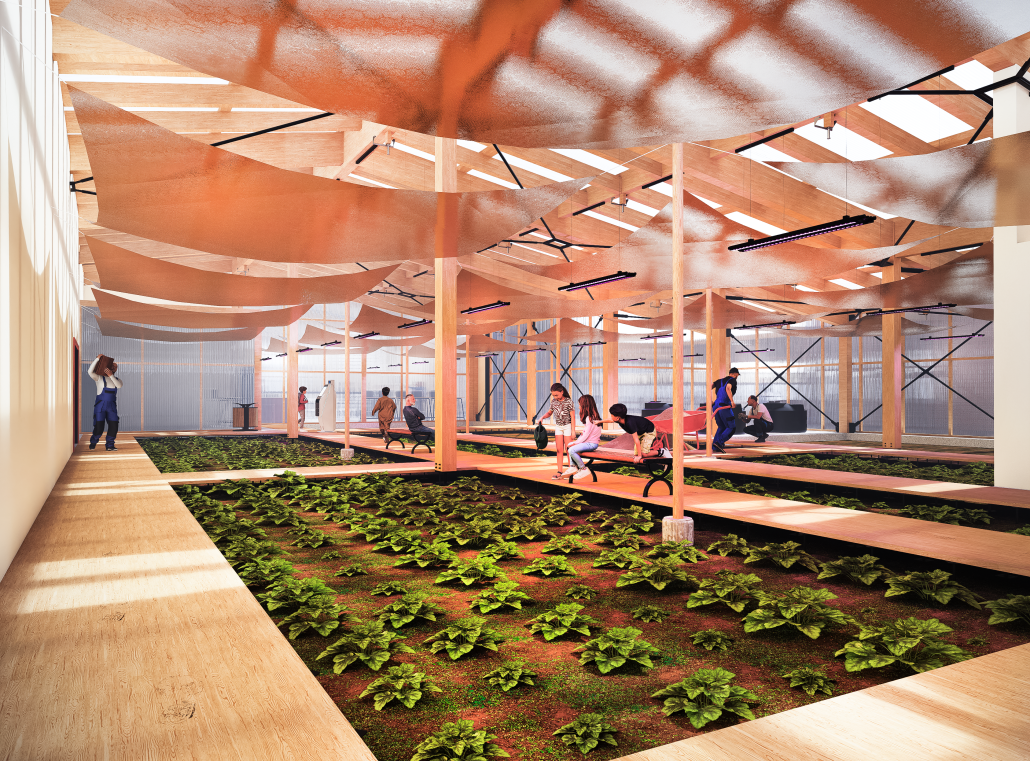
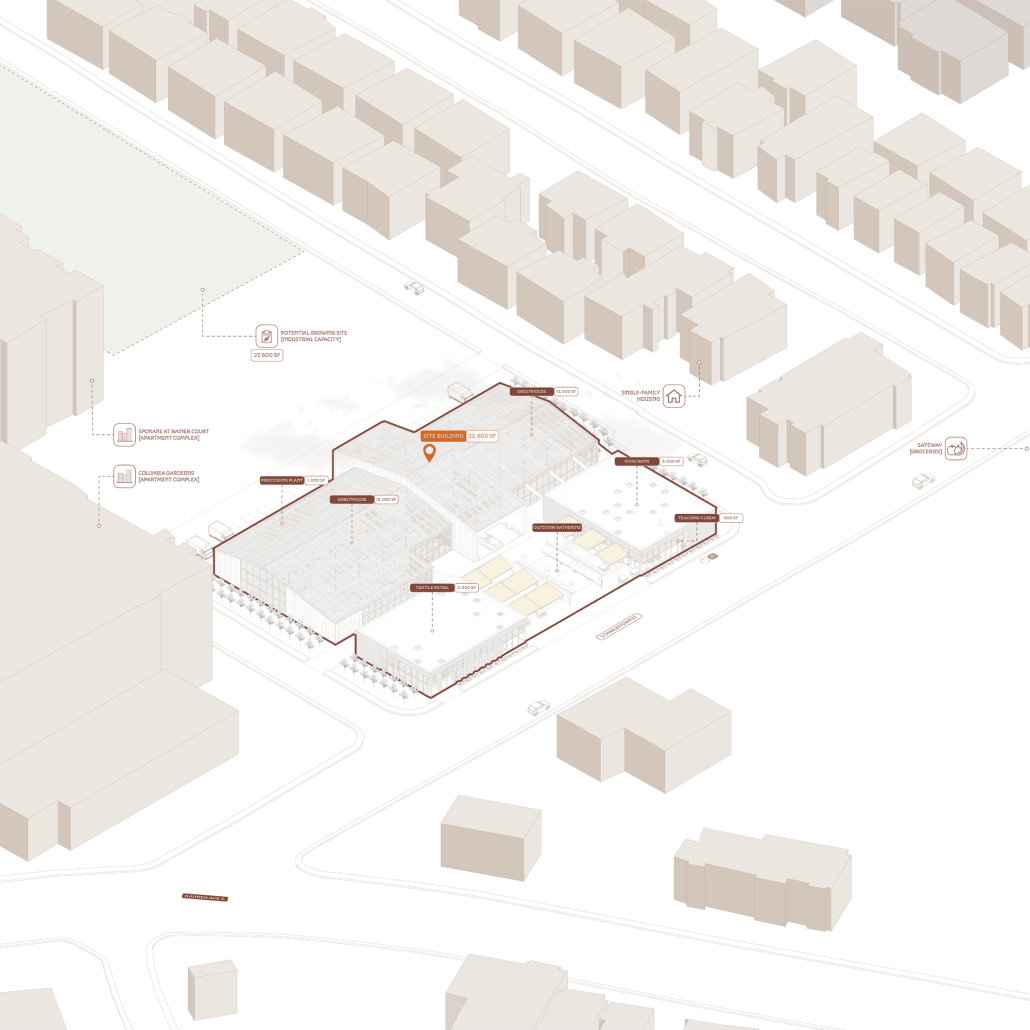
Mount Baker Urban Farm [CLT Cannibalism Studio] by David Oluwamayowa Asokeji, M.Arch ’25
University of Washington | Advisor: Susan Jones
“Mount Baker’s Urban Farm” is a transformative community-based project that confronts food insecurity and economic disinvestment in Seattle’s Black and African American neighborhoods. Designed as a local response to systemic inequities in food access, the project reimagines urban agriculture as both a cultural anchor and a platform for environmental resilience.
At its heart is the Cassava plant—an essential staple crop widely used across West Africa, Southeast Asia, and South America. Known for its versatility and low-waste processing, cassava becomes both the functional and symbolic backbone of the farm. The crop supports not only flour-based food production but also textile, paper, and material research initiatives, making it a dynamic resource for community-building and circular design.
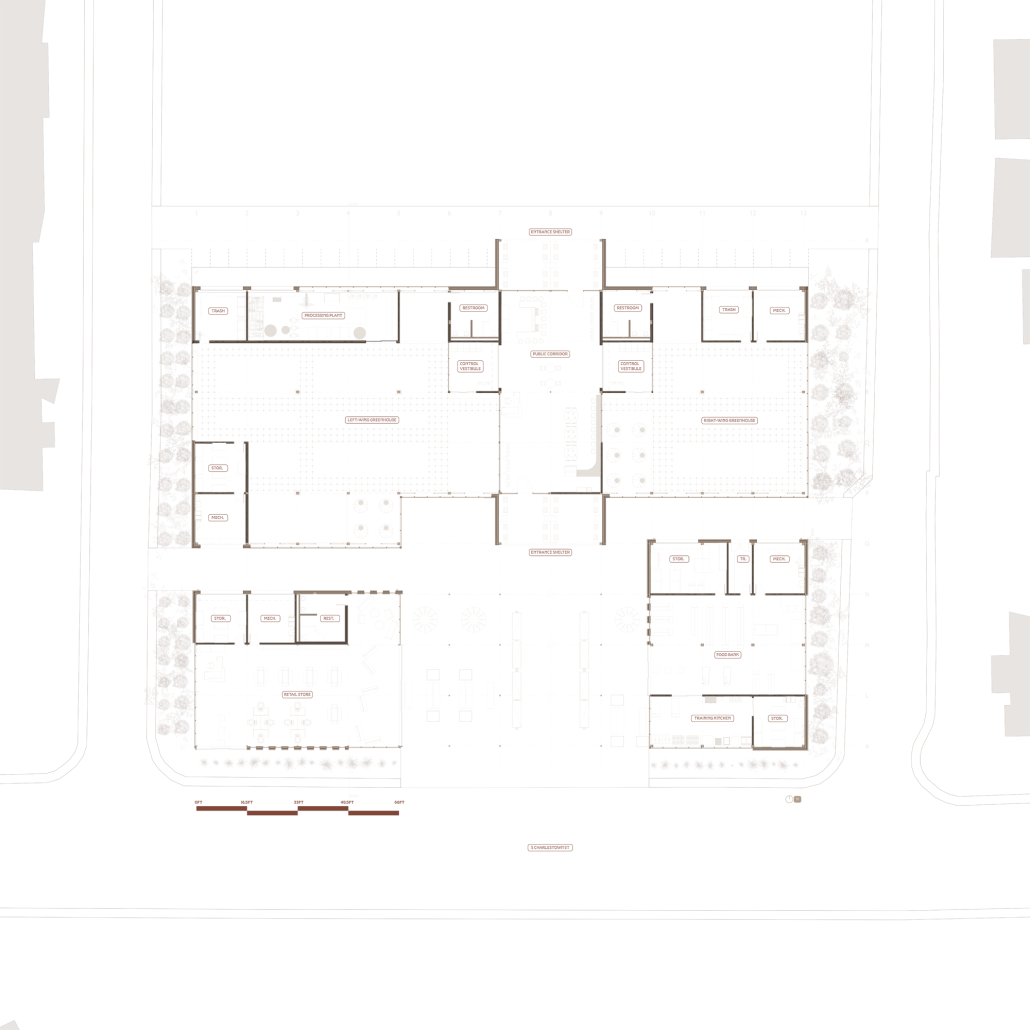
This urban farm integrates a greenhouse, processing plant, teaching kitchen, community food bank, textile fabrication studio, and a public-facing retail space. Together, these programs create a closed-loop system of cultivation, education, and empowerment. The design fosters hands-on learning through cooking classes and sustainable farming workshops, while simultaneously supporting food relief through onsite distribution.
An open-air courtyard anchors the project, acting as a communal gathering space and visible nexus of exchange. Here, architecture supports transparency, wellness, and social cohesion—inviting the public into the often-hidden processes of food production and collective stewardship.
More than just a farm, Mount Baker’s Urban Farm positions architecture as a tool for social equity, ecological intelligence, and economic resilience. It exemplifies how built environments can honor cultural heritage, activate underutilized spaces, and nourish both people and place.
Instagram: @davidasokeji_0, @dbaarchitecture, @atelierjones
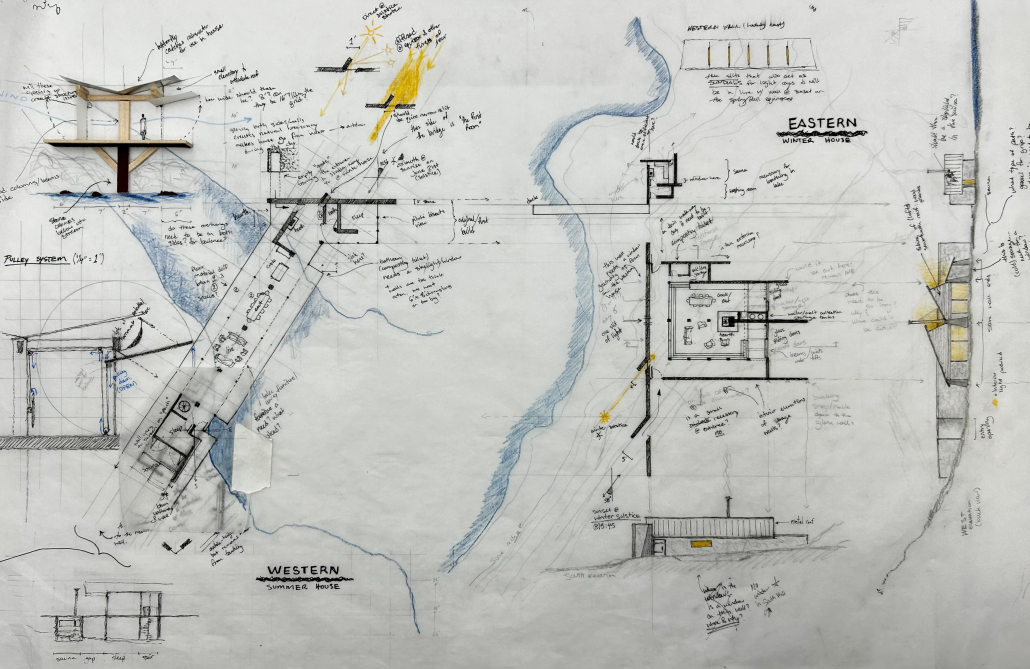
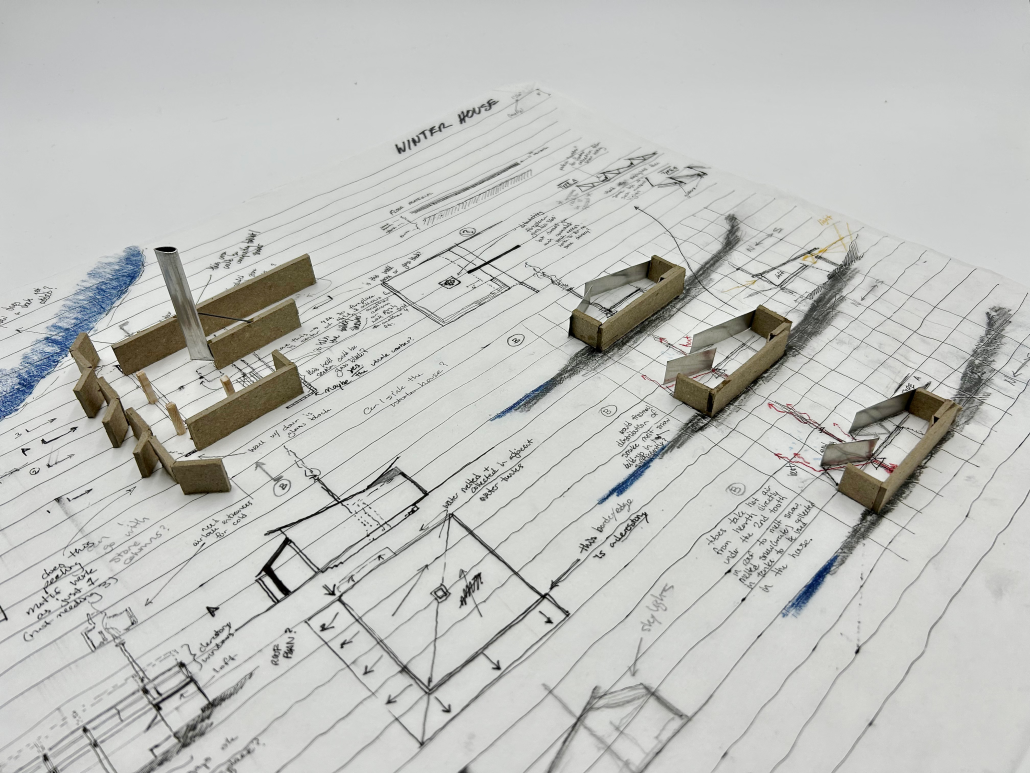
Equinox House: Contextual Materiality of a Residence by Austin Small, B.S. in Architecture ’25
University of Virginia | Advisor: Peter Waldman
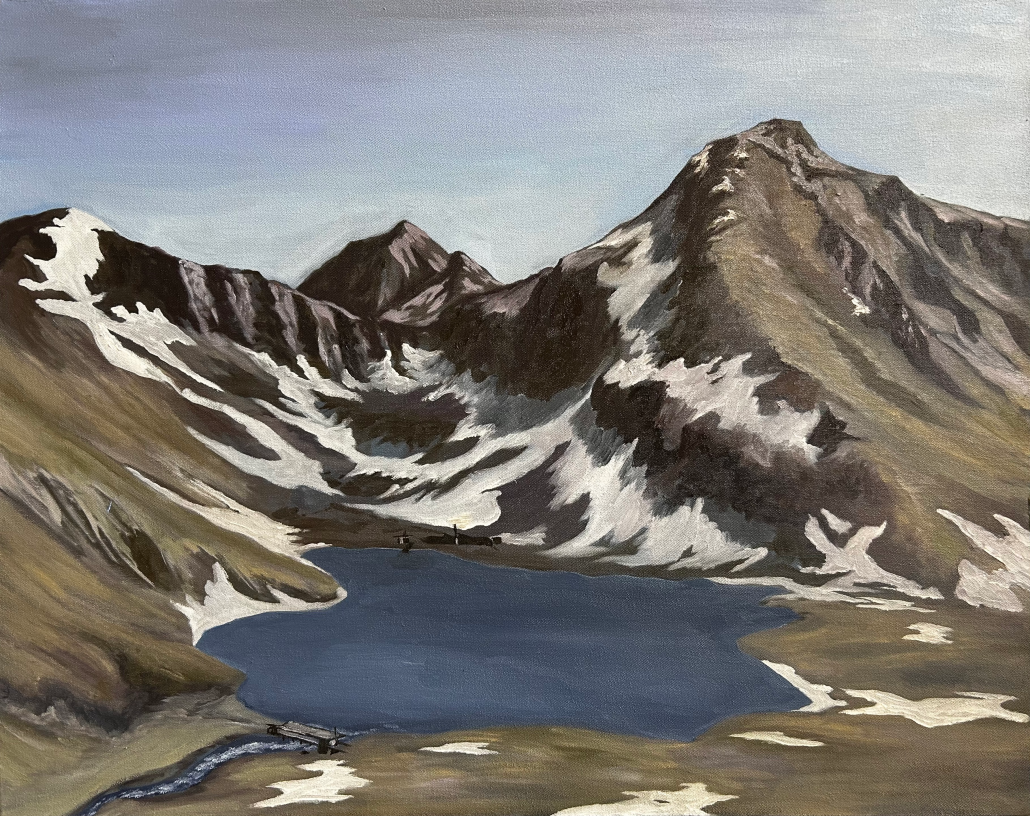
Rabbit Lake, southeast of Anchorage, Alaska, is a peacefully calm, yet brutally intense landscape tucked into a corner of the Chugach Mountains. Reaching the lake involves a two-mile hike from the nearest road access point after driving 10 miles out of the city. Sitting higher than the alpine line, roughly 3200ft above sea level, the lake and its surrounding mountains are void of trees; the shores instead are dotted with shrubs and littered with rocks that have been shed in avalanches over the years.
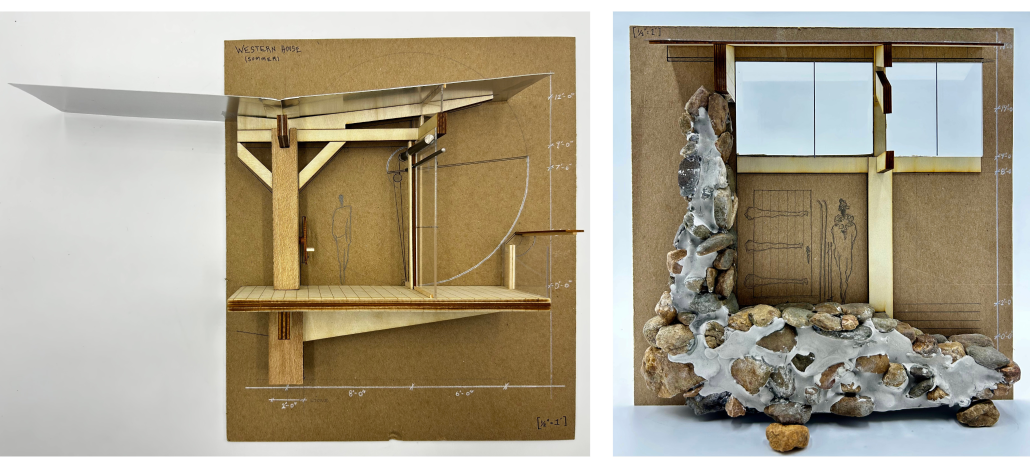
One half of the project sits atop a bluff on the western bank, bridging a creek fed by the lake: this is the summer house. Across the lake, directly to its east and braced into the mountain behind, lies the opposing winter house. The two dwellings are connected by their compass alignment and the journey made between them; one that the project proposes is initiated by the solar path on both the vernal and autumnal equinoxes. With one window in both structures directly facing the other, the sunrise and sunset on the equinoxes act as a seasonal sundial, initiating the changeover journey between winter and summer.
A more immediate indication of movement, the long covered bridge of the summer dwelling is a kinetic structure proposing a blend of interior and exterior. The glass walls on each side of the bridge are designed to rotate and open upward, transforming the span into a livable breezeway. While the Western dwelling is light, breathable, and tectonic, the Eastern house is a burly cave in contrast. Made from the stone found on site, [its] thick walls and a centrally located hearth offer protection and comfort from the sub-zero temperatures of the winter months. The protective western wall guards the structure from harsh winds coming off the lake, while the clerestories of the saw-toothed roof take in as much of the minimal daylight as possible and offer views of the “Aurora Borealis” in the northern night sky.
In an attempt to design a house precisely unique to its setting, this project proposes a response both to the seasonally extreme nature of Rabbit Lake and to the traditional Alaskan lifestyle, a way of living that is intrinsically exterior. The proposal imagines a cast of characters: a nomadic countryman with a possible family, living off the land and lake as much as possible, and maintaining the dwellings in a simple and slow lifestyle by returning to nature. As a result of the drastic seasonal differences in both light and temperature, the project splits the home into two respective dwellings, living not only on the site but with the site; allowing the landscape, and interaction thereof, to complete the proposed design.
This project received the Highest Honors for the 2025 Fourth Year Thesis at the UVA School of Architecture.
Stay tuned for Part VII!