2023 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part XXXIII
Welcome to the final edition of the 2023 Study Architecture Student Showcase! In Part XXXIII, we highlight student work that centers on public spaces. The showcased designs include public parks, meeting spaces, community centers, commercial retail spaces, parking structures, pools, and more.
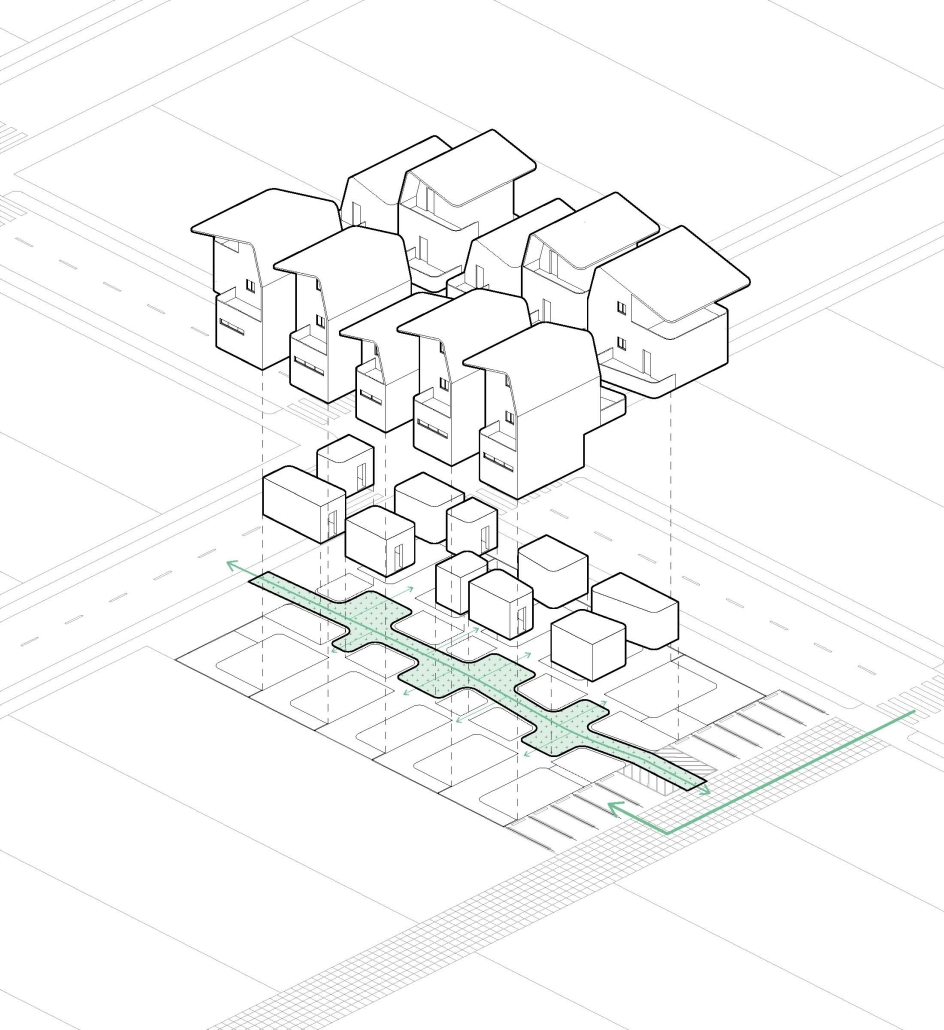
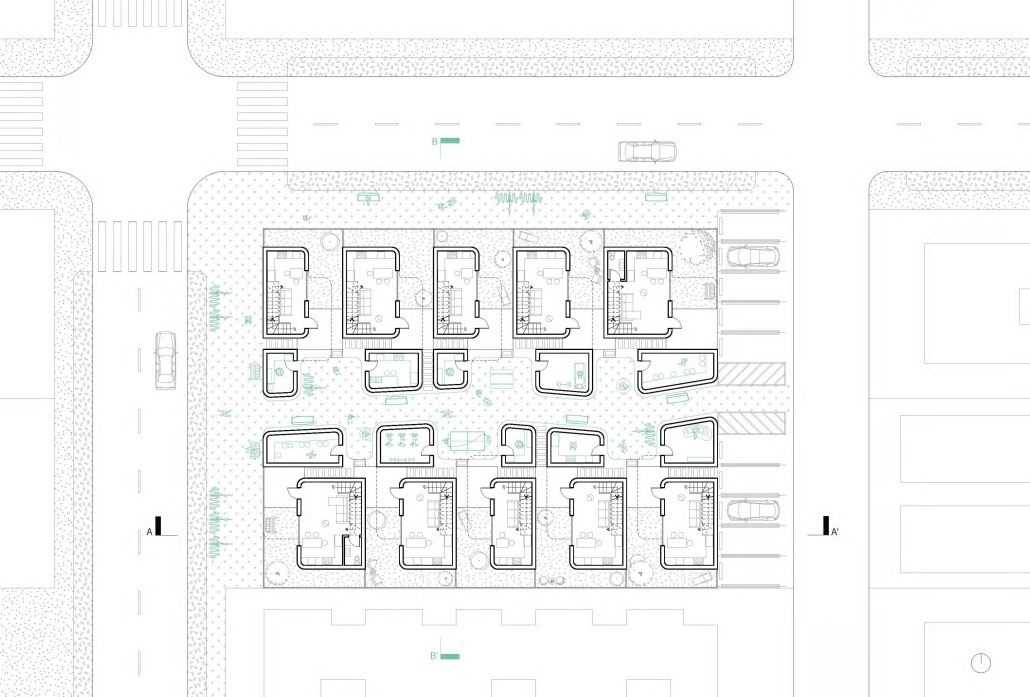
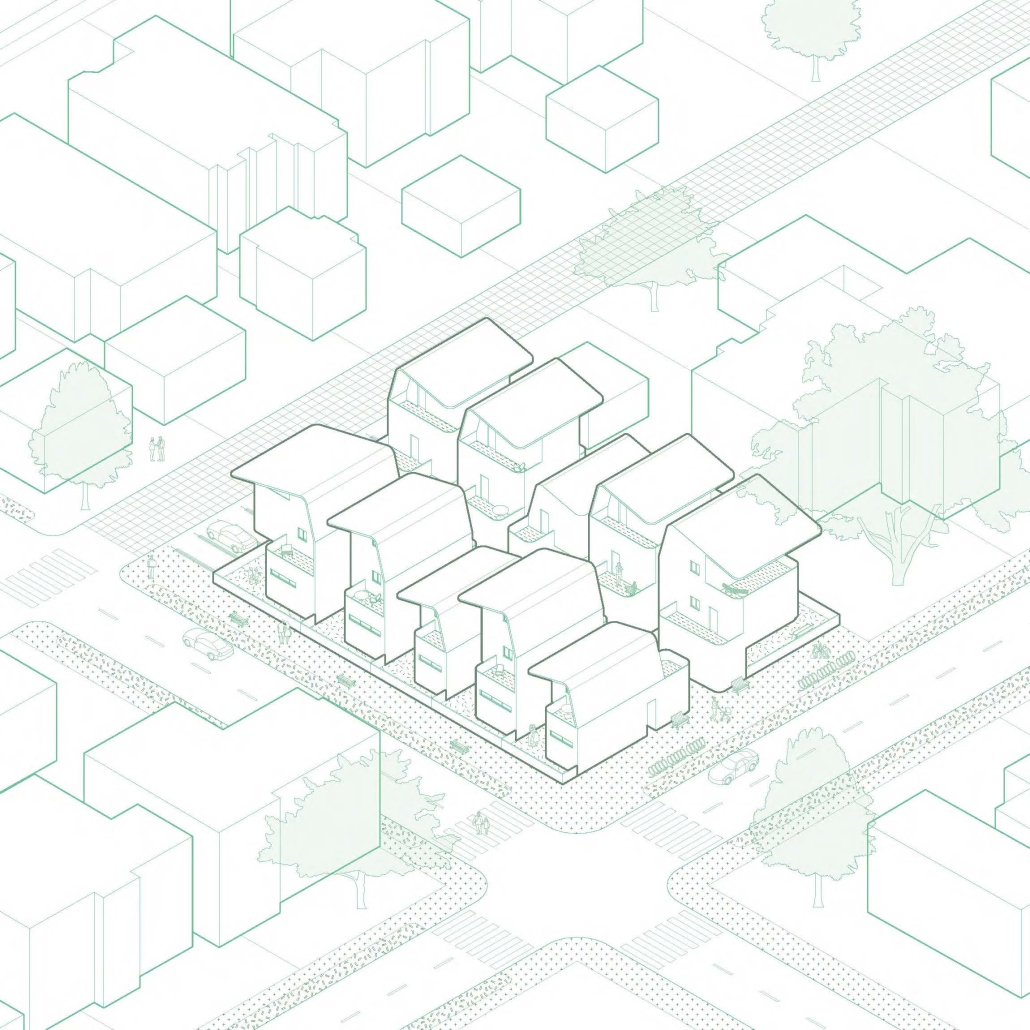
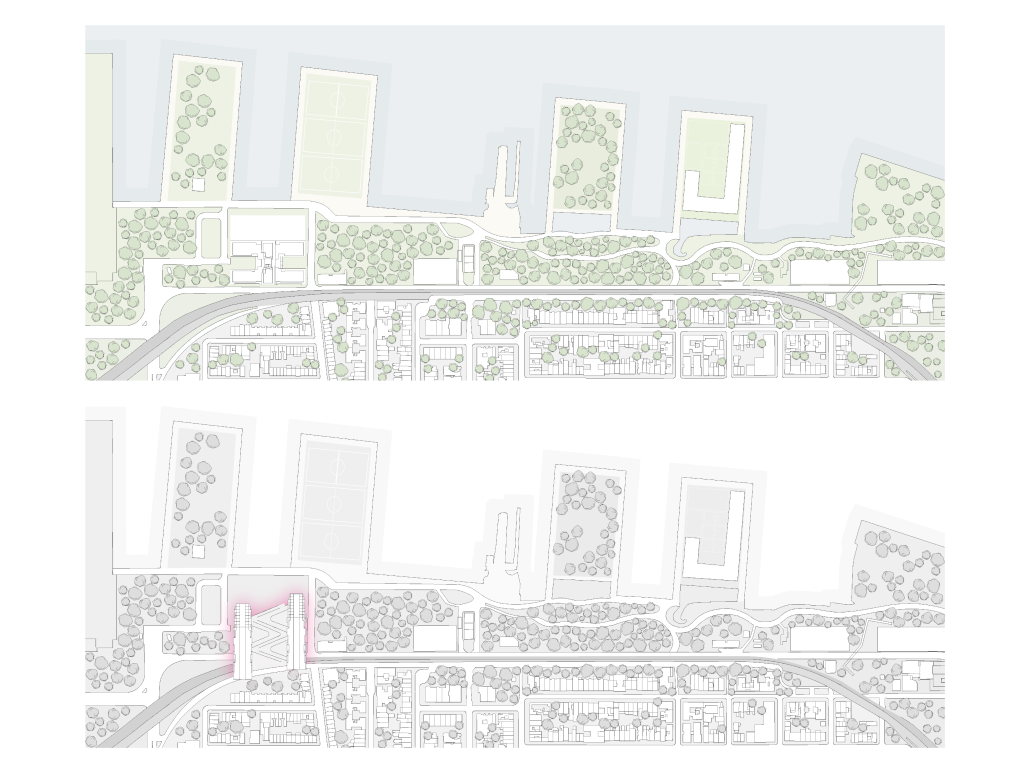
Re-encontrarse (Re-united) by Sophie Esther Zurhaar Ortiz, B.Arch ‘23
Universidad Anáhuac Querétaro | Advisors: Jorge Javier & Francisco Paille
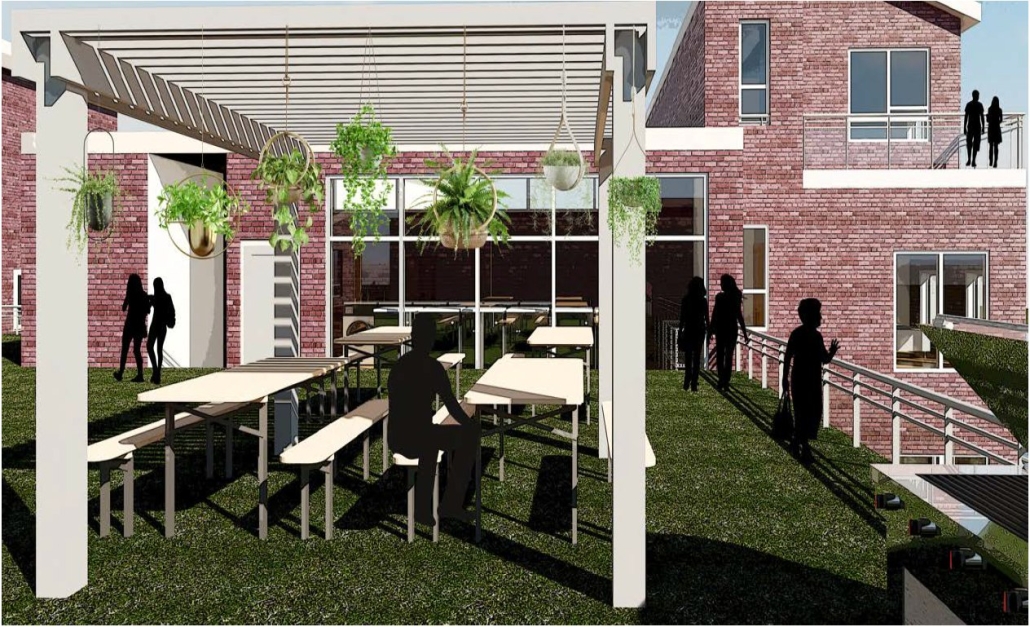
This project seeks to generate an urban design proposal for the recovery of public space in Felipe Carrillo Puerto. Aiming to propose meeting spaces where all kinds of activities can be carried out, recover the railroad tracks to stop being a physical barrier, and defragment the urban fabric, offering cohesive, healthy, and functional meeting spaces that together can regenerate the social fabric.
Instagram: @sophiezurhaar, @arqwave
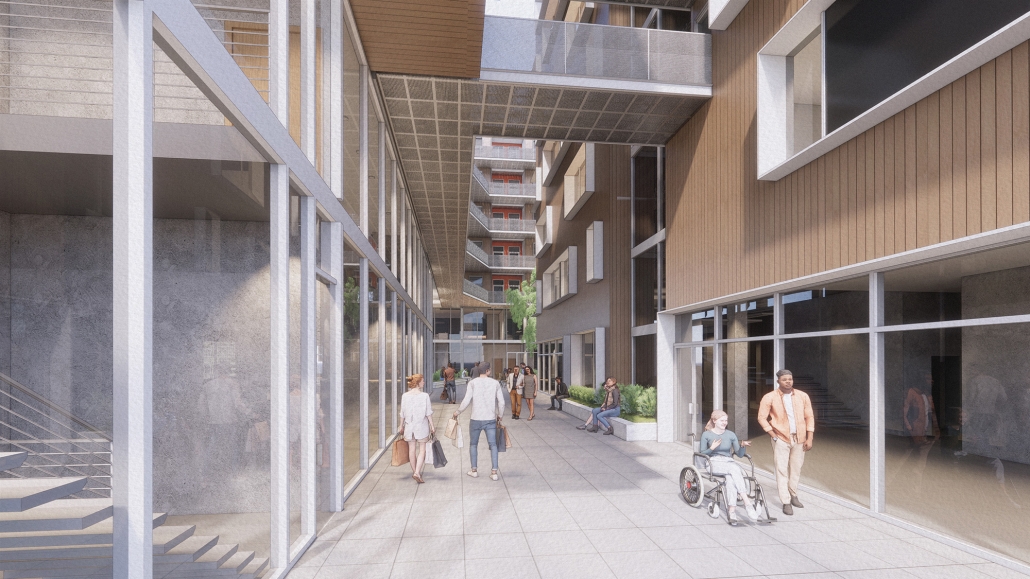
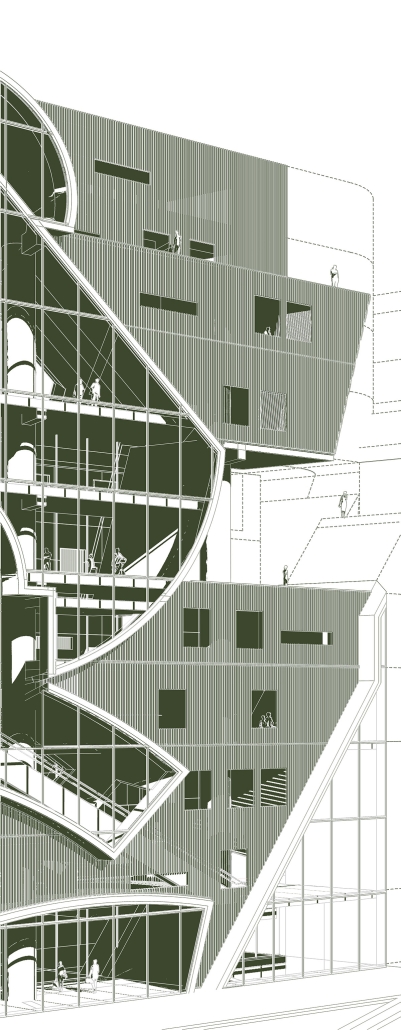
PROSPECT NEW ORLEANS by Olivia Georgakopoulos, B.Arch ‘23
Tulane University | Advisor: Ruben Garcia-Rubio
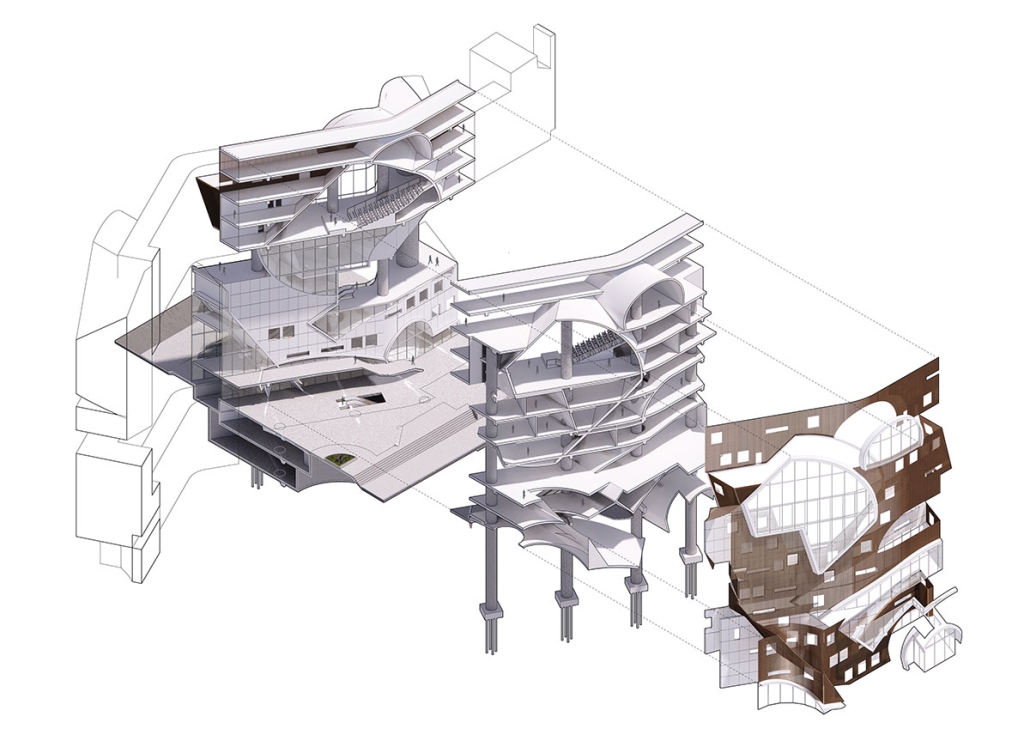
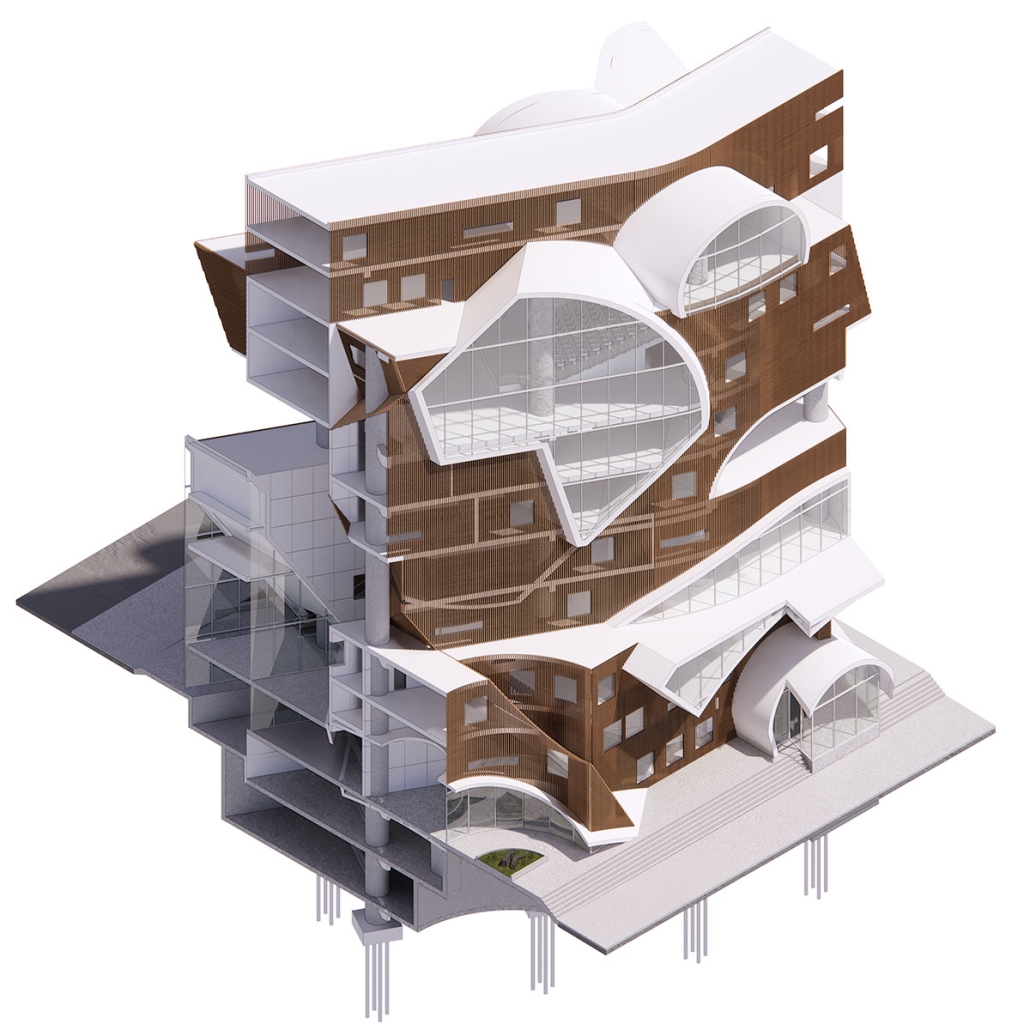
This project proposes to open the building to the city, creating a place that adds to its rich urban fabric. The site is a parking lot at the corner between the Contemporary Arts Center and the WWII Museum. While there are many voids in the surrounding context, like this site, they are not habitable. This project provides a much-needed public space for the many visitors to the surrounding museums. Taking inspiration from the L-shaped building typology in New Orleans, the building opens to the city, creating a public plaza.
The building functions as an open-public platform connecting Camp Street and Andrew Higgins Blvd. The glass-enclosed first floor is fluid and can be completely opened, allowing for space not to be defined by interior or exterior. Rather, programs can spill out and interact between the interior and the plaza. The ground floor then becomes animated by human activity. The public programs, gallery, cafe, lobby, and lounge are housed on the first floor, and spaces to support the art center are above.
Transparency of the building is achieved through the aluminum louvered facade, which acts as a theatrical scrim. This veiled facade reveals the animation on the inside of the building. This transparency is also experienced from the inside looking out: the interior programs interact with filtered and framed views of the city.
A chain of internal double-height spaces forms a visual cascade through the building, providing internal transparency and animation with continuous views from the bottom floor to the top floor and the sky. The overall design provides continuity between the interior, the plaza, the street level, and the city.
Instagram: @rubgarrub
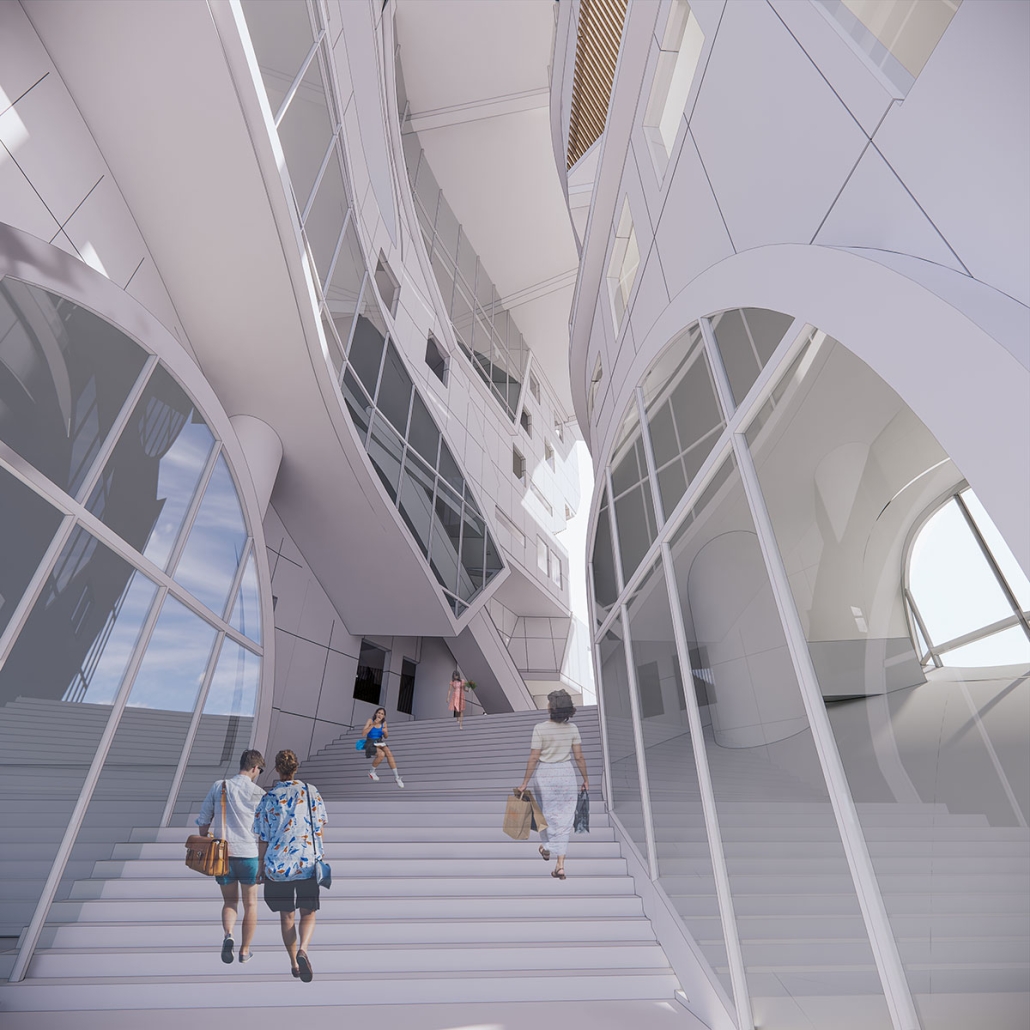
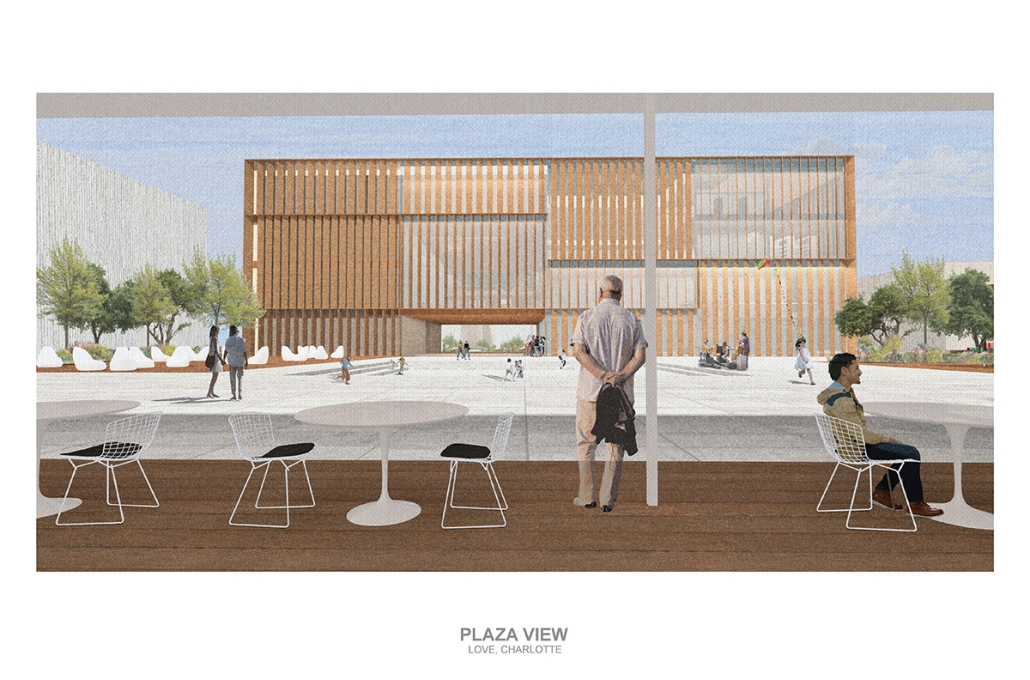
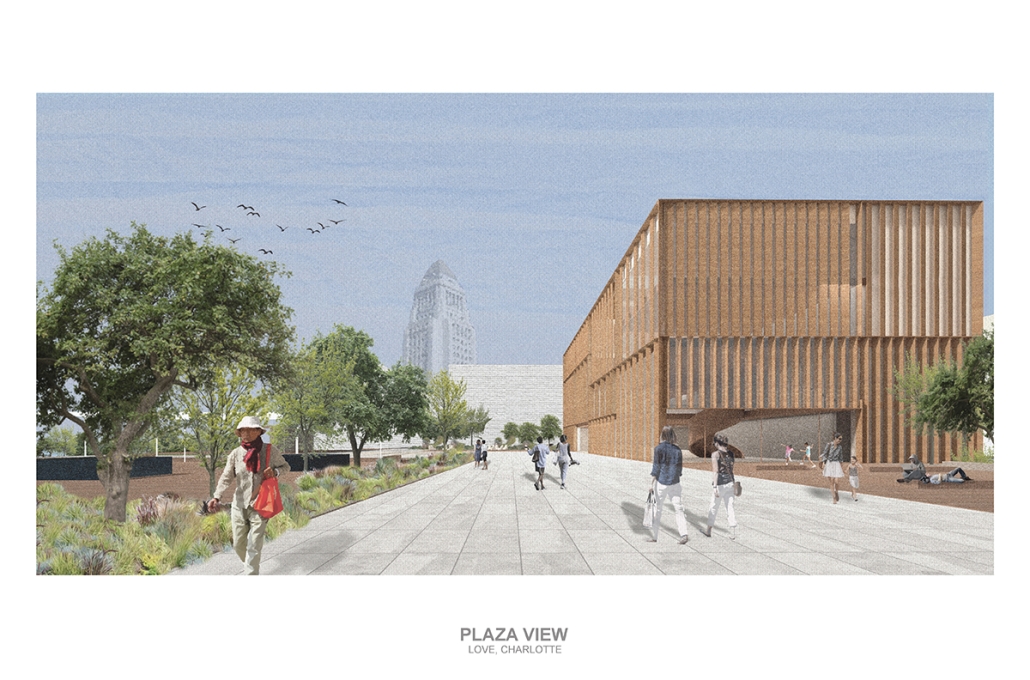
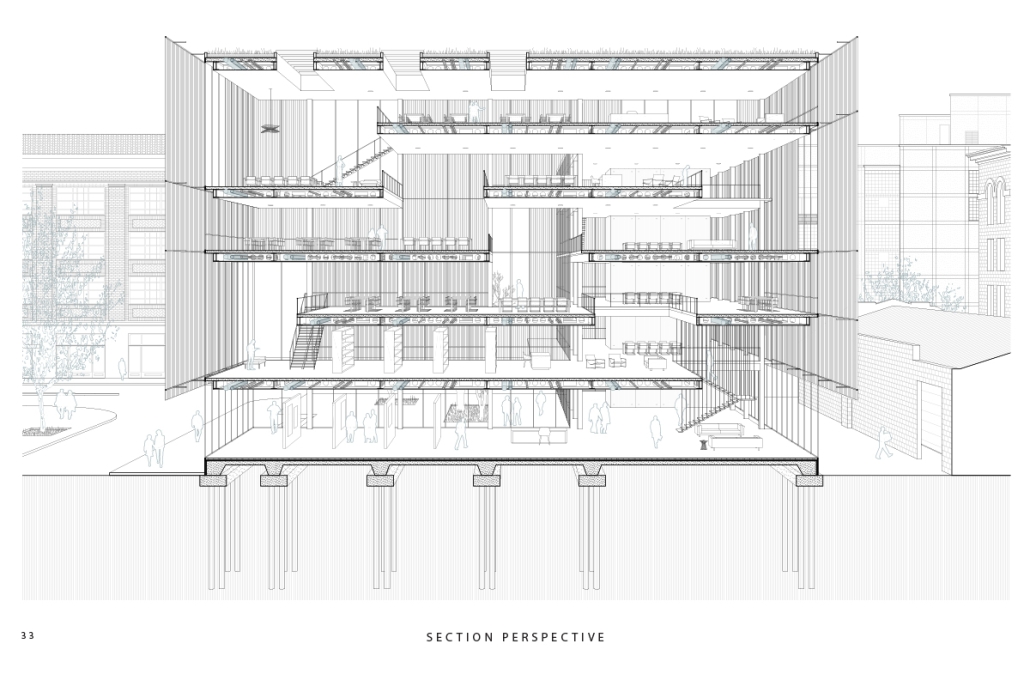
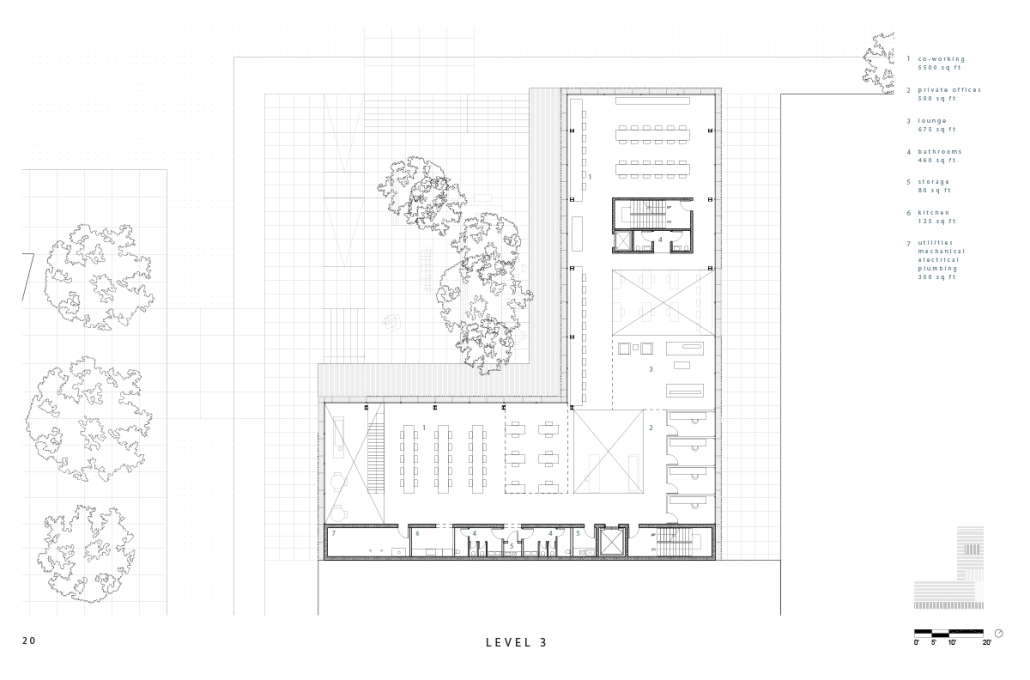
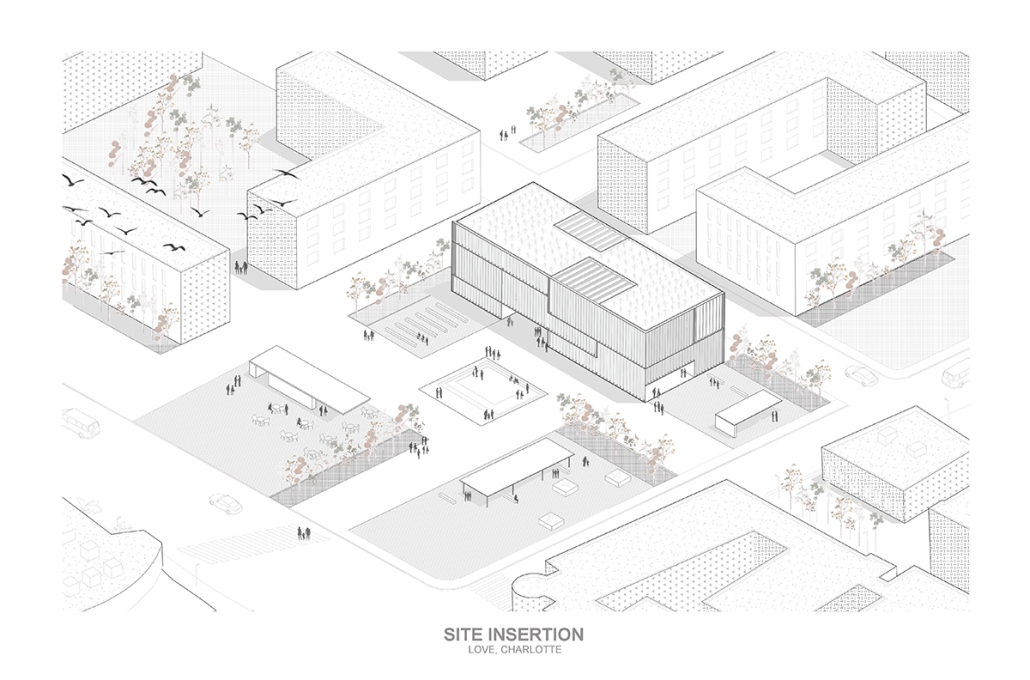
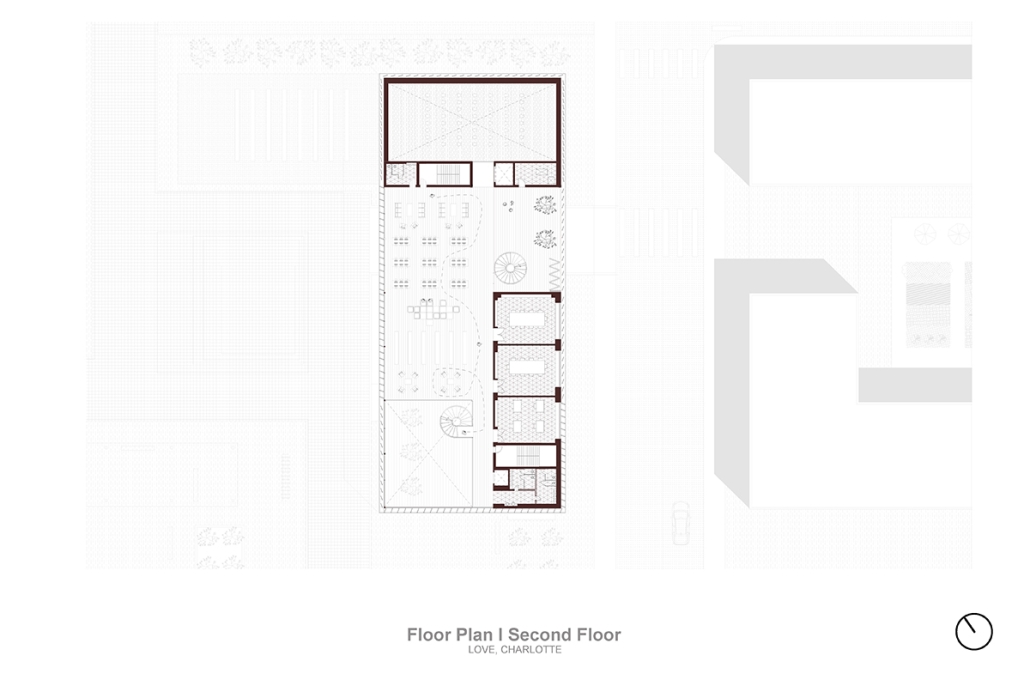
Los Angeles Media Library by Charlotte J. Love, B.Arch ‘23
Tulane University | Advisor: Ruben Garcia-Rubio
The Los Angeles Media Library began by building upon the urban design. The building began with the broken urban block typology found throughout the site, this promoted a continued focus on mobility within the project. The urban block shape was altered to accommodate one large building wrapped in louvers and two smaller pavilions hosting different program focuses on a plaza. This iteration of the broken urban block creates an inviting place for a public plaza. This plaza being at the literal intersection of the business and arts district makes it a perfect spot to hold a media center and library. This is relevant for both the site and the Greater Los Angeles.
The plaza has a number of public transportation stops and is located across the street from two museums making the plaza equally important to the design. The open space has a café, reading area, pavilion, and an outdoor theater. The buildings and walkways align with the surrounding roads and buildings leading to a central sunken space at the center of the plaza. Held within the building are two zones with thickened walls holding private programs such as classrooms, dark rooms, offices, etc. This allows the rest of the building to be much more open with a number of double heights as well as spaces with an indoor-outdoor feeling. This allows the building to be fluid and connected to the plaza, blurring the line between public and private spaces.
Instagram: @rubgarrub
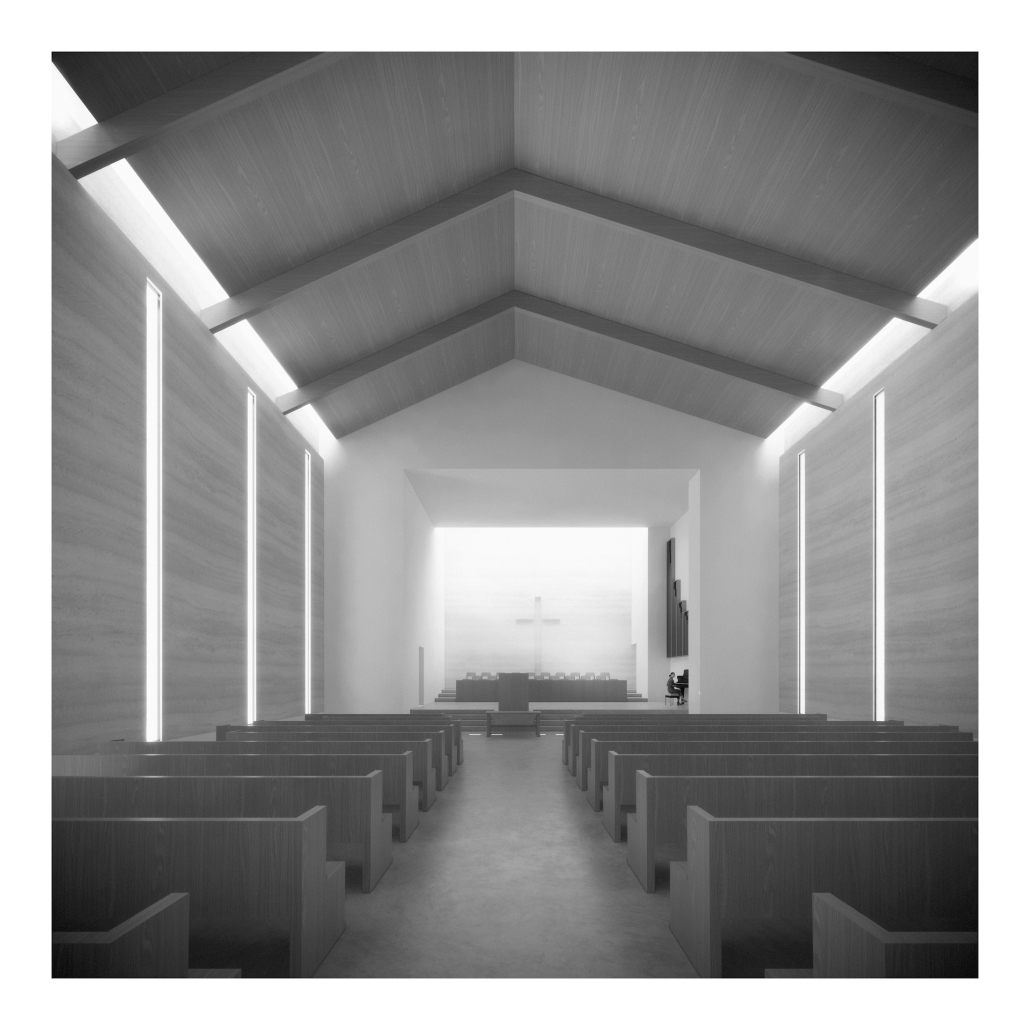
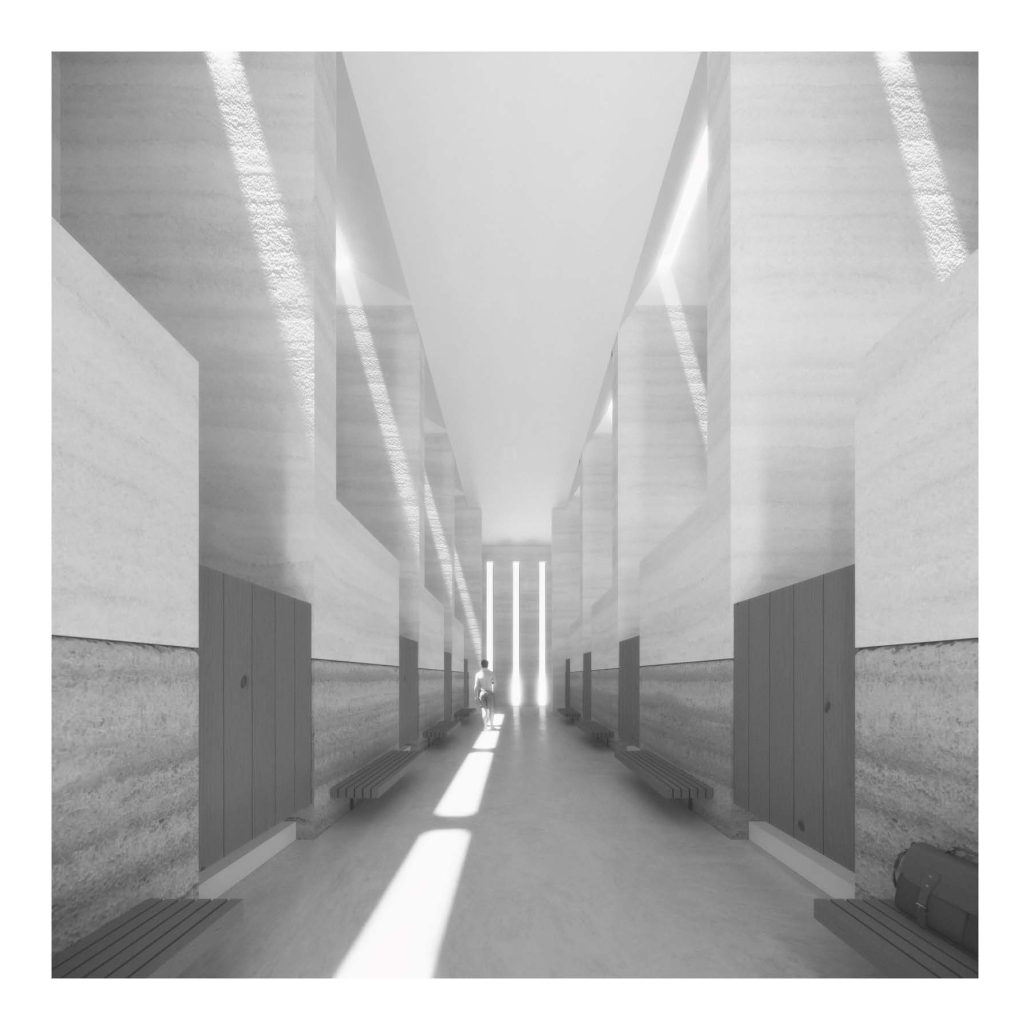
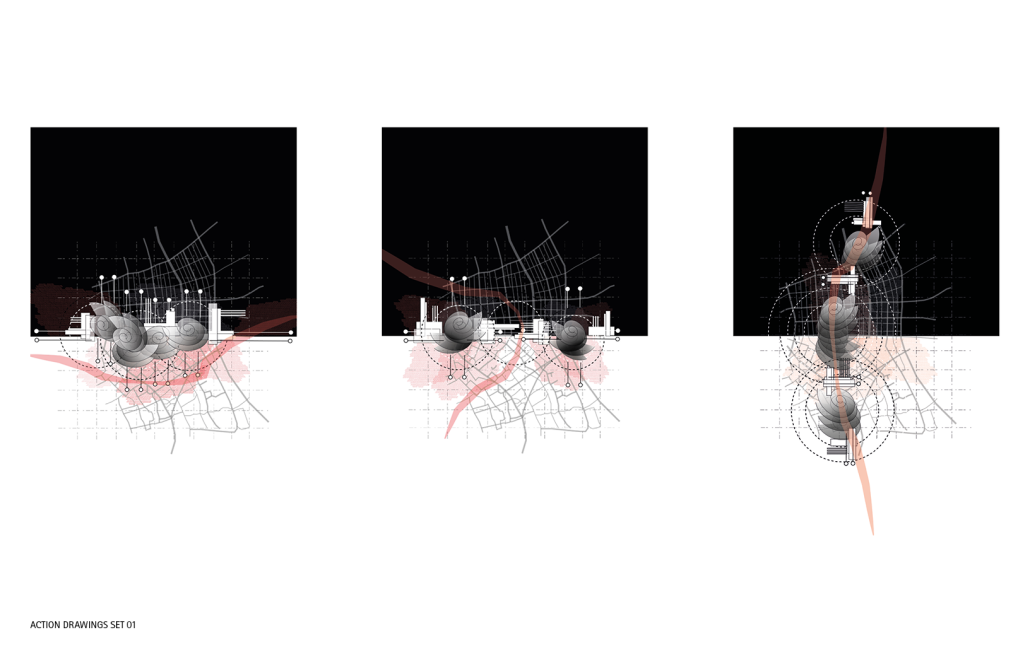
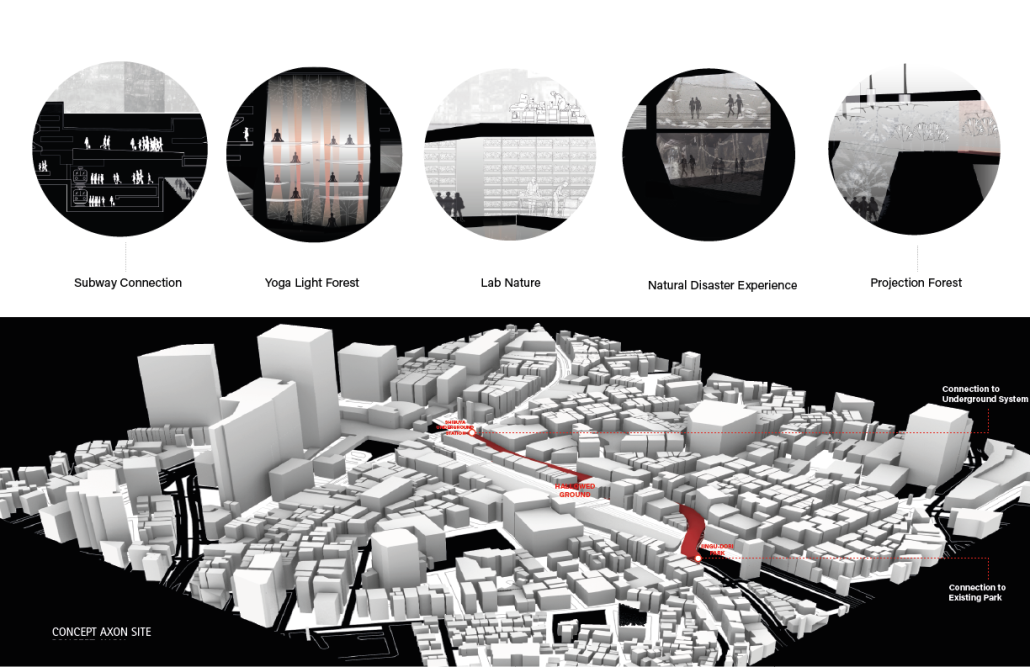
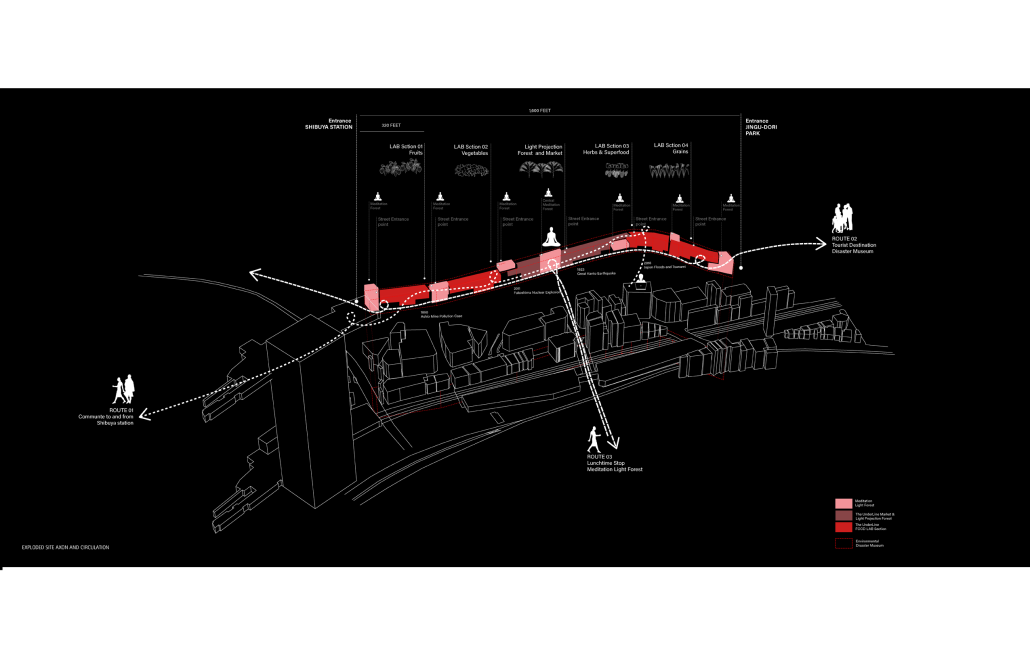
HALLOWED GROUND by Ramona Reinhart, M.Arch ‘23
University of North Carolina at Charlotte | Advisor: Chris Jarrett
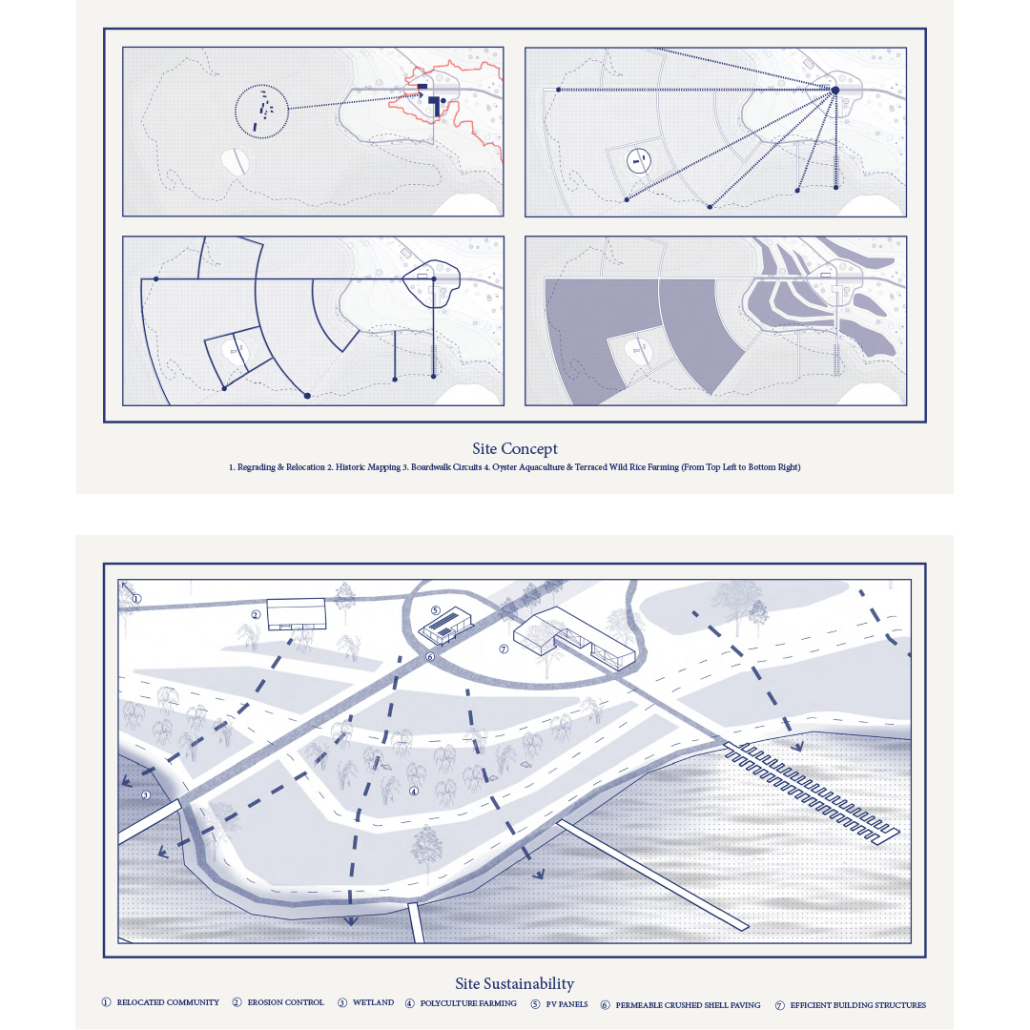
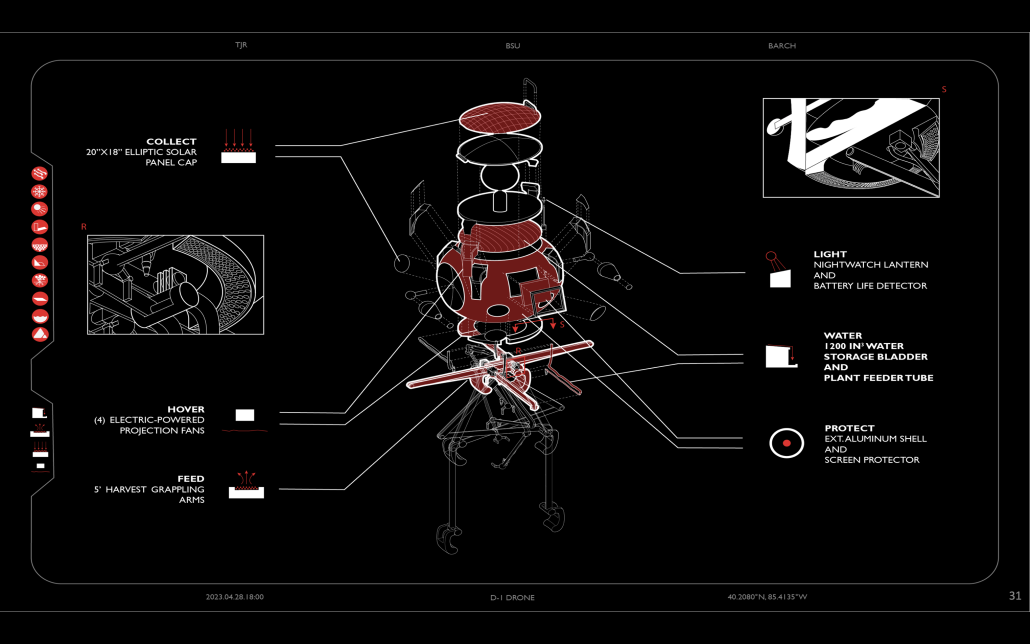
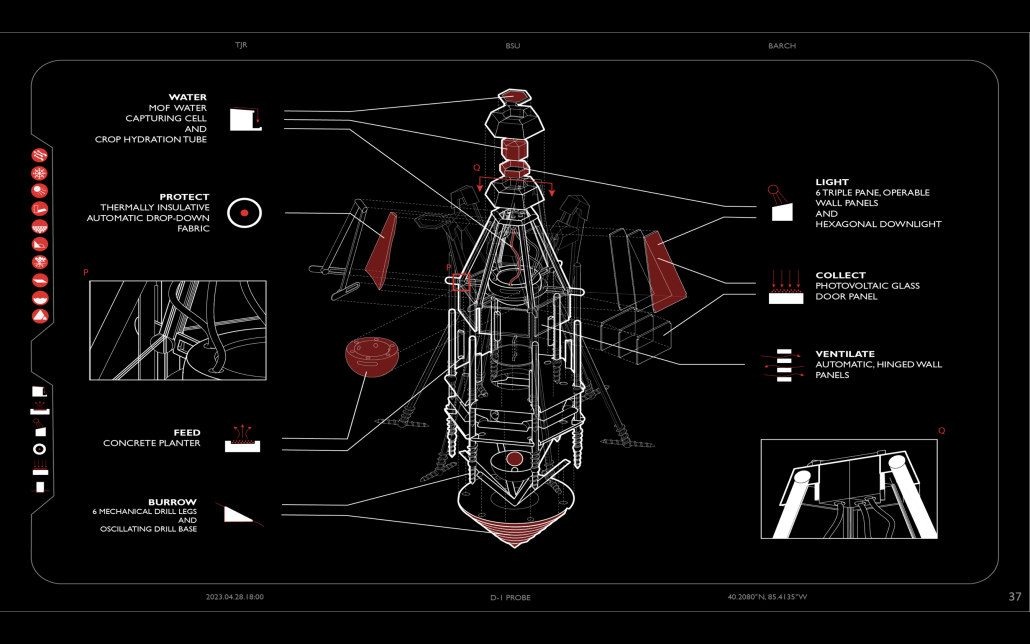
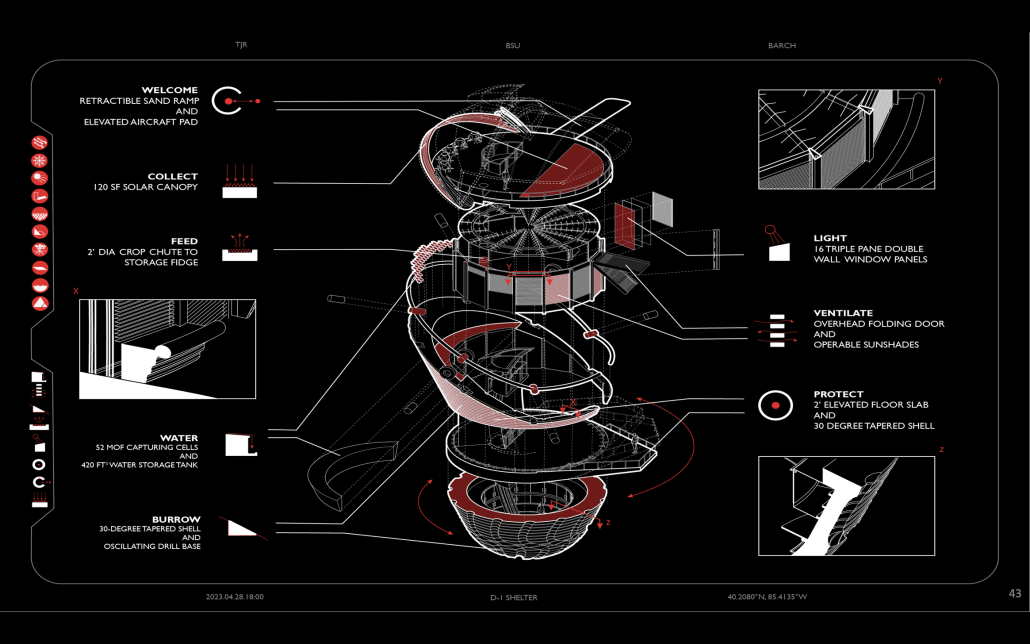
In “Taoka Reiun and Environmental Thoughts in the Early 1900s,” Ronald Loftus addresses Reiun’s cultural critique of Western modernization and the devastating forms of pollution that followed during Japan’s Meijin state beginning in 1880. As an early environmentalist and anti-modernist, Reiun argues that these natural disasters are ultimately a result of humanity’s disconnection from the natural and spiritual world.
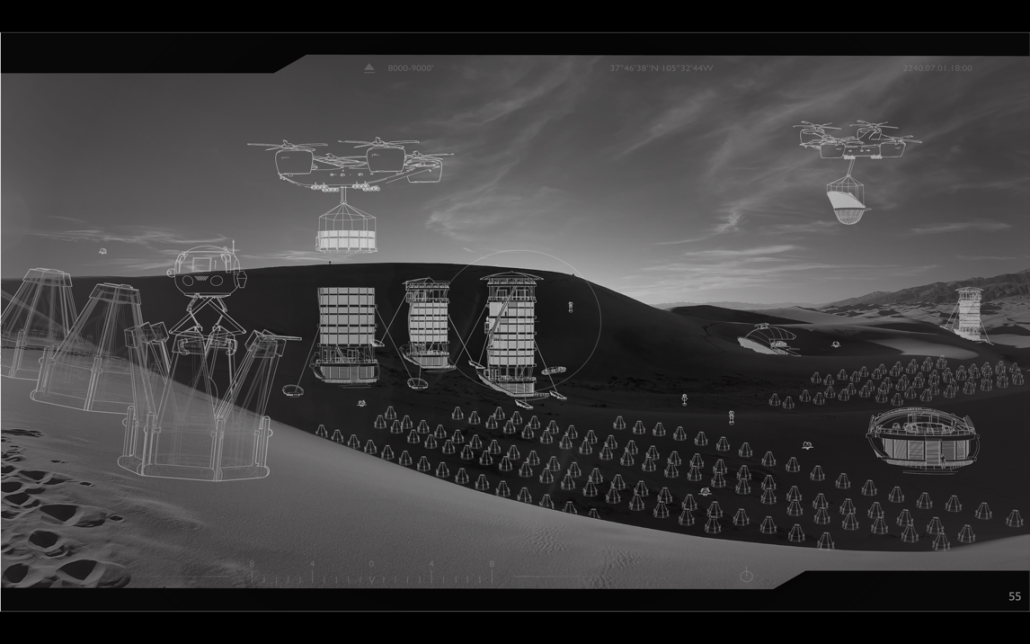
Located in Shibuya, Hallowed Ground proposes “The Under Line,” a linear futuristic public park, lab farm and market, integrated urban meditation spaces, and a museum for environmental disasters as a response to Tokyo’s culture of hyper-consumerism and capital development that “buried” many of Japan’s spiritual traditions and natural ecologies. The constant strive for economic growth resulted in large areas of impervious surfaces in the city. Surfaces that are now being hollowed out.
This project won the 2023 Best Architectural Diploma Project. As well as 2023 Excellence in Architectural Representation.
Instagram: @_ramonareinhartg
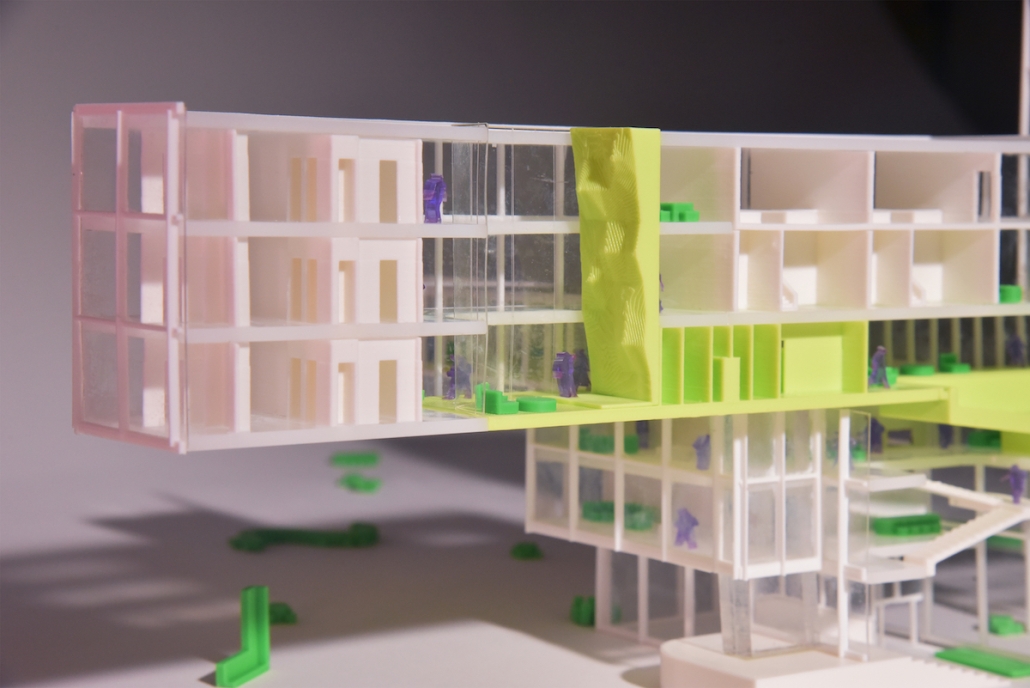
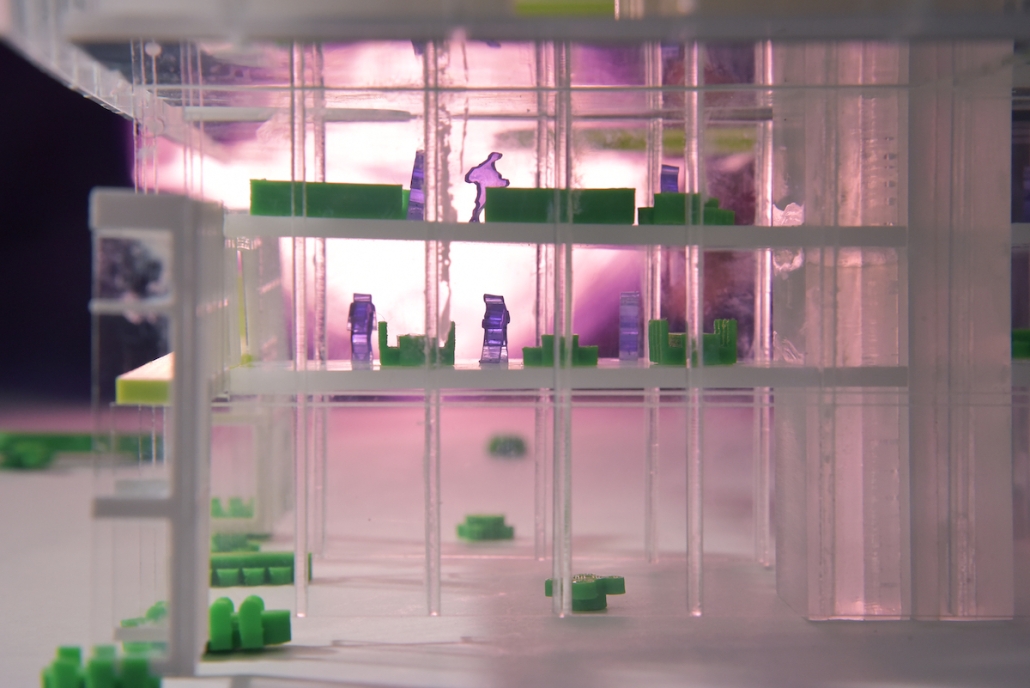
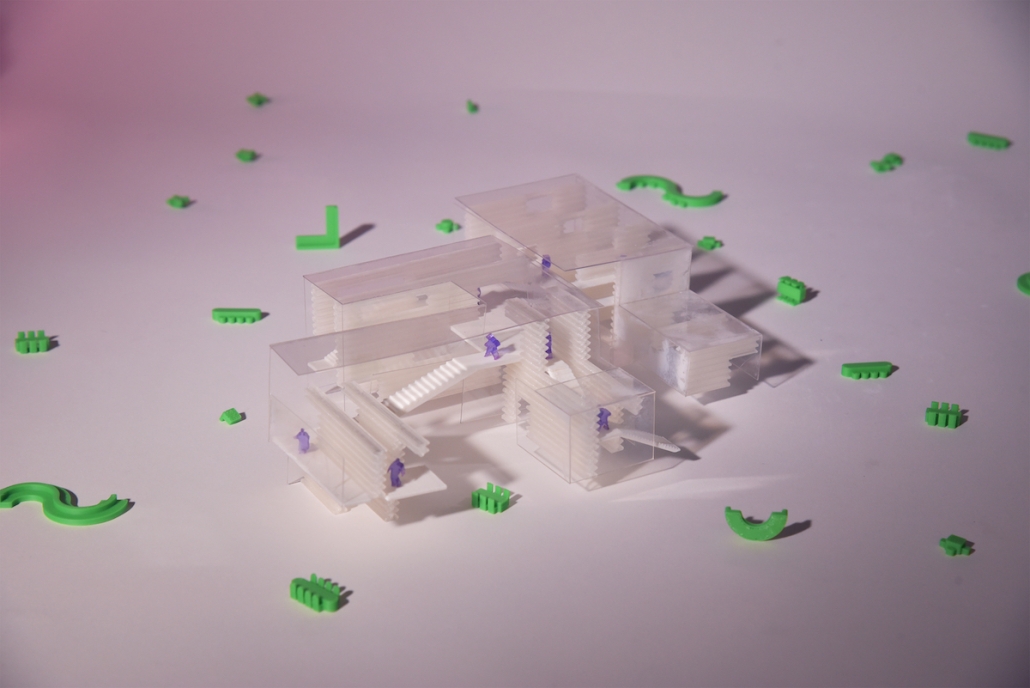
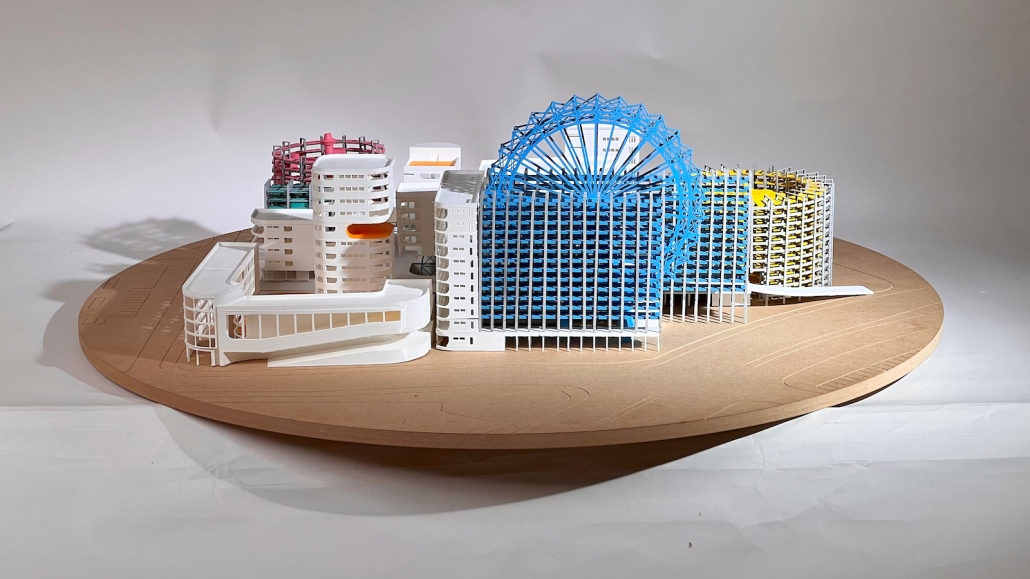
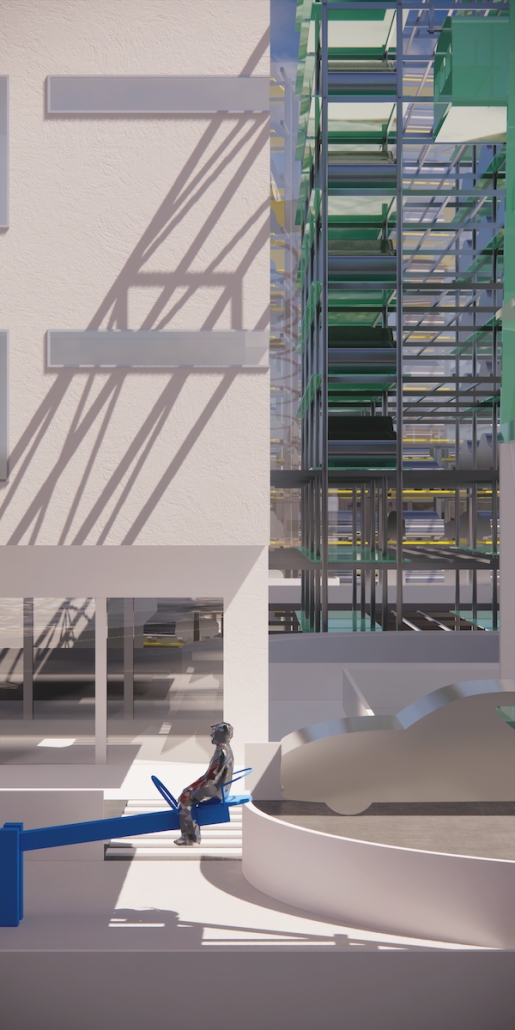
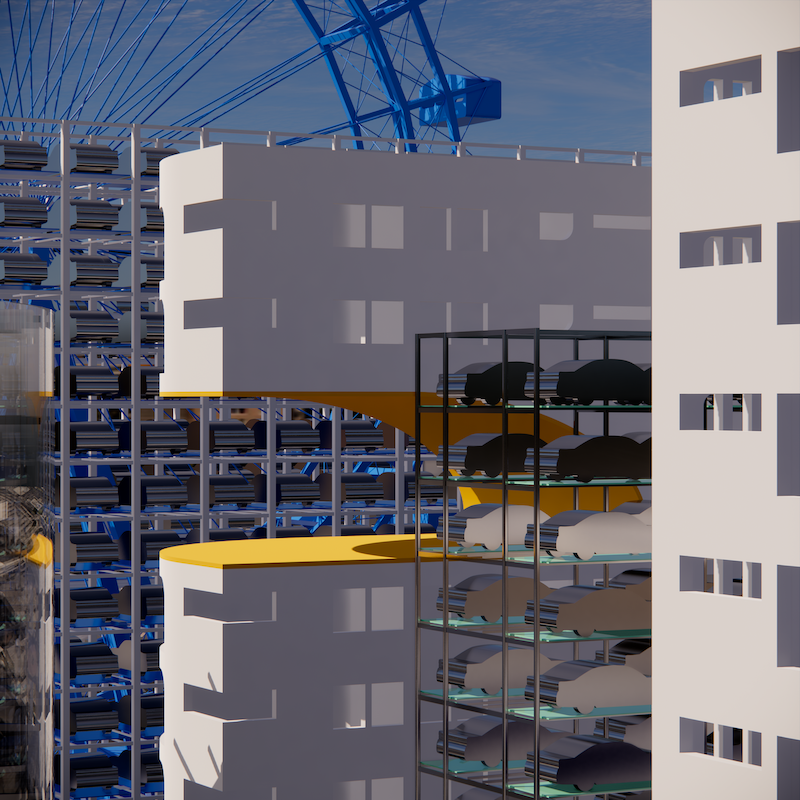
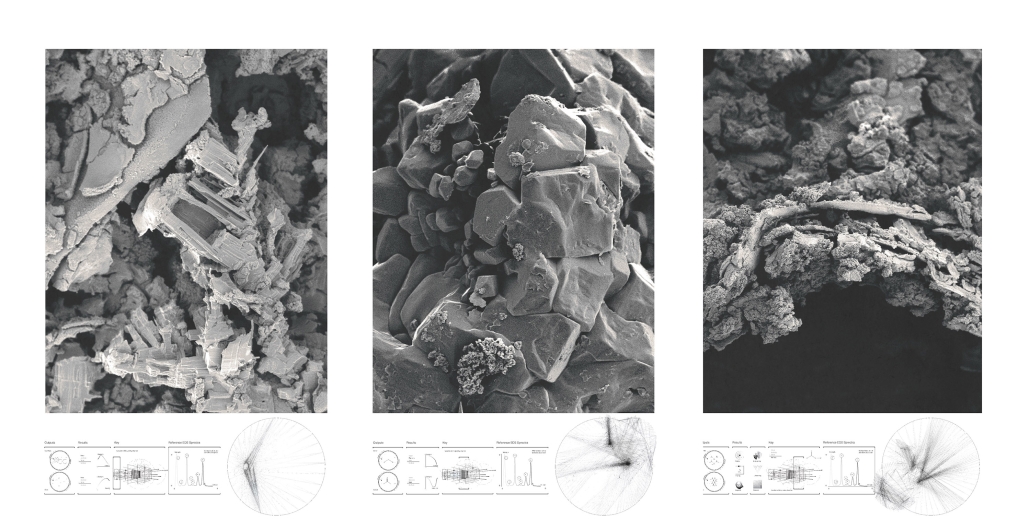
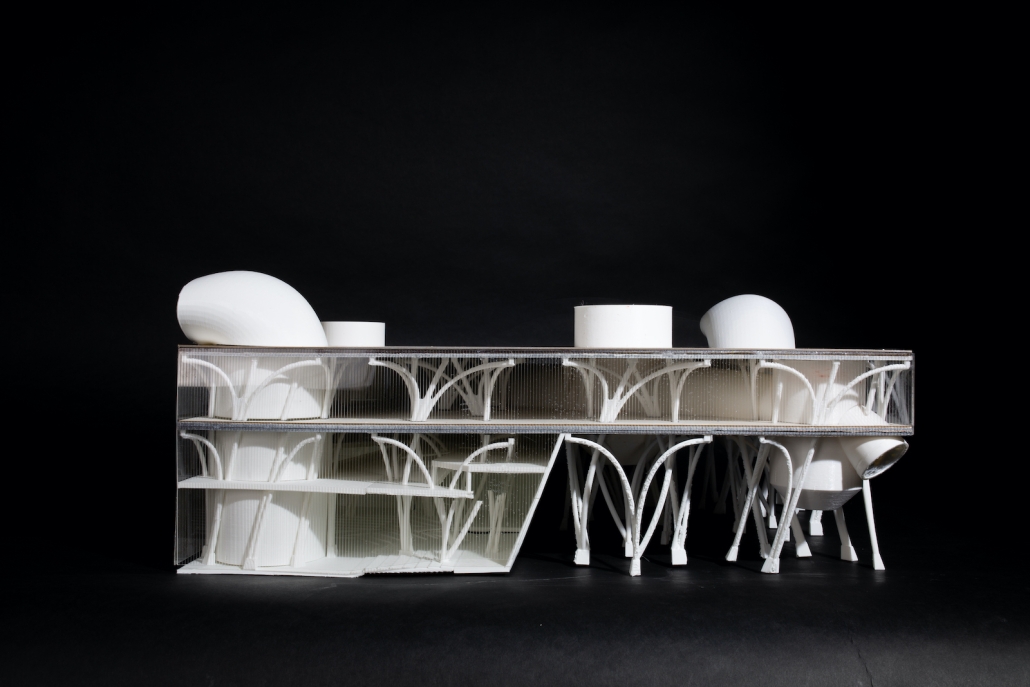
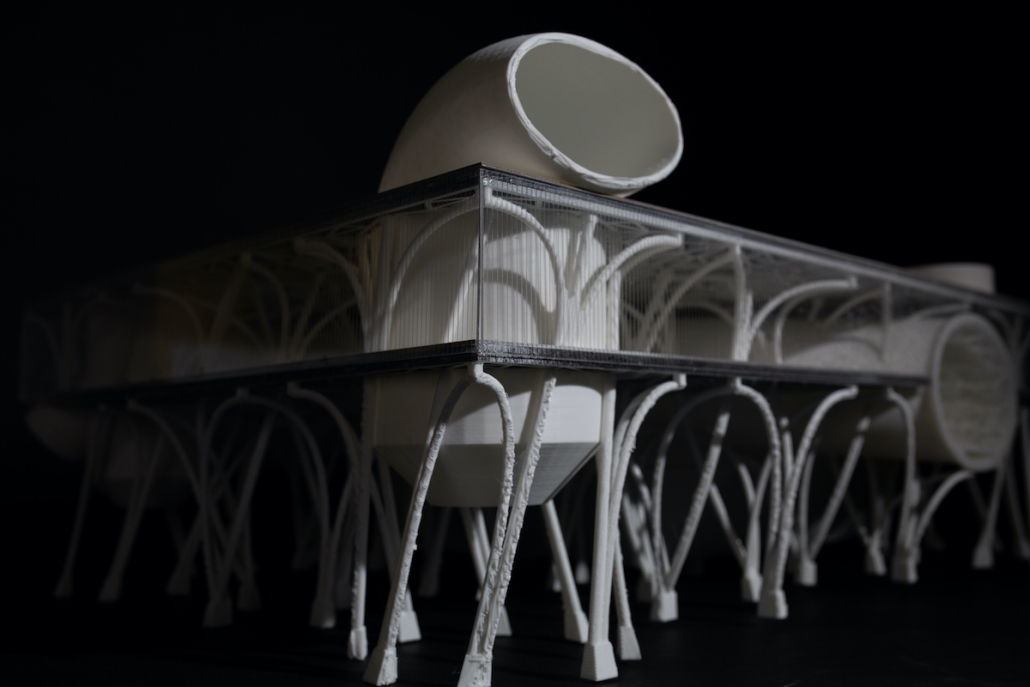
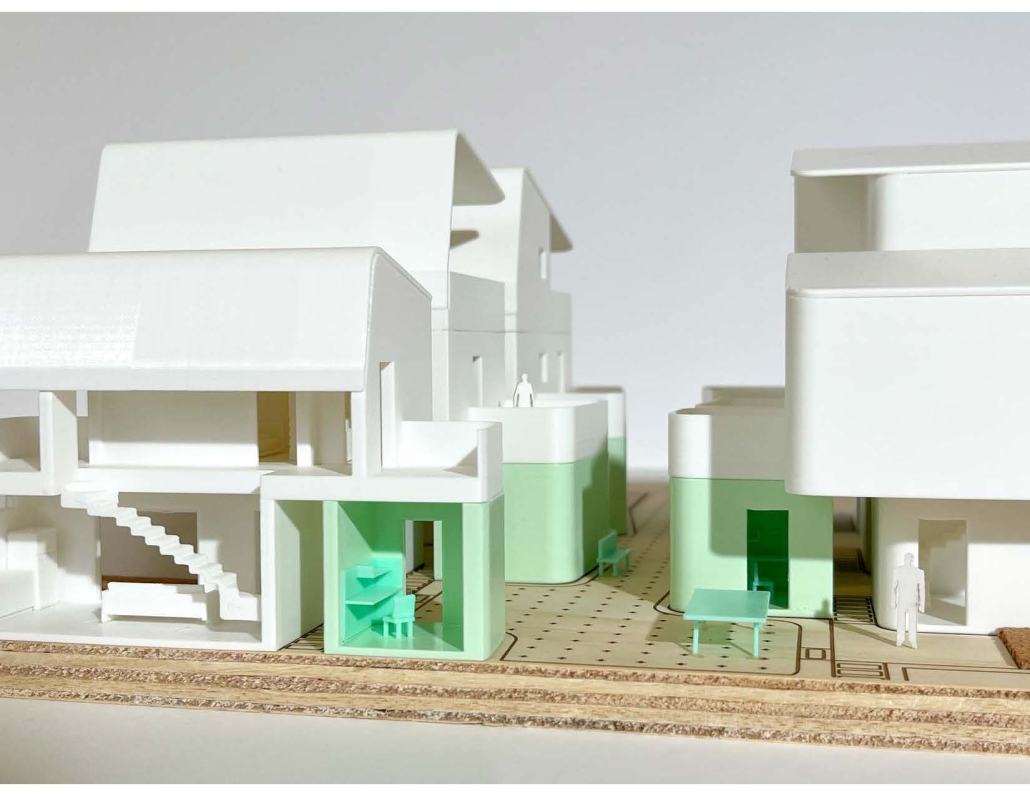
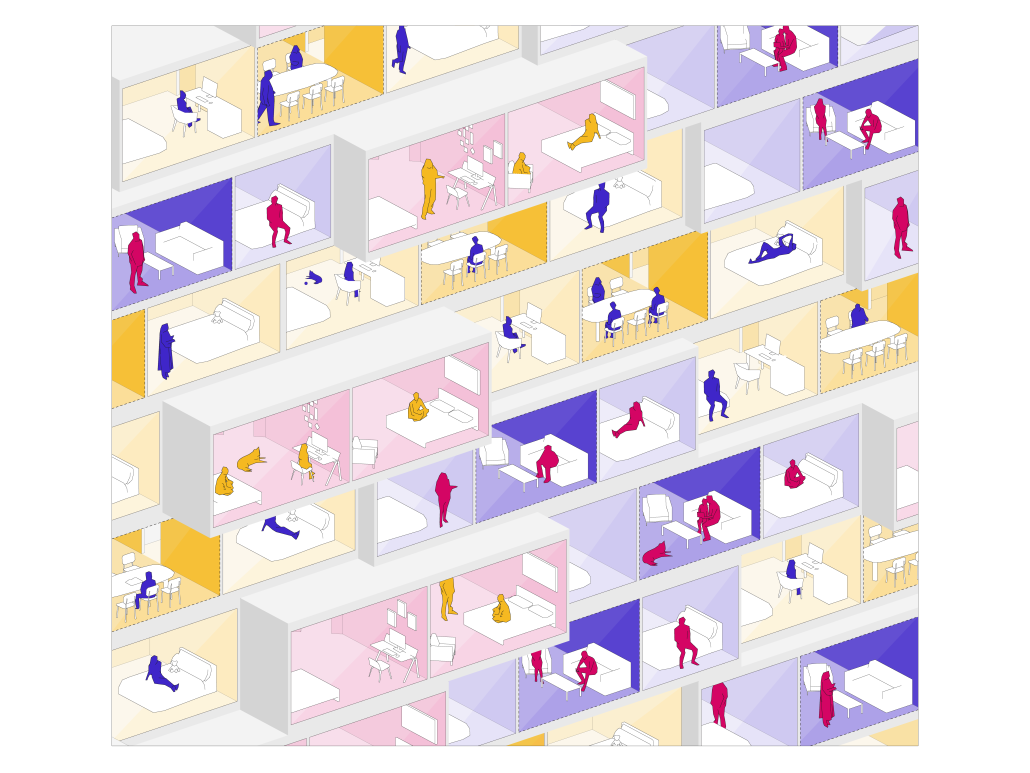
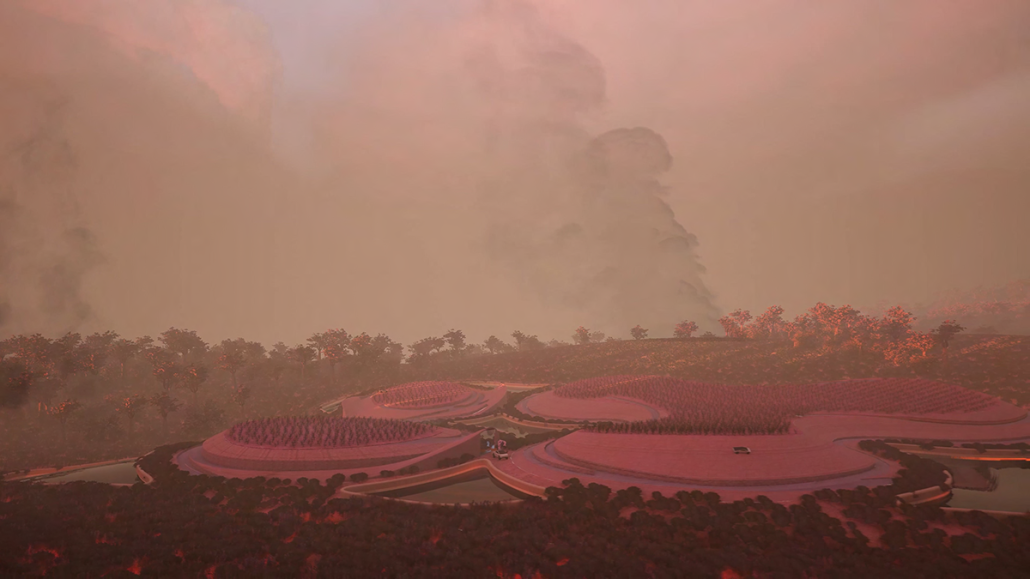
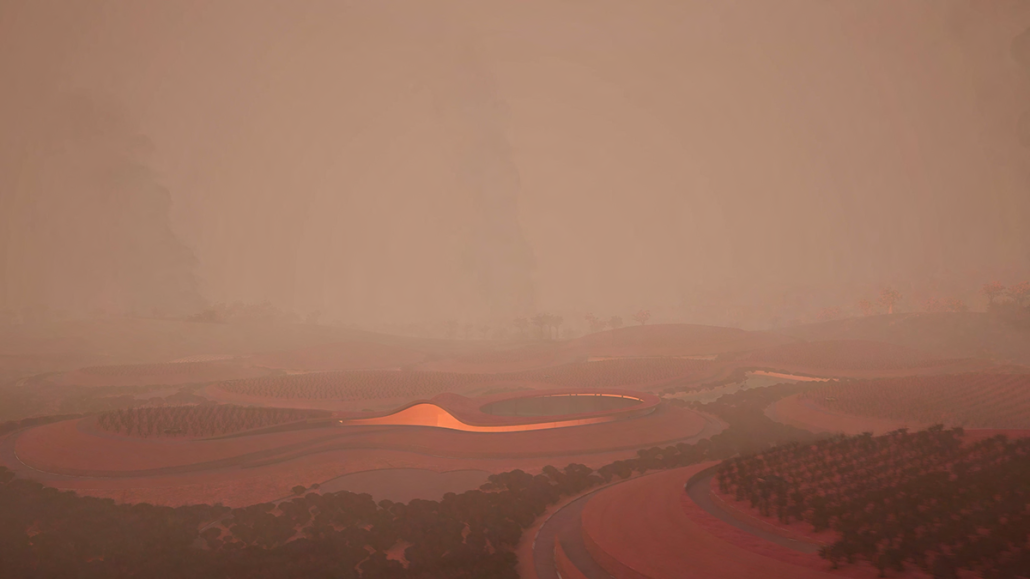
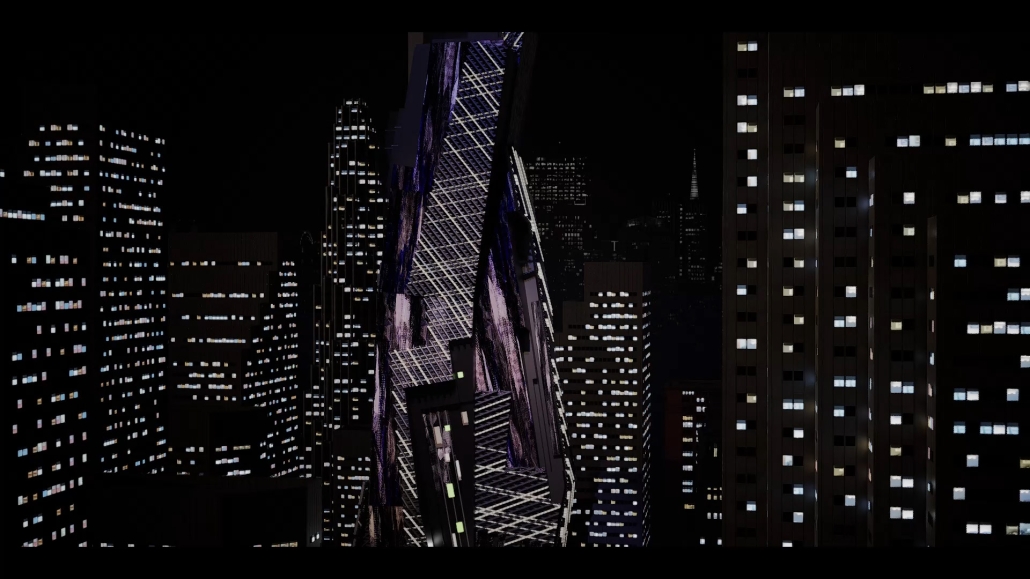
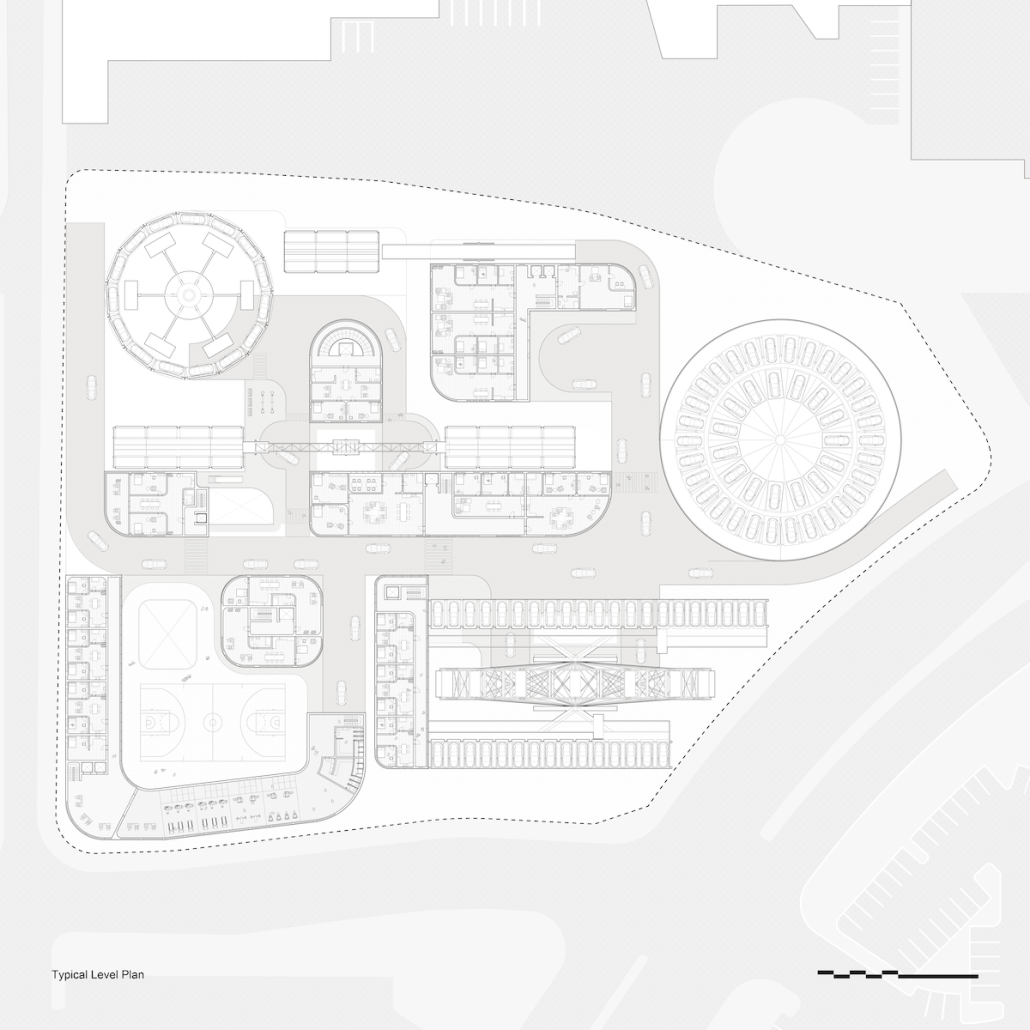
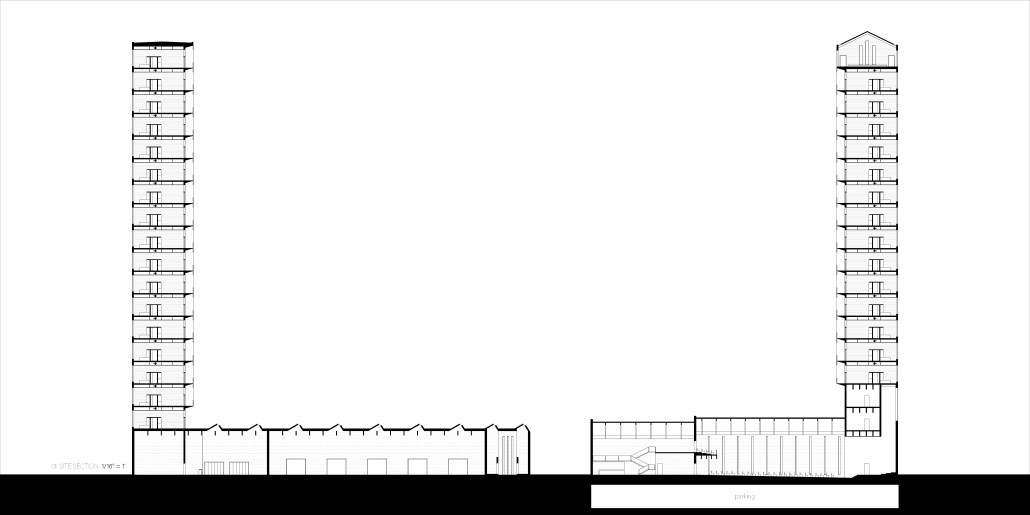
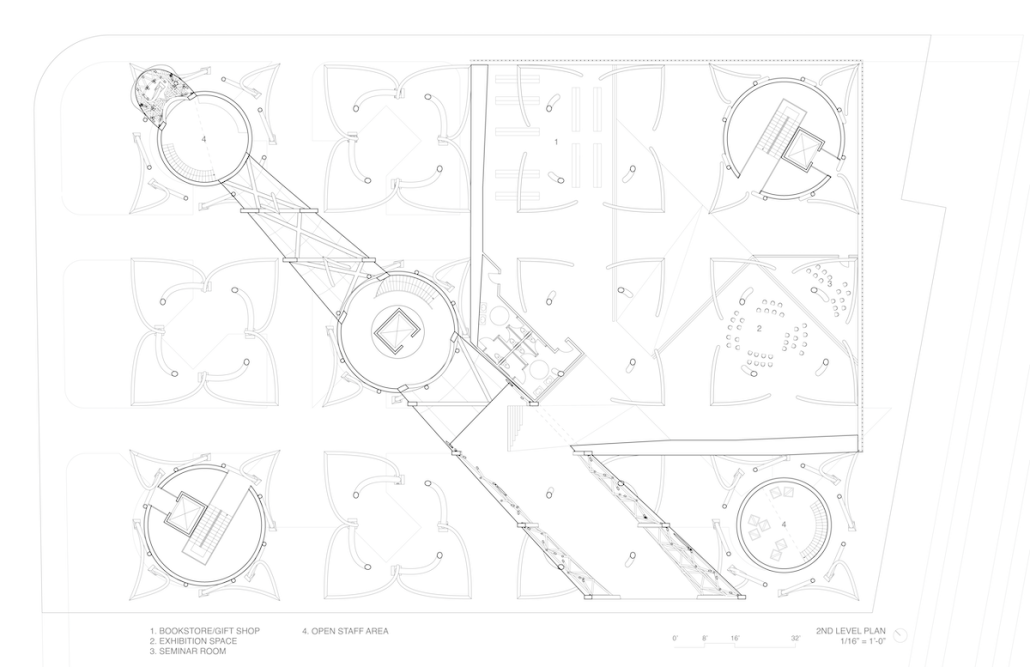
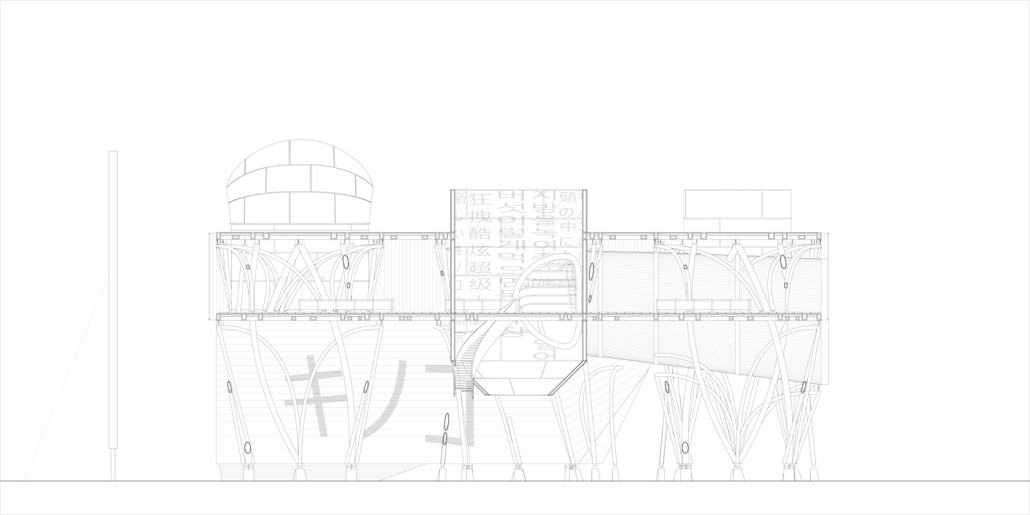
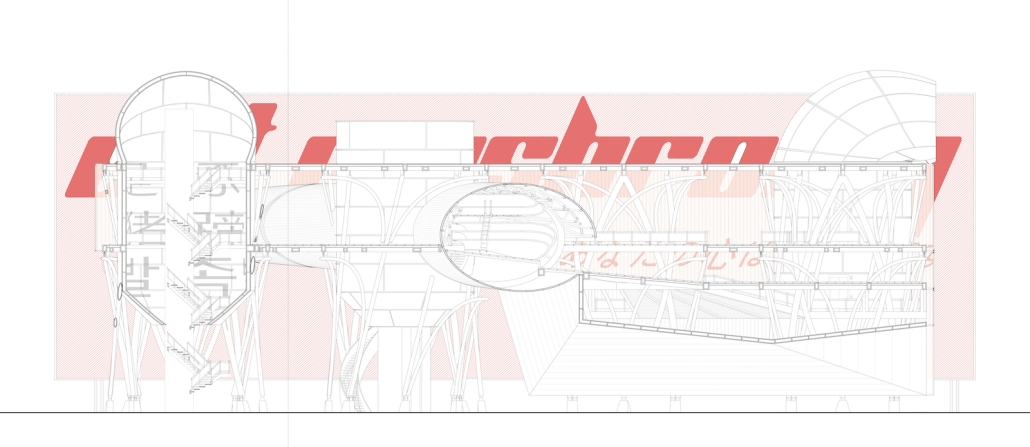
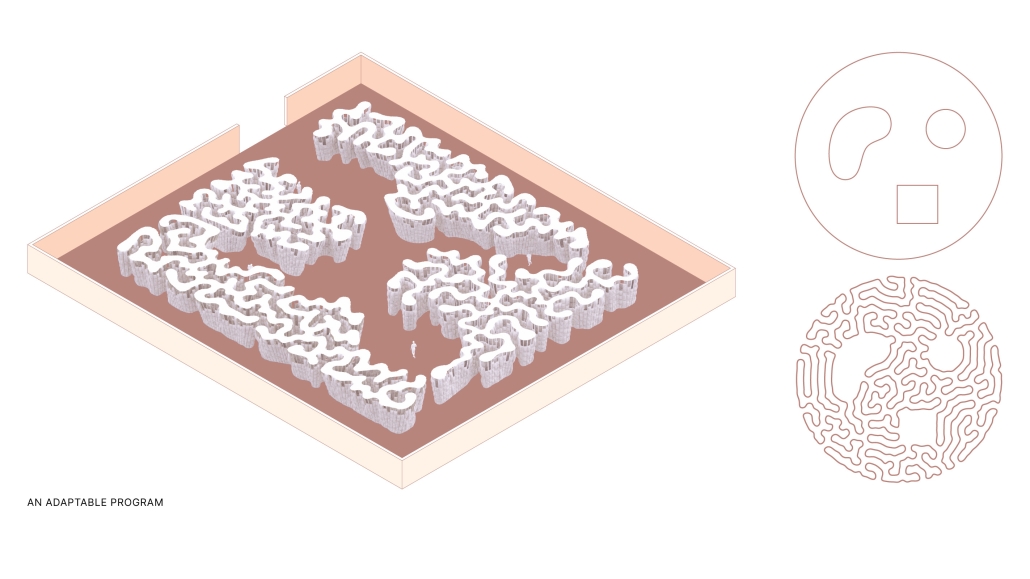
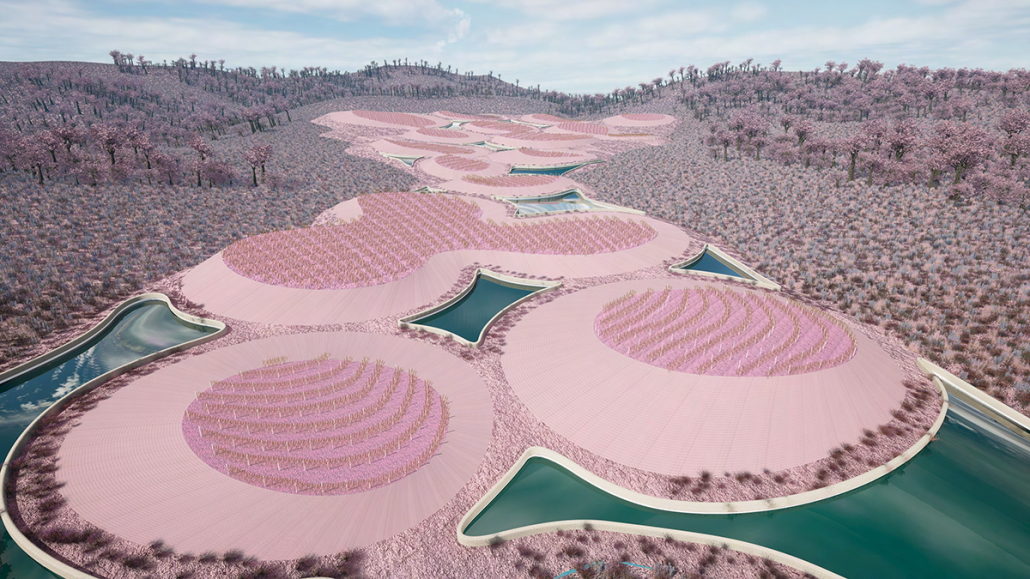
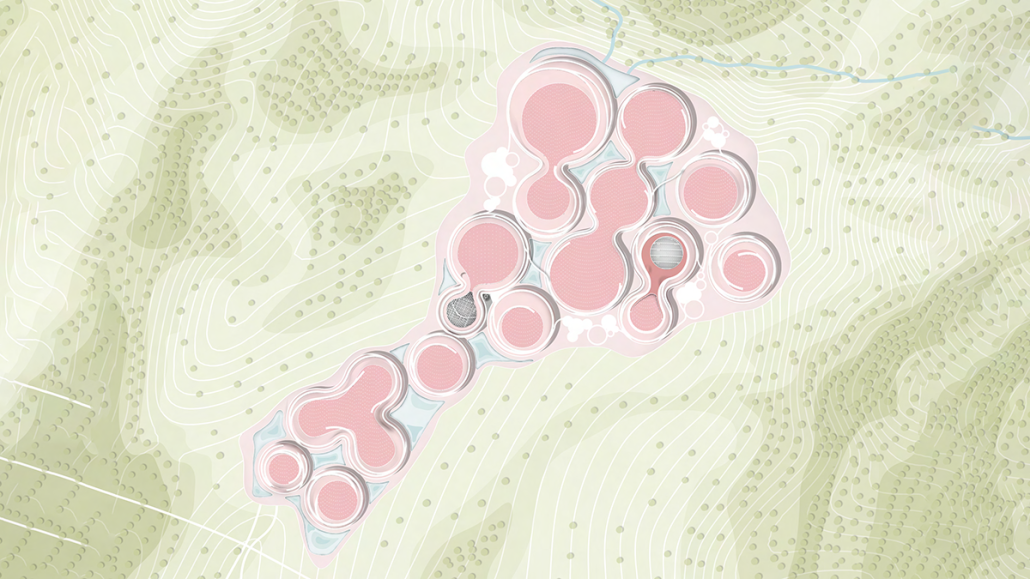
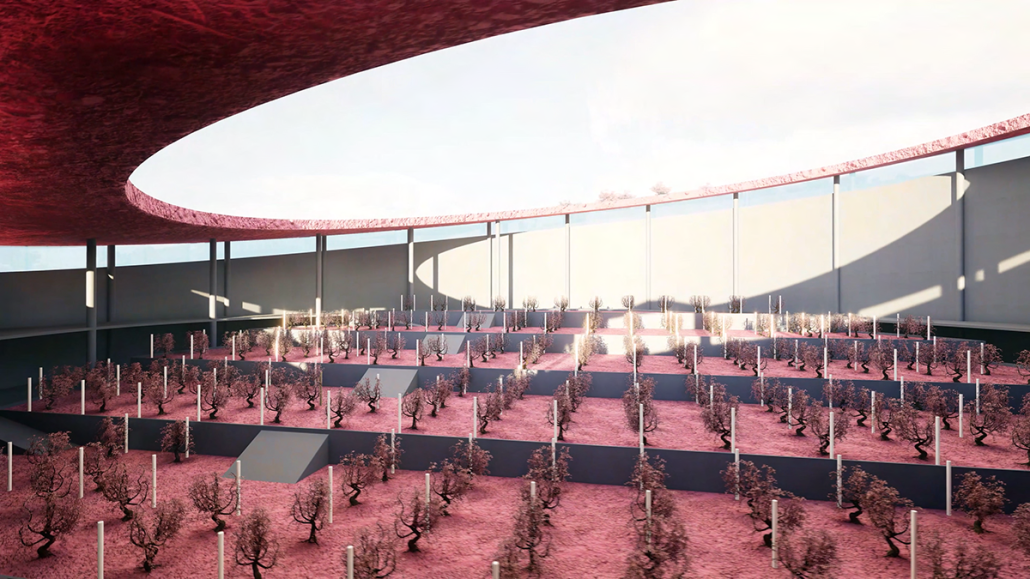
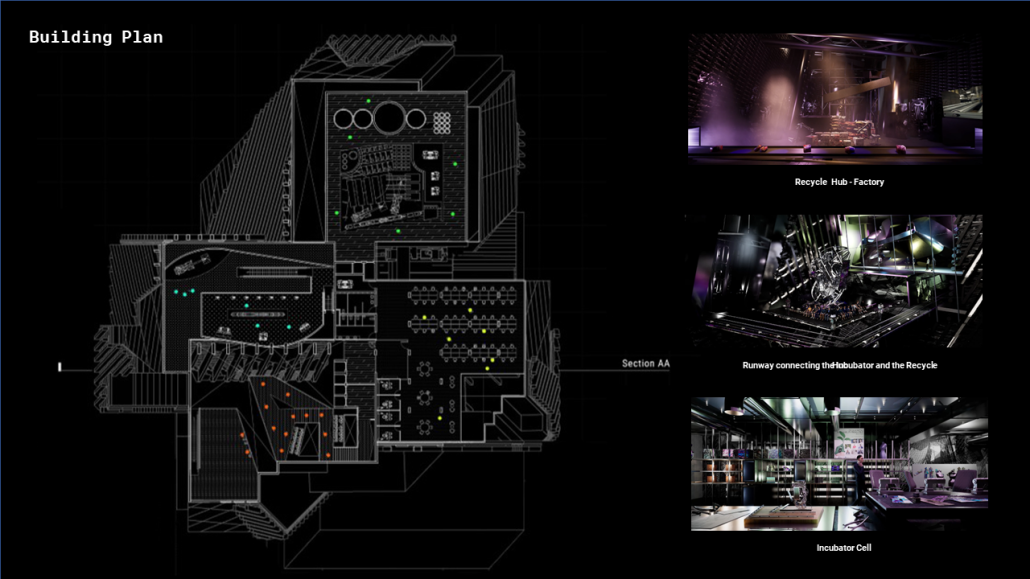
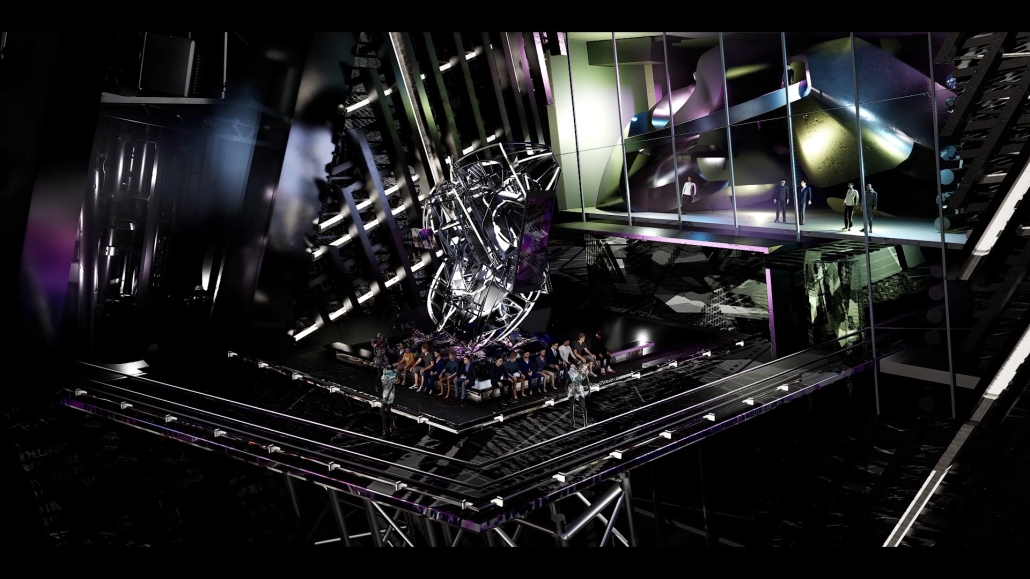
Little Megastructure by Yiman Yiman, M.Arch ‘23
UCLA Architecture and Urban Design | Advisor: Greg Lynn
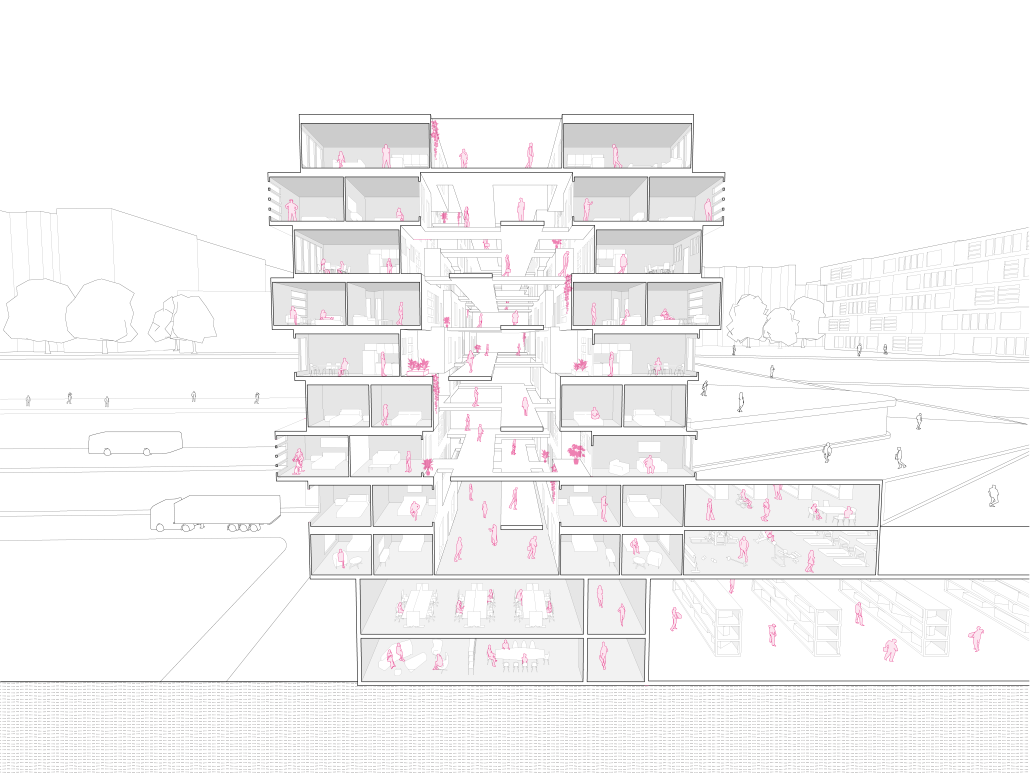
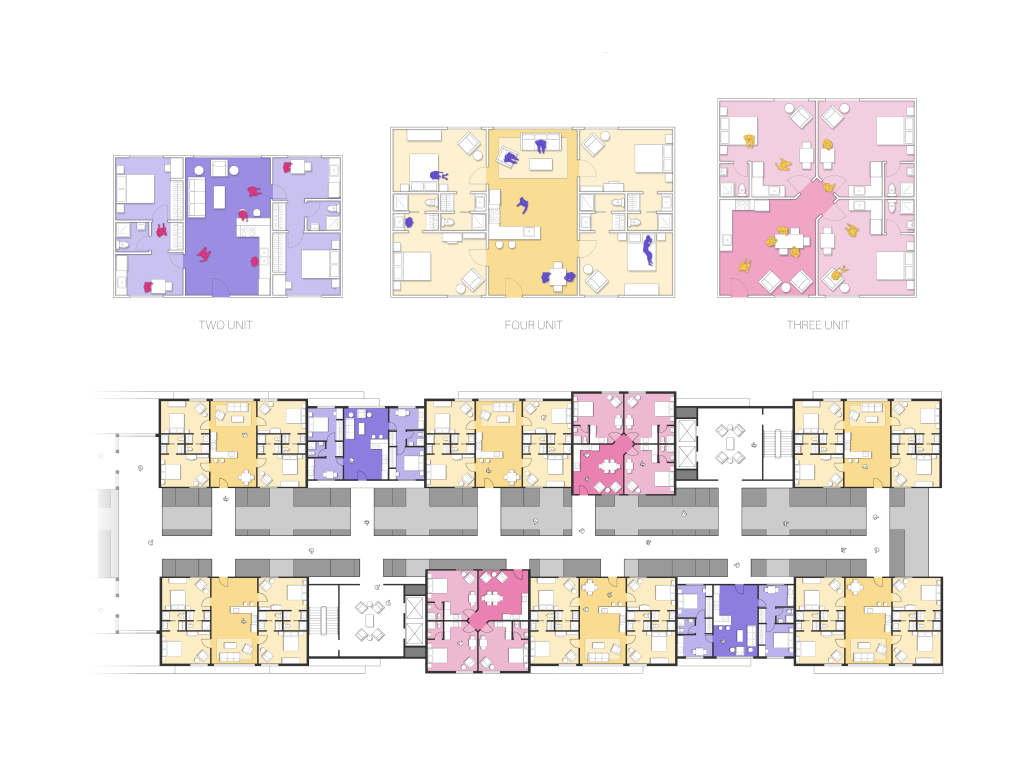
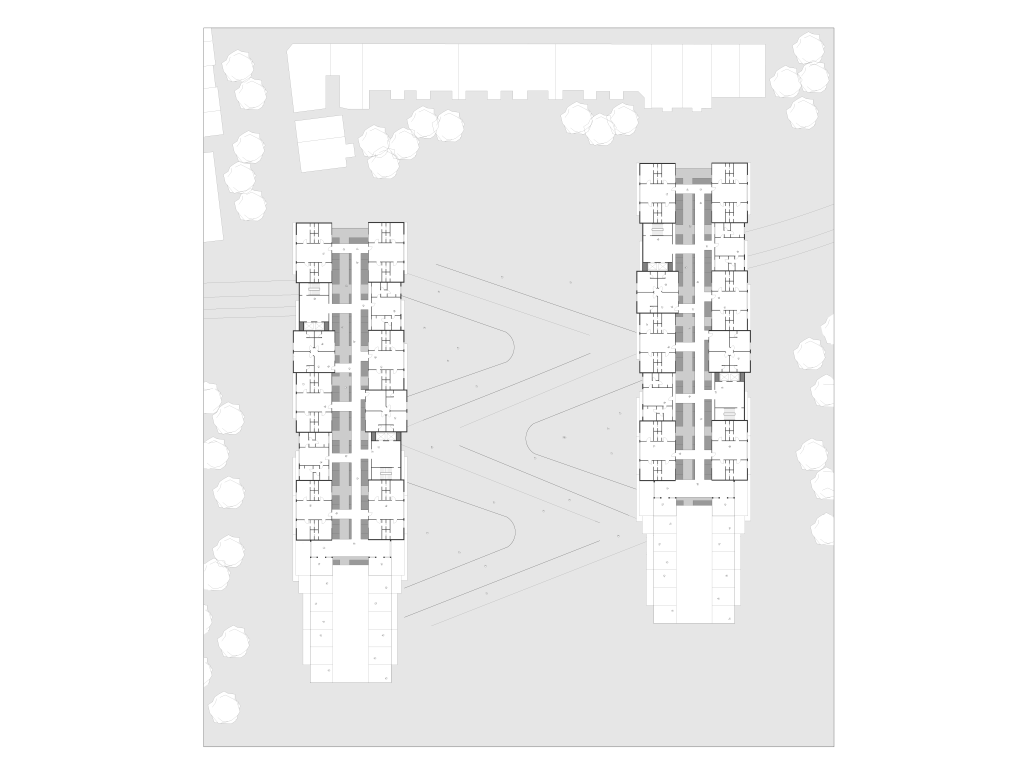
“Little Megastructure” configures an inclusive community of aggregated spatial prototypes that celebrates social connection and belonging while supporting individuality. The prototypical forms can be combined and composed in a variety of ways to create a wide range of spaces. Clusters of parks, plazas, courtyards, and atriums in between modules throughout the megastructure foster a sense of community and belonging. With a clear hierarchy of spaces that are designed for different purposes and activities, having all the components of a city creates a sense of urbanism.
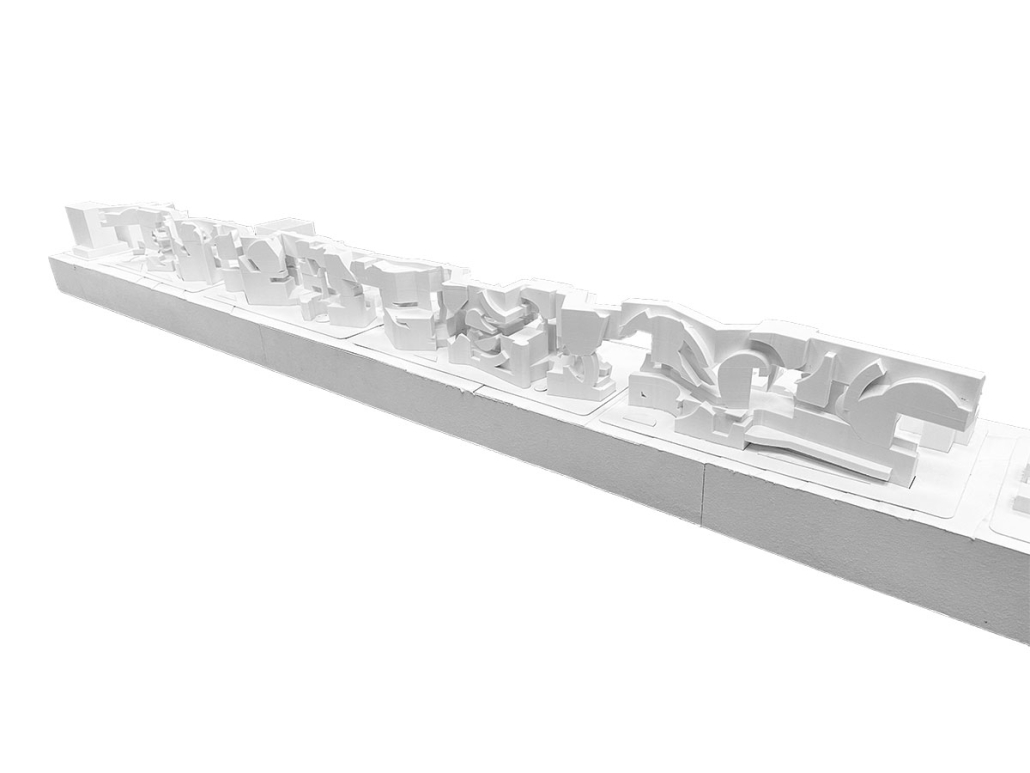
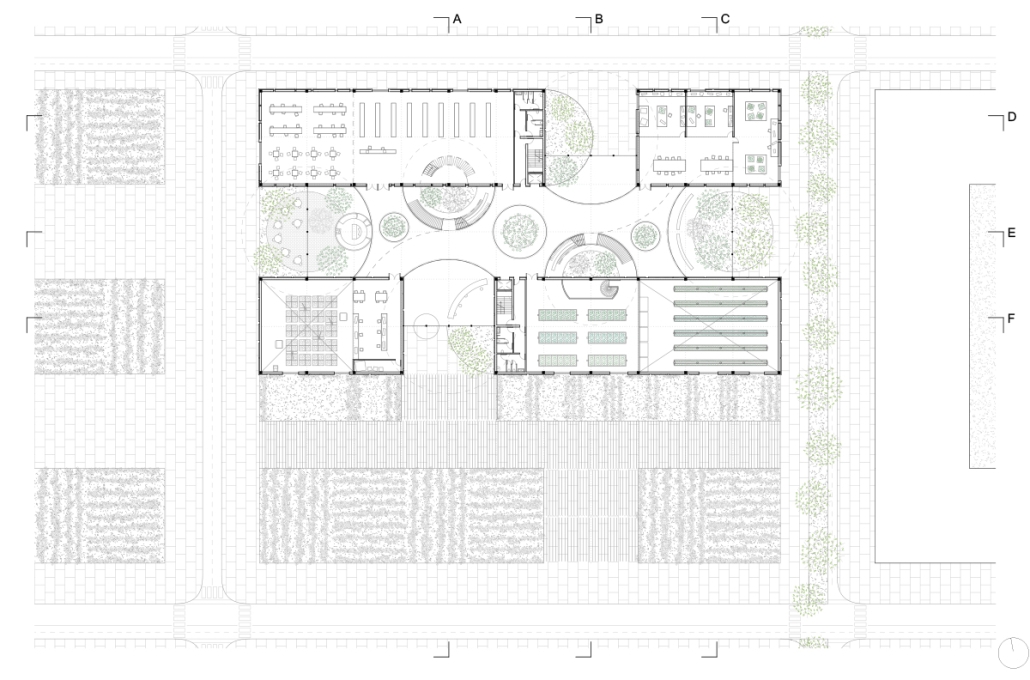
Park! Park! by Motomi Matsubara ‘23
UCLA Architecture and Urban Design | Advisor: Greg Lynn
“Park! Park!” offers a set of housing towers, their shapes, and scales informed by the interplay between the behavior of residents inside and automobile traffic outside. One of the towers is taller and leaner; another more lateral and rectangular. Here, fillets perform not only as an intimate icon, each interacting softly with adjacent housing towers, but also as mediators of the different scales of motions between two different physical bodies–people and cars.
Instagram: @m2c_works
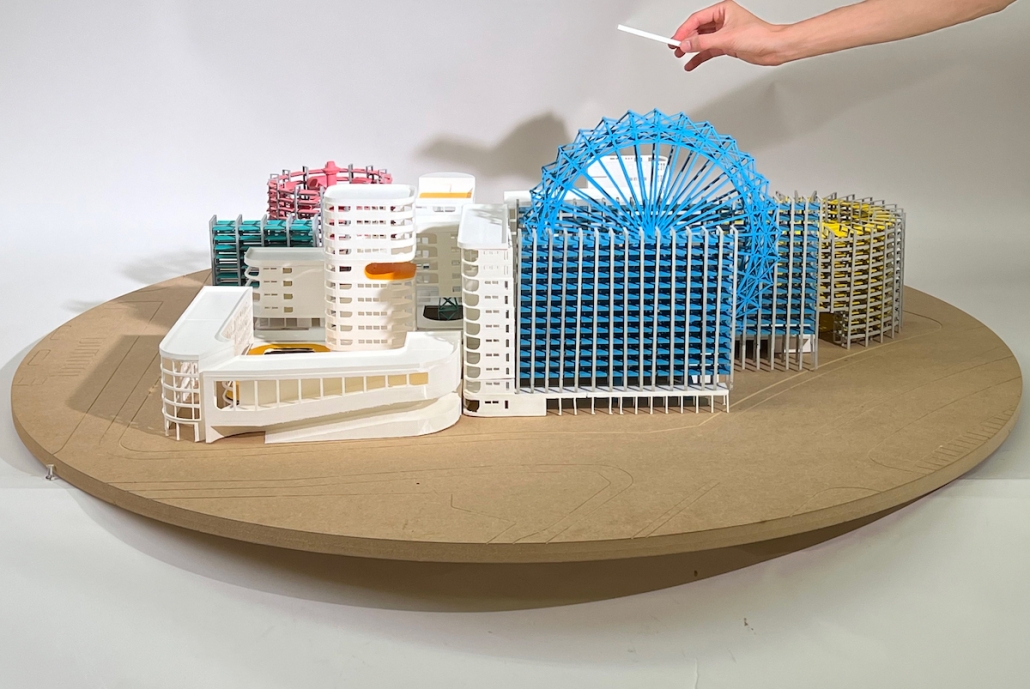
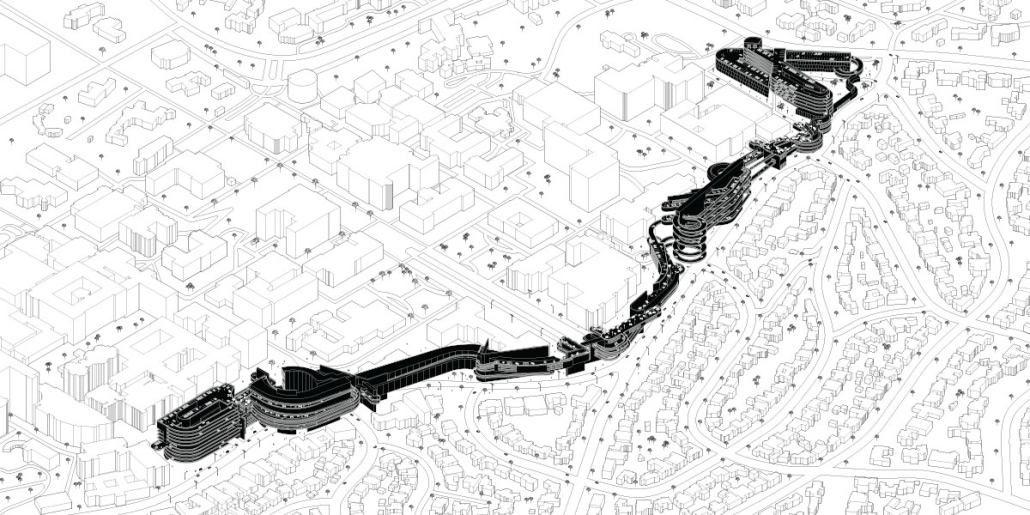
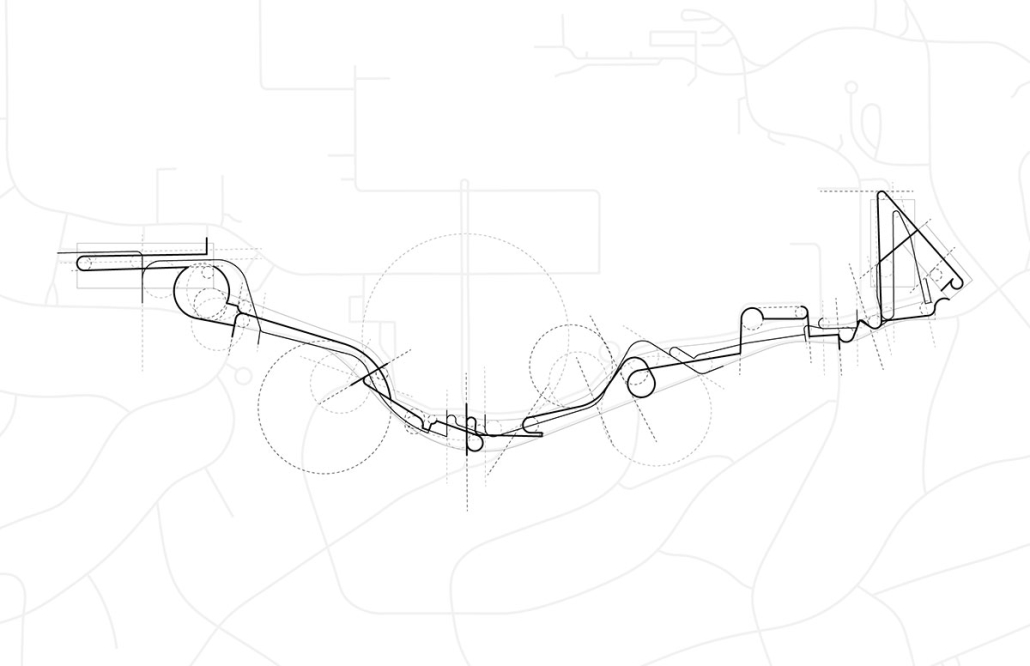
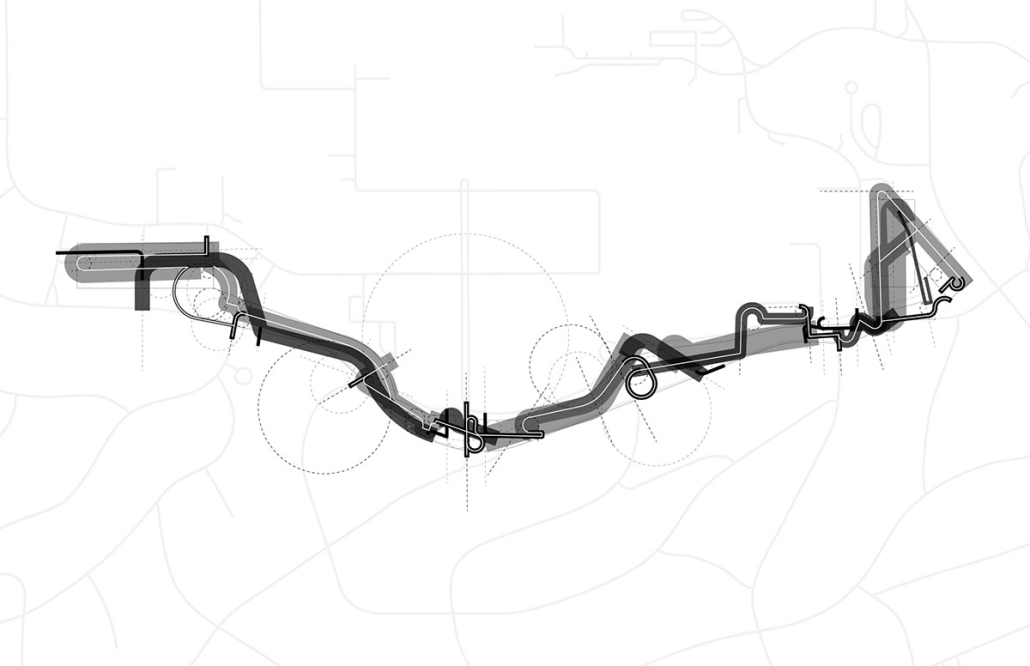
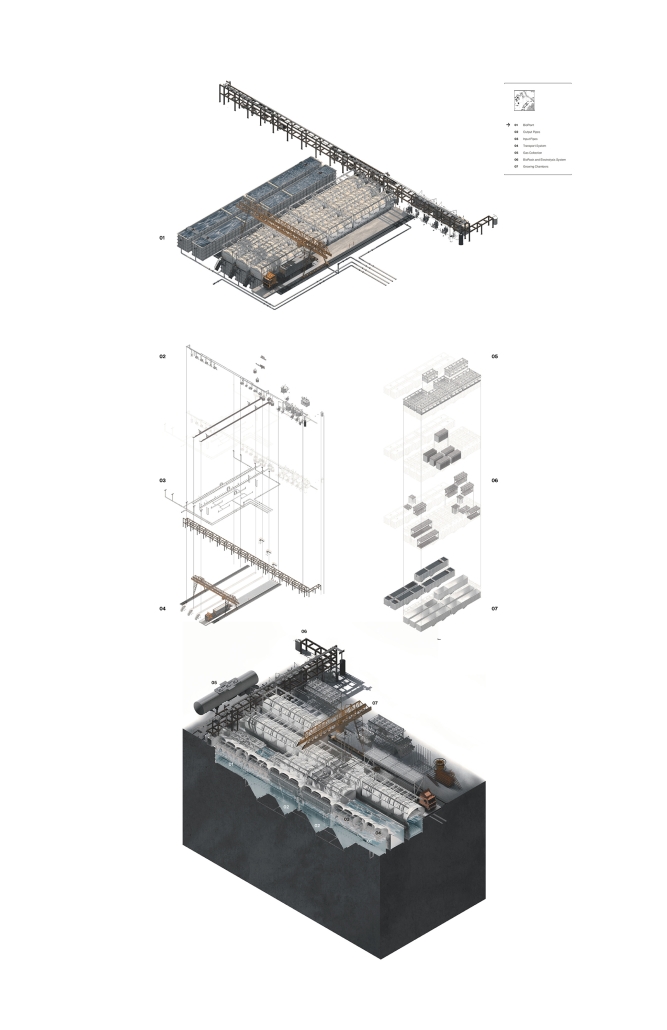
Undefined Parking by Katie Yuan, M.Arch ‘23
University of Southern California | Advisor: Yaohua Wang
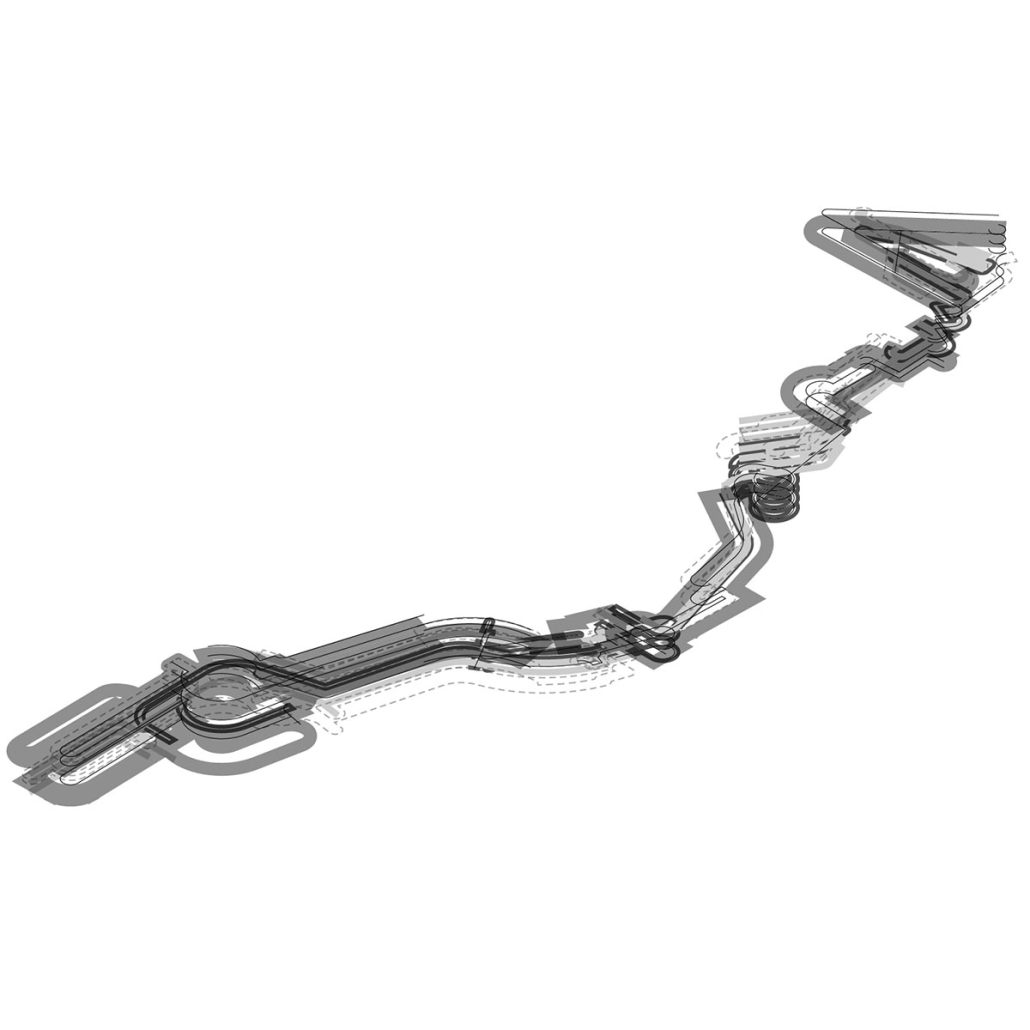
The lines drawn on maps to define the borders of countries and territories may appear solid and definitive at a glance. However, when magnified and viewed at a larger scale, these lines are composed of segments, curves, and dashes that intersect, connect, and overlap. Lines are one-dimensional, but when given 3-dimensional qualities, they become less concrete and defined. In other words, when lines are given different widths and heights, they are no longer elements that separate or confine objects, but rather they embody multiple conditions that can become spaces, tectonics, connections, and circulations.
Formed through a series of intersecting, shifting, and offsetting lines, Undefined Parking appears as an urban boundary that separates the UCLA campus and residential area at an urban scale. In this condition, the boundary becomes a partition wall. At an architectural scale, the parking structure becomes the destination for both entering and exiting the site. Yet simultaneously, the structure’s various programs (offices, classrooms, green space, etc.) blur the distinction between the university campus and the urban site. In this condition, the boundary becomes a destination. At a model scale, the volumes, ramps, walls, and planes are interlocked and joined together through the distinct tectonic elements of each individual piece. In this condition, the boundary becomes a connection.
Perhaps, lines or boundaries exist in multiple conditions and cannot be defined…
This project was awarded the USC Master of Architecture Distinction in Directed Design Research.
Instagram: @katie0712yl, @yaohua_wwww
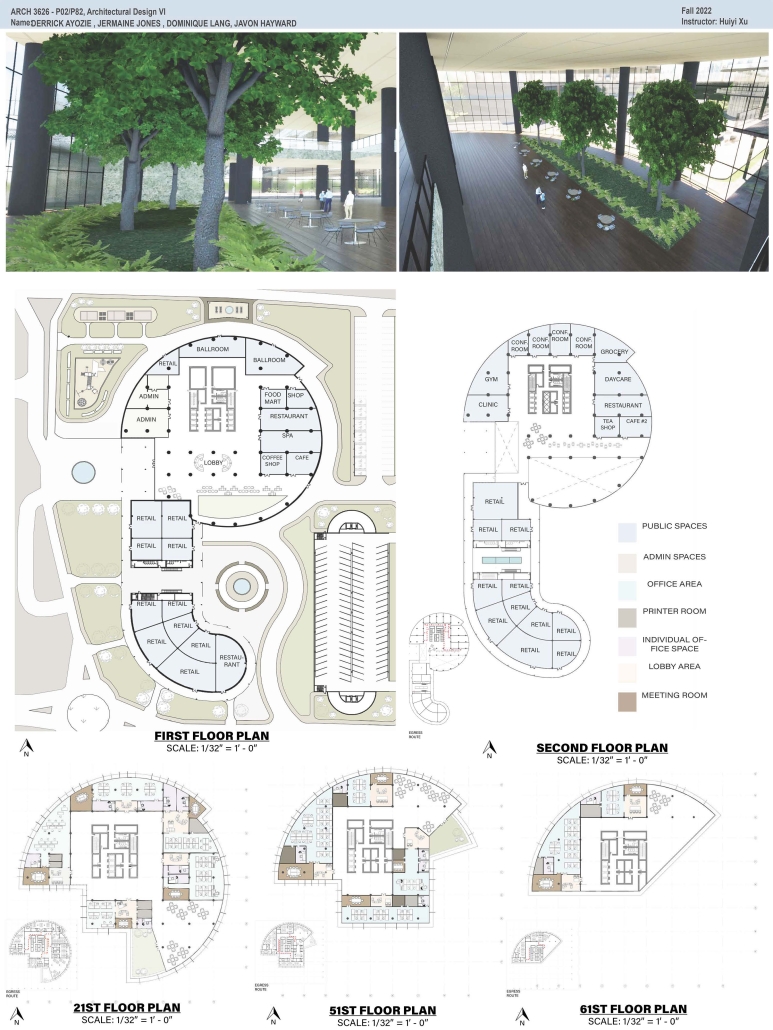
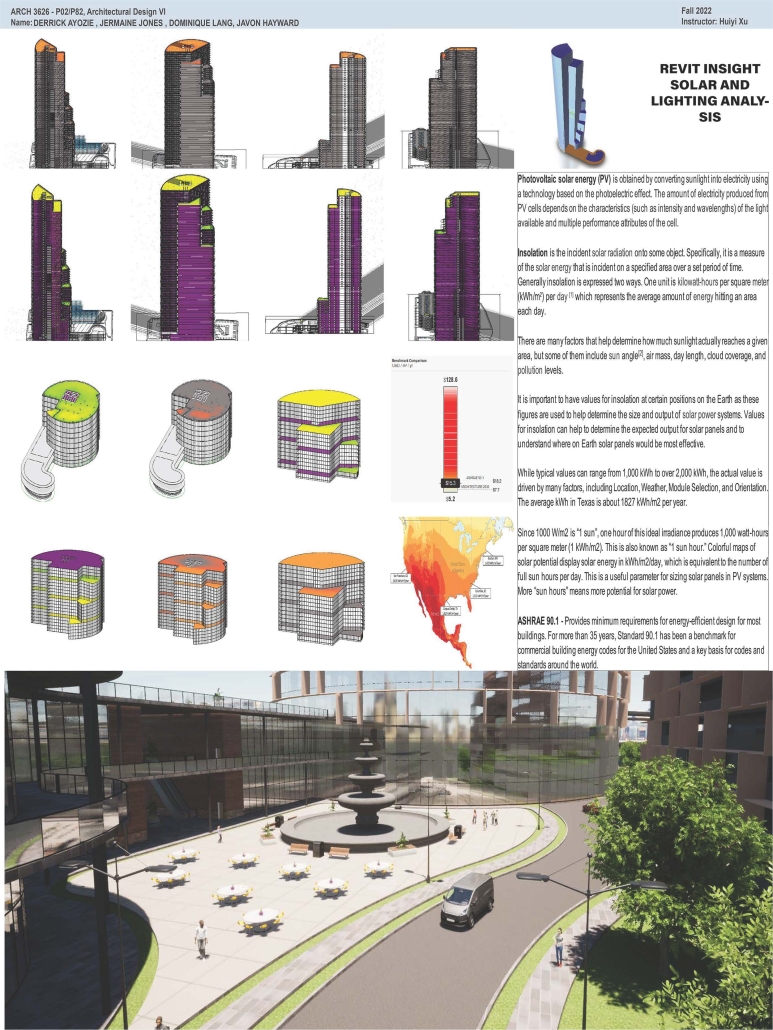
High-Rise Building by Jermaine Jones, Dominique Lang, Javon Hayward & Derrick Ayozie, B.Arch ‘23
Prairie View A&M University | Advisor: Huiyi Xu
According to the U.S. Census Bureau’s population estimates from 2021, there were 69,094 new residents added to the Greater Houston area. Some developers have purchased land in the Houston City Centre area, on the corner of I-10 Hwy and Beltway 8 in the City Centre, and plan to build an iconic high-rise building. This project is a mixed-use office building. The location of the project is in the Memorial City district of Houston, Texas. City Centre is a 50-acre development with 2.1 million square feet of gross floor space, including 400,000 square feet of retail, restaurants, and entertainment, a 149,000 square foot fitness facility, 425,000 square feet of office space, a variety of rental, and non-rental residential developments: a Microsoft office, Memorial Hermann Hospital, Memorial City Mall, Houston of City College, and diversified restaurants such as Taste of Texas, Pappadeaux Seafood Kitchen, and other retailers are all around it.
This project will bring more people to this area to contribute to the local business and land value. The potential tenants of the high-end office building with commercial spaces and a parking garage will be the headquarters offices, banks, medical offices, high education offices, etc.
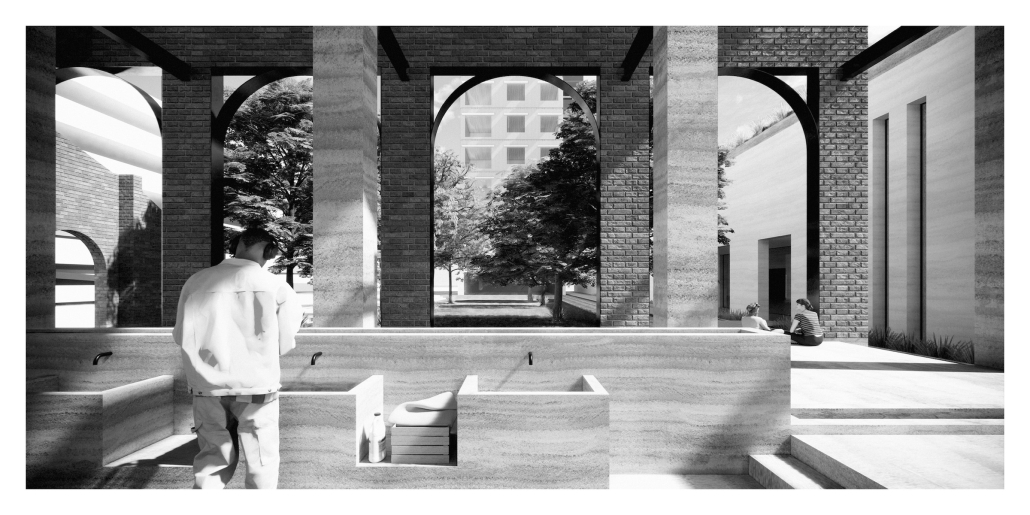
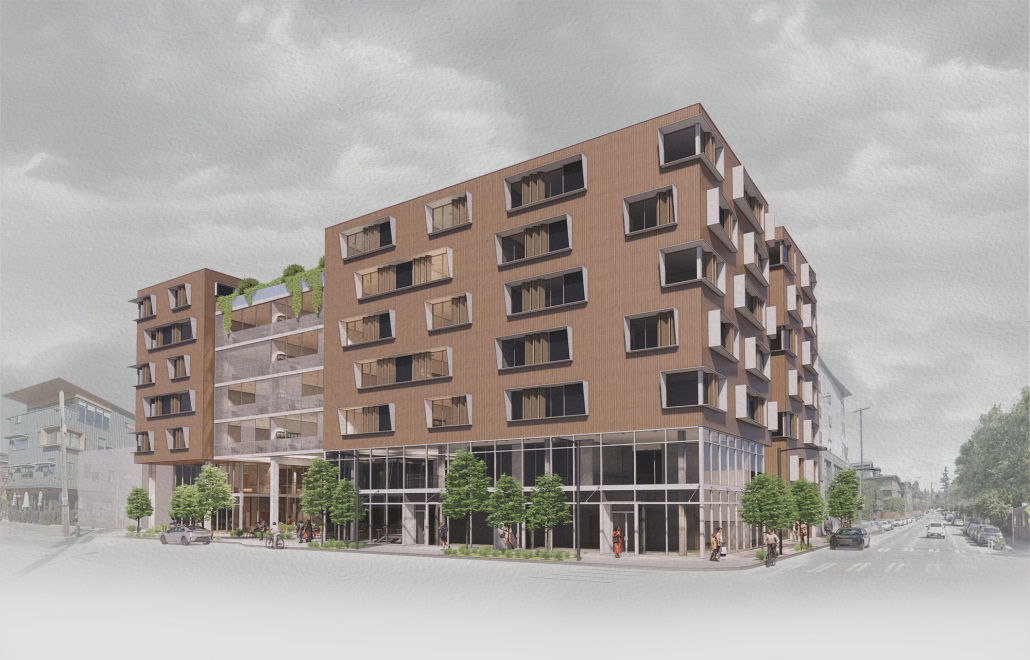
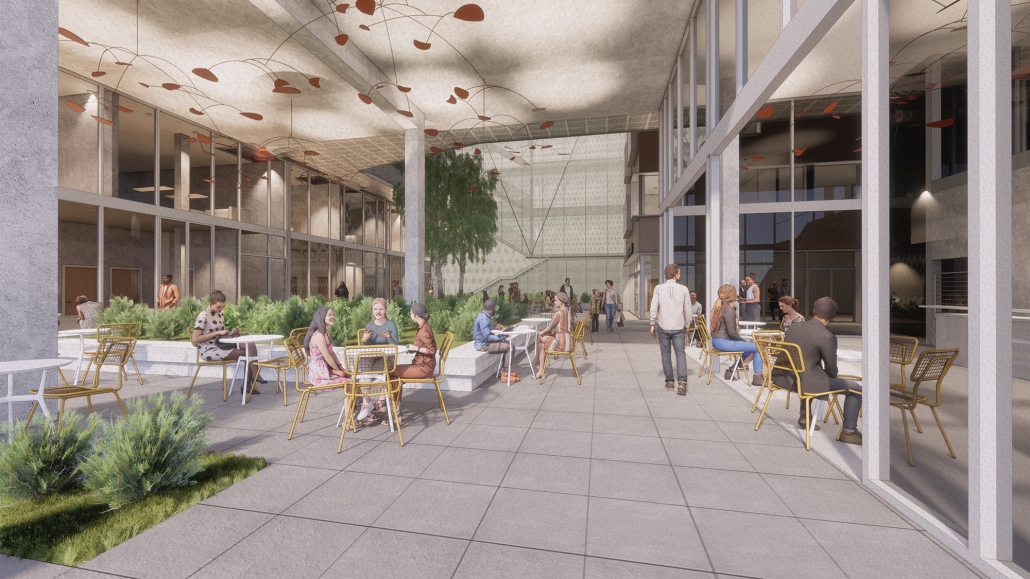
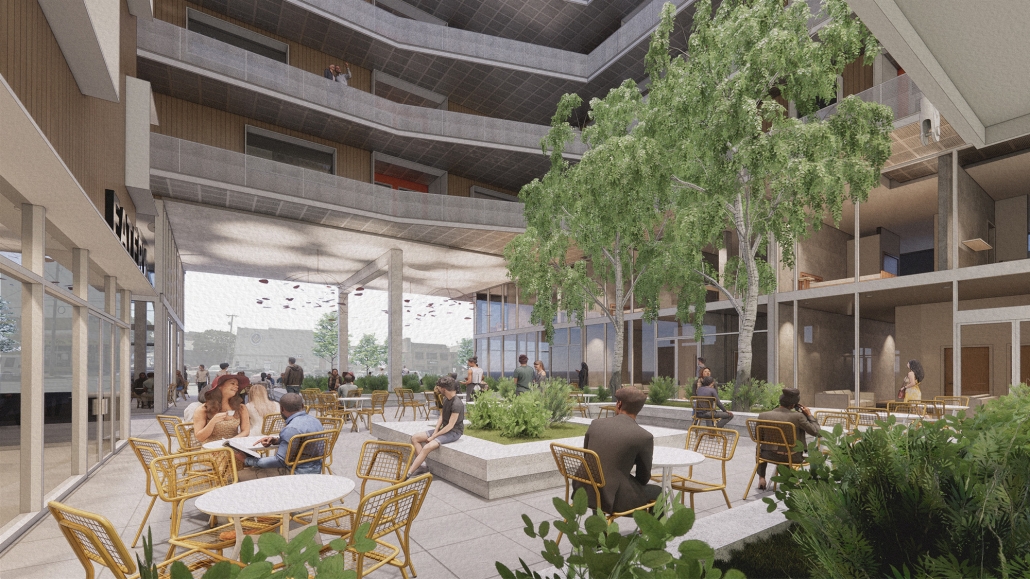
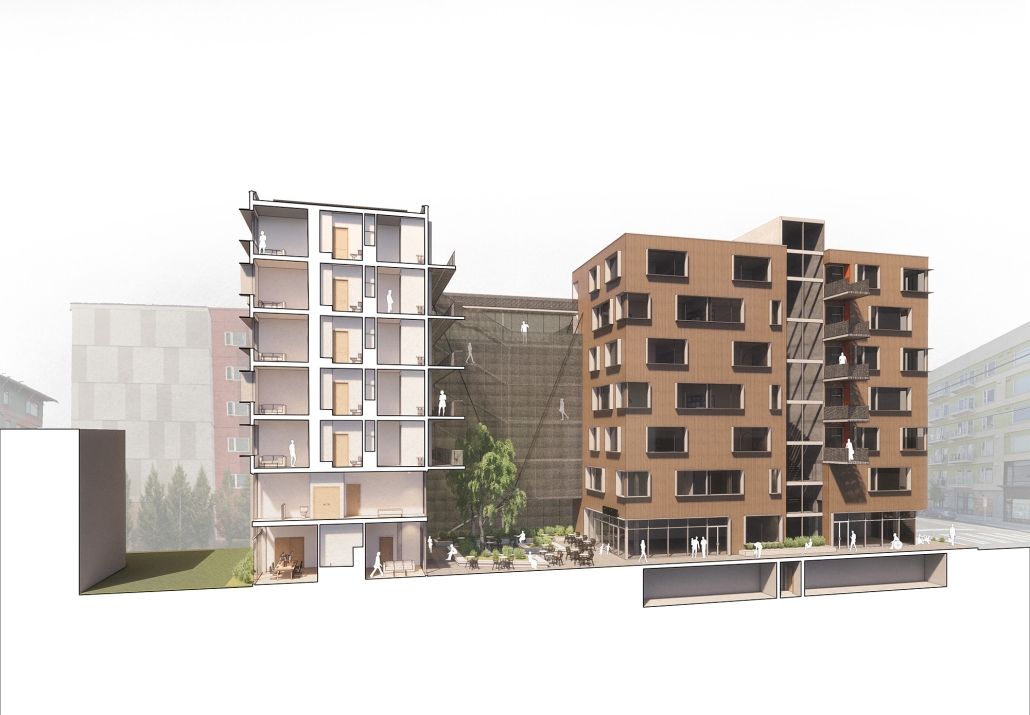
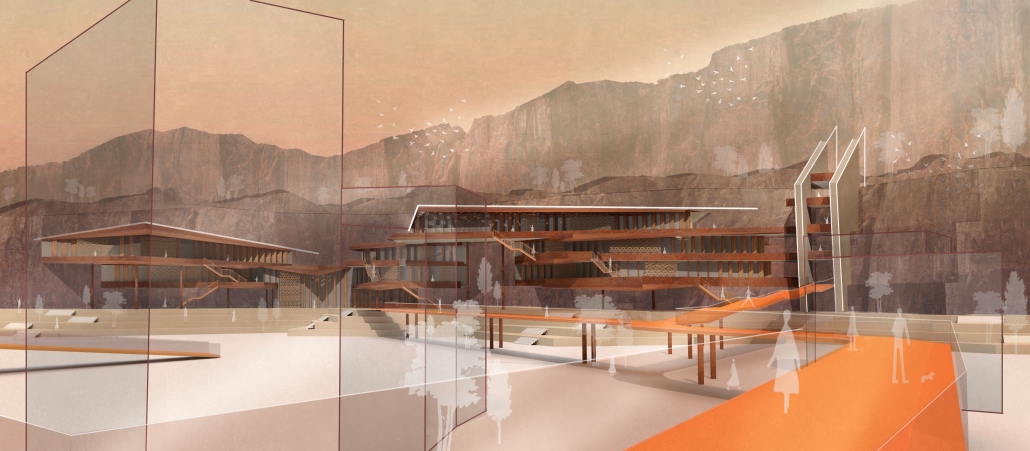
DIGNITY by Macinnis Kraus, M.Arch ‘23
The University of Texas at Austin | Advisor: Nichole Wiedemann
Working with a local church in West Campus and inspired by the student interest in “serving” over “services,” the design is for a re-combination of worship, living, and service. Two transitional housing towers provide residences for formerly itinerate populations and create bookends to the public landscape. The individuals may work here –apprenticing in the artisan maker space or running the restaurant– providing some financial stability for the immediate and the future. In addition, public showers, laundry, and bathroom facilities support the broader community. Embracing the pragmatic and poetic potential of water, light, and body (human-scale moments), the project seeks to provide dignity for all user groups.
This project was nominated for Design Excellence at the UT School of Architecture.
Instagram: @nicholewiedemann
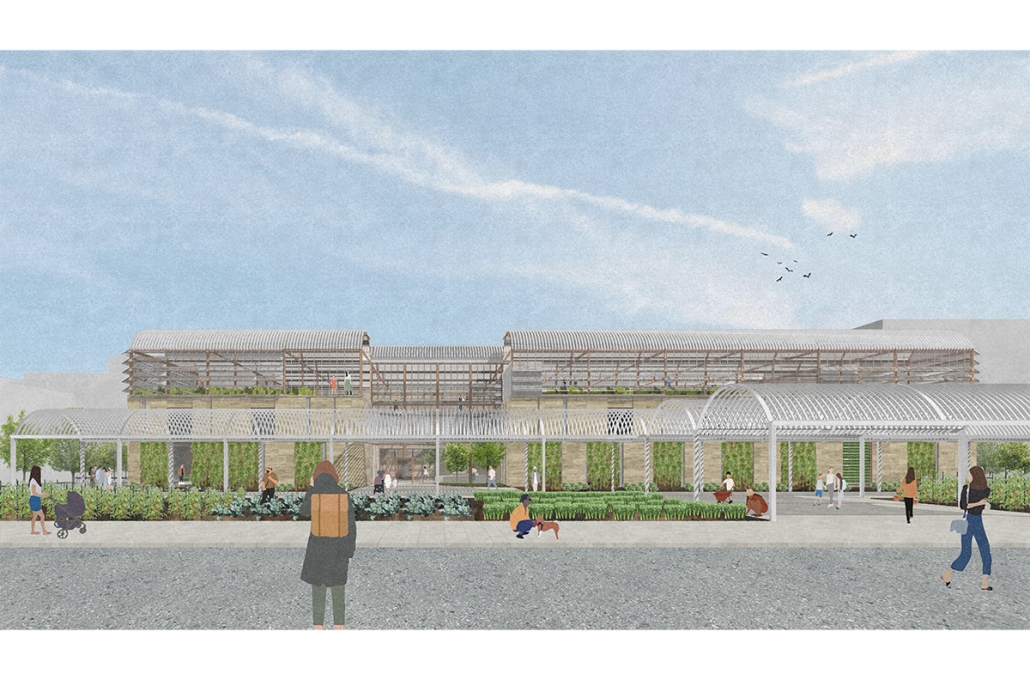
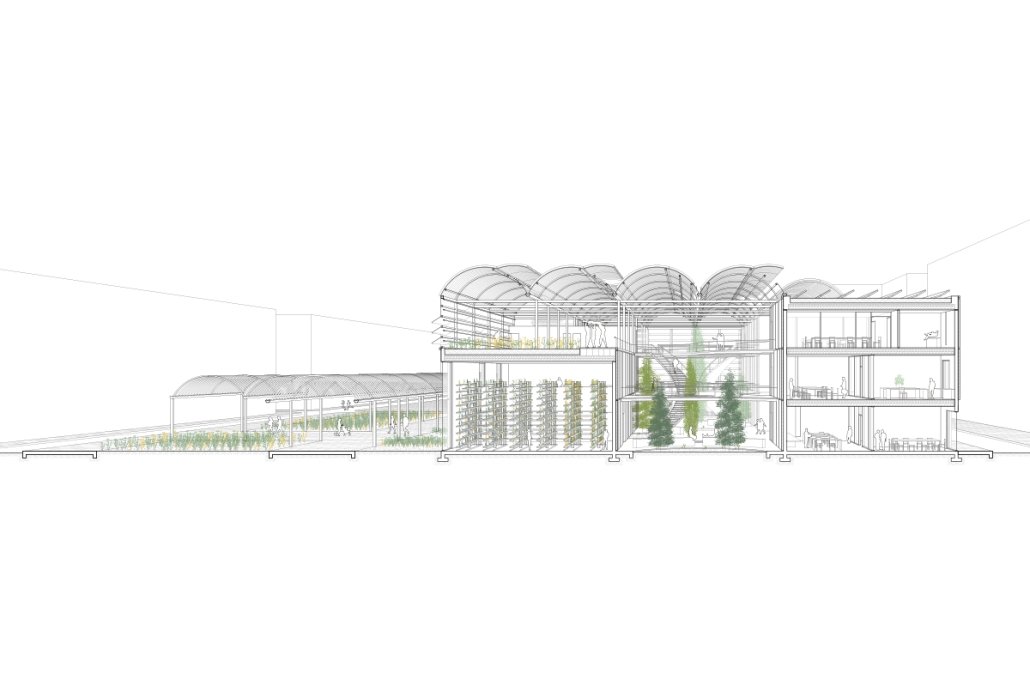
Intertwining blocks in Los Angeles by Joey A. Tomshe, B.Arch ‘23
Tulane University | Advisor: Ruben Garcia-Rubio
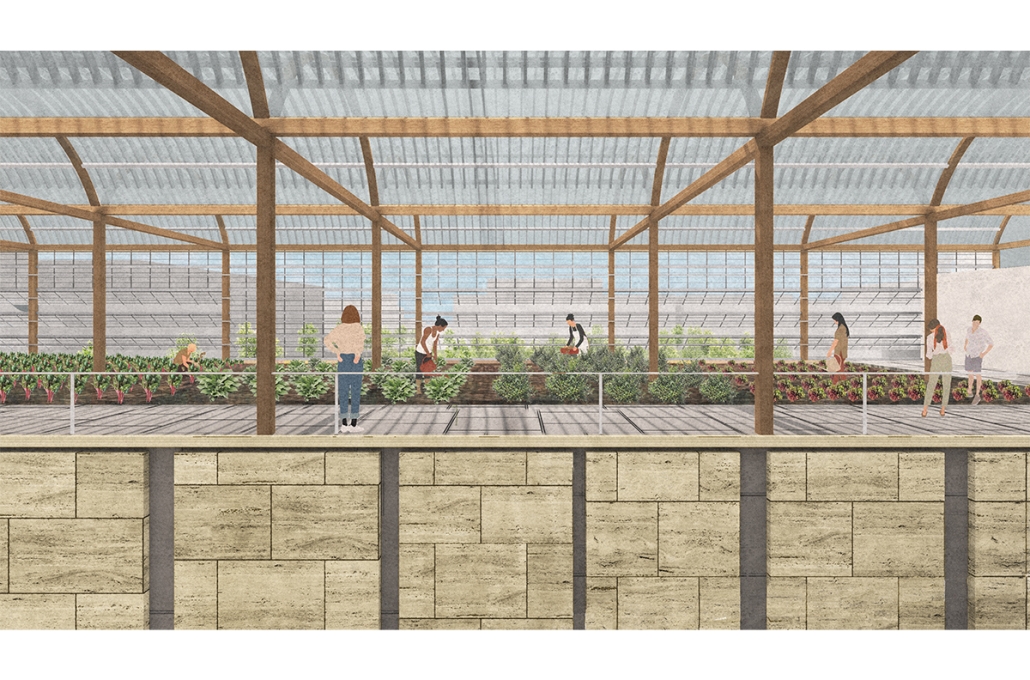
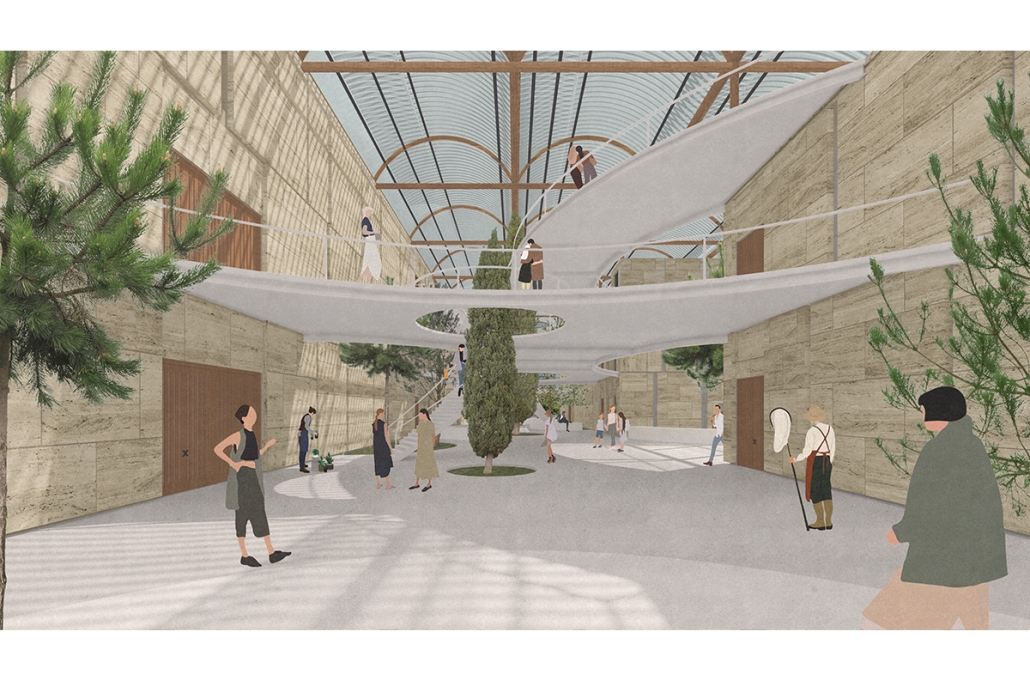
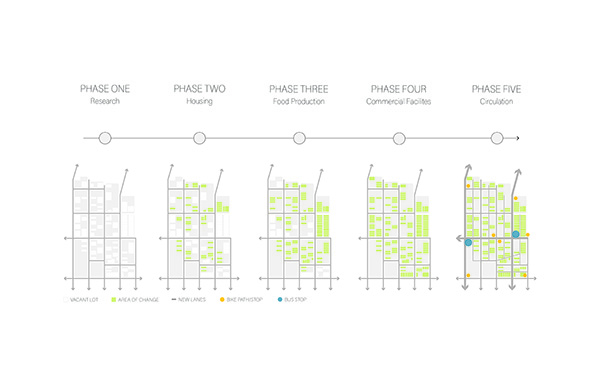
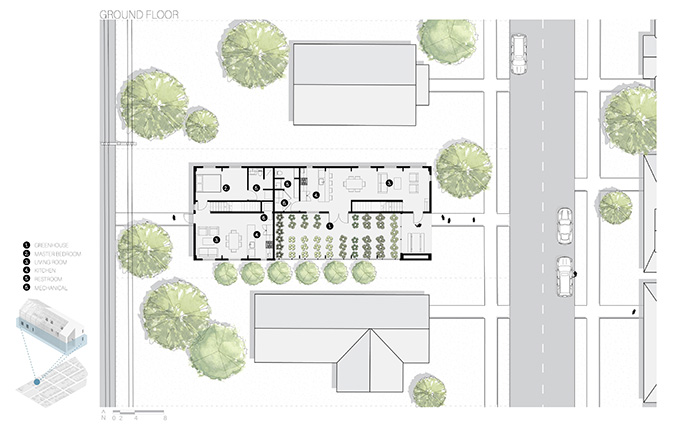
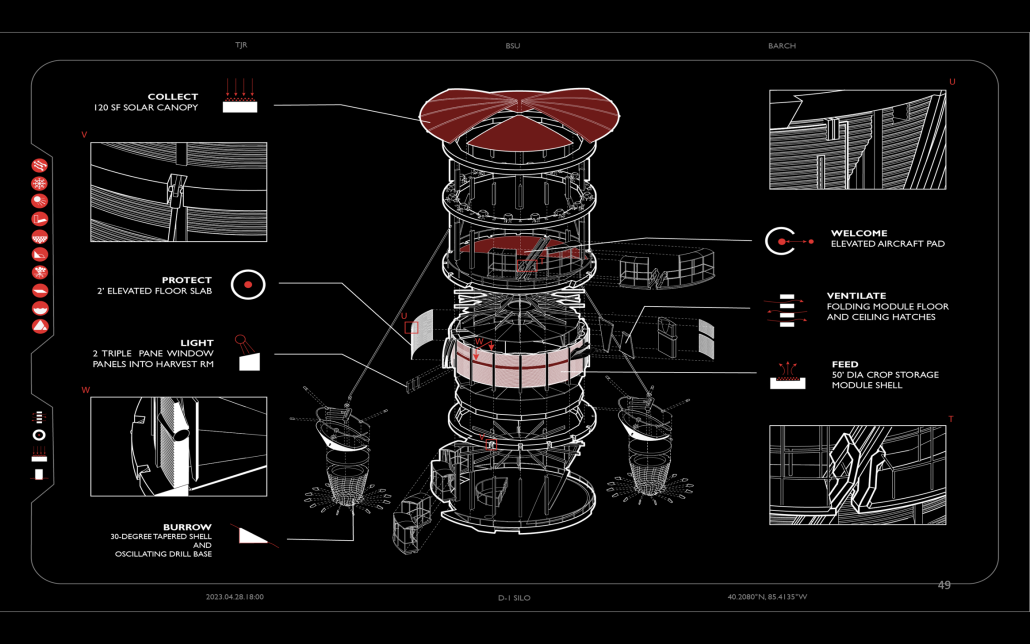
Intertwining blocks is proposed to act as an agricultural information and research center for the previously designed master plan, and, in the future, there would be more of these spread out around LA which are connected. It will feature many new innovations in the agriculture field with the goal of informing the public about the advanced research being performed in LA today.
The initial concept for this project was to intertwine four blocks, creating an indoor street that acts as a social condensing space, relating to the distinct street types created in the master plan, with the social condensing space containing lighter elements than the heavier blocks. The project features six types of farms, a mediateque, and research stations for botanists. The form of the social condenser space comes from trees in plan view, then those same circles are introduced in sections to influence the roof. To combat the heat from glass roofs, the proposal will be installed with an automated computer system that processes and manages a database to optimize comfort and energy efficiency. Along the face of the roof structure is a series of operable louvers that can open and close, which allows for natural ventilation as well as sun deflection. Similarly, on the roof the northern faces of the arches can pivot open, allowing for full circulation. Furthermore, the roof allows for rain collection with built-in gutters and features solar panels on the north two blocks. Due to the repetition of louvers on the roof, a facade of varying size stone panels is introduced to disrupt this rhythm and add variation. Some panels were removed for windows and others, on the south facade, were turned into farming panels that interact with the farm in front.
Instagram: @rubgarrub














![layout [Converted]](https://www.studyarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/MArch-SP23-403C.3-RS-Lynn-Yiman-DG-01-Travis-Dagenais-1030x572.jpg)
![layout [Converted]](https://www.studyarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/MArch-SP23-403C.3-RS-Lynn-Yiman-DG-02-Travis-Dagenais-1030x572.jpg)