2022 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part I
Welcome to the first installment of the 2022 Study Architecture Fall Student Showcase series! To give you an insight into what it is like to study architecture, we are taking a closer look at student thesis and capstone work from 2022. Throughout this series, we will feature work from recent graduates of ACSA member schools across the globe, highlighting a wide array of unique architectural explorations. For the next couple of months we will feature weekly installments of design student’s final projects covering a range of topics. This week we take a look at the intersection of architecture and climate change, specifically as it relates to sea level rise.
We will be sharing these projects on Instagram at @studyarchitecture and @imadethat_ so let us know your favorite there.
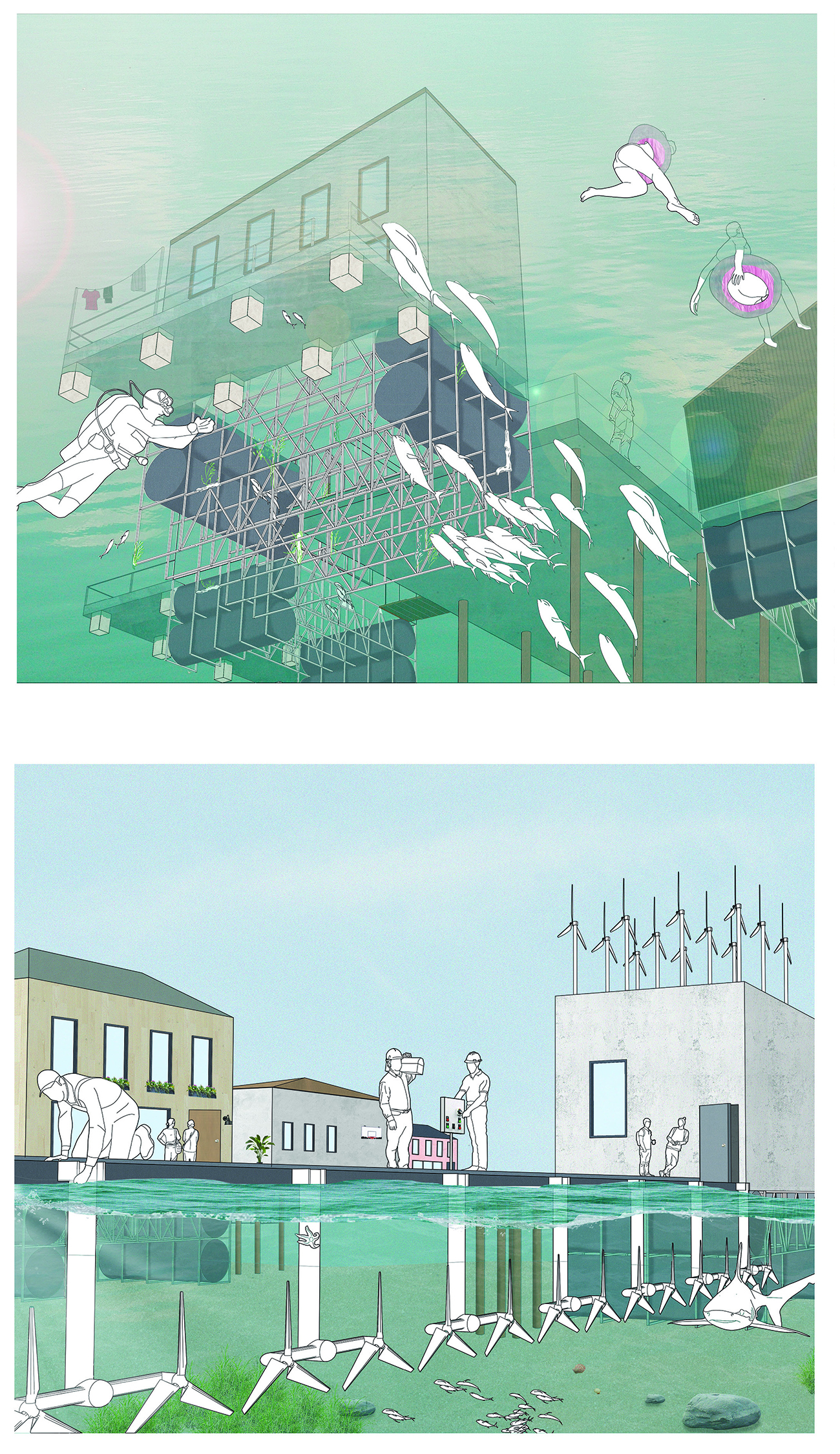
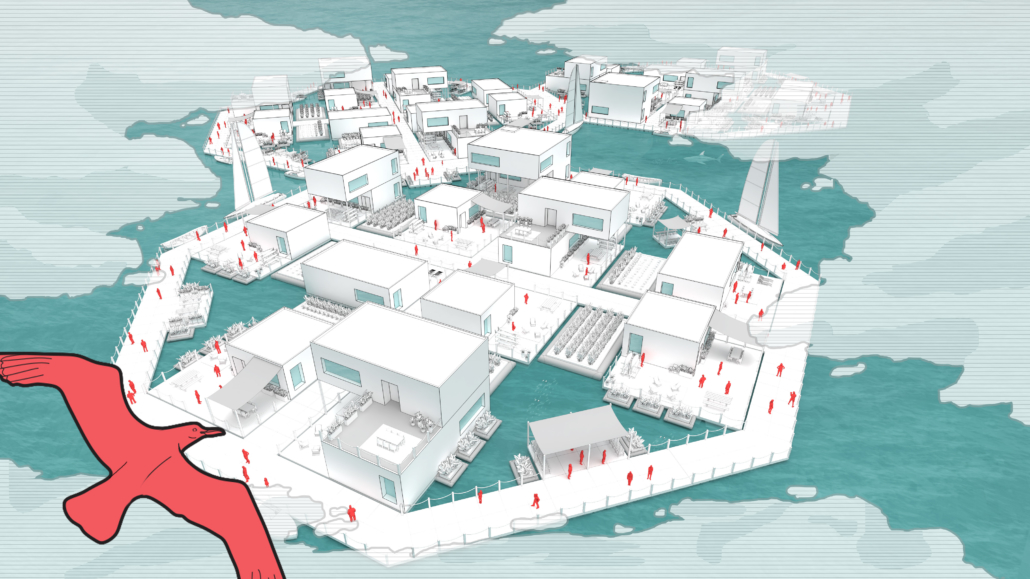
Floating Omnitopia by Jessica Smith, M.Arch ’22
University of Virginia | Advisor: Mona El Khafif
Norfolk, Virginia, is staring climate change in its full force as many residential areas are experiencing flooding throughout the year. These residential areas range in value of social vulnerability. The risk of flooding is not considered when determining “vulnerability.” It is observed that many areas of high vulnerability are also areas prone to flooding and are not protected by flood resilience projects. Other areas of low vulnerability are also affected by the flooding, but these residents have the resources to relocate out of Norfolk if needed. If they move, this will have a negative effect on the local economy. As more of Norfolk is taken by rising sea levels, where will these residents go?
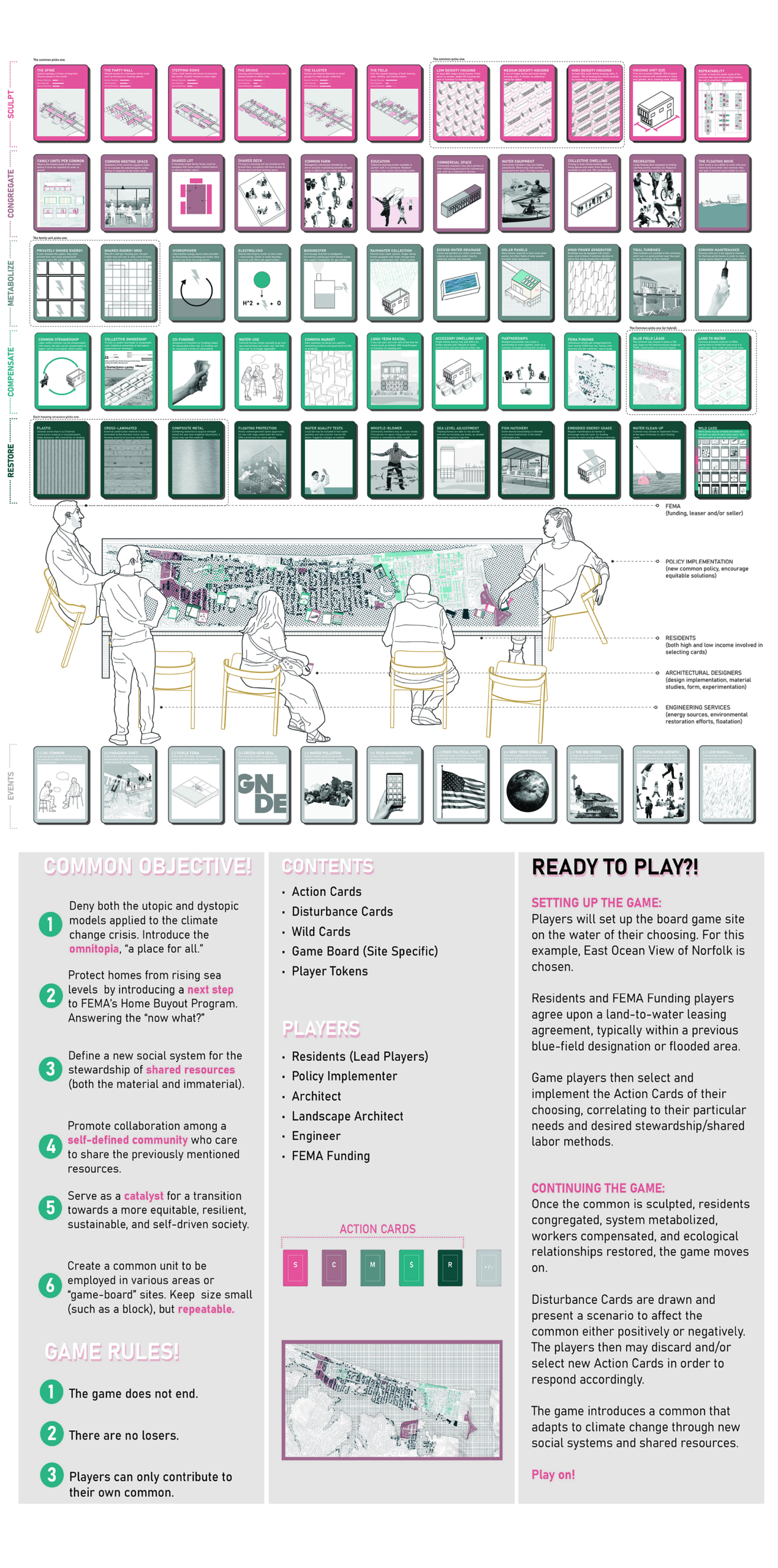
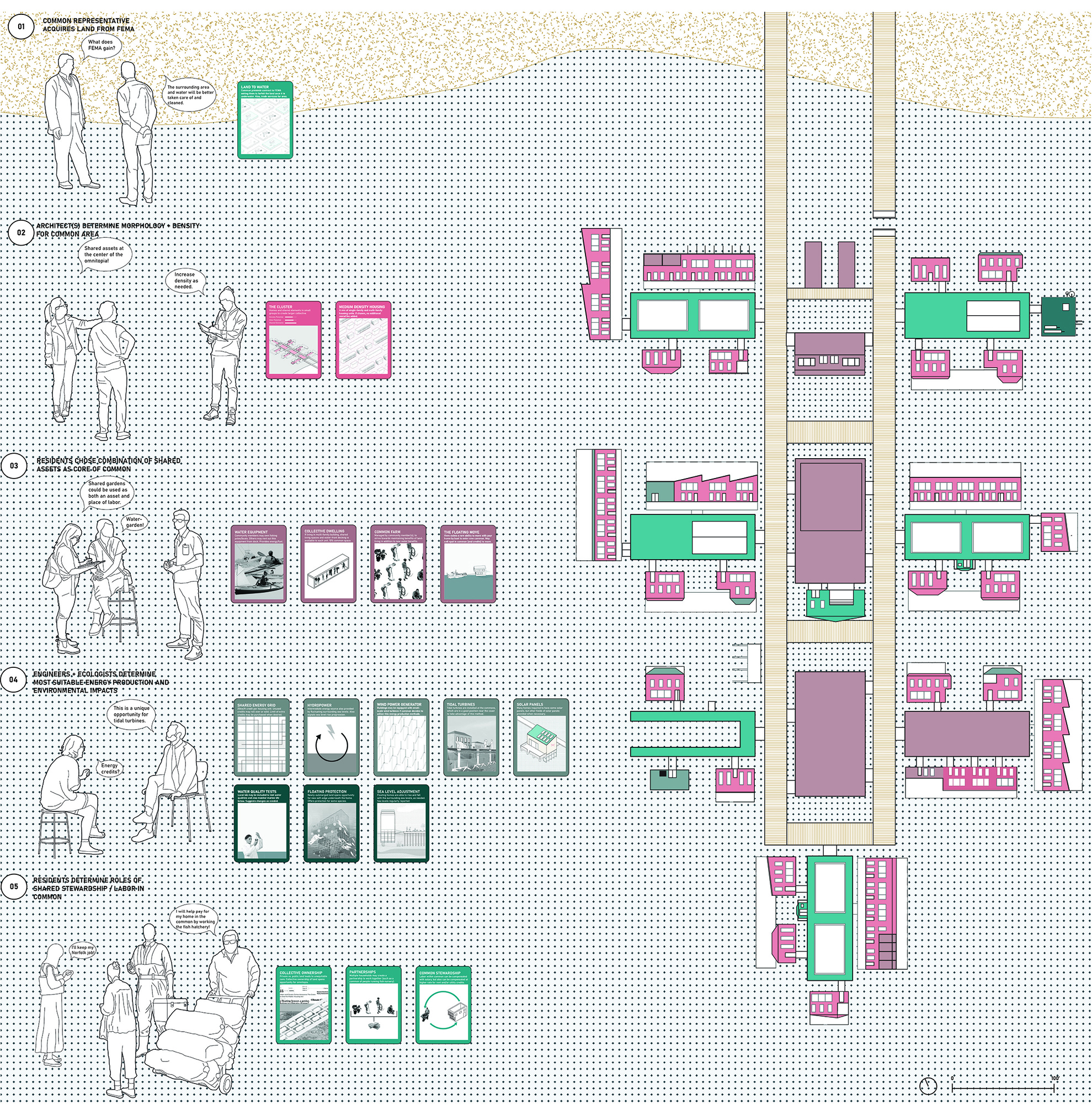
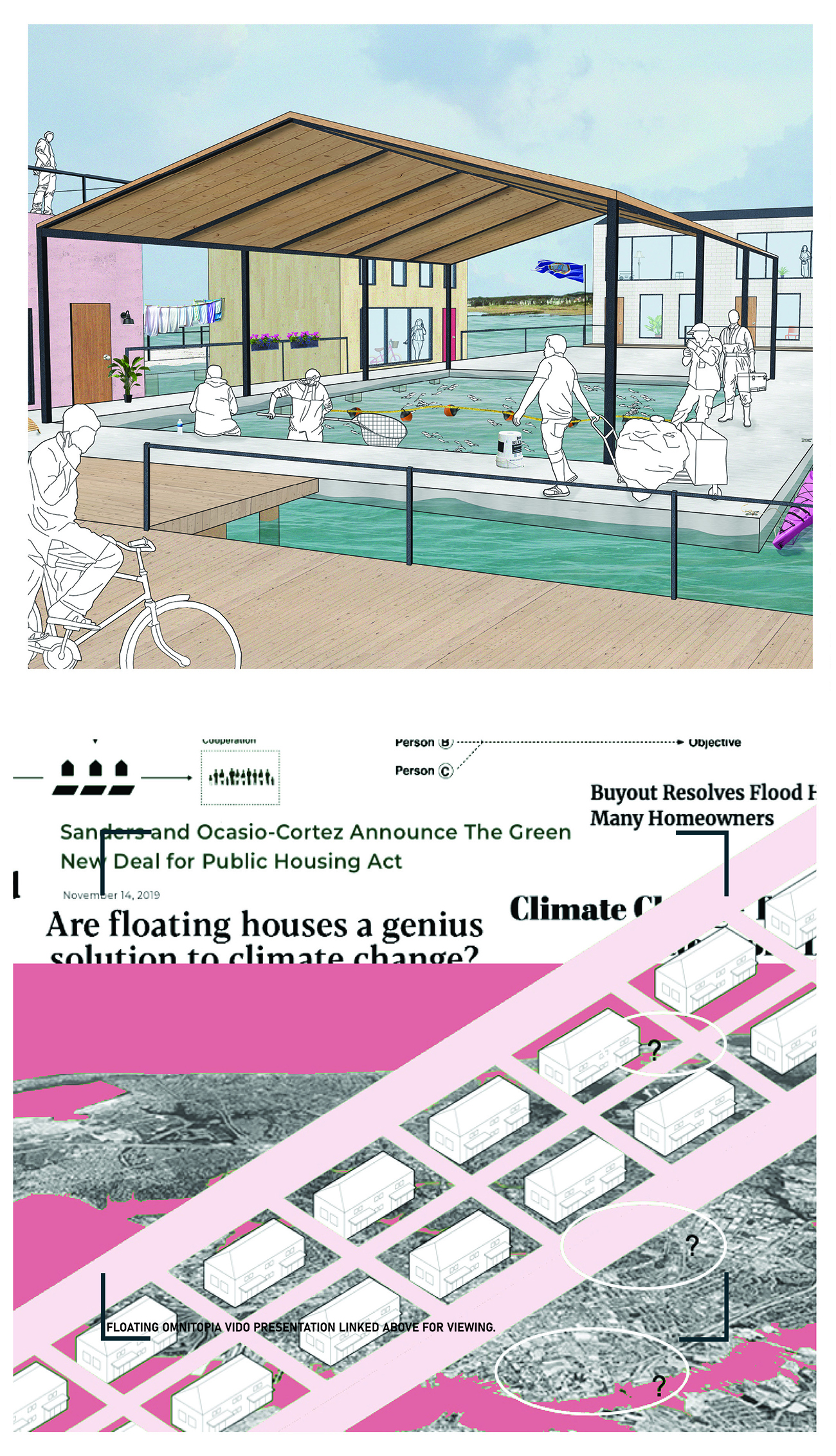
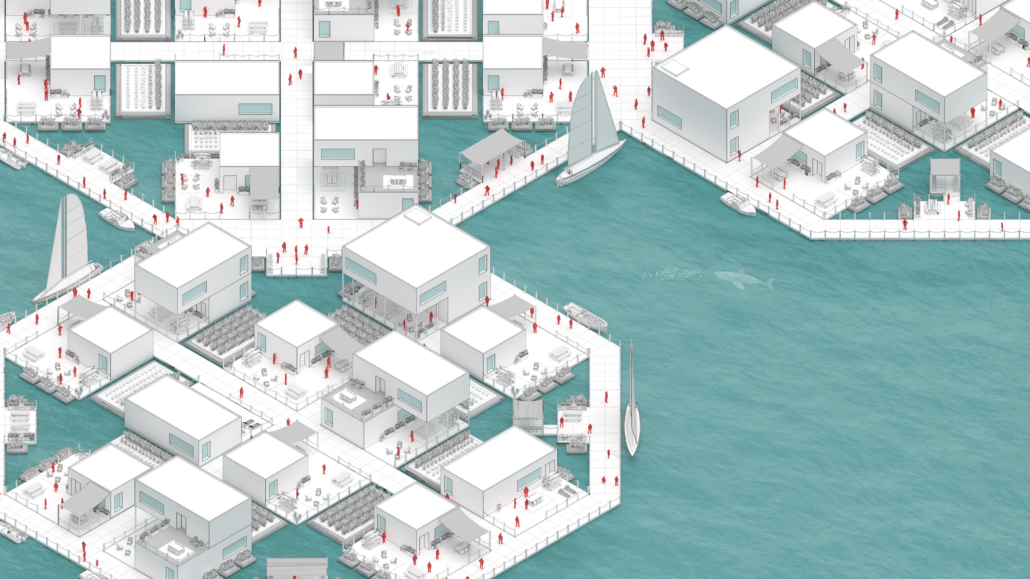
FEMA has identified areas of recurring flooding, which will be called blue-fields. The homes within these blue fields are eligible for the FEMA Home Buyout program where a home-owner may sell their home to FEMA for that lot to be cleared. This project proposes another relief effort beyond this, in which this buyout funding from FEMA is used within a partnership to form a common.
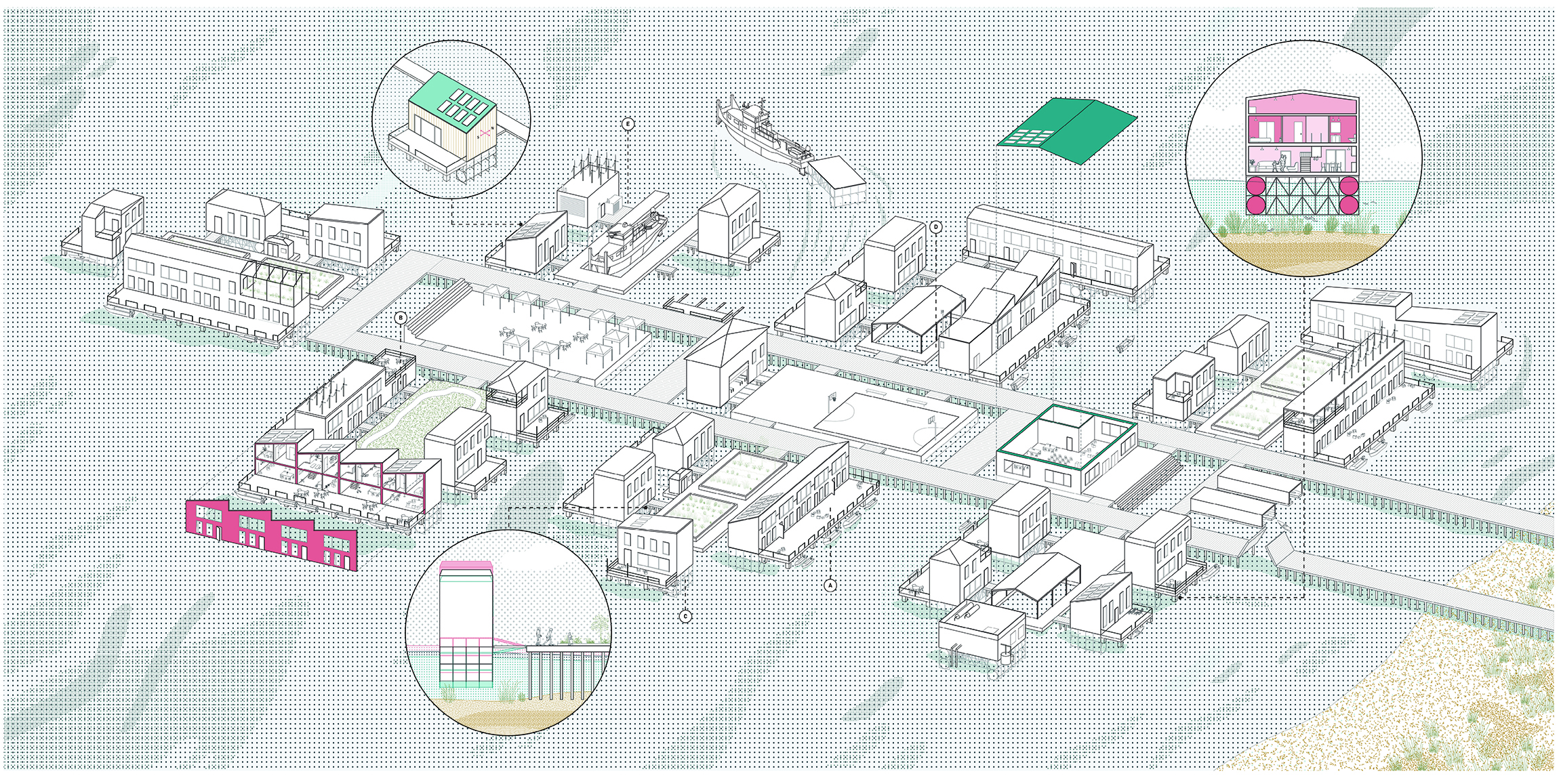
This is the current prompt, and the urgent response should be an alternative to retreating, reject-ing both the utopian and dystopian models commonly associated with efforts to combat climate change. All the people in this area have a shared goal of protecting their homes, which creates a common ground. This is the basis needed for a new common of Norfolk of both shared assets and stewardship, existing on the water. It is a place for all, or the omnitopian common.
Inspired by projects carried out in the Netherlands, the omnitopia typology of housing is being implemented in Norfolk to create a collective partnership between residents and rising water conditions. It comes in the form of a common, a water-based community within which land(/water) and certain assets ownership is redefined as shared at the block-scale. Shared stewardship allows for growth / development / maintenance at a more concentrated (therefore, more effective) scale.
Forming the common of their choosing, the residents and various professionals are presented with a card game. The game is used to sculpt the form, congregate the residents, metabolize the system, compensate those involved, and restore ecological relationships. The players of the game hold various roles, from FEMA funding to the architect and residents. Select cards of the system are chosen to piece together the policies and creation of the common, making it adaptable to various people groups and sites. A sample common is formed to present an example of the omnitopia, using cards such as the medium density option in a cluster typology.
Instagram: @jessc.smith
Beyond the Barrier: The Resilience of Connecting People to Place by Eric Resnick, M.Arch ’22
University of Maryland | Advisor: Michael Ezban
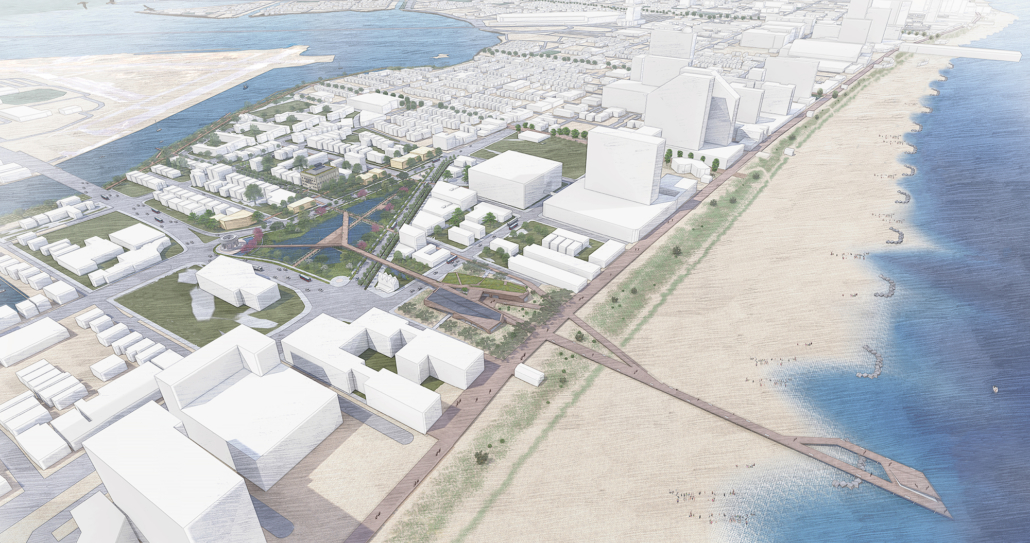
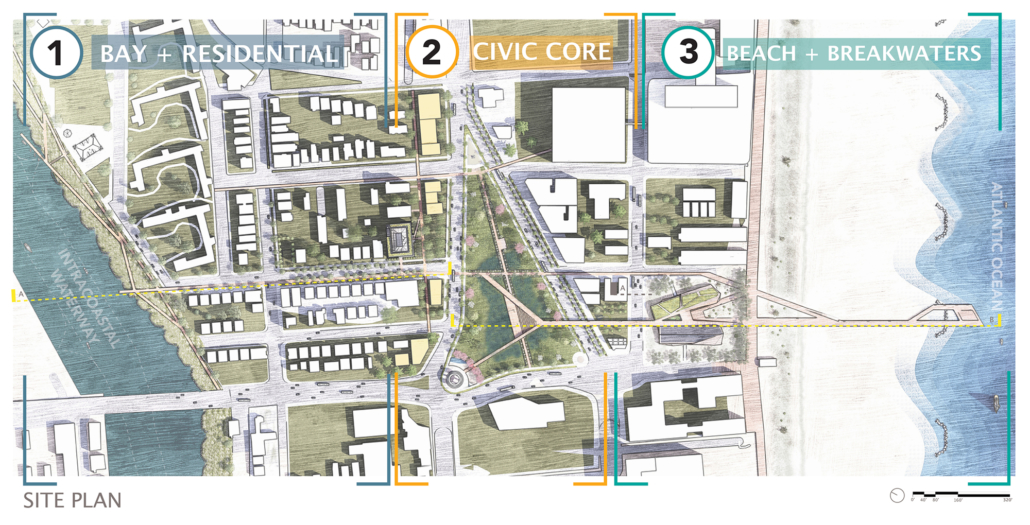
Atlantic City, New Jersey is globally cited as one of the most vulnerable cities to the effects of climate change and sea level rise, representing the socioeconomic, cultural, and ecological threats that all coastal communities will face within the next half-century. 2060 projections indicate that Atlantic City will experience up to 155+ flood events per year and 50% of the city could be uninhabitable.
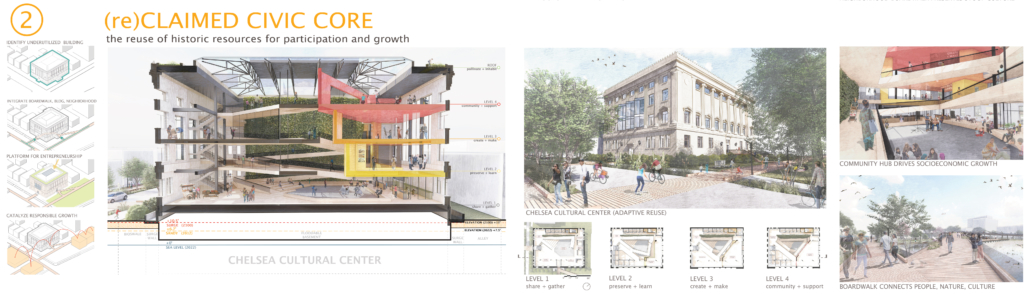
In leveraging the city’s coastal location, current institutions, and historic tourism-based infrastructure, the Resilient Transect becomes a framework for adaptation and growth, engaging the public and attracting an international cohort of researchers, designers, and policymakers to test and implement globally applicable and revolutionary strategies for coastal resilience. The iconic Atlantic City Boardwalk is abstracted as a beach-to-bay datum to catalyze adaptation, support, research, and participation along the transect, adaptable to environmental change and socioeconomic needs within and beyond Atlantic City.
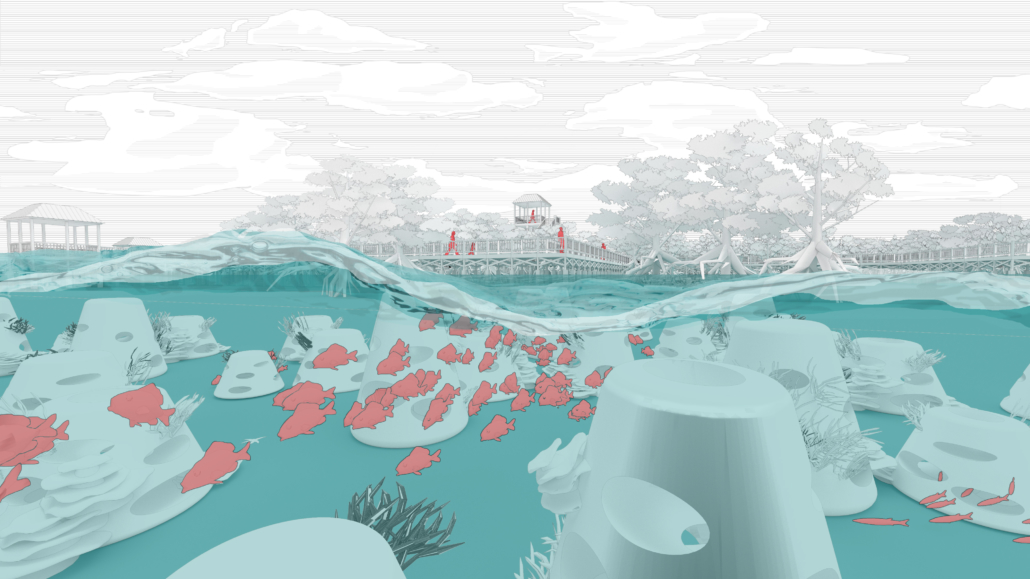
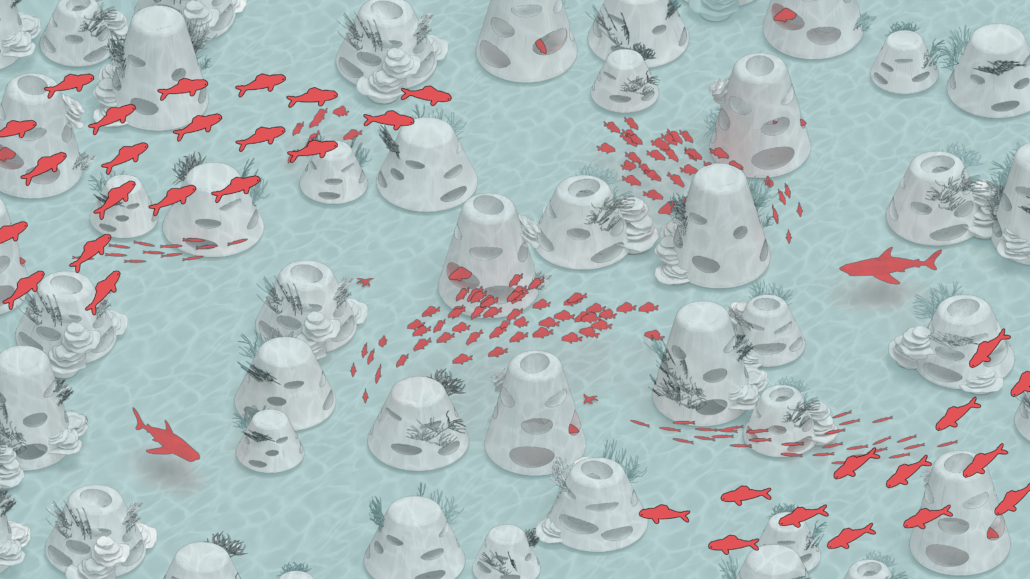
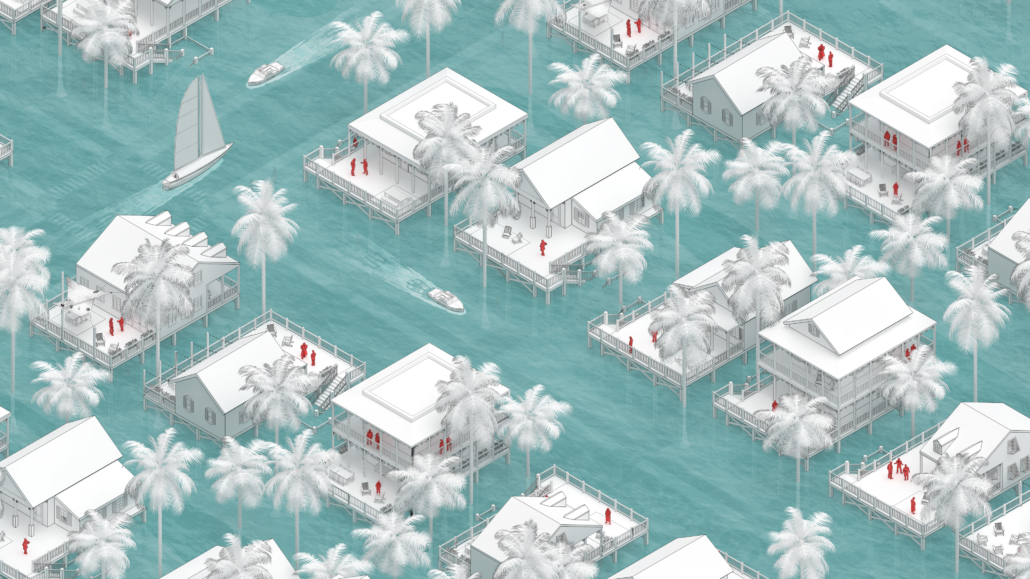
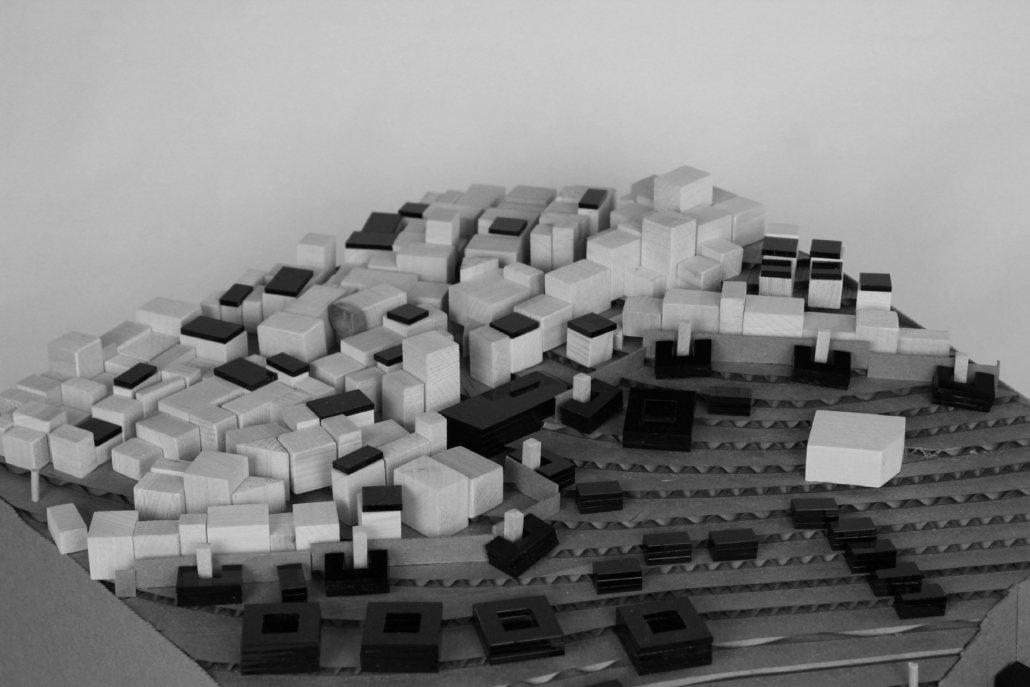
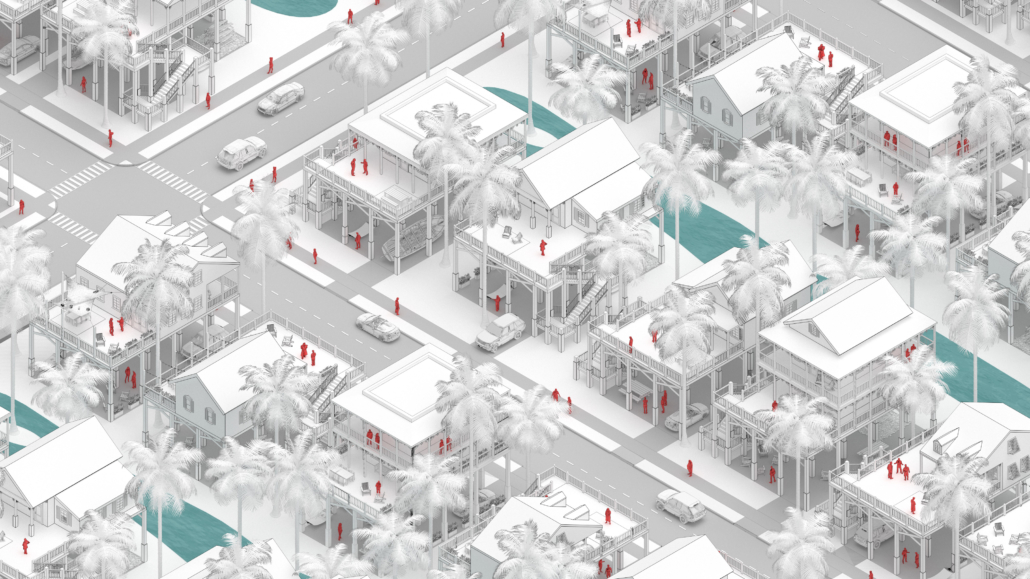
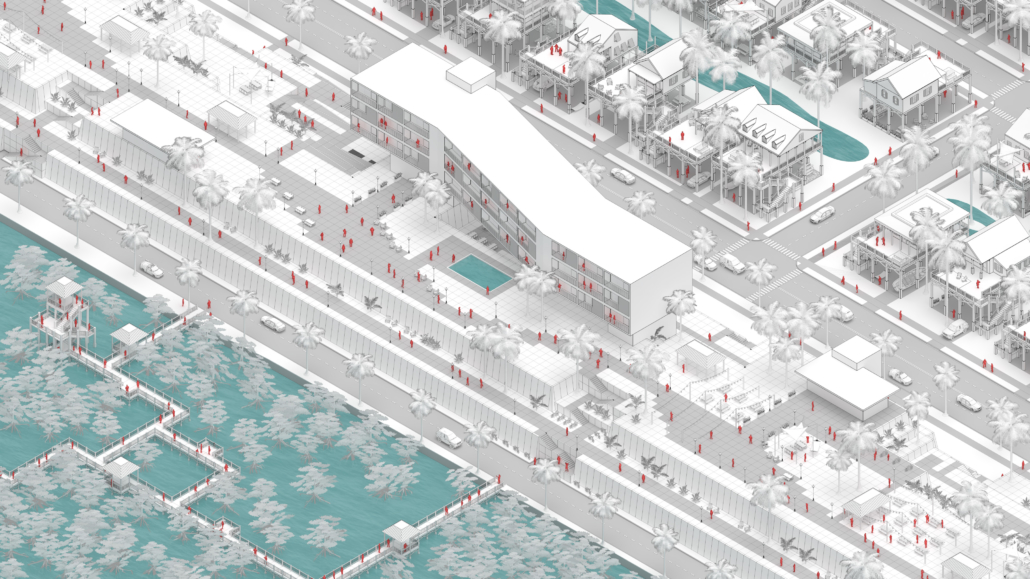
Rising Seas: Cataloging Architectural Response in the Conch Republic by Christine Sima, M.Arch ’22
University of Cincinnati | Advisor: Edward Mitchell
Thesis research focused on architectural and environmental responses to sea level rise. Following this research, a catalog of architectural responses was created as a design framework for future architects.
The selected site of Key West Florida helps show the utilization of the four major response categories from the catalog; Evacuation, Protection, Adaptation, and Adoption. All included images show theoretical implementation of the catalog across different zones of the island.
Instagram @christinesima.arch
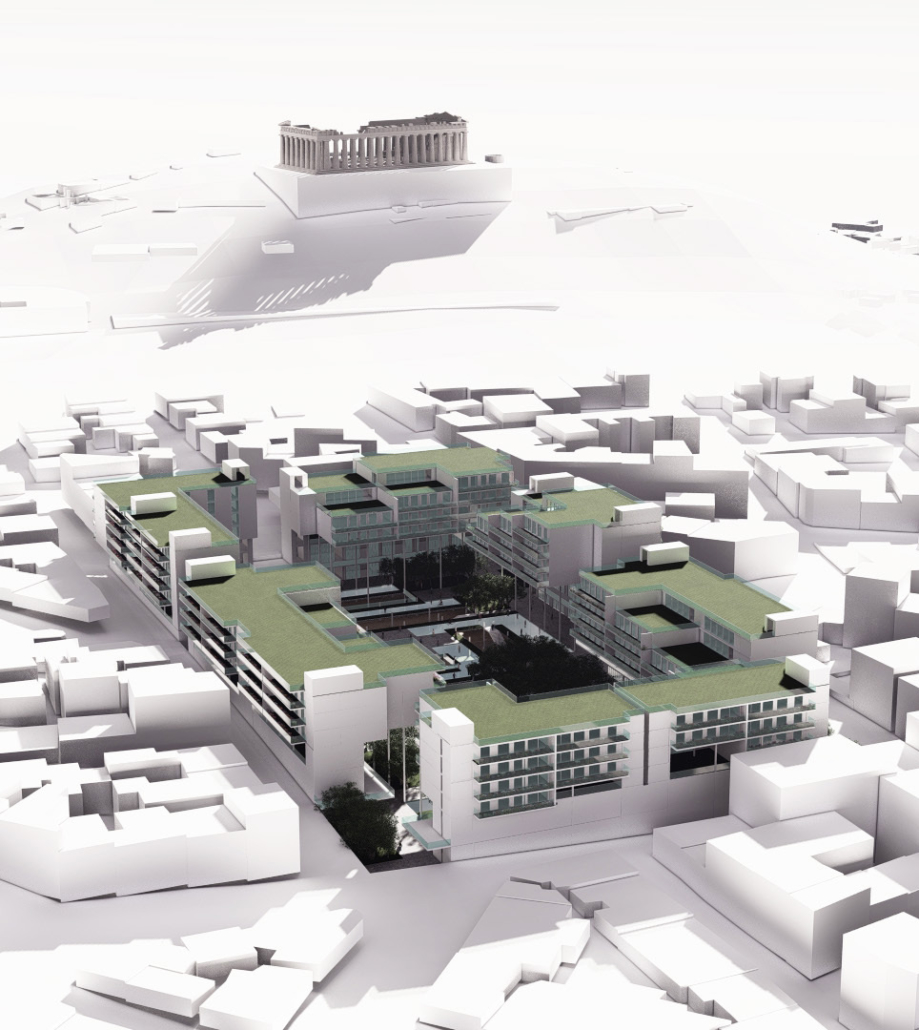
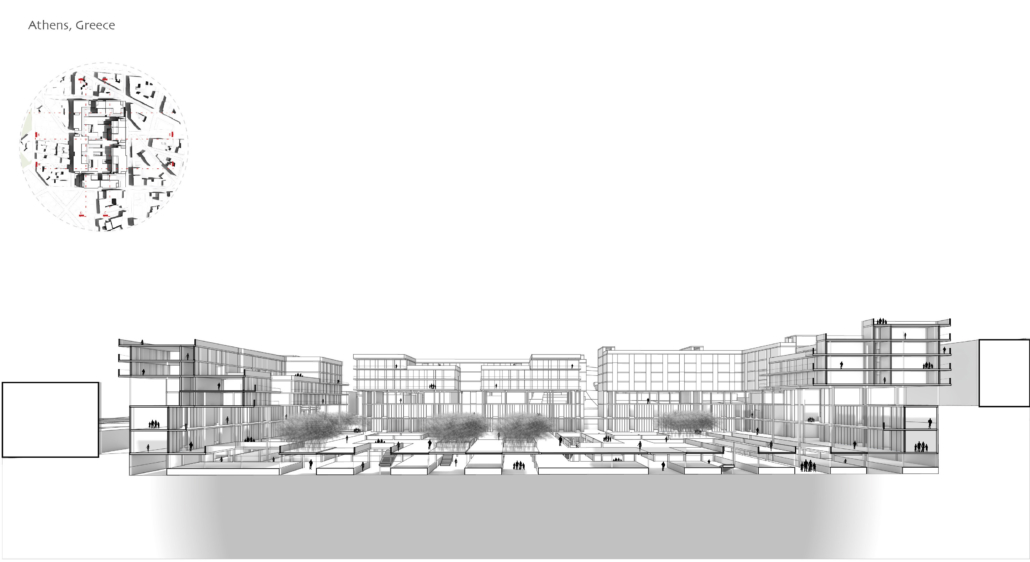
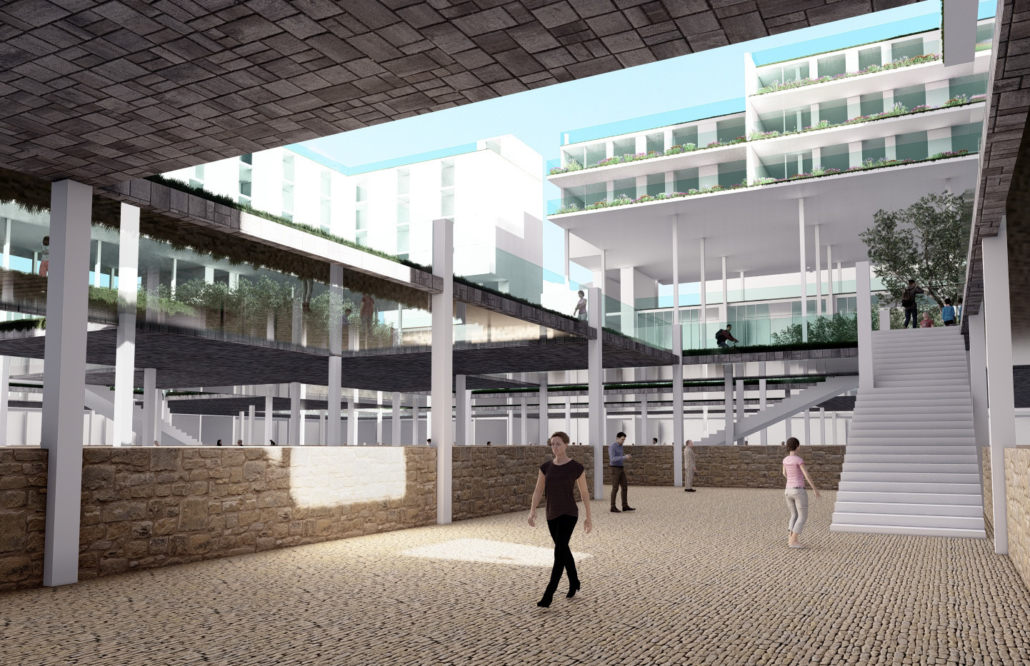
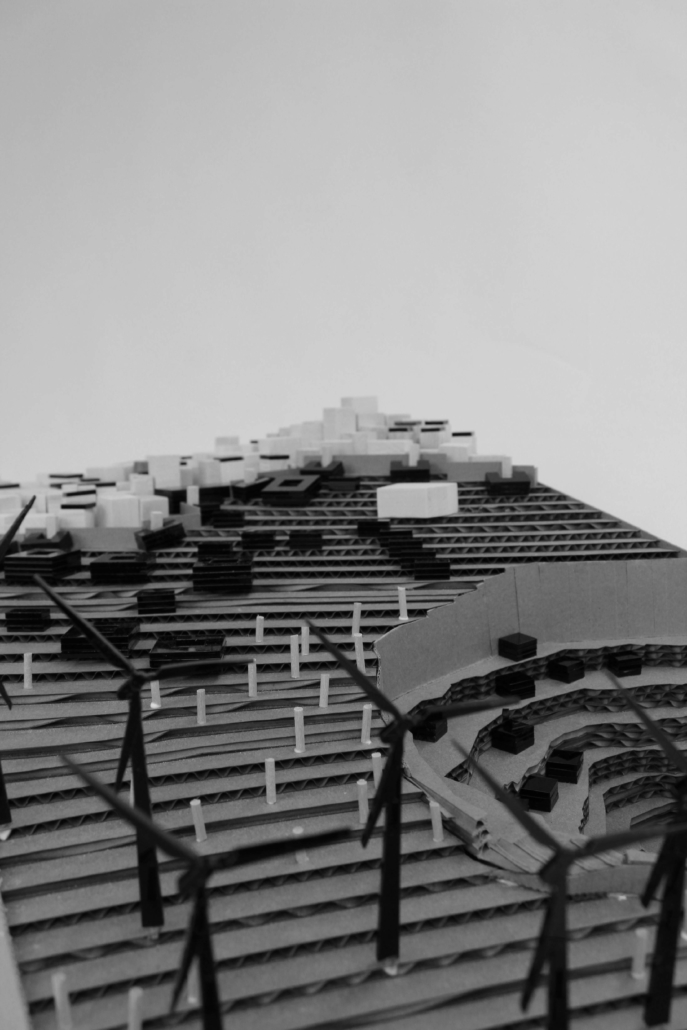
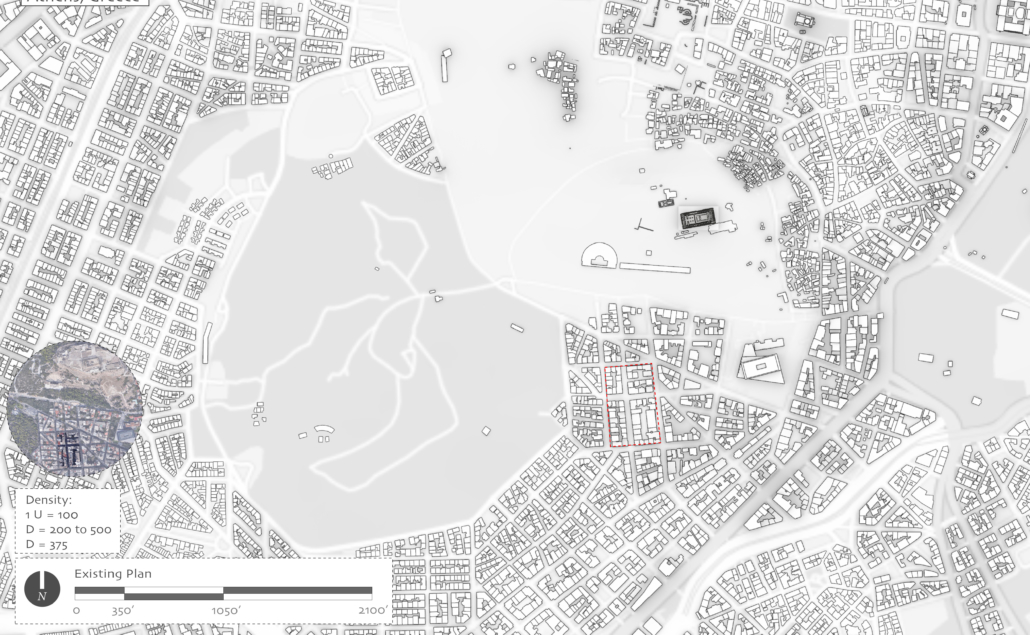
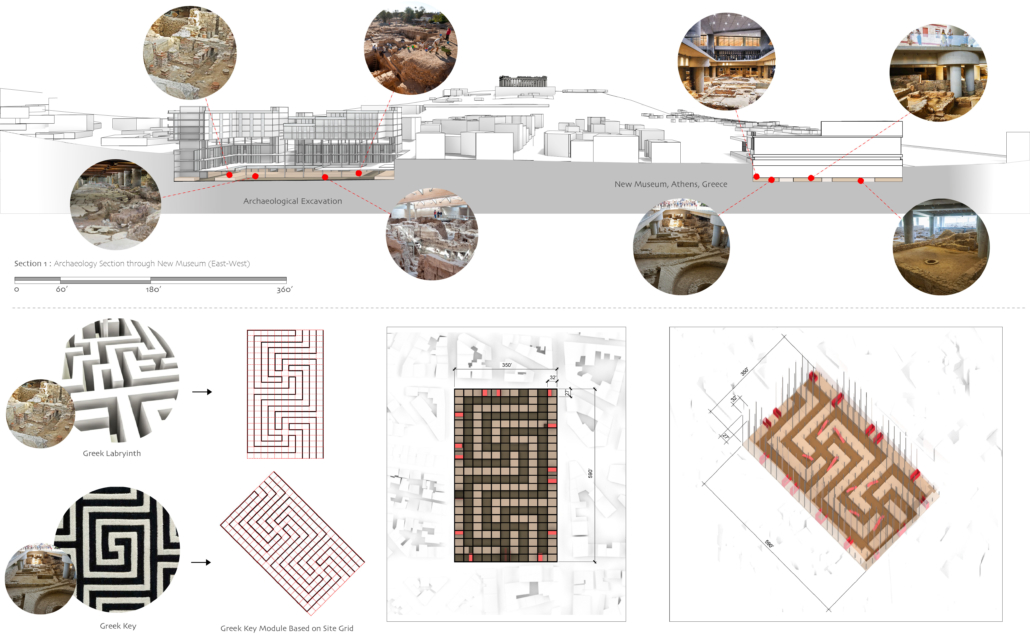
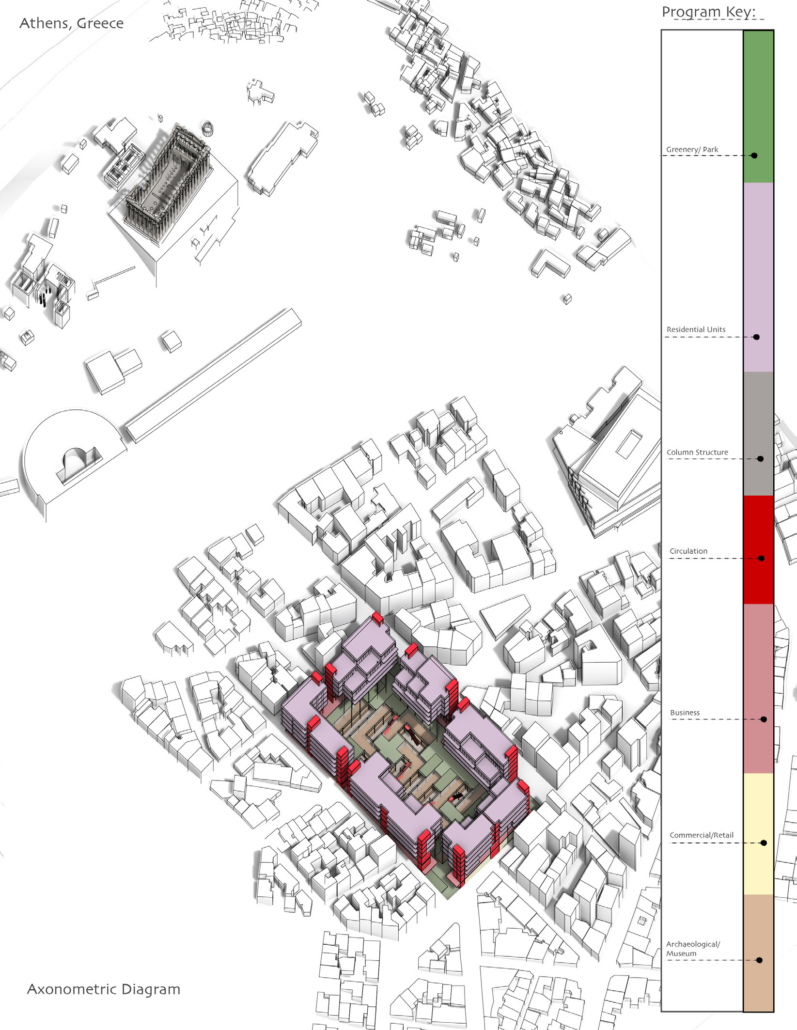
Demo-Polis for Athens, Greece by Maria Lazaridis, B.Arch ’22
NY Institute of Technology | Advisor: Jonathan Friedman
Athens, Greece occupies a significant role in the history of architecture as the birthplace of classical order. Its associated role in history however, developed a sprawling city ignorant of its ancient architecture and organizational urban plan order . This congested metropolis is filled with brutal concrete apartment blocks and lack of green space, overall contributing to larger issues of congestion and heat island effect due to climate change.
This thesis explores a development of a resilient Athens, equipped for its density whilst promoting sustainability. This thesis explores the design of an efficient city plan that no longer ignores un-excavated archaeological sites to create a poetic relationship of old city to new city, while overall improving quality of life.
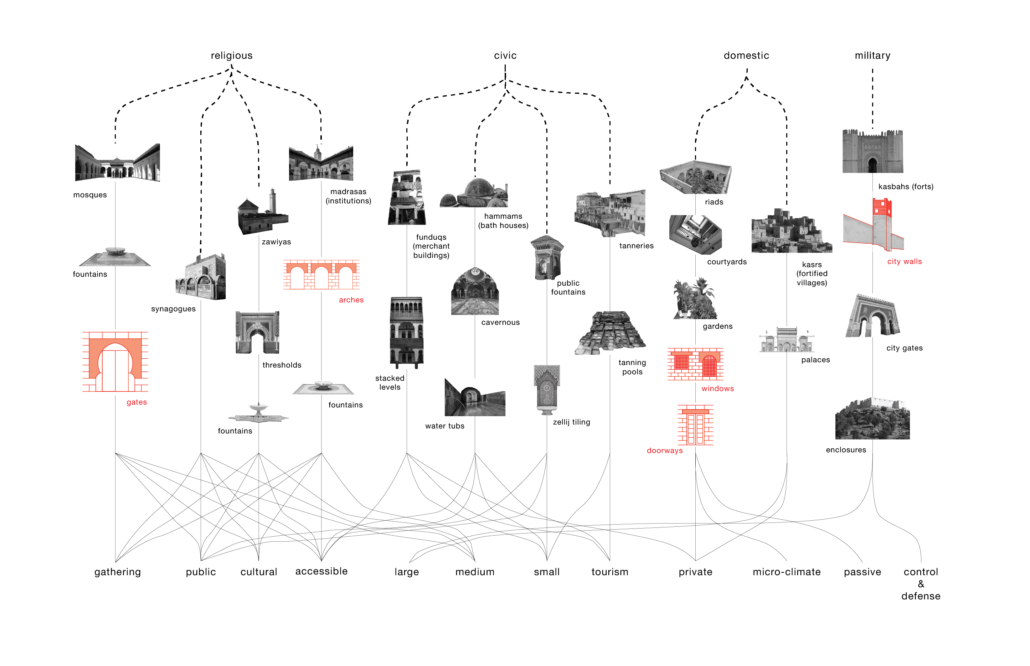
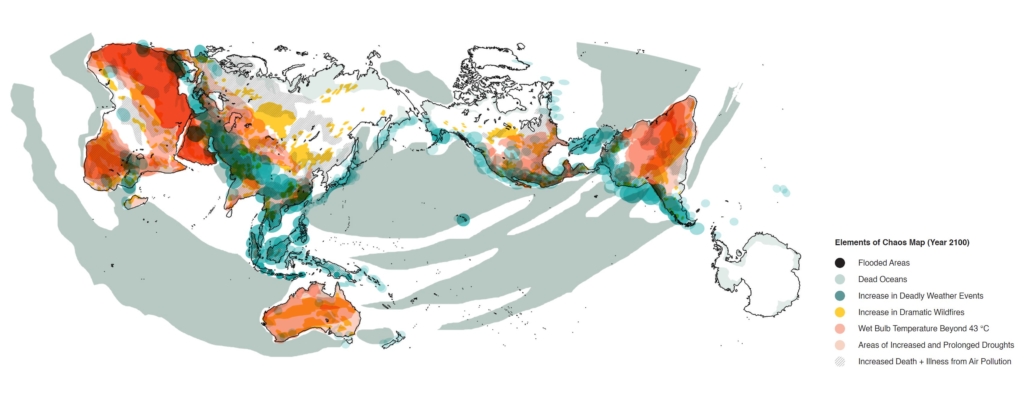
Pale Blue Dot: Adaptation in the Flux of Chaos by Jasmin (Minji) Kim, Taylor Marshall, Jeannette Wehbeh, M.Arch ’22
Toronto Metropolitan University | Advisor: Marco Polo
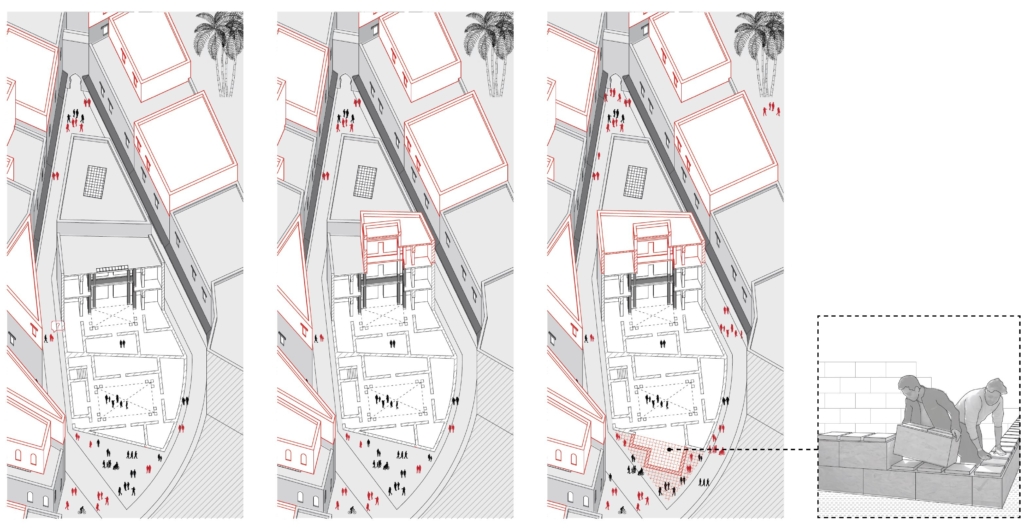
The impact of climate change will not spare a single aspect of life as we know it and adaptation is our only option at this point in the trajectory of the world’s demise. Although we will be experiencing similar climate catastrophes around the globe, each region will have its own adaptation method dependent on location and culture. Synthesizing our research resulted in a new map of adaptability conceived of Goldilocks Zones deemed habitable lands. These Goldilocks Zones will be the most vulnerable to the elements of chaos and the most significant regions affected by the year 2100. Fez, Morocco was selected as the geographical area of study due to its numerous elements of chaos, including natural disasters, high land surface temperatures, wildfires, air pollution, rising air temperatures, and an influx of migrants.
Flux is chaos-seeking balance through adaptive processes. Our research towards the year 2100 and the layers of the climate chaos we will face, combined with conceptual theories on adaptation, shows no ‘single’ solution for adaptability. To adapt to our current and future evolving environment, a series of fluctuating initiatives that tackle issues at various scales is instrumental for present and future change. Nine strategies, applied to Fez, Morocco, can be applied to any other city within the Goldilocks Zone. It is a framework to guide the evolution of architecture through climate change while maintaining tradition, meaning, and comfort.
Instagram: @jasminkimm, @taylormade.arch
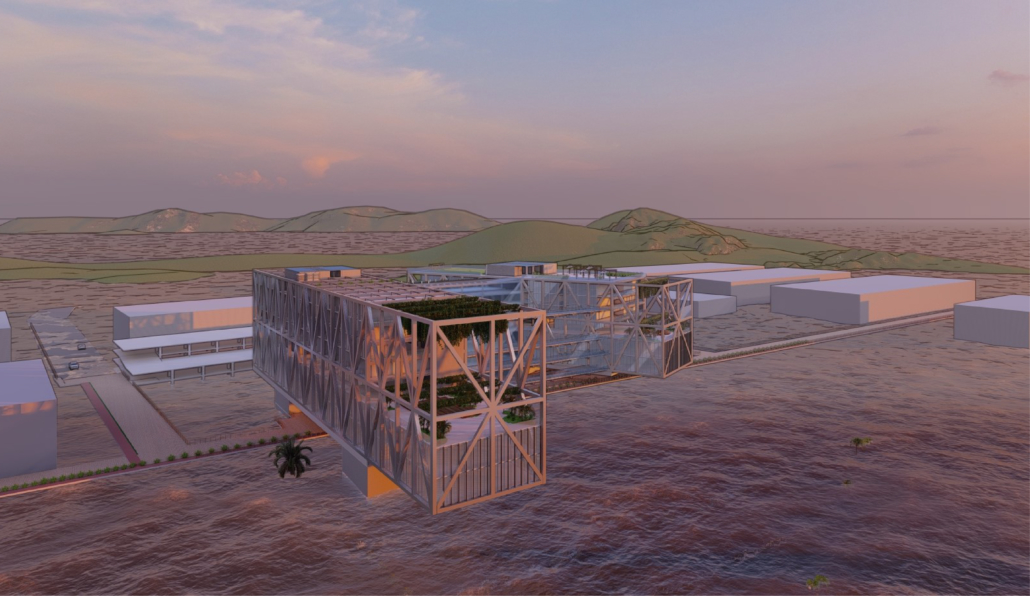
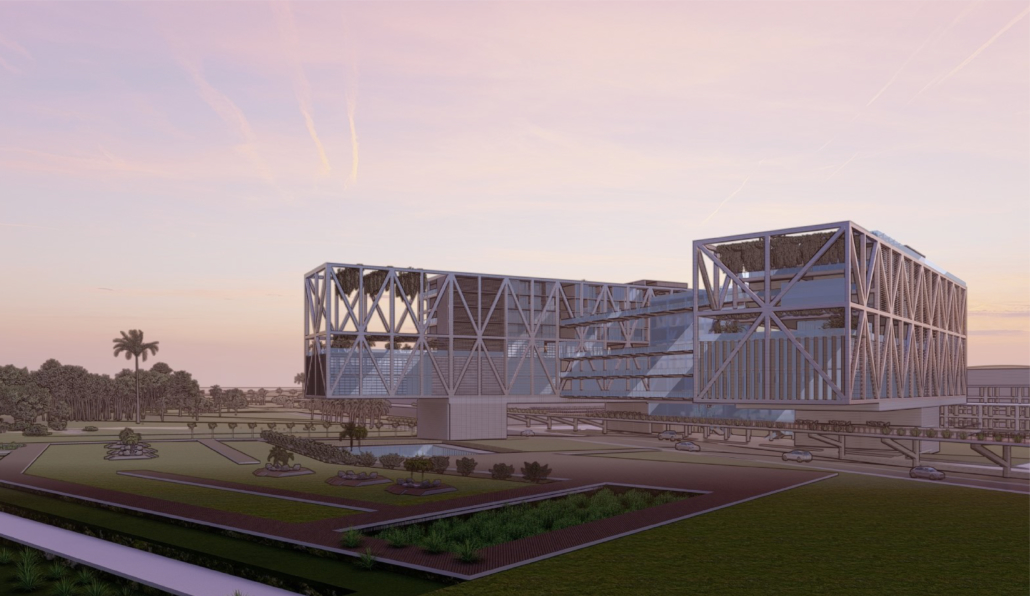
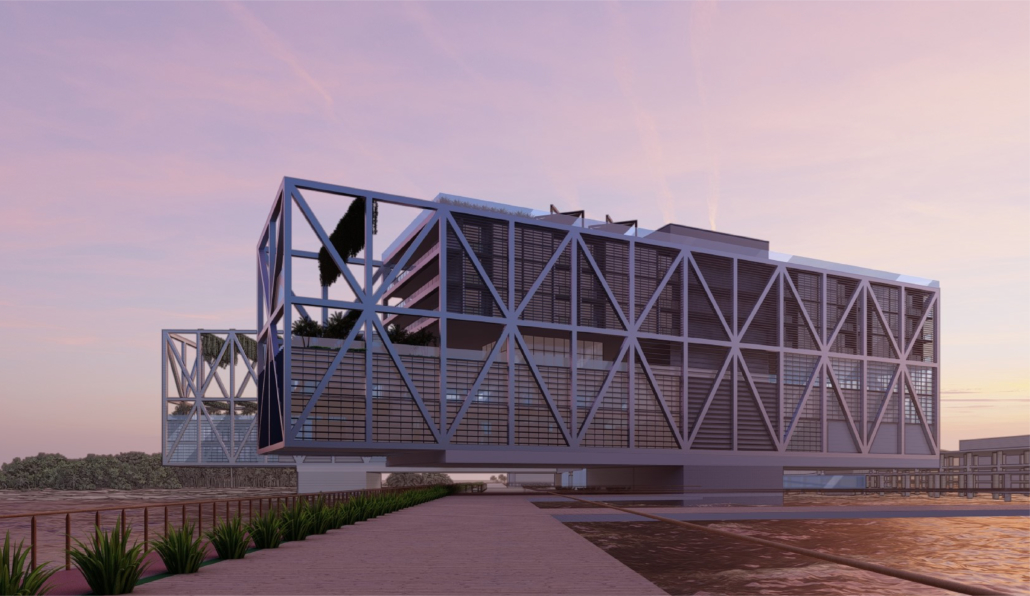
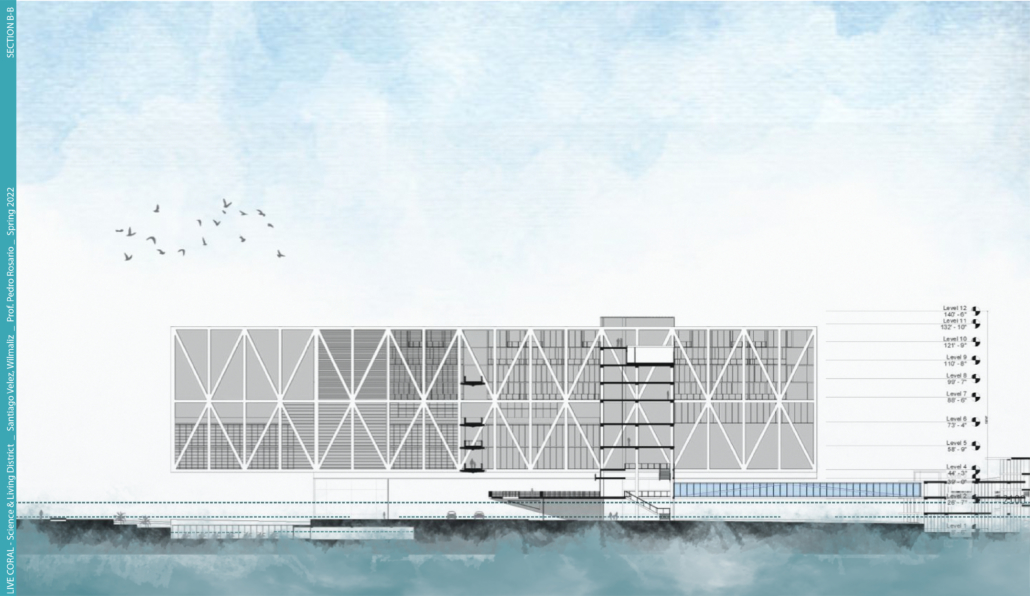
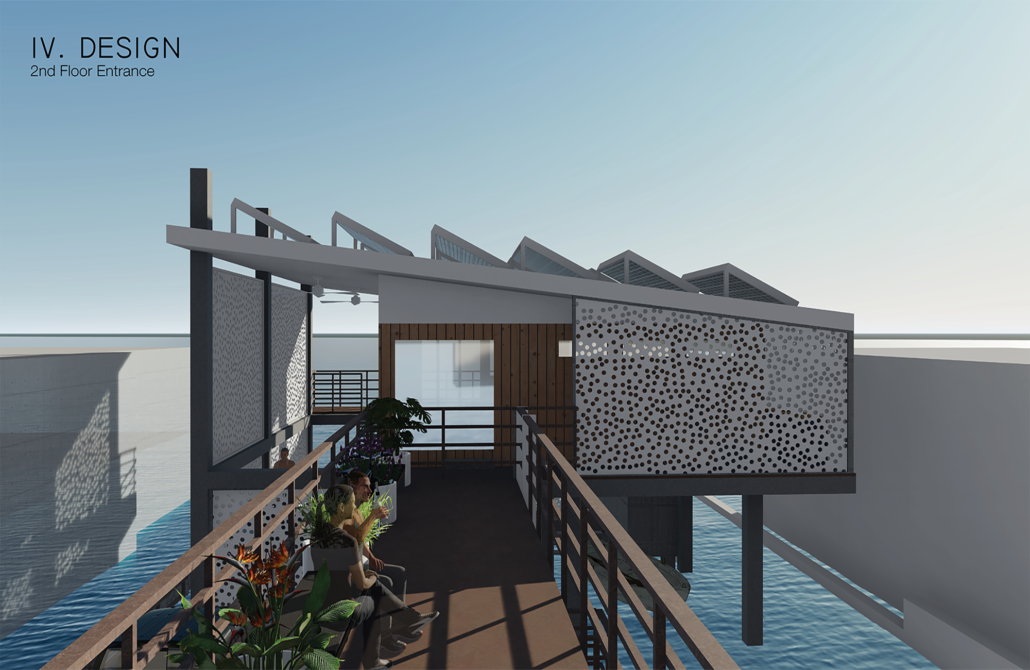
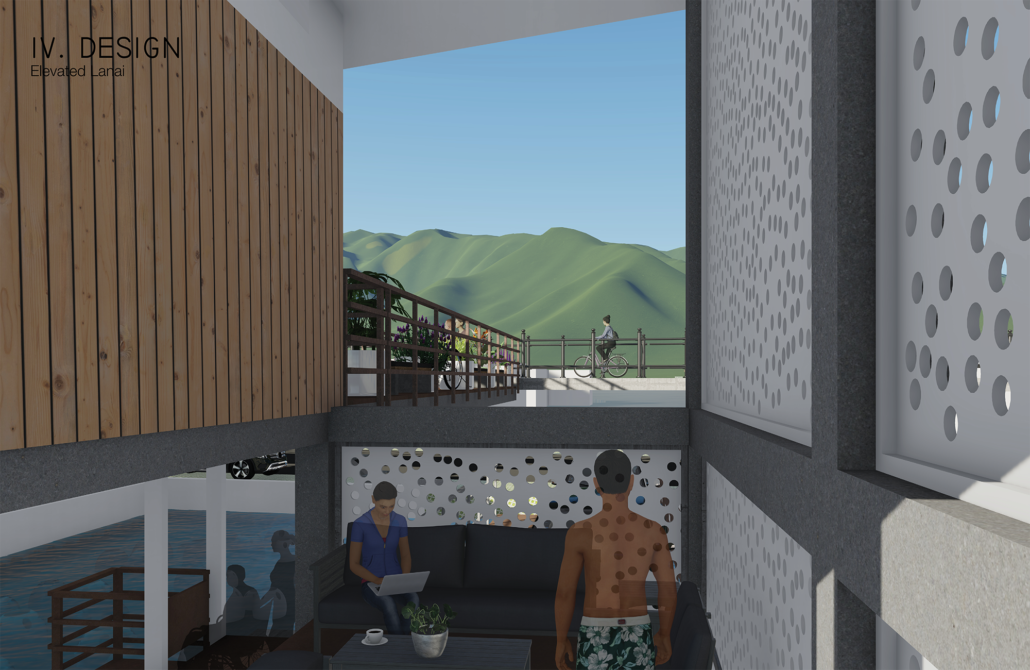
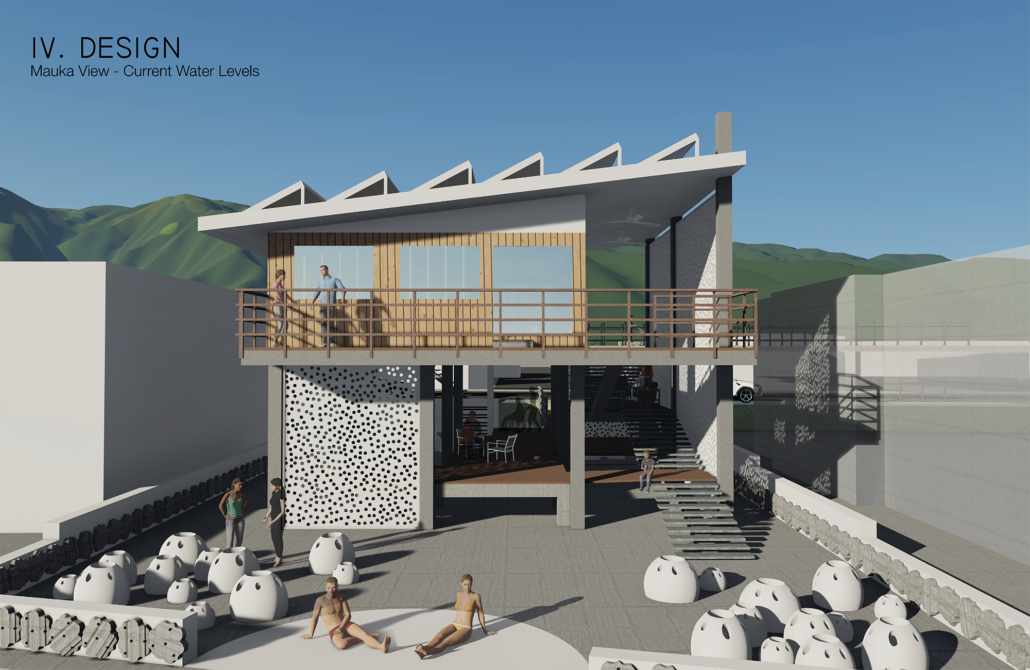
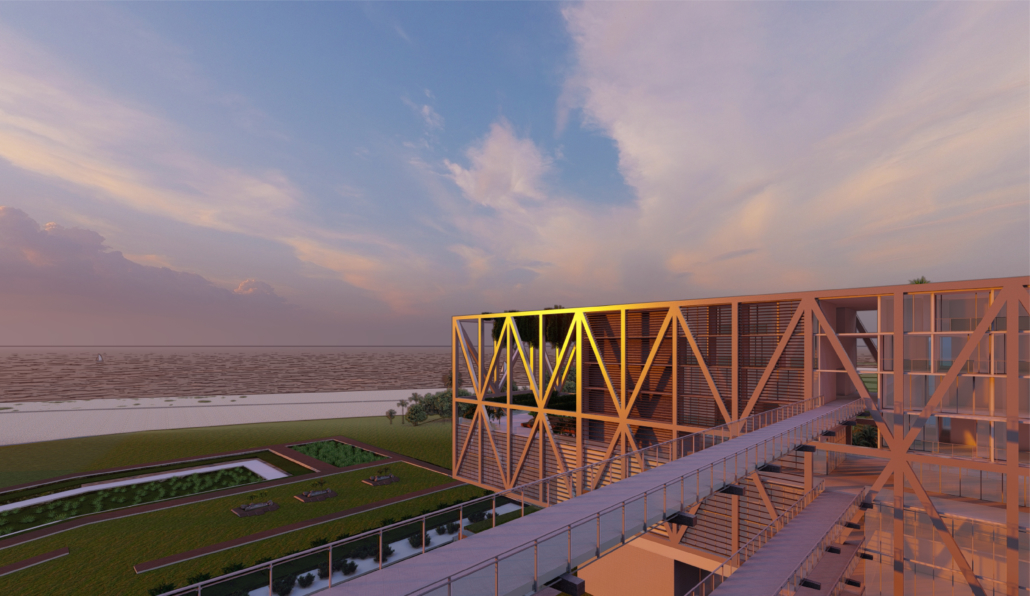
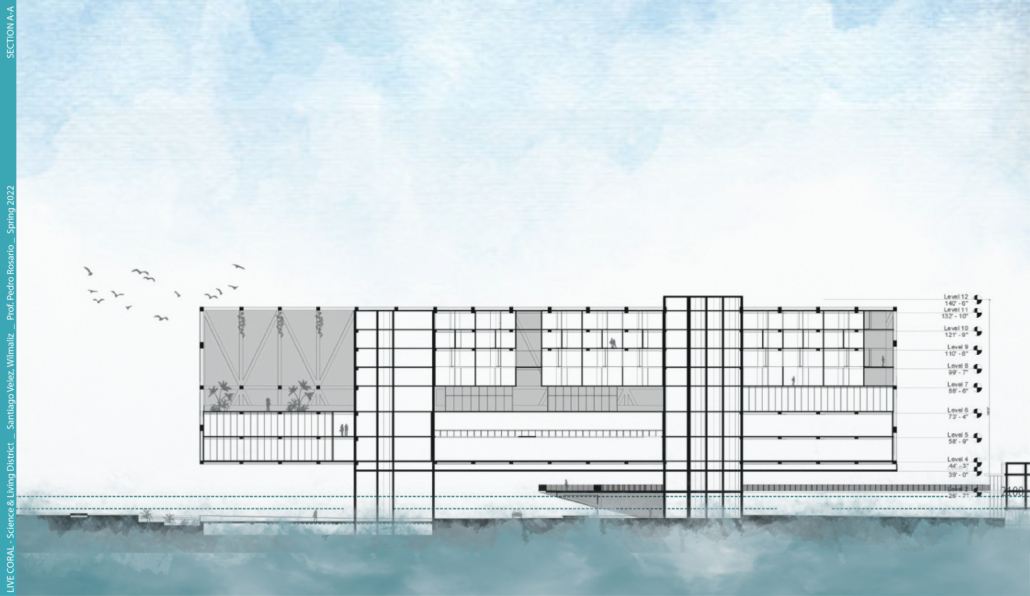
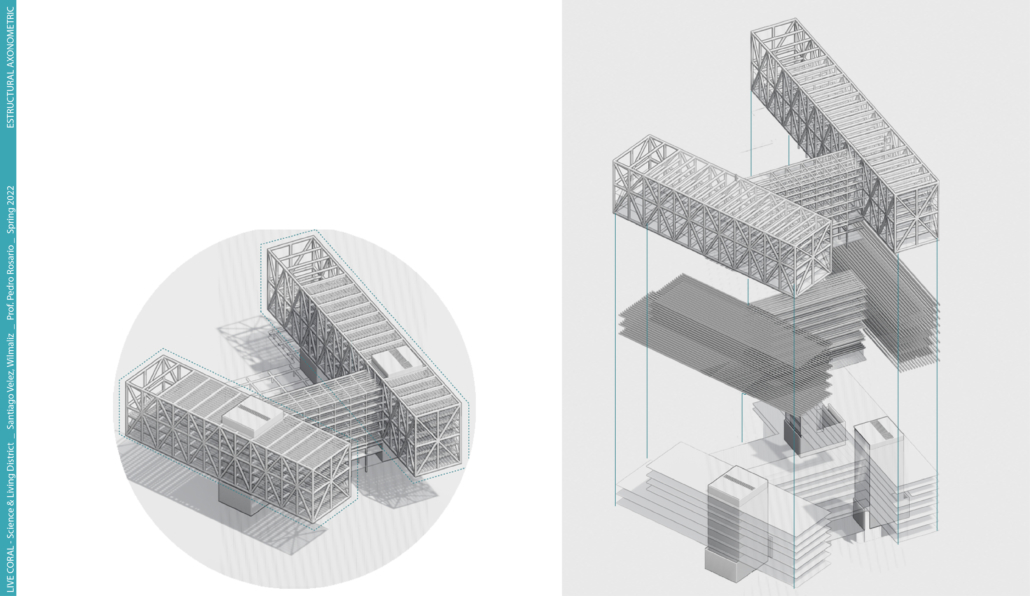
LIVE CORAL: Science & Living District by Wilmaliz Santiago, B.Arch ’22
Pontifical Catholic University of Puerto Rico | Advisor: Pedro A. Rosario
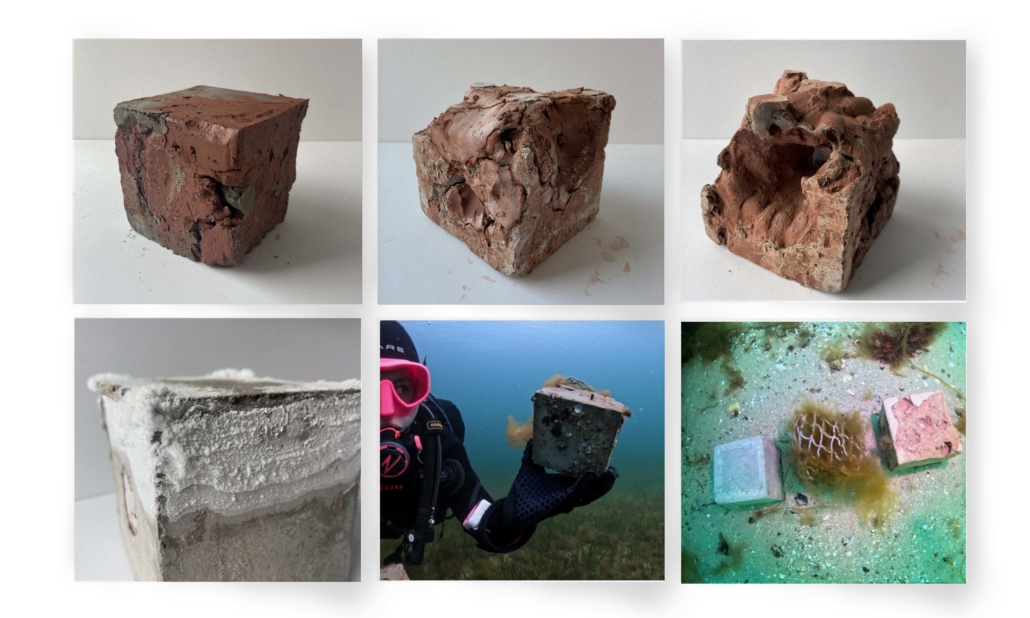
At the global level, climate change has brought with it several transformations, among them the rise in sea level. There are two main reasons why this happens, thermal expansion and glacial melting, both caused by global warming. Scientific research points out two important dates for this situation, in 2030 changes in sea level will begin to be felt and/or noticed significantly in all parts of the world, leaving a few years on the way to 2100 where we will have sea level at its peak. For that year it is estimated that hundreds of cities will be under flooded areas and many of them will disappear. All this has great consequences for all forms of life on the planet. And it is that not only humanity would be suffering the ravages, but also the flora and fauna, especially marine life. Sedimentation, the offset of nesting waves, high temperatures, the bleaching of coral reefs and endless situations that leave us with great consequences.
The project located in Rincón, Puerto Rico, is one based on scientific theories and predictions. The LIVE CORAL proposal seeks to provide a safe place for both humanity and marine life. A building is created where marine life can be researched and protected through this process of adaptation to sea level rise. In the same way, human life will have a safe place to live without limiting its quality of life, in addition to creating awareness and educating humanity about these changes and the effects it will have on other species and how this ends up affecting us.
The future in some way will always be uncertain and difficult to predict. However, thanks to the technological advances of our time there are many things that can help us foresee it. For this reason, this proposal seeks a complete adaptation over the years from the present to the imaginable 2100. Maintaining its efficiency, quality and use in its best state.
Instagram: @wilmaliz_santiago
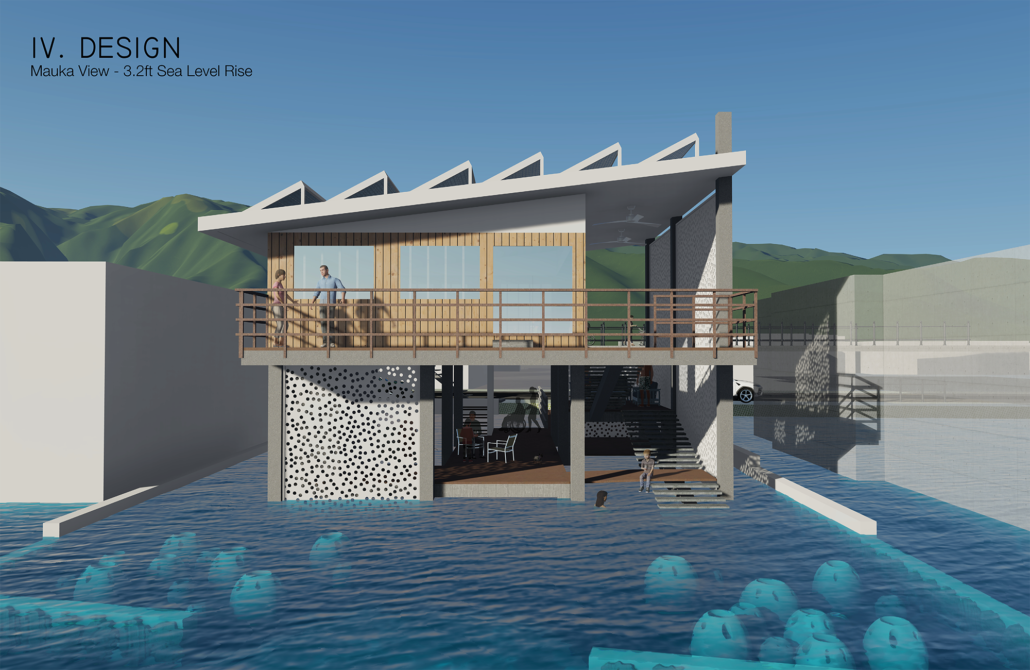
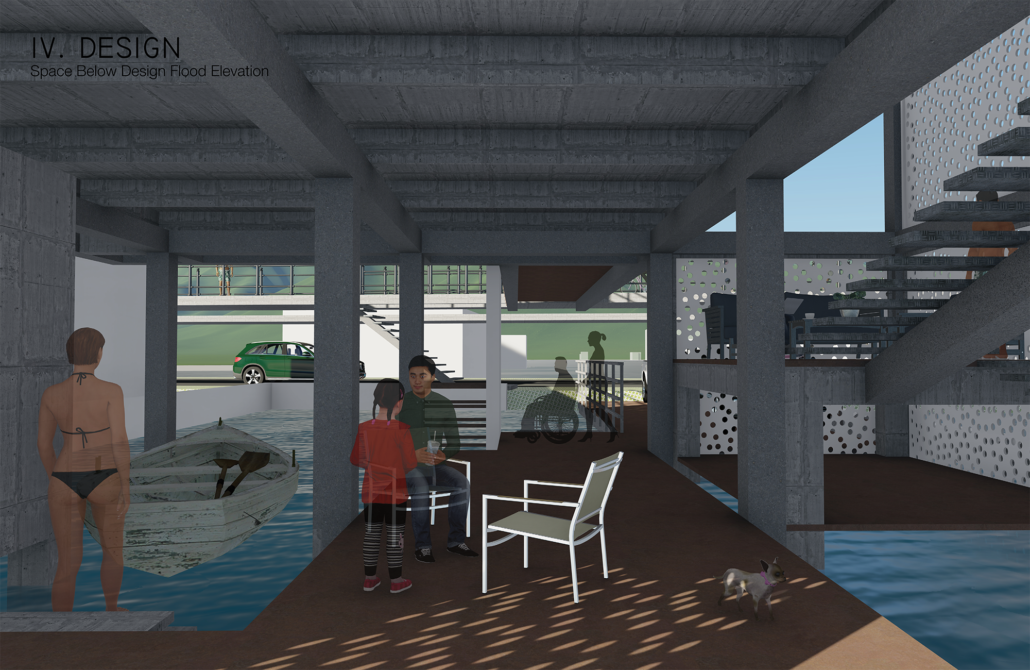
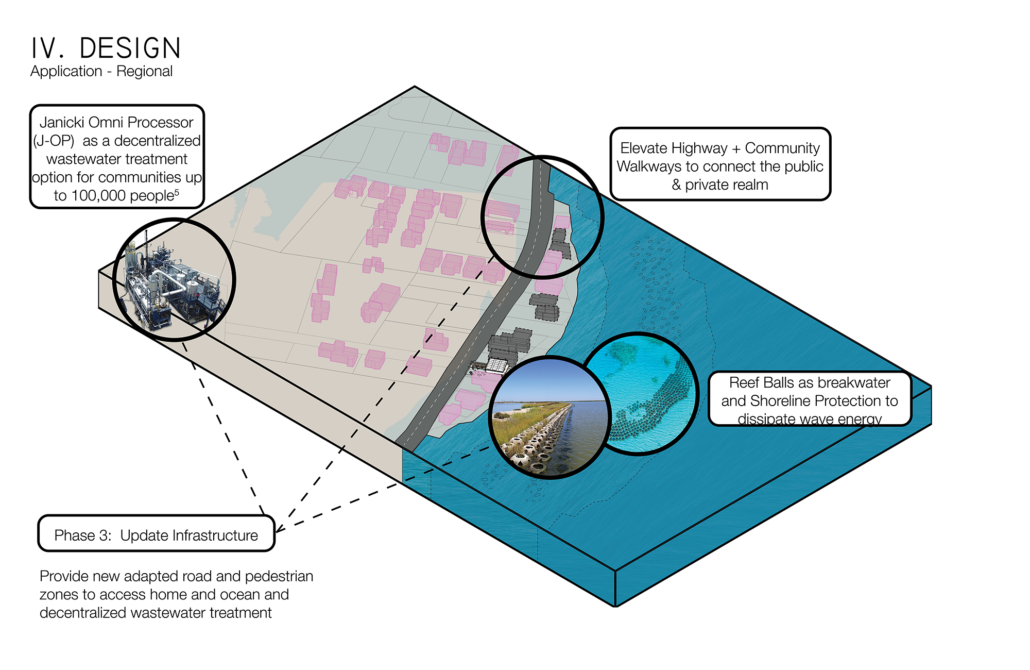
A Residential Guide for Redesigning Coastal Homes in Hawai’i for Future Sea Level Rise: Punalu’u, O’ahu by Josephine Briones, D.Arch ’22
University of of Hawaii at Manoa | Advisor: Wendy Meguro
The ongoing consequences of climate change, due to human activity, have created a need for a shift in the ways we live, think, and build (Oppenheimer, 2019). For sea level rise, its effects like beach erosion, flooding, and inundation continue to persist; impacting coastal communities, especially those that lie on the shorelines, that will remain at risk if adaptive measures are not used (Oppenheimer, 2019).
On Oahu, Hawai’i, there has been a shift to increase resilient communities, however, small-private landowners, such as single-family homes along the shorelines have been left with limited guidance, education, and resources compared to large public/private landowners (City and County of Honolulu, 2020). As O’ahu’s efforts cater to large-scale development, like high-rises and/or mixed-use commercial structures for sea level rise adaptations, there is a demand for localized adaptation for communities not described by current guidelines and local land use ordinances. 72% of potential economic loss with 3.2 feet of sea level rise will be residential structures and land (Hawaiʻi Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation Commission, 2021). As coastal communities prepare to adapt for sea level rise, new design thinking is necessary to exceed the requirements and recommendations that are currently practiced.
In alignment with the 2017 Hawai’i Sea Level Rise Vulnerability and Adaptation Report that states, “More research is needed to improve understanding and projections of localized vulnerability of beach and coastal environments to combined impacts of poorly sited beachfront development and erosion and flooding with sea level rise” (PacIOOS, 2021). This research uses a case study home along the shoreline of Punalu’u/Hau’ula to envision a new coastal typology in Hawai’i with adaptation solutions that are phase-able for living with increased sea levels. By providing shoreline homeowners of Hawai’i, especially those who own detached single-family homes that are at risk to the effects of sea level rise, with building adaptation guidance, practical design solutions, and accessible knowledge gives individuals the insights needed to protect their property, increase communities’ resilience to sea level rise impacts and, globally, provide solutions as incremental change that can be used to inform future shoreline homes on a large-scale.
Instagram: @jojo_briones
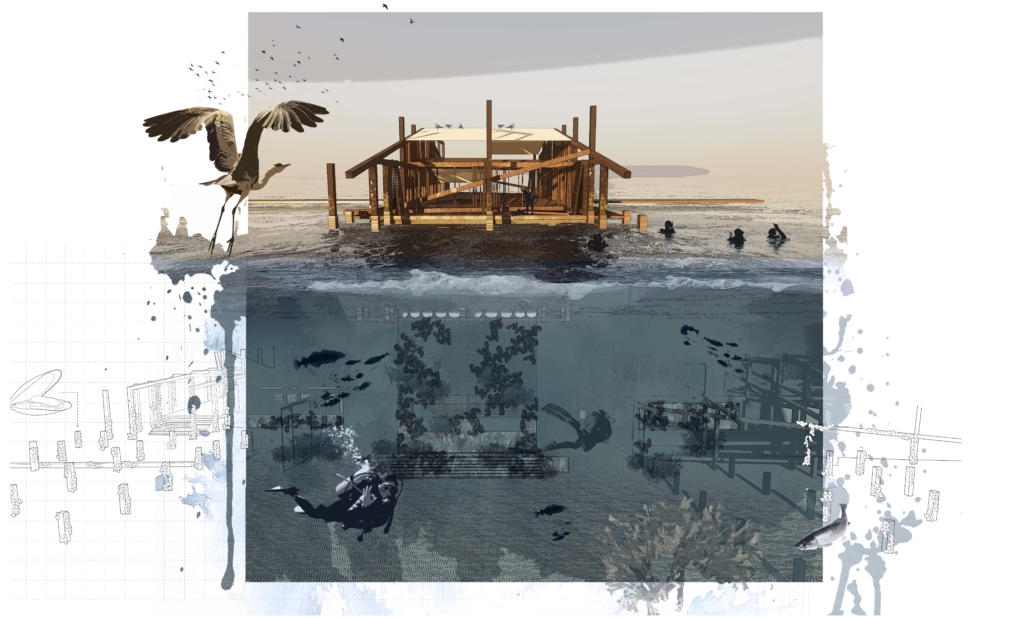
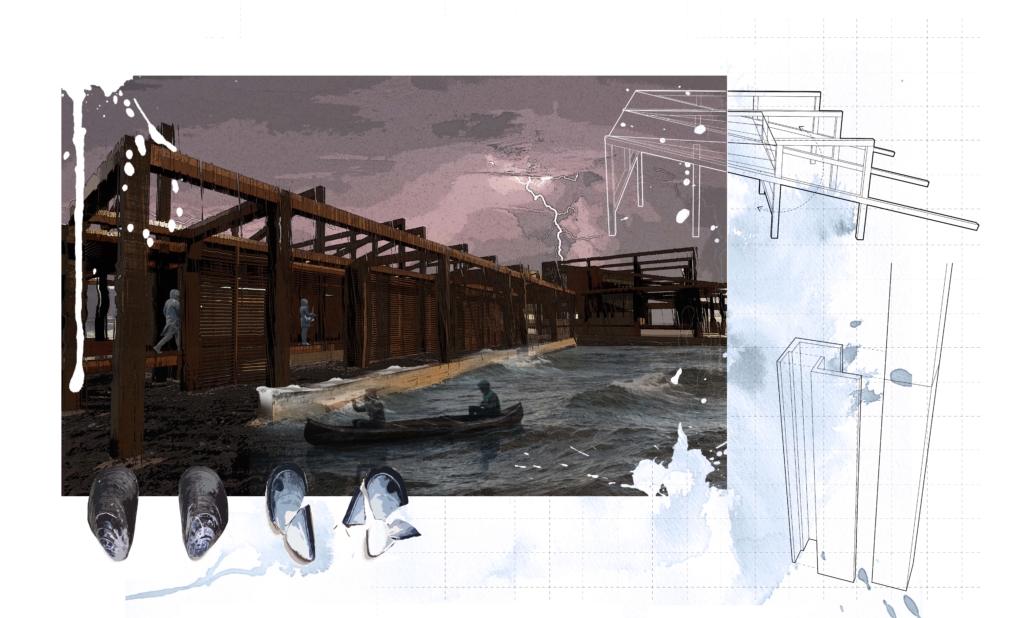
Shifting Sediments: Inhabiting the Land, the Sea, and the Space In-Between by Natasha Zubricki, M.Arch ’22
Dalhousie University | Advisor: Catherine Venart
The coastline is a dynamic edge between land and sea ruled by natural forces and illustrated through material processes of erosion, accretion, and deposition. As our climate warms with an increase in storm conditions and sea levels, the natural forces at work accelerate. Cycles of growth and destruction are an inevitable aspect of our environment that can be analyzed through hydrological impact, geological structures, and ecological networks, all forming ruins off fragments of the earth.
This thesis examines Prince Edward Island as a case study of how to shift our perspective and embrace the ocean as an instigator of opportunity. Three locations along an edge are investigated exploring various material and programmatic relationships that can be utilized as a layered strategy to become a catalyst for new life. A temporal architecture that works as both measure and armature is implemented as an infrastructural approach aimed to adapt to inevitable uncertainty.
The thesis focuses on the relationships between humans and oysters as main actors for adaptation while engaging with the natural forces at play. The project moves through time adapting to rising seas and the changing environment, allowing new possibilities to be formed off a ruin of the past. Through engaging with natural forces instead of fighting against, we can create new edges, establish home for both humans and oysters, as well as use inevitable decay to provoke new life.
Instagram: @tash_zubri
Check back next week for Part II of the 2022 Study Architecture Student Showcase.