2023 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part XXXII
In Part XXXII of the 2023 Study Architecture Student Showcase, each project highlights water in various capacities. Viewers can browse designs ranging from the reimagining of a floating Girl Scouts campsite to a holistic hydrotherapy spa. The featured student theses and designs also address threats to water by proposing systems for water collection and distribution and creating new infrastructure for wastewater plants.
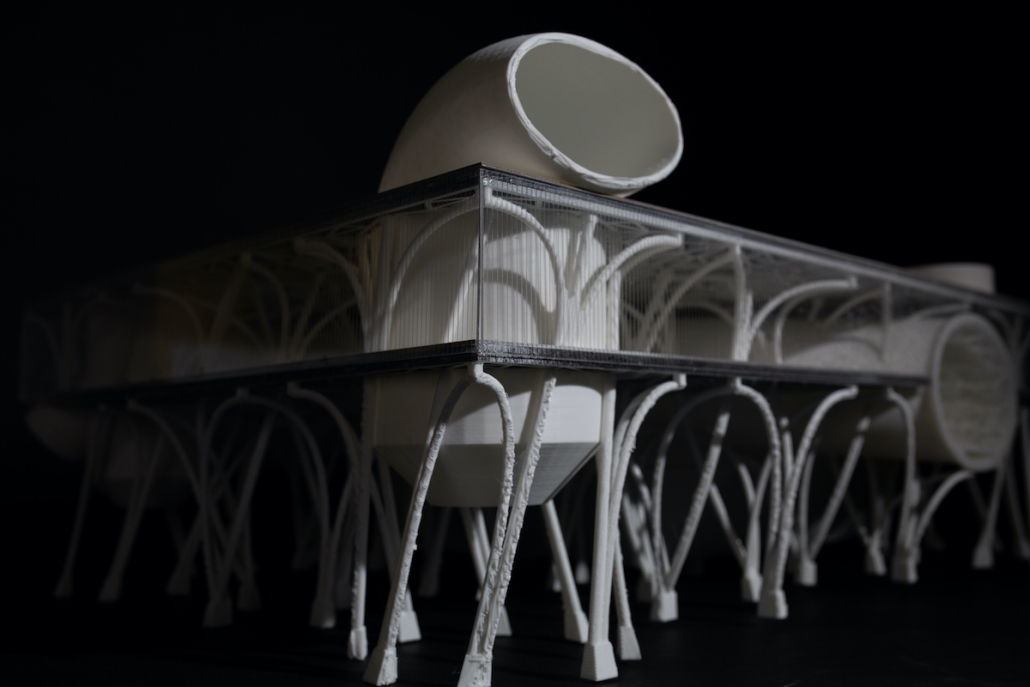
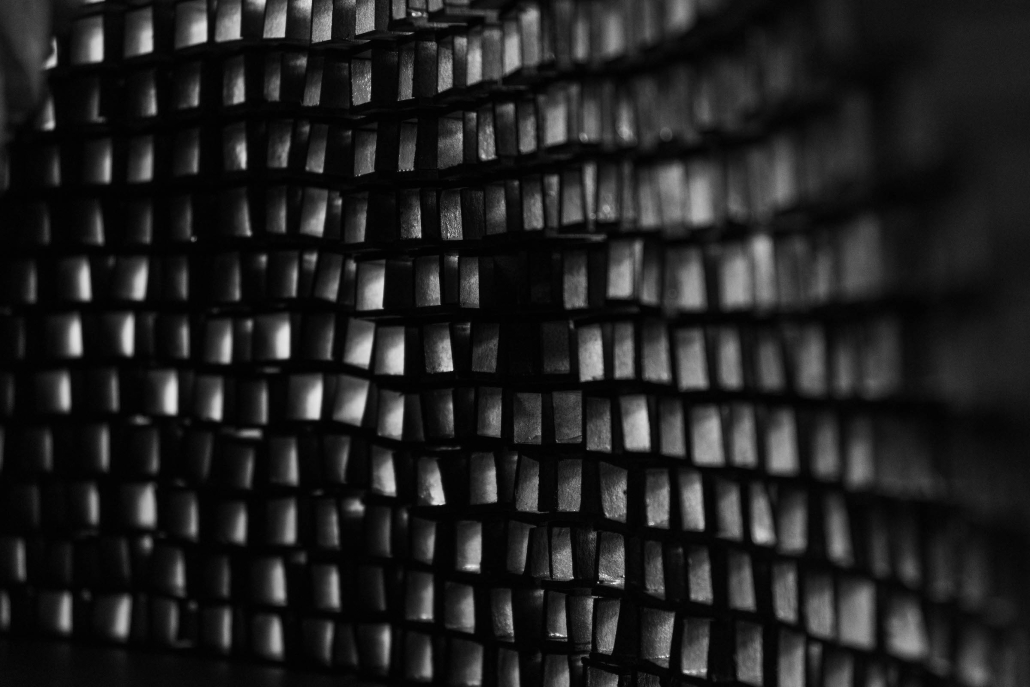
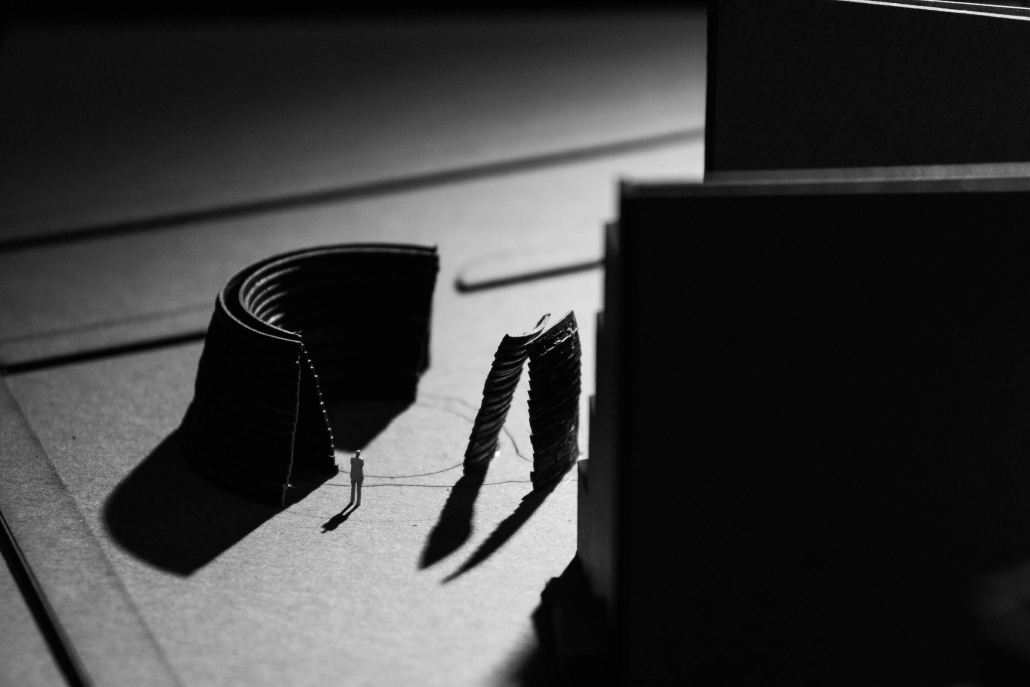
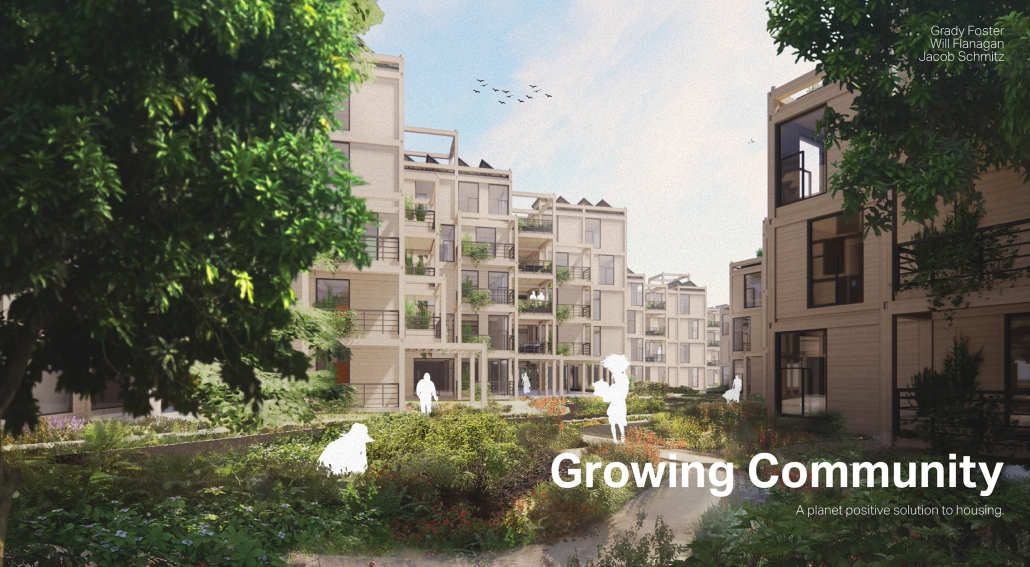
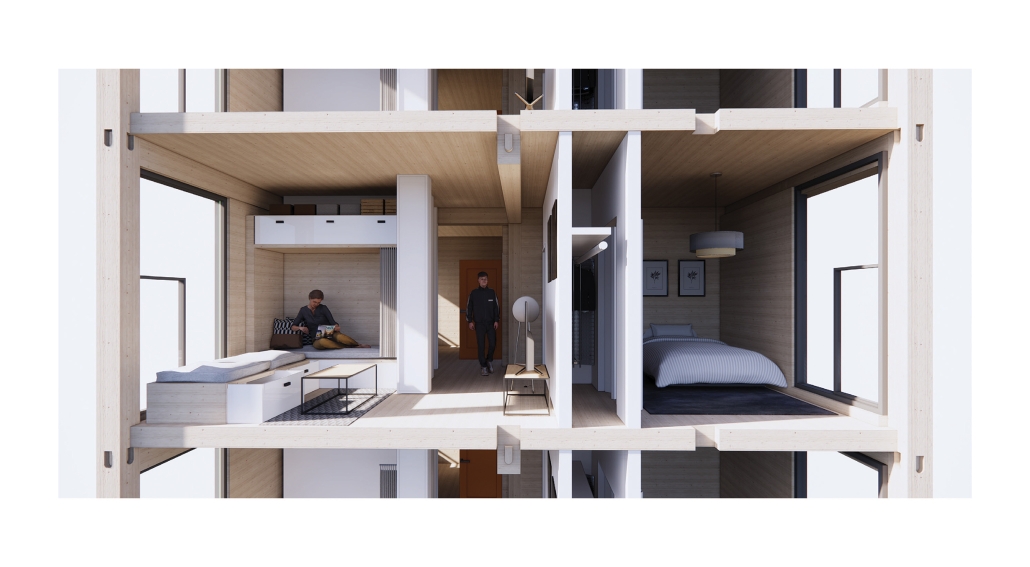
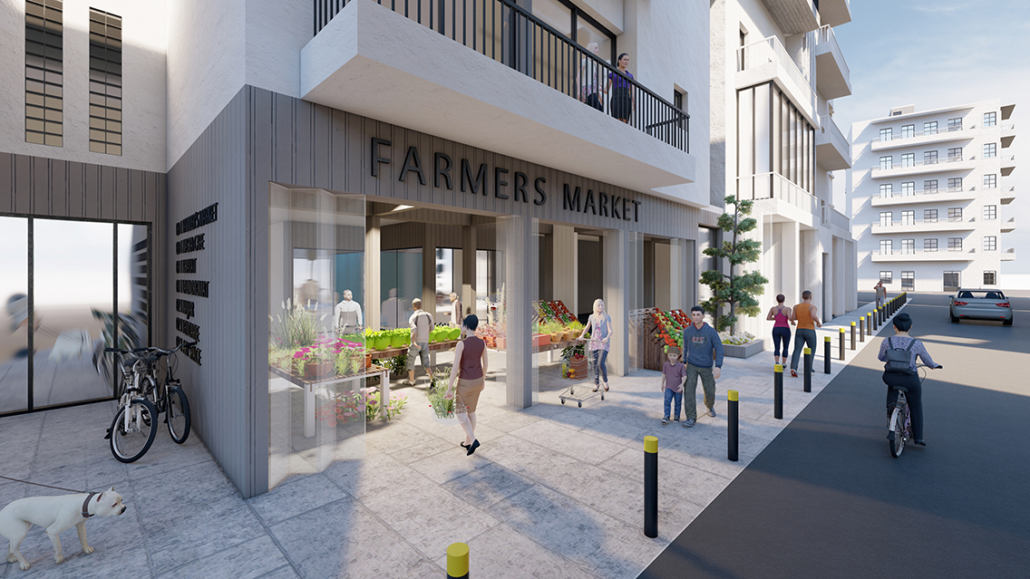
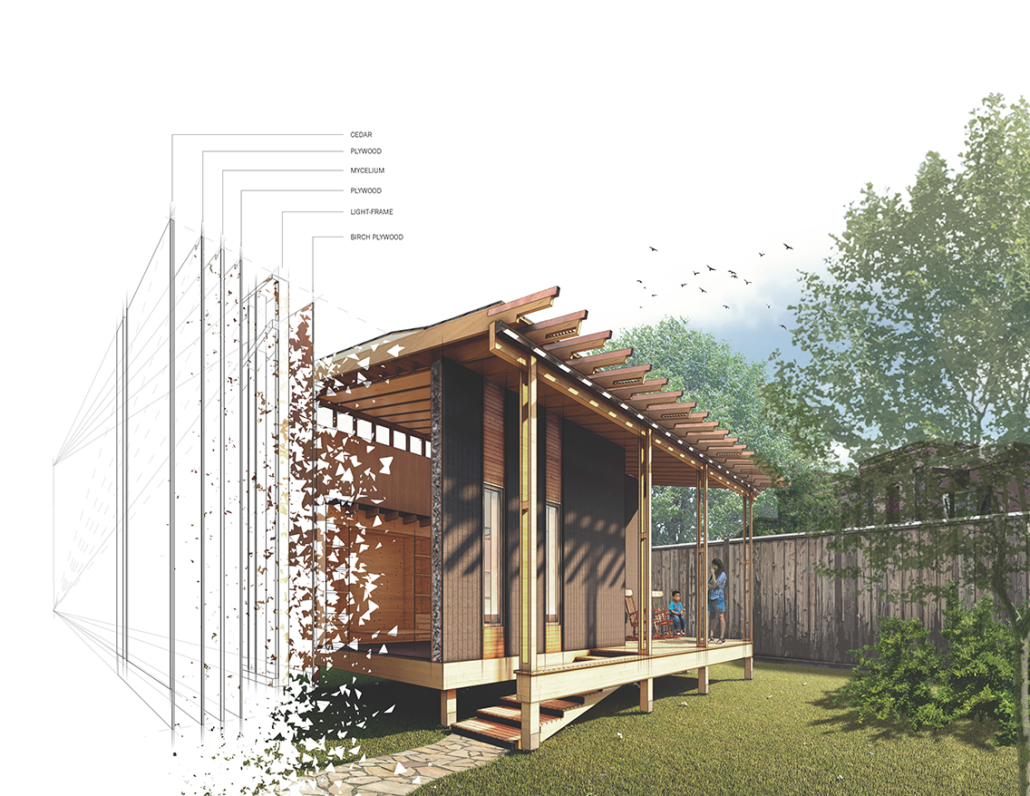
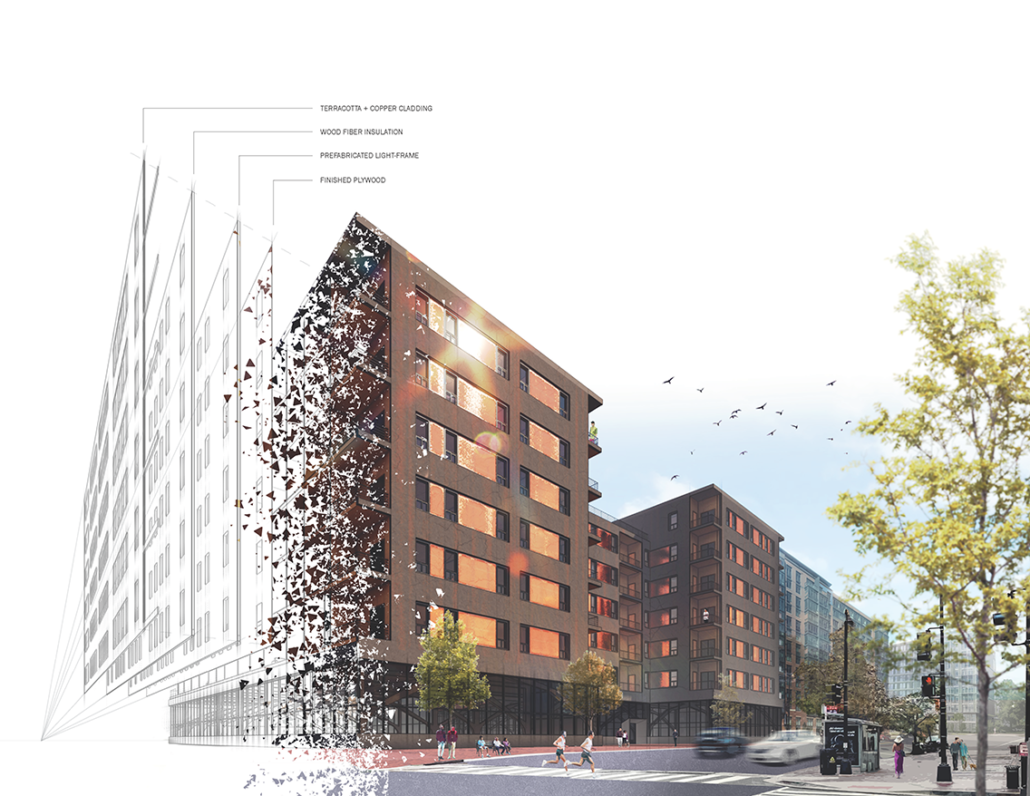
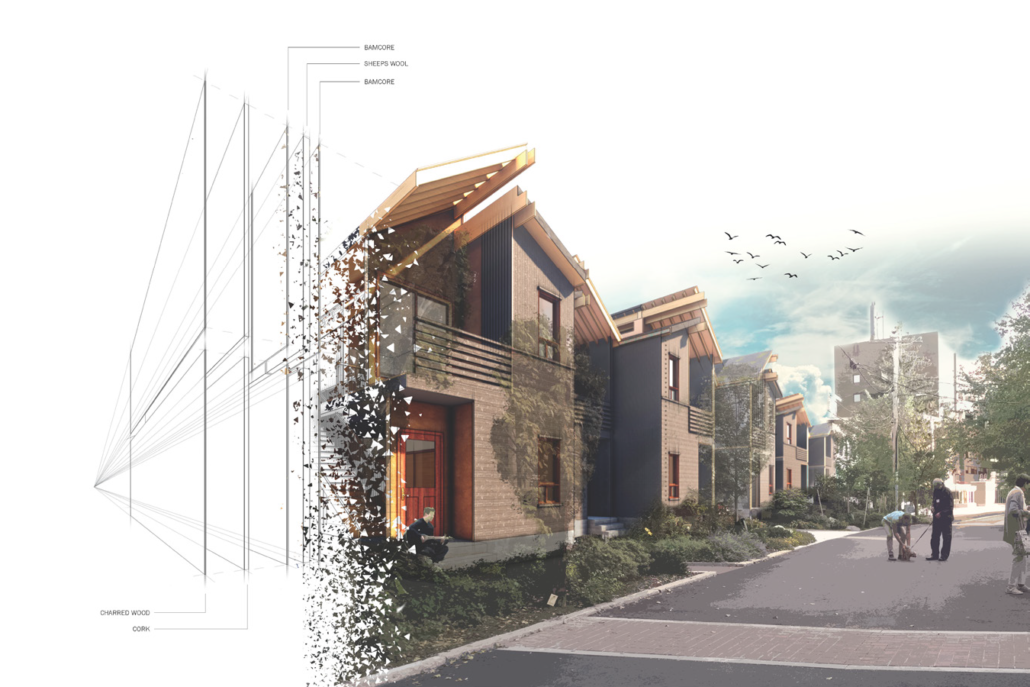
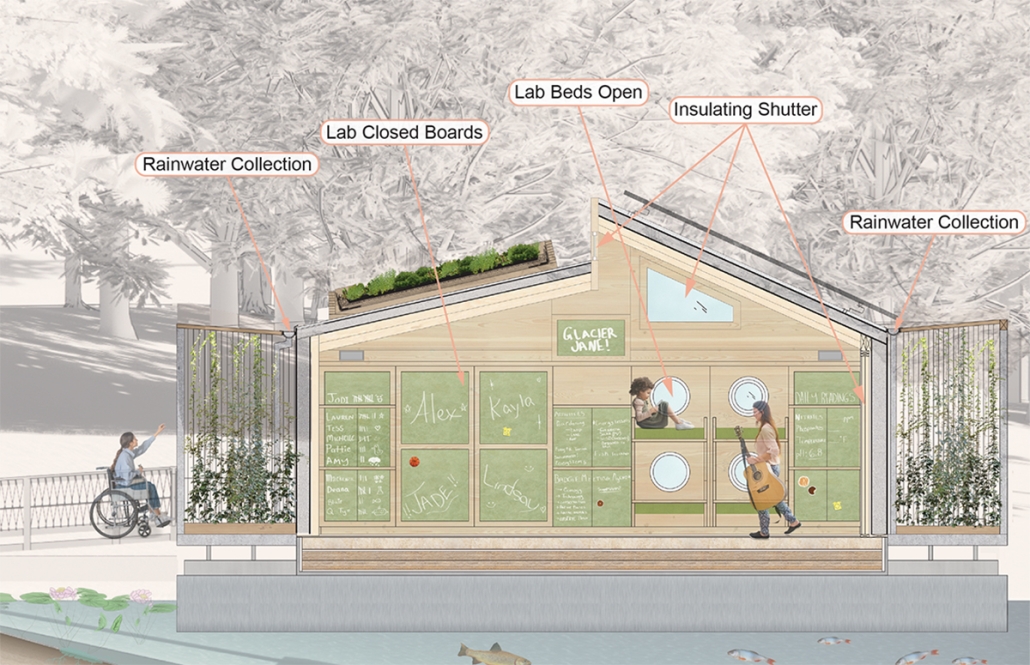
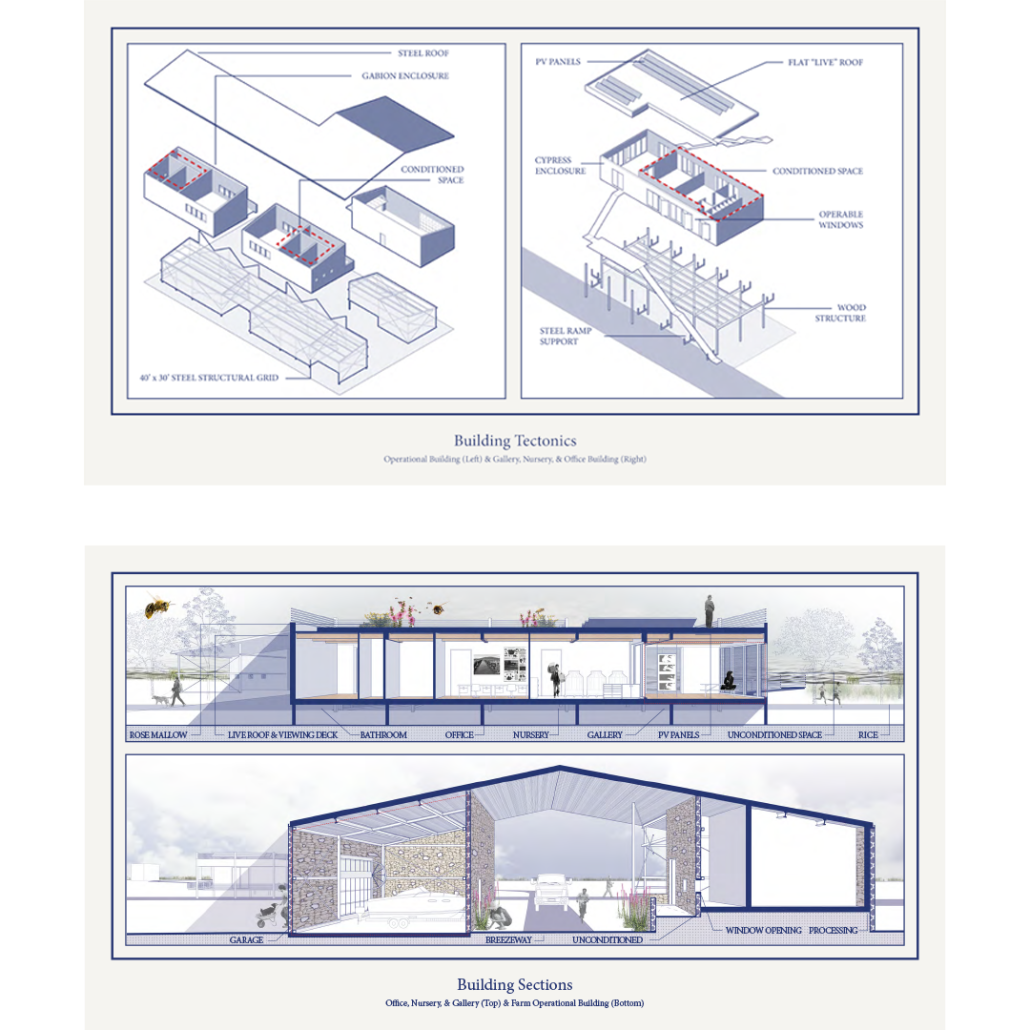
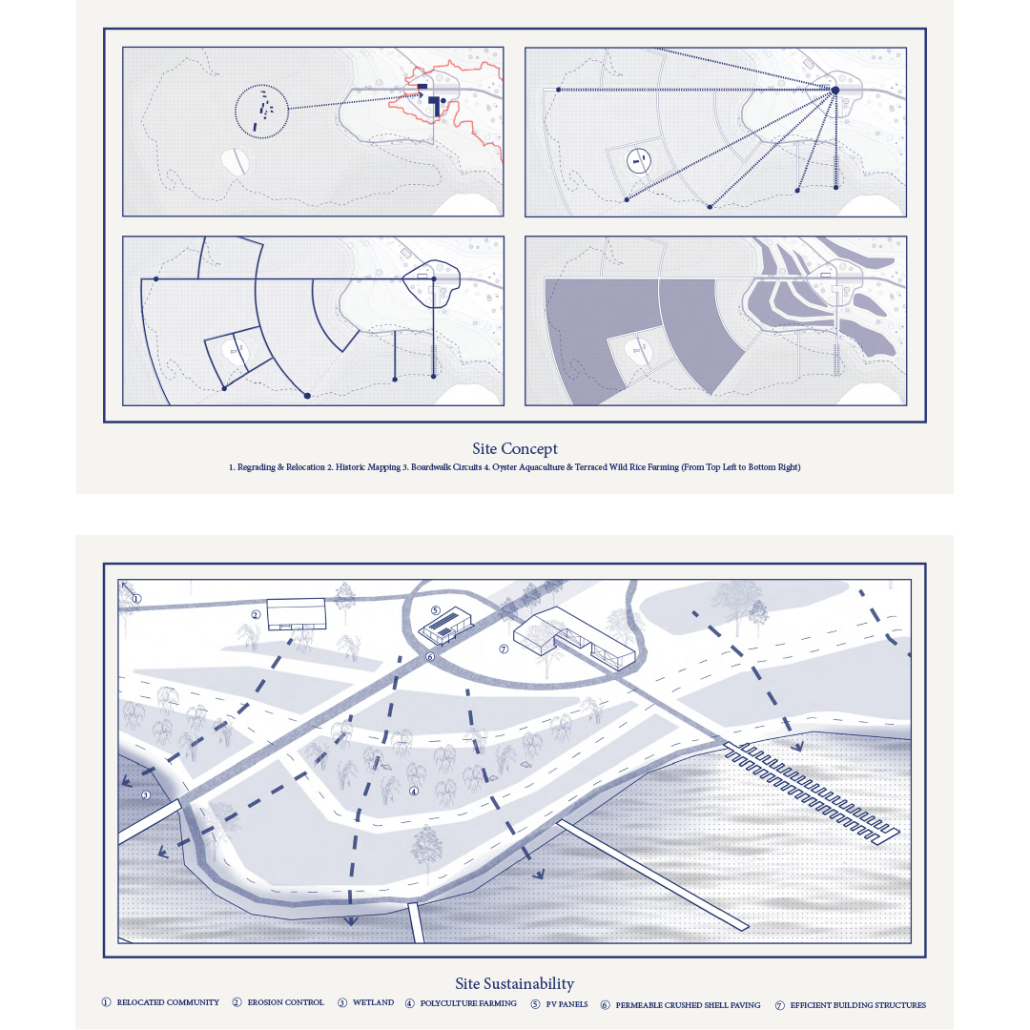
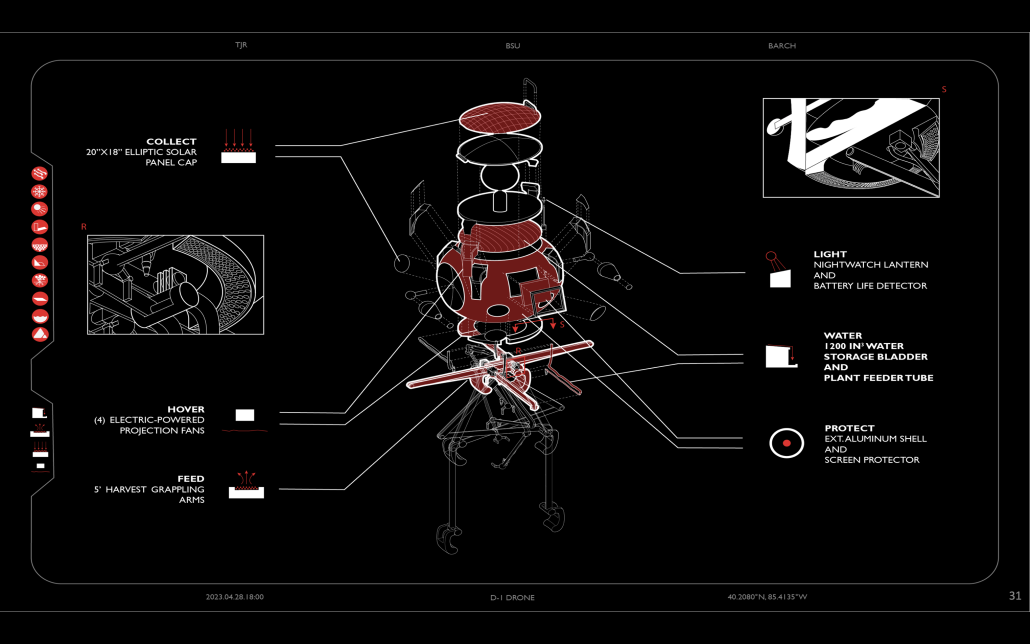
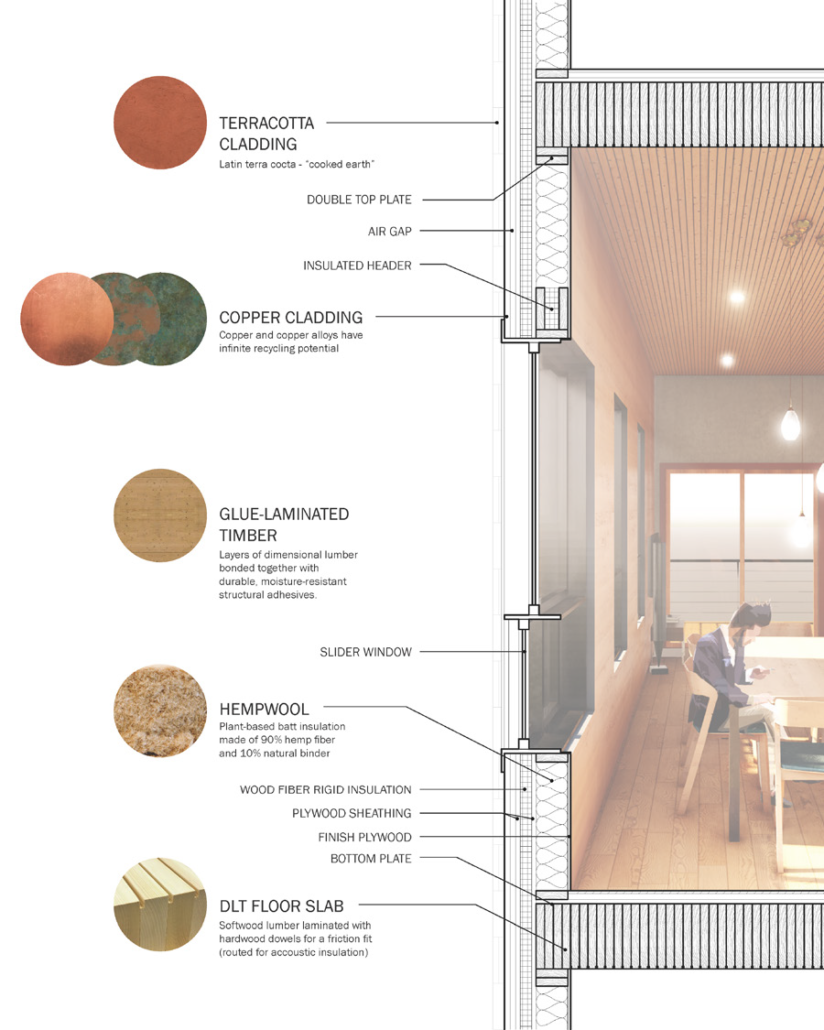
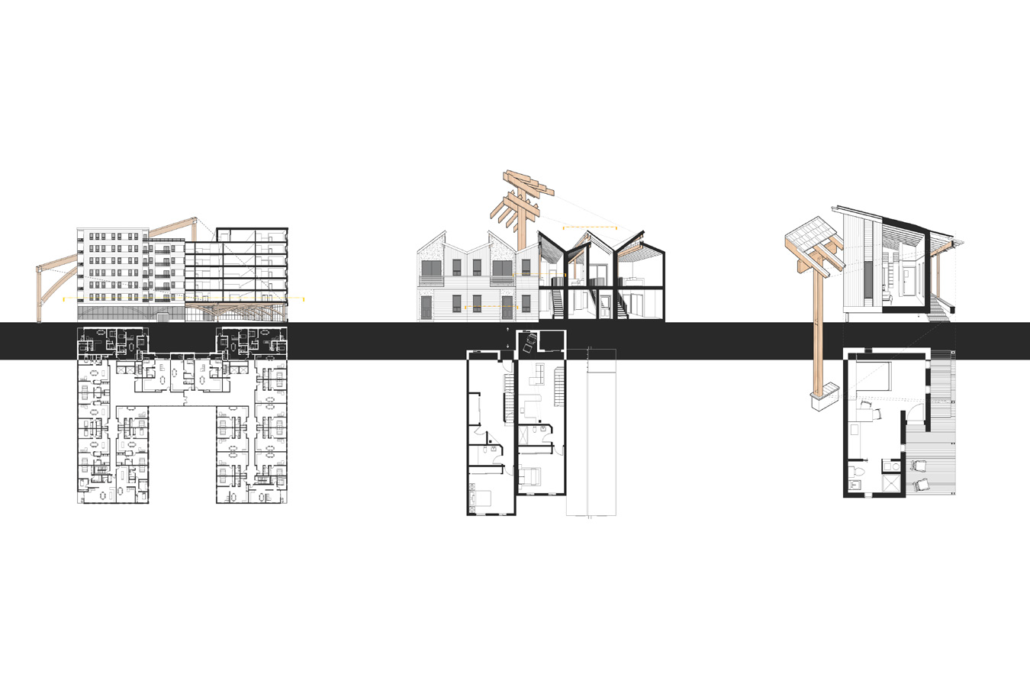
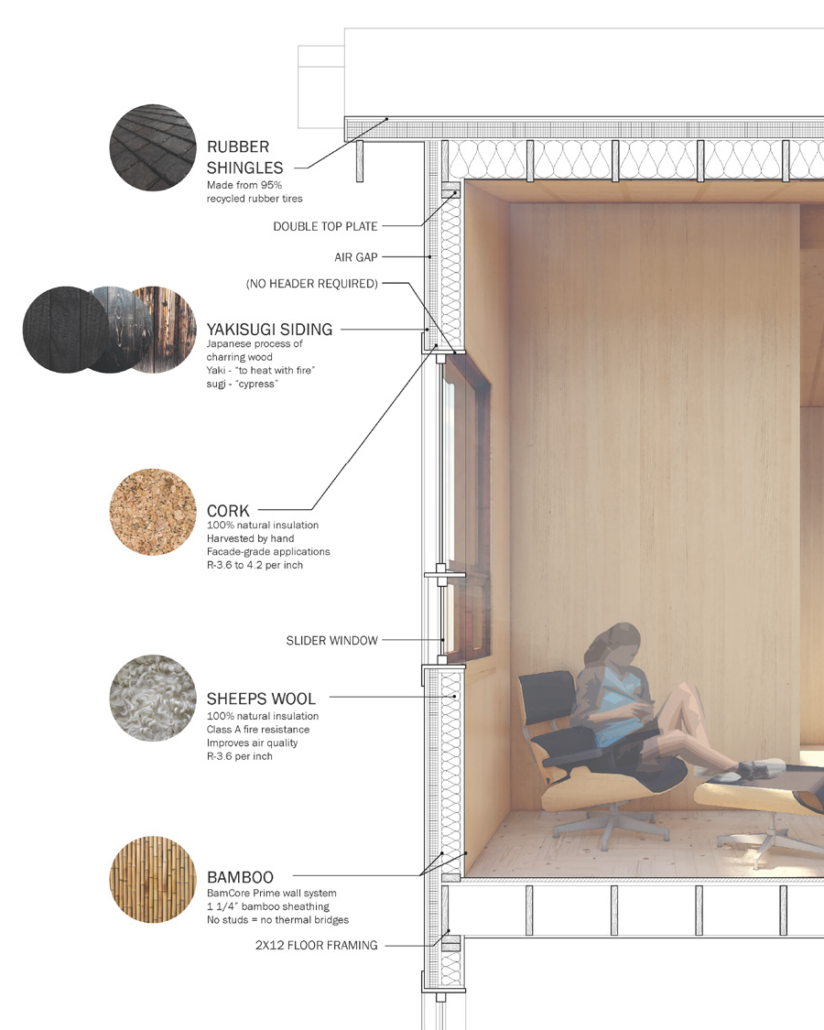
Glacier Jane by Lauren Beemer, Tess Brown, Sandra (Lindsey) Chaplik, Ryan Fitzsimmons, Kayla Flyte, Dean Hemminghaus, Alex Hernandez, Samantha Labrosky, Alexander Laudone, Patrick Moorhouse, Tyler Muir, Michelle Petrik, Tyler Quick & Jade Rolon, B.Arch ‘23
Marywood University | Advisors: Jodi La Coe & Maria MacDonald
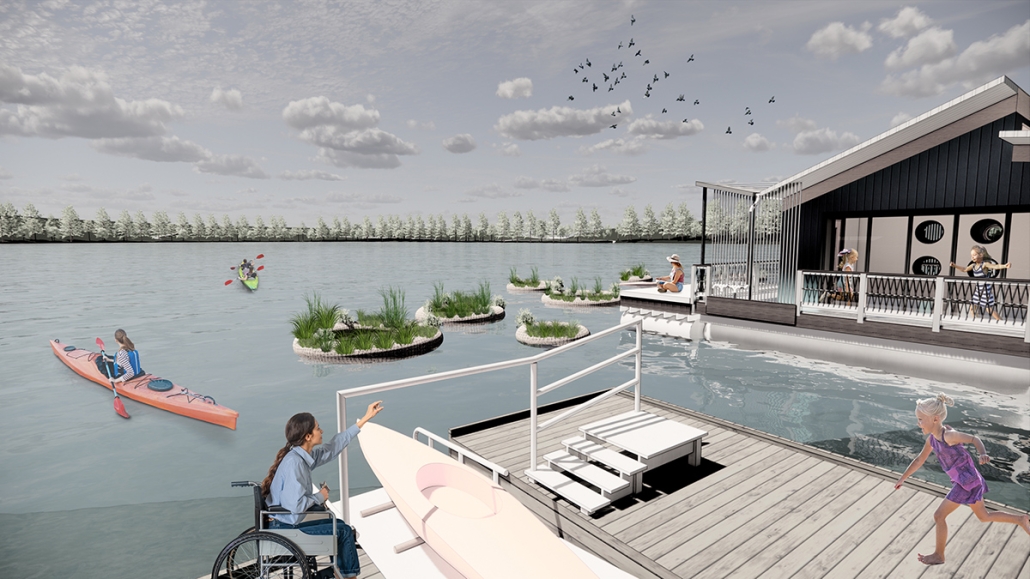
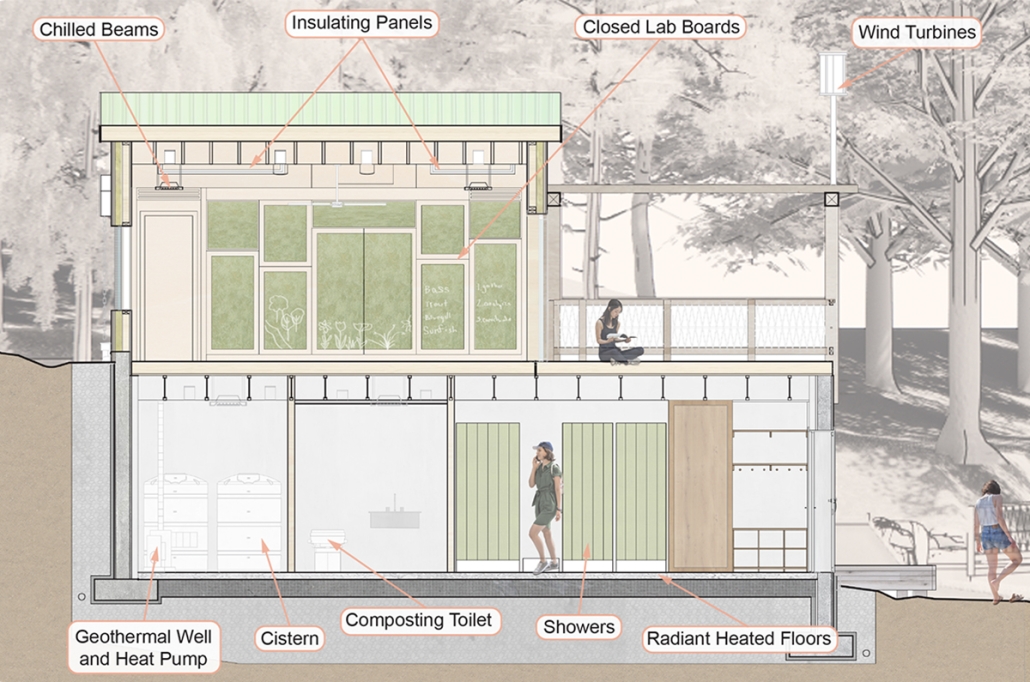
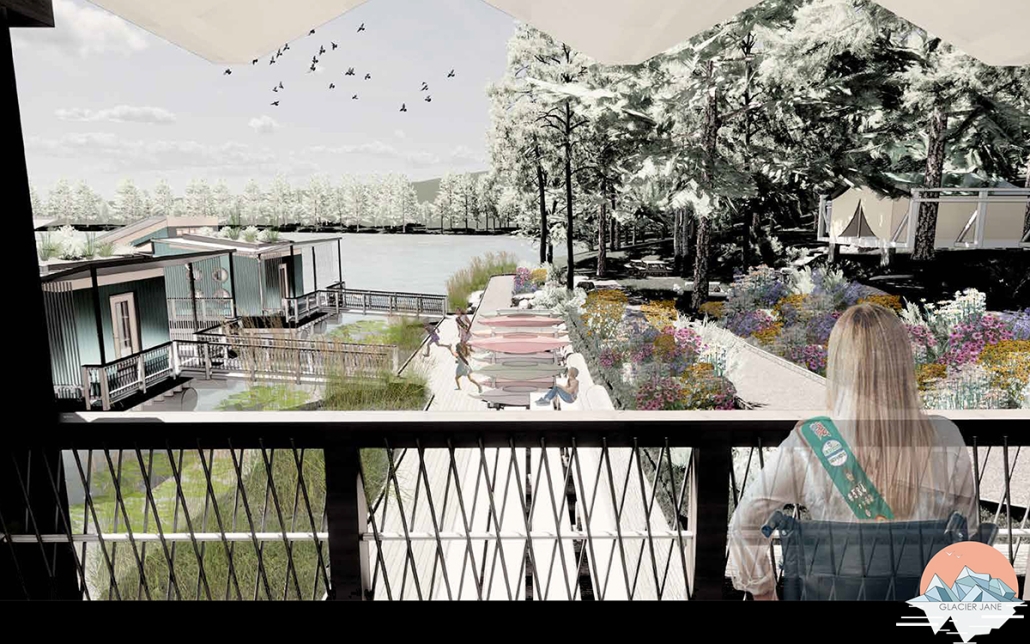
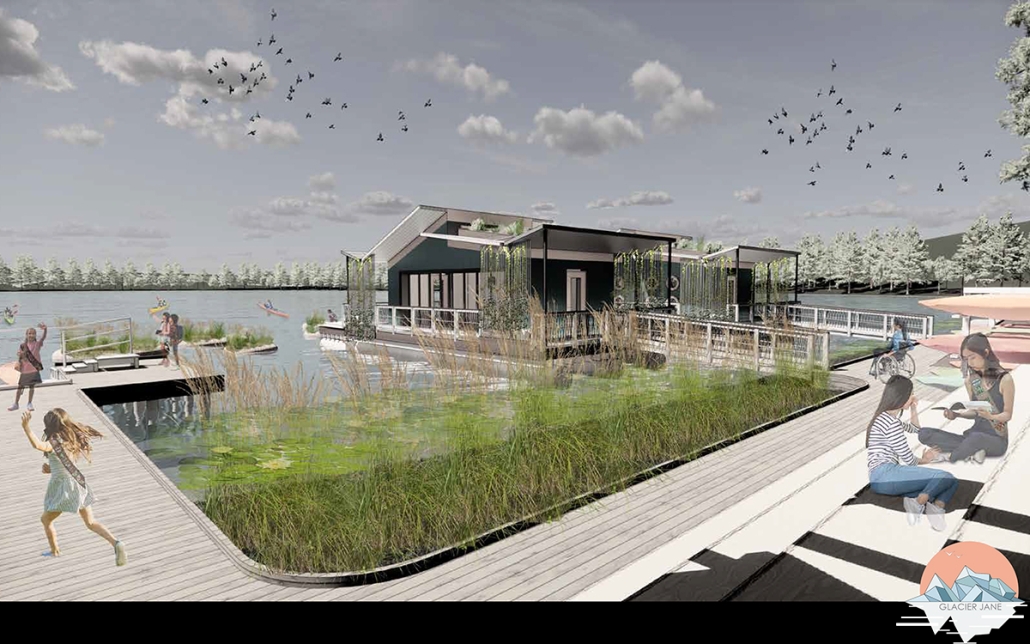
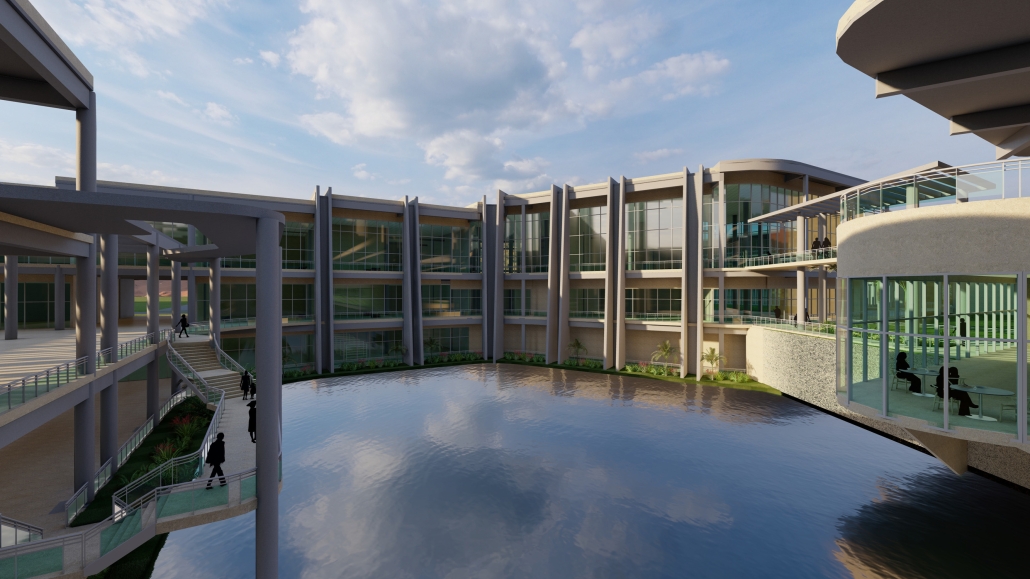
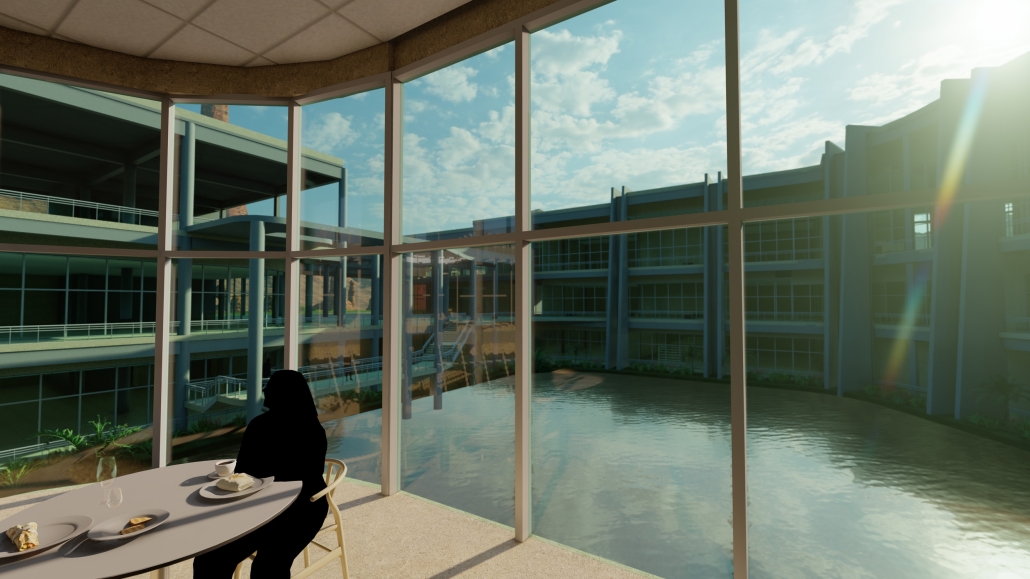
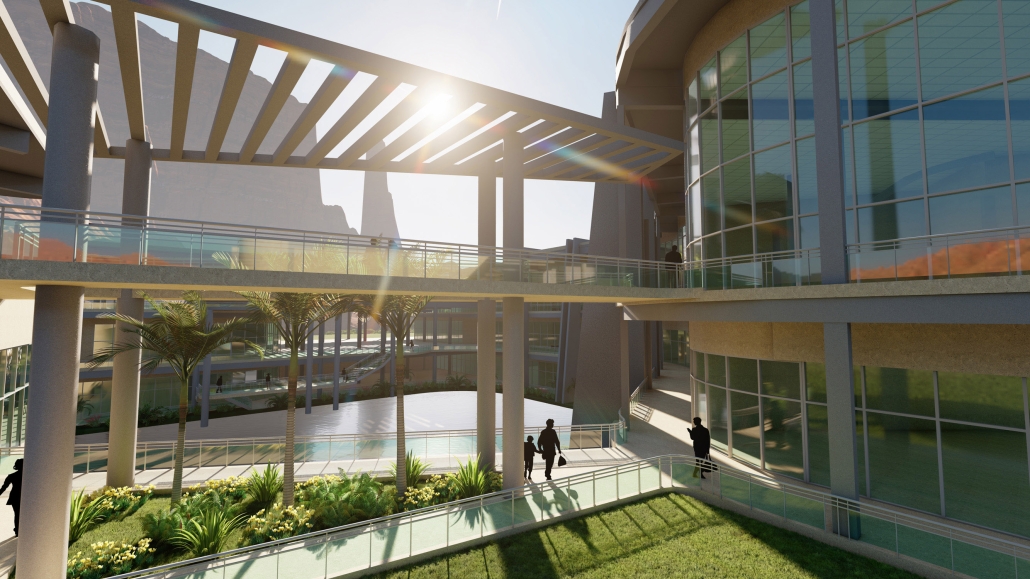
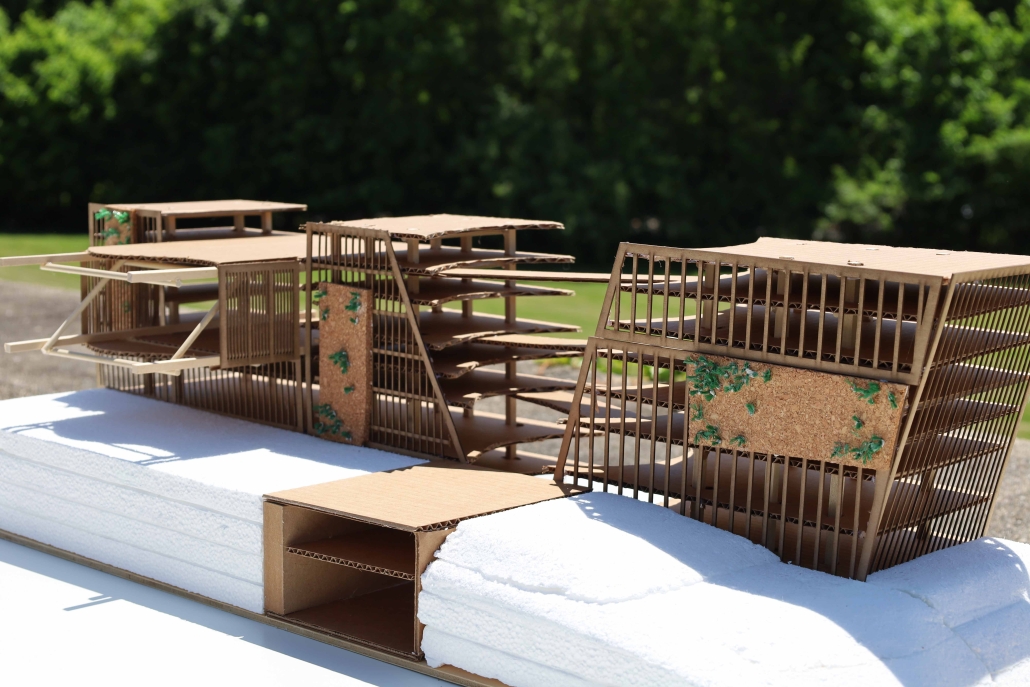
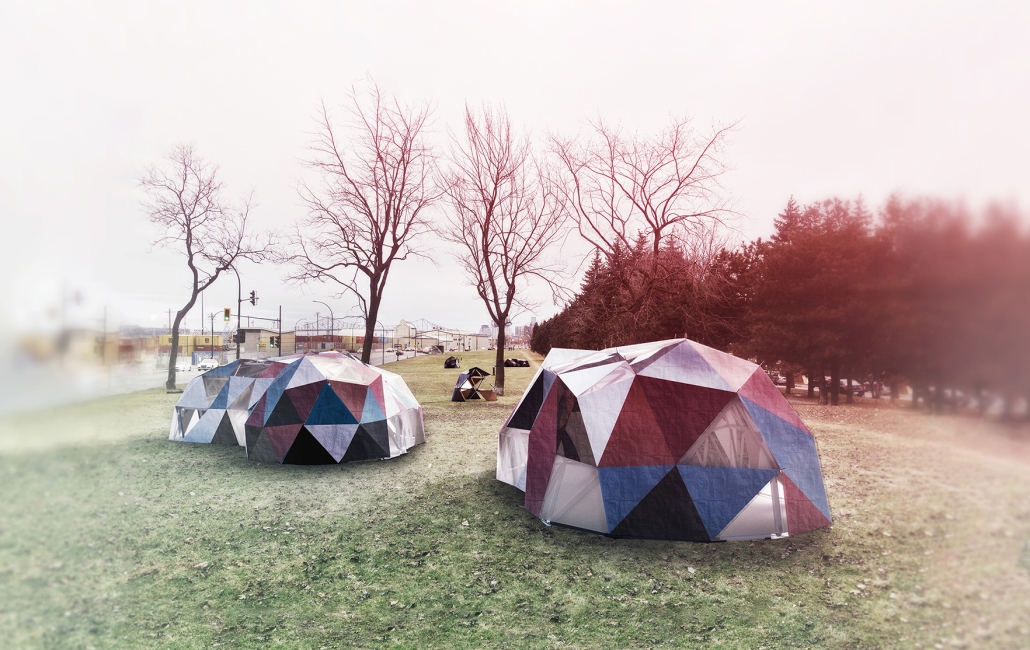
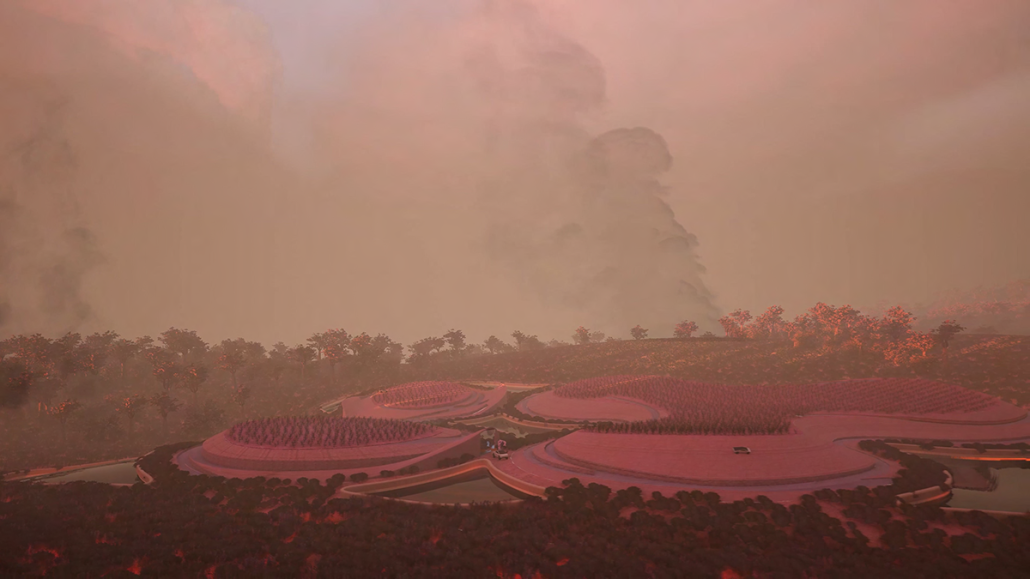
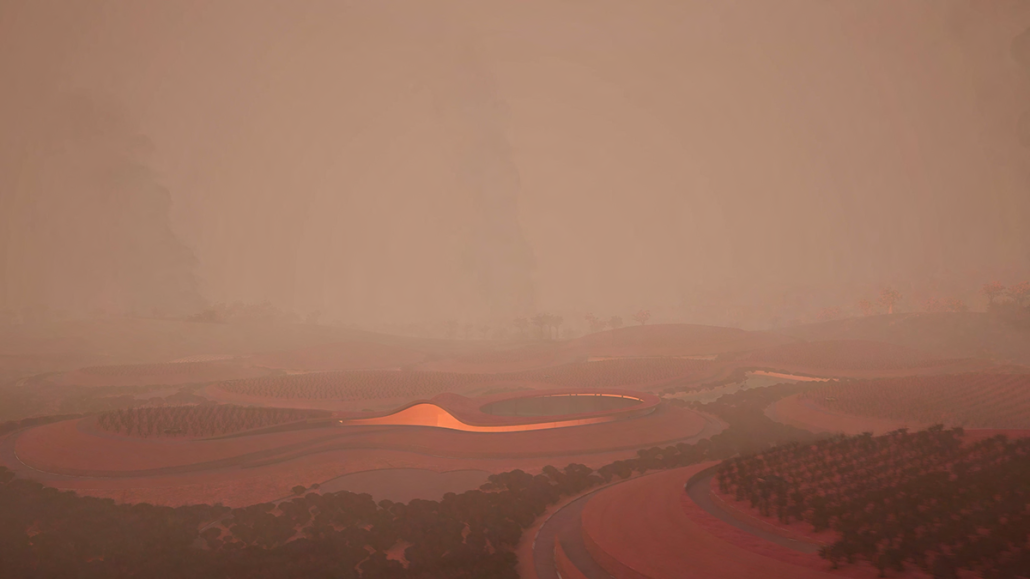
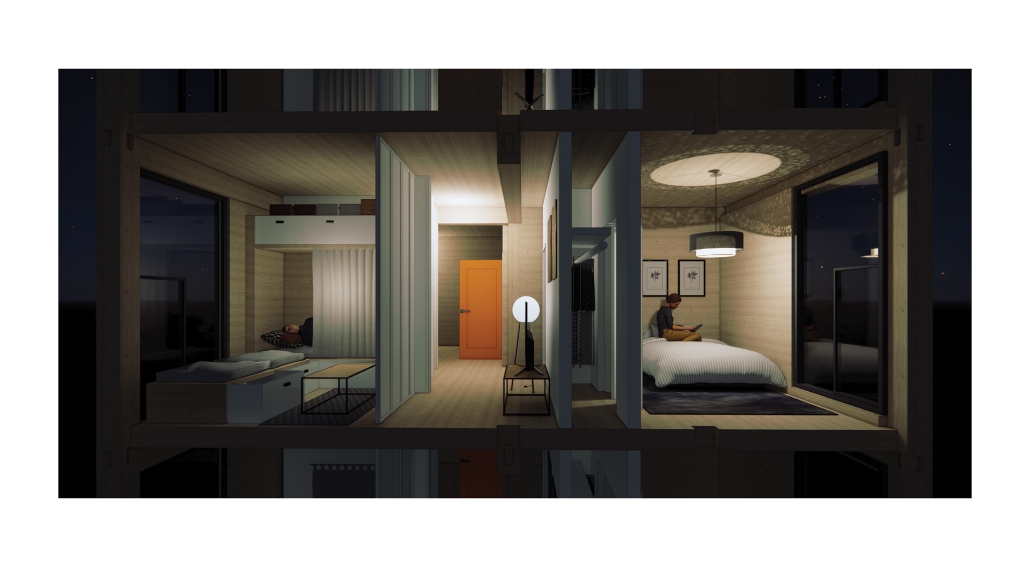
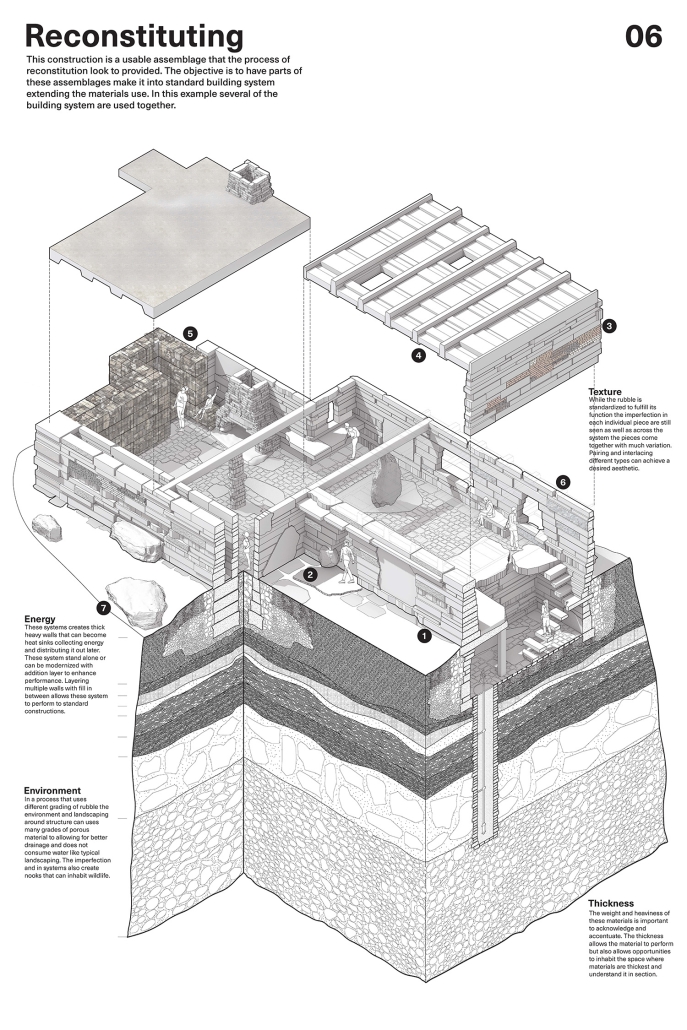
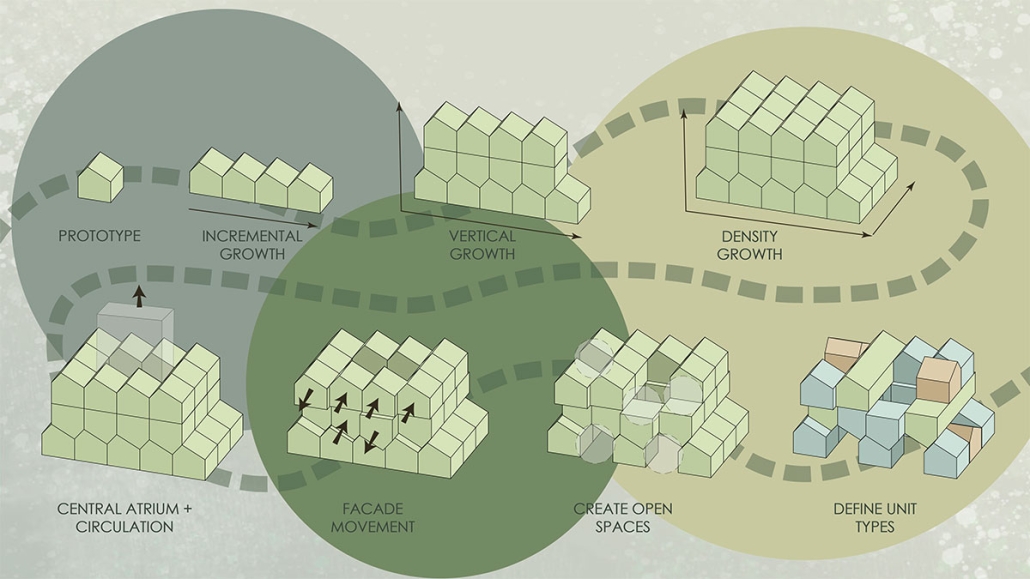
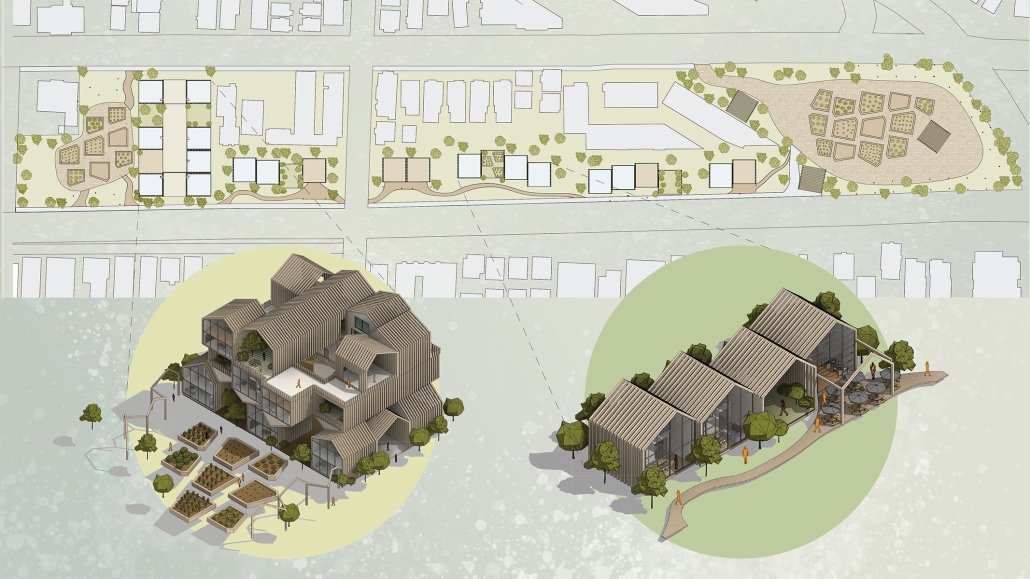
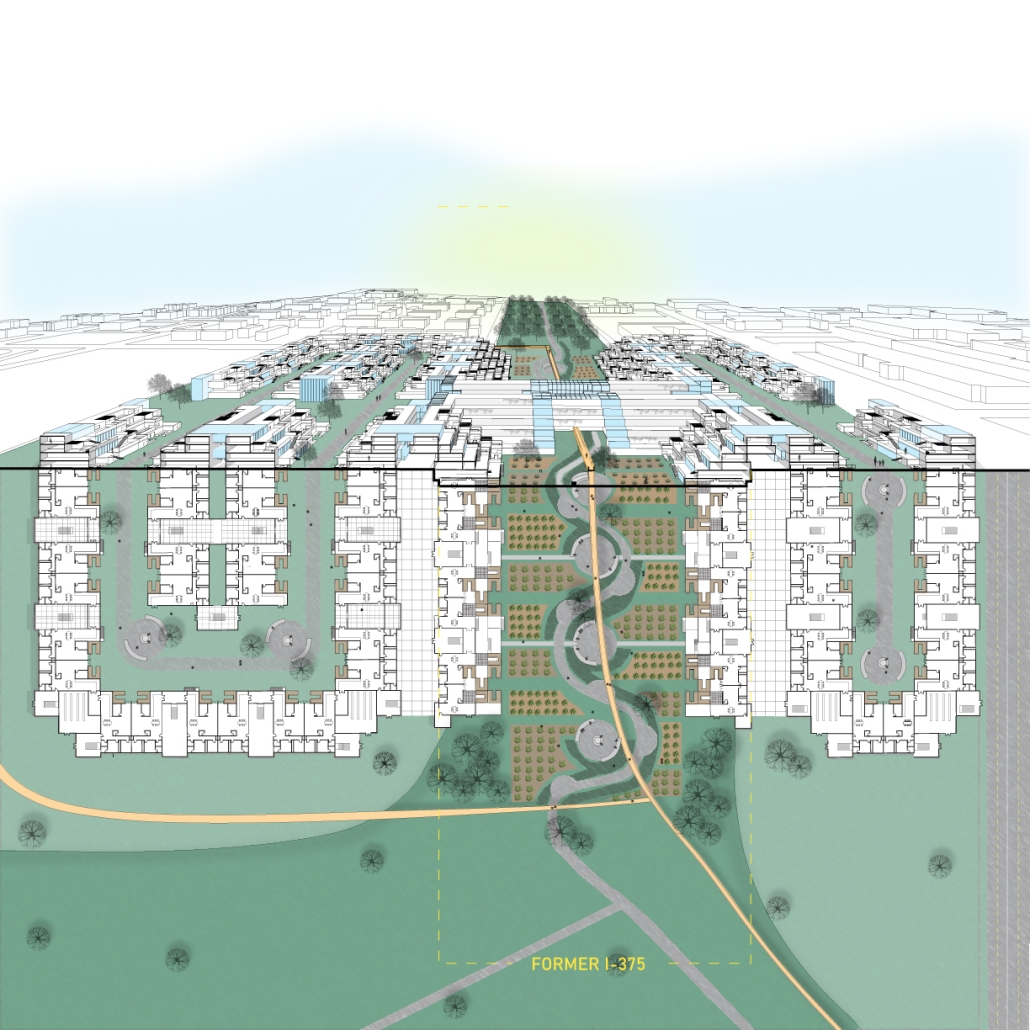
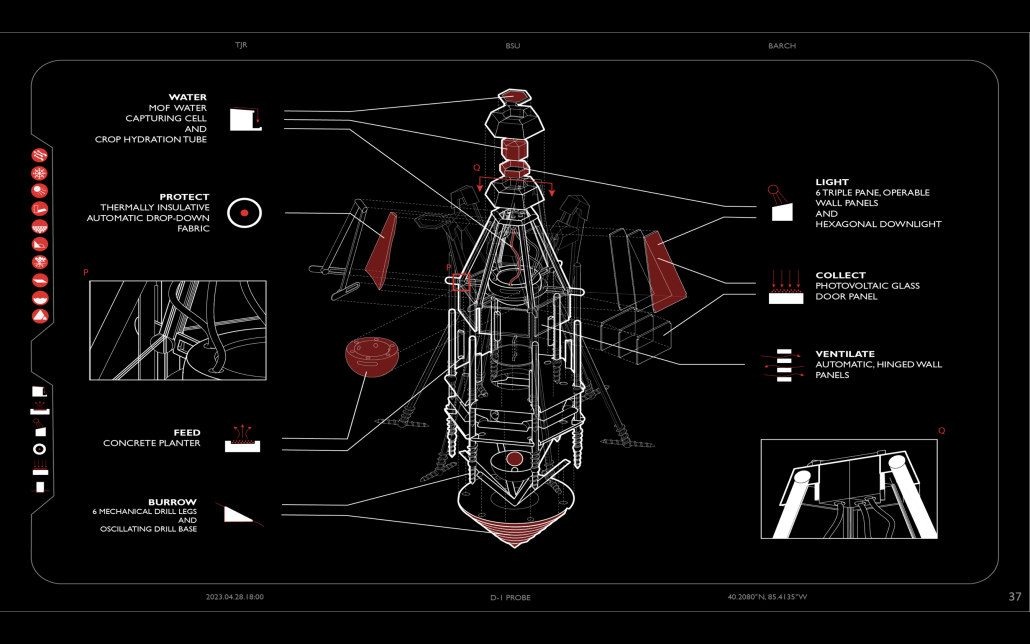
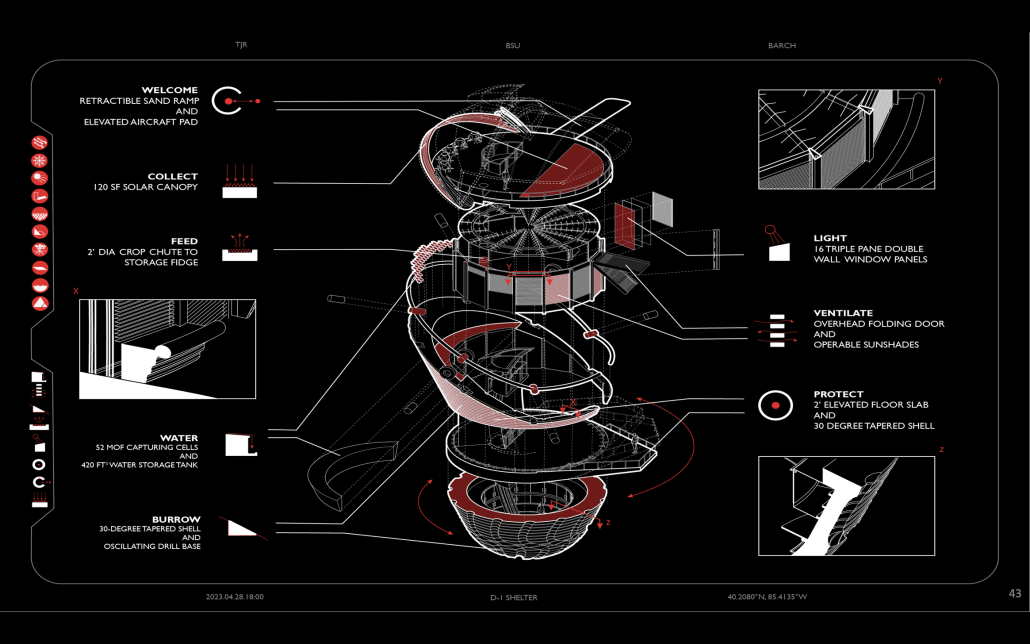
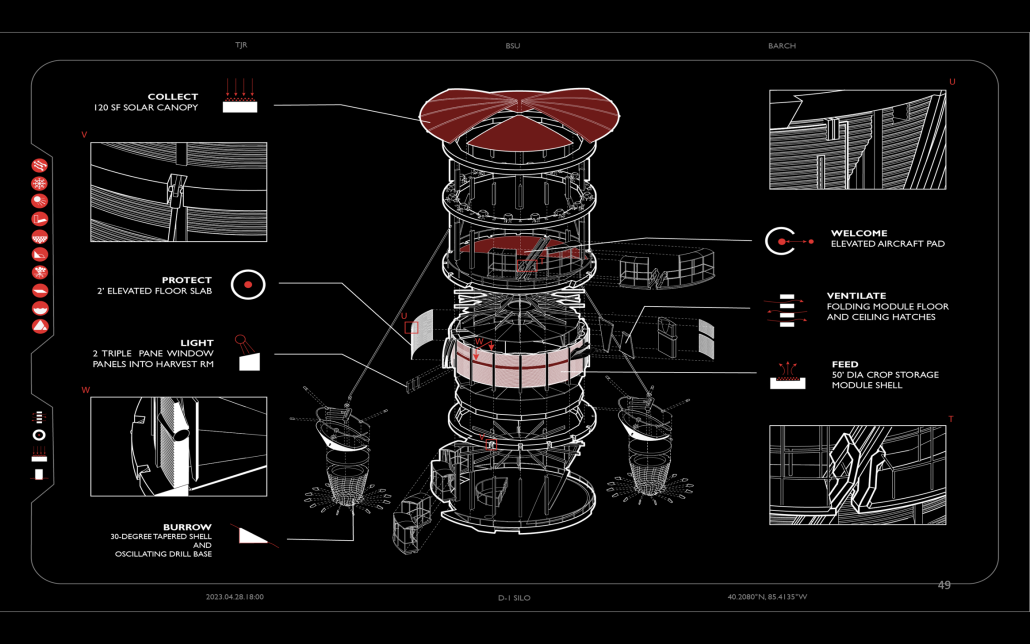
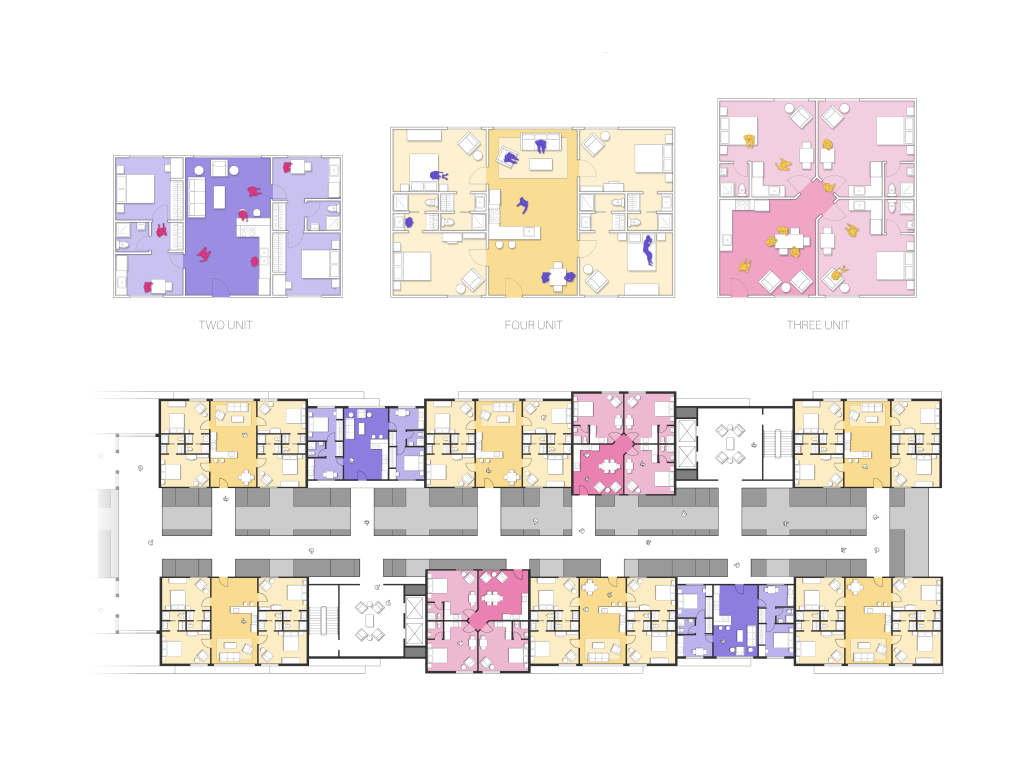
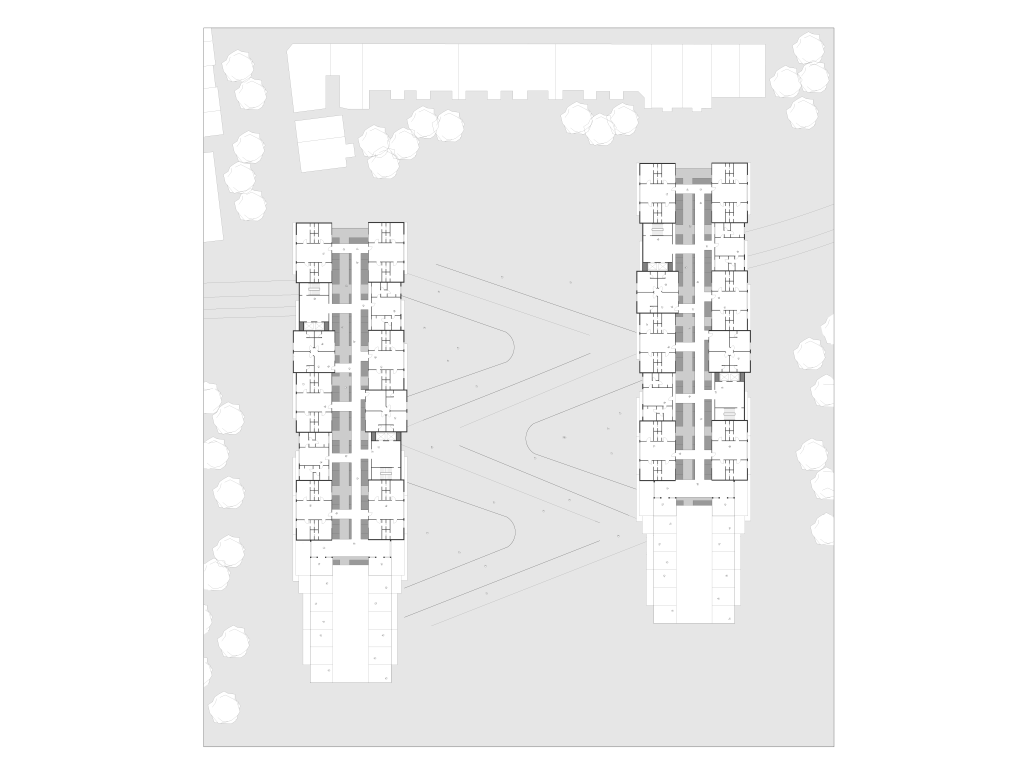
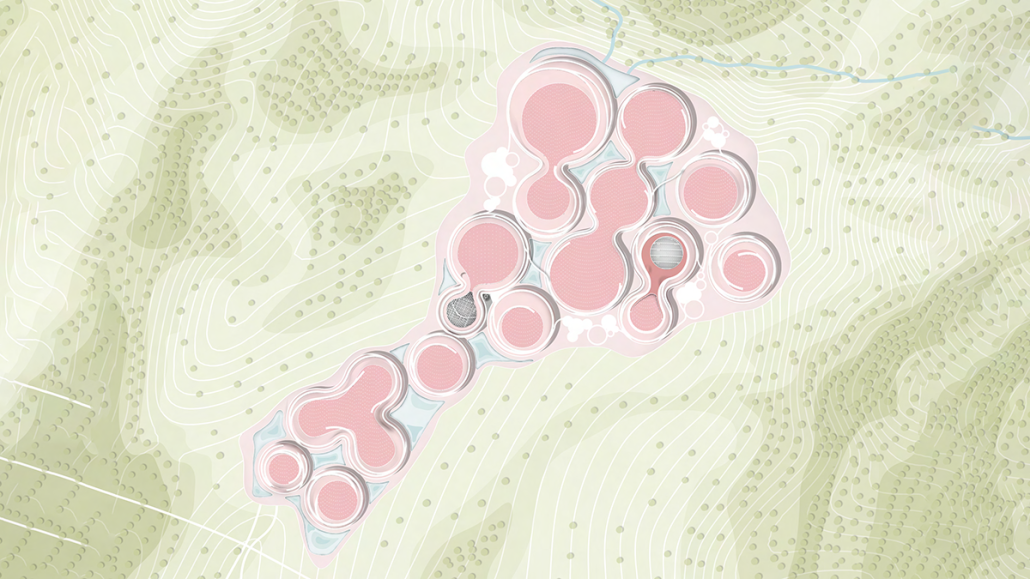
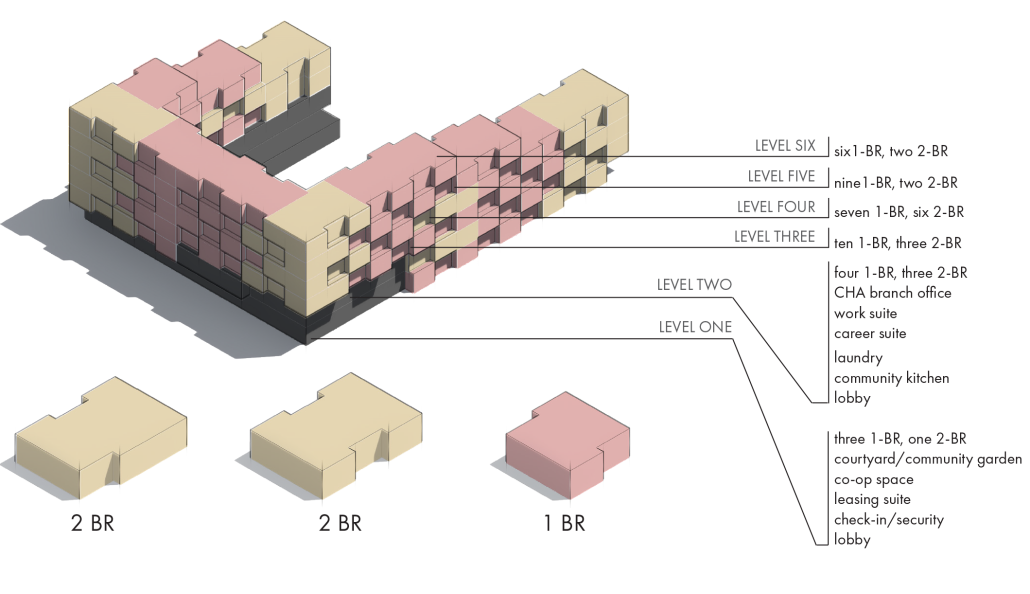
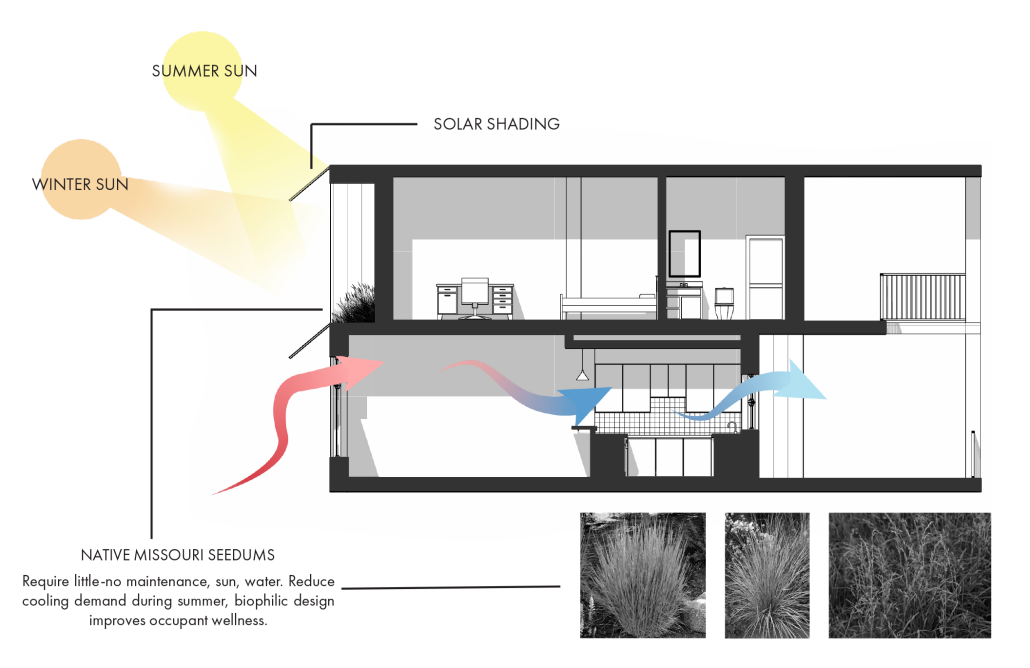
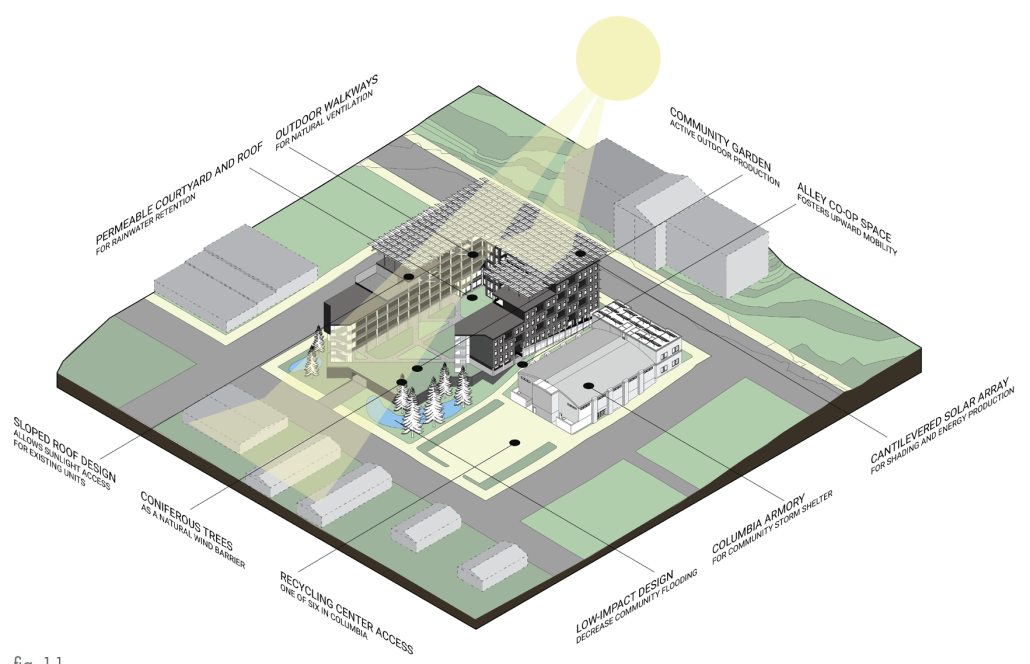
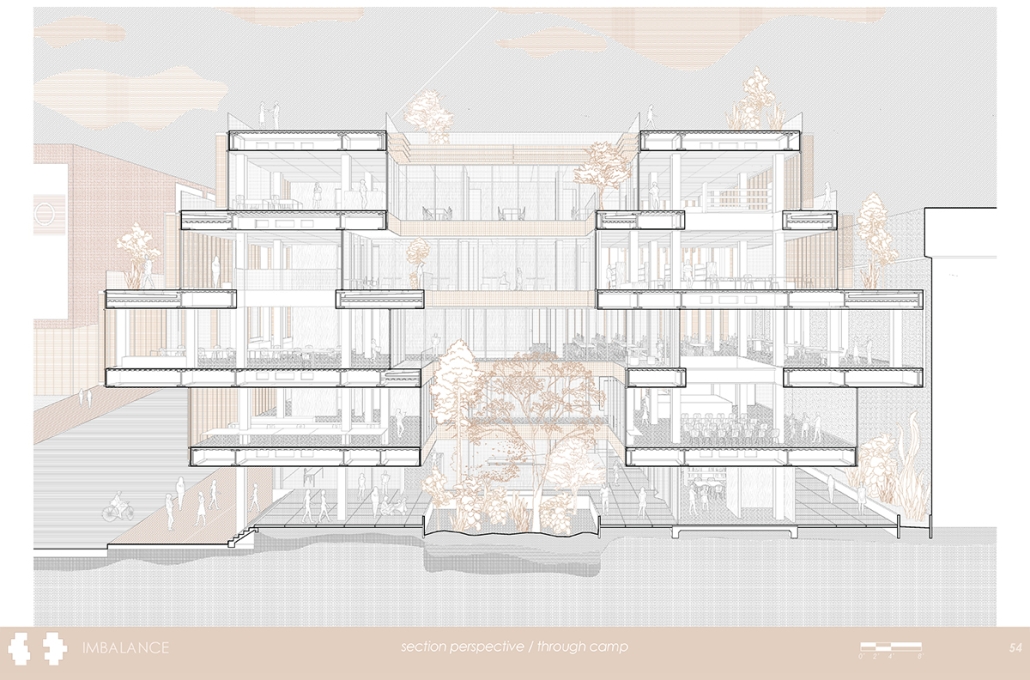
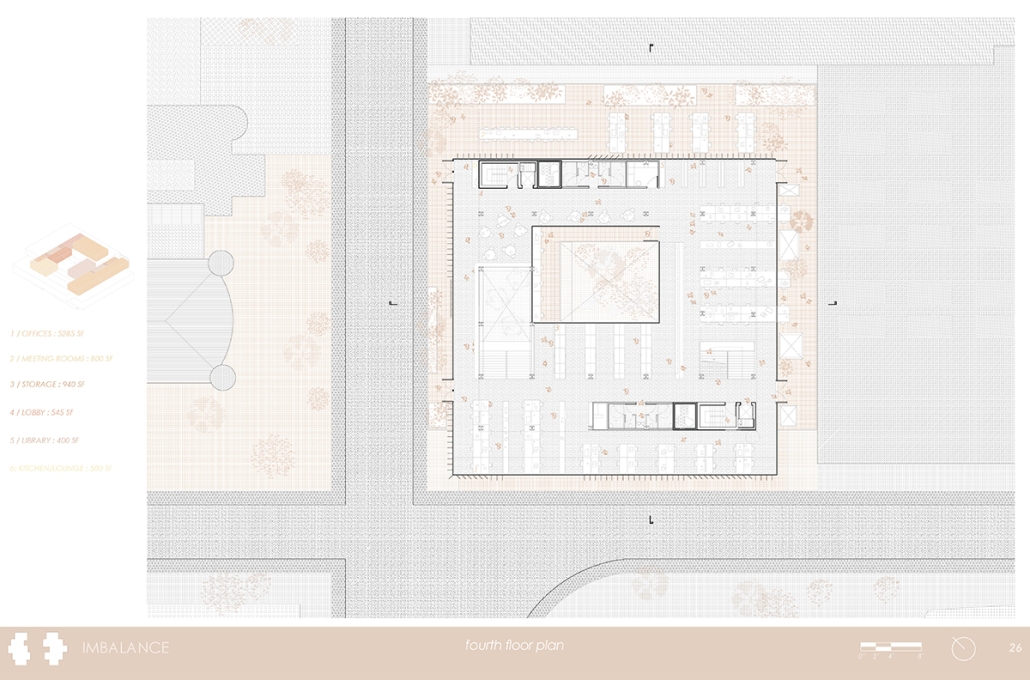
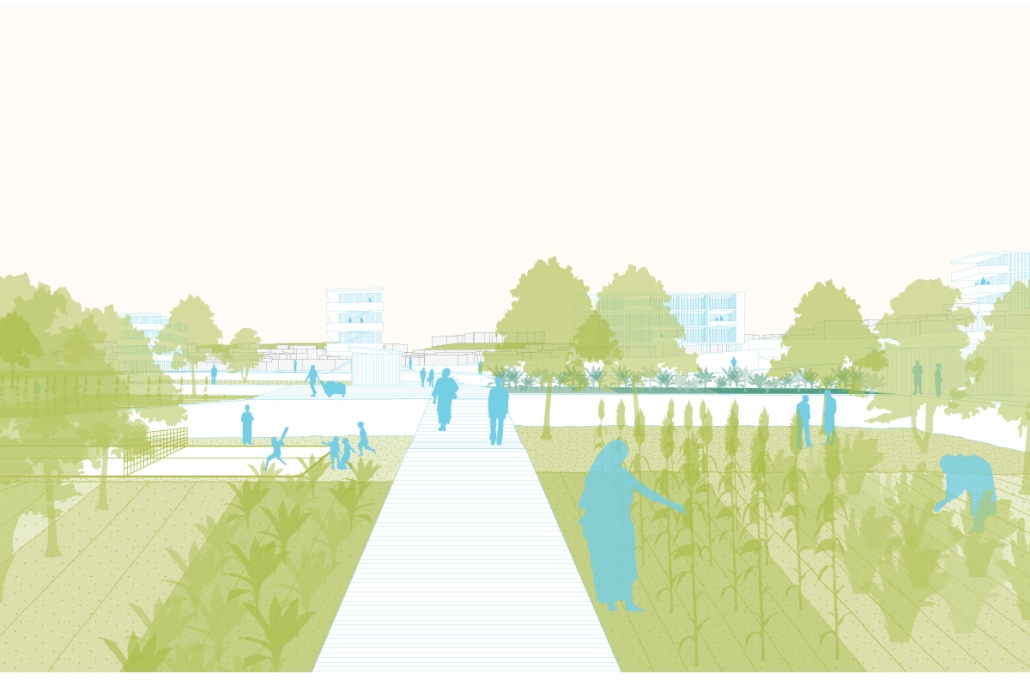
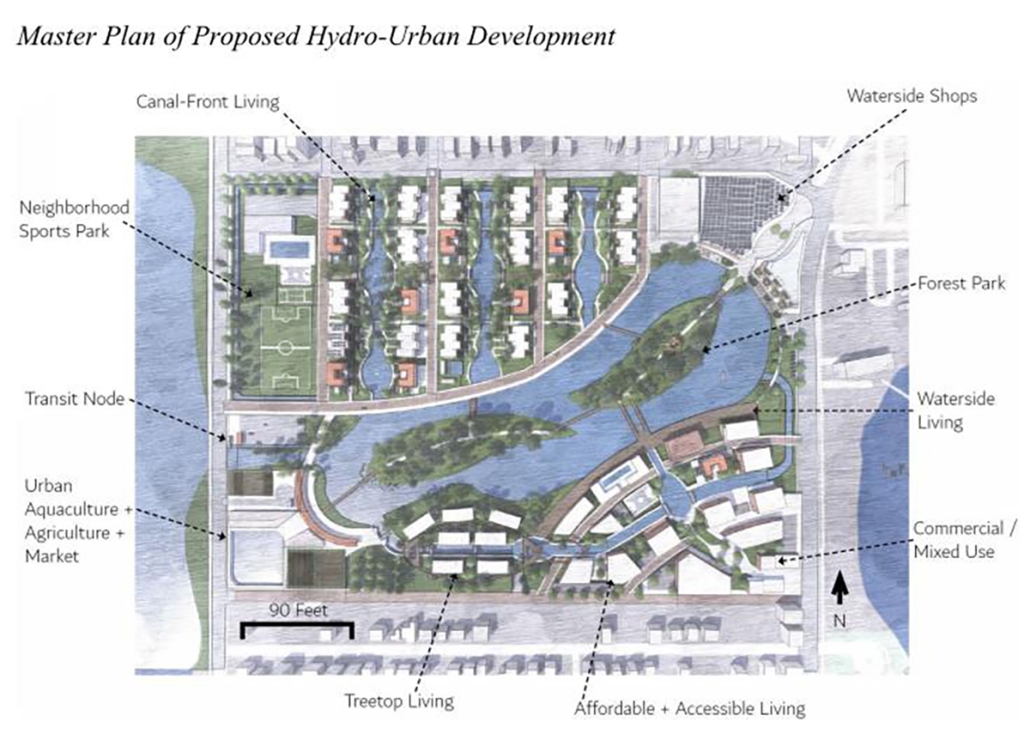
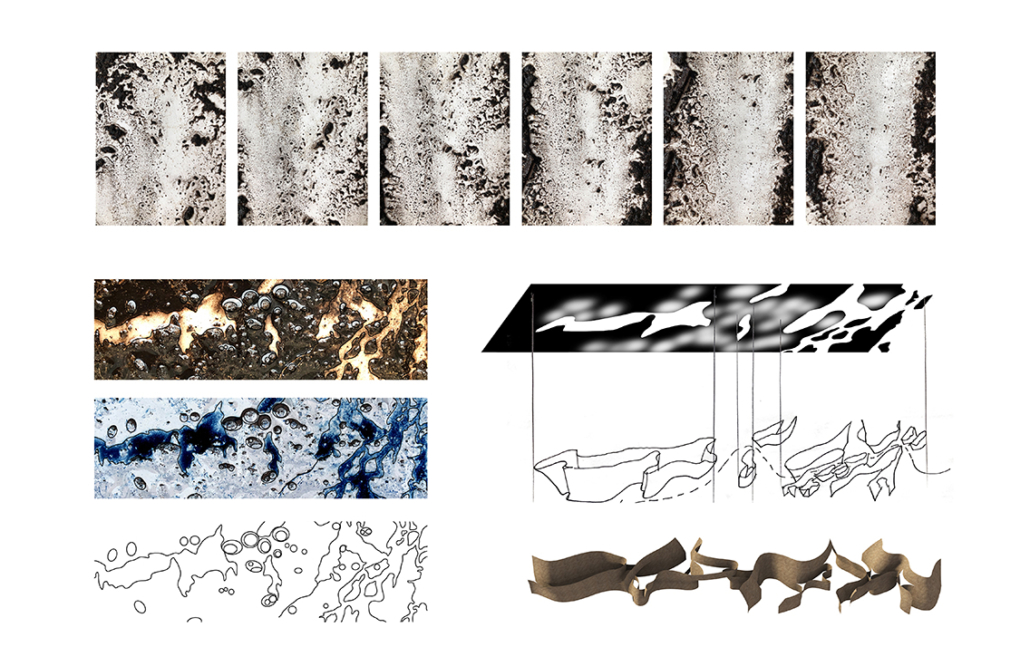
Glacier Jane envisions a zero-energy revitalization of Mariners’ Camp at Girl Scouts’ Camp Archbald, where urban activist Jane Jacobs trained her powers of observation on the riparian ecology surrounding Ely Lake. In 1938, Mariners’ Camp was constructed for a teenage troop on the north shore of a 45-acre glacial lake and boasted the first floating cabin ever built for the Girl Scouts of the USA. Today, Mariners’ Camp includes three pontoon platforms, two of which have floating cabins, a separate troop house with attached latrines, a standalone outhouse, a water station, platform tents, and a campfire circle.
Floating on the pristine waters of Ely Lake as they slowly flow into nearby Meshoppen Creek before joining the north branch of the Susquehanna River en route to the Chesapeake Bay, Glacier Jane will serve as a living laboratory for water research. Its gardens – planted with native species on the roofs, hanging from the railings, floating in the water, and terracing the landscape – will integrate with the dense lily pads and vegetation ringing the sunny side of the lake and with the surrounding shade of the evergreen forest to filter chronic acid rainfalls and nitrate-ladened, stormwater run-off. In addition to improving the water quality of the Chesapeake Bay, Glacier Jane will also extend the Girl Scouts’ focus on combining observation, self-reliance, and harmonious living with hands-on, STEM educational activities.
This project won the Second Prize, Retrofit Housing Division of the 2023 Solar Decathlon Design Challenge.
Instagram: @glacier_jane, @jodilacoe, @tessrose13, @alaudone, @maria_iarch, @marywood_architecture
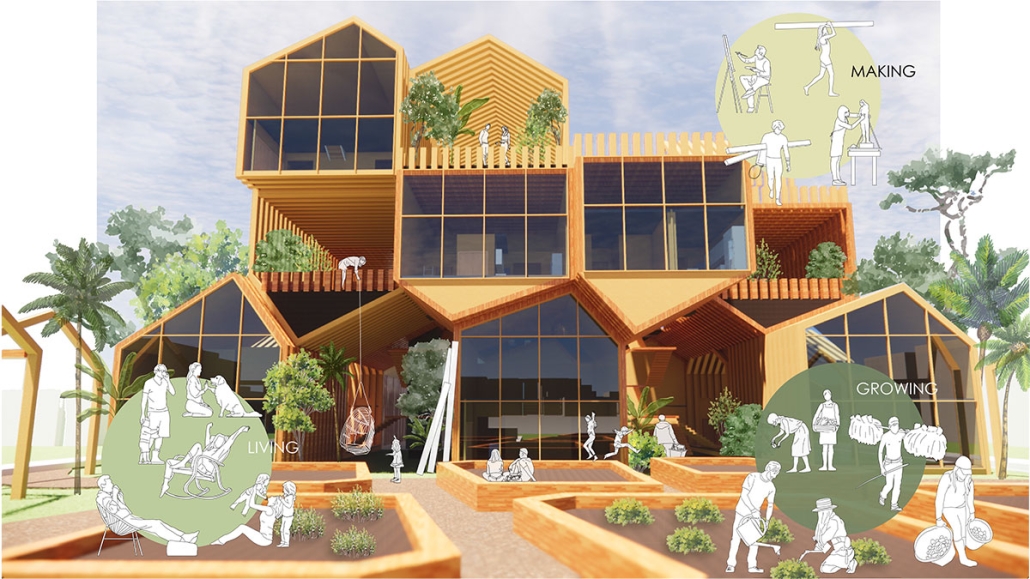
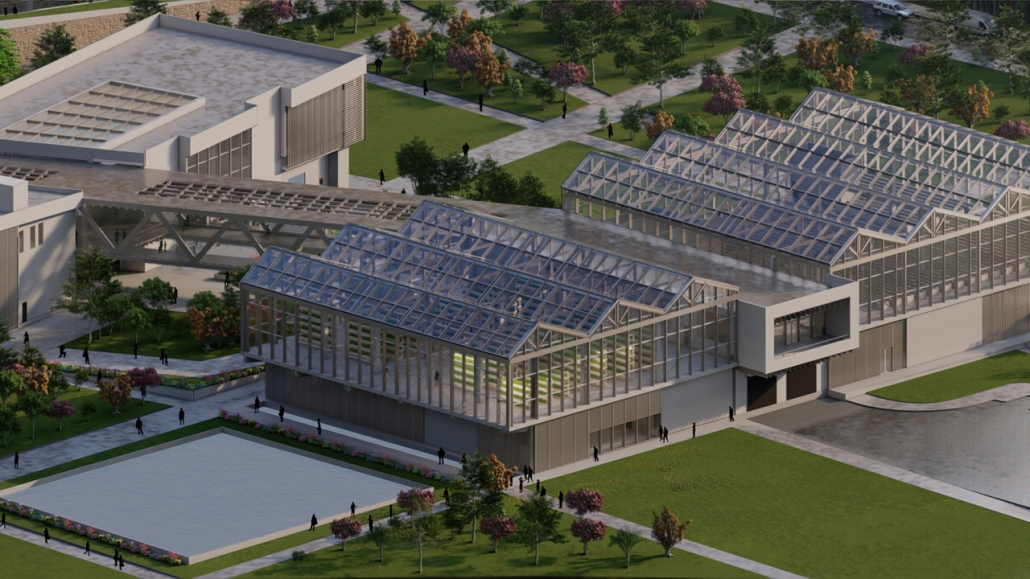
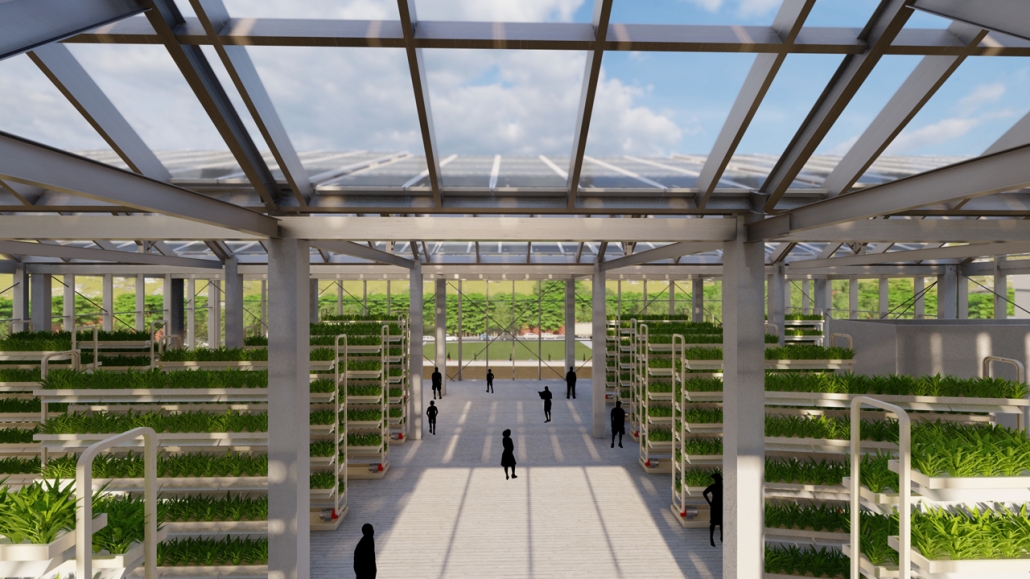
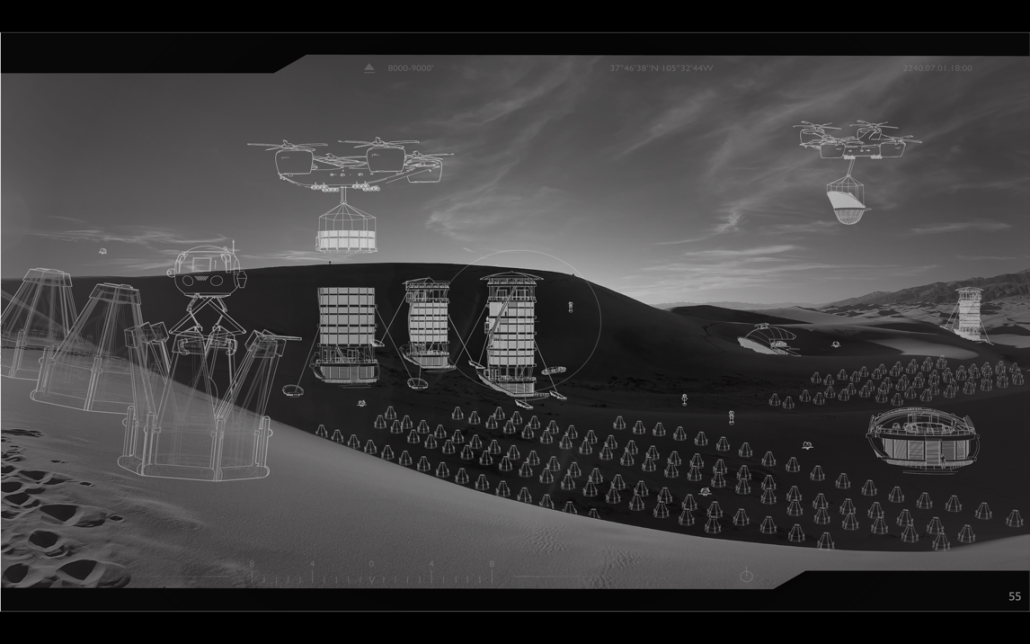
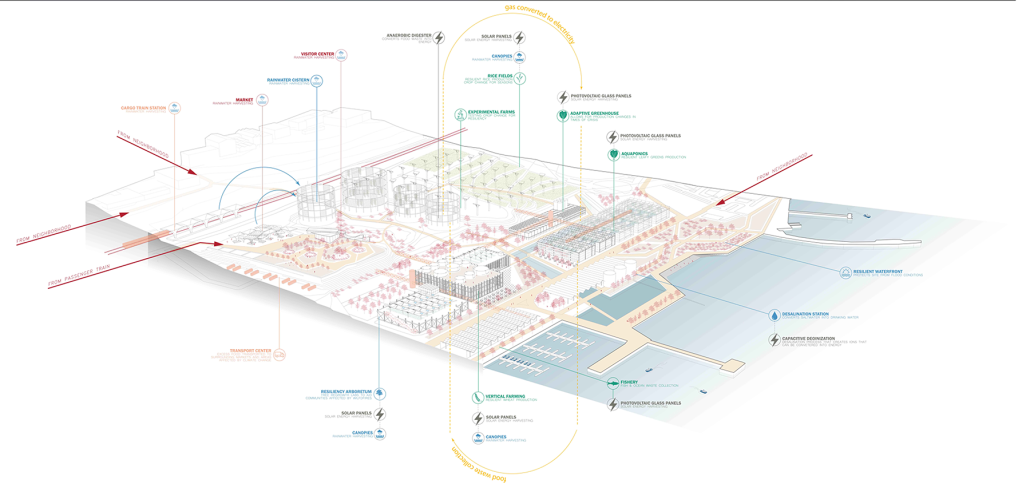
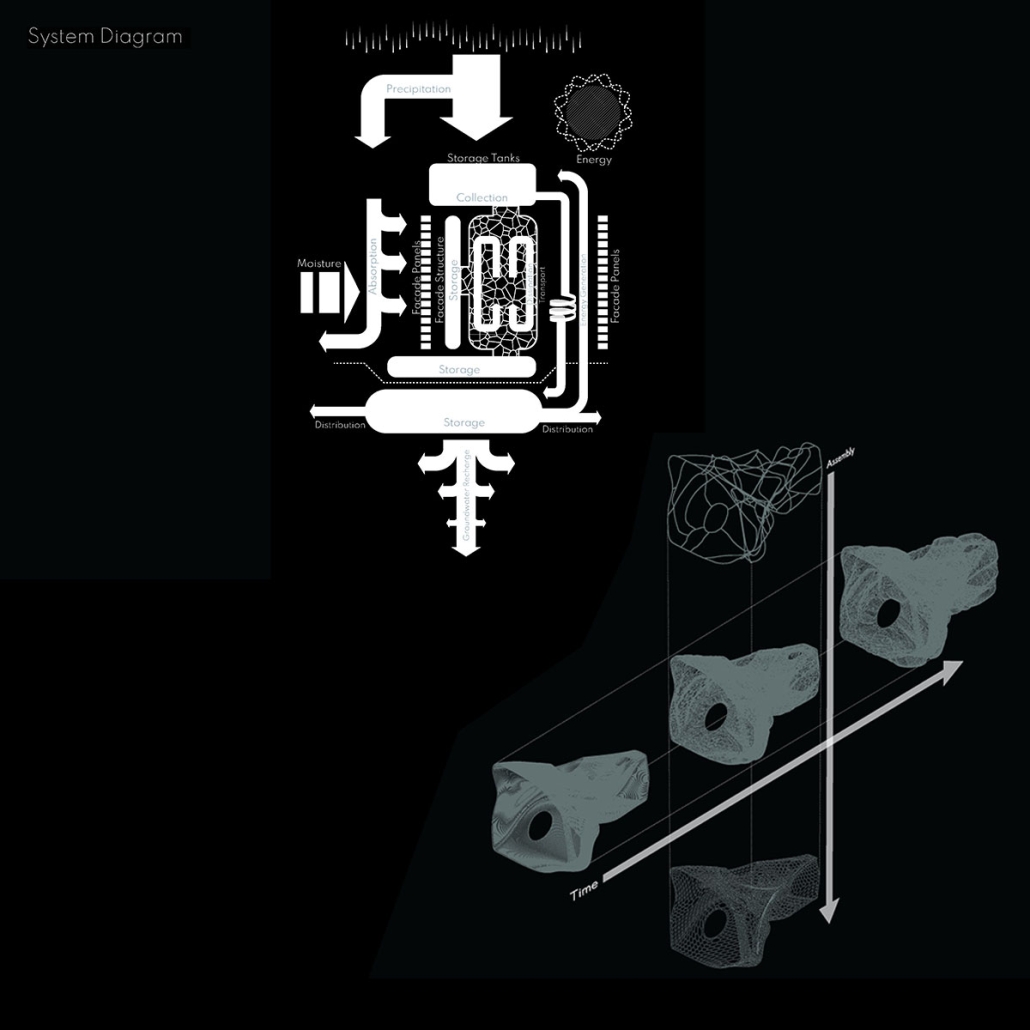
Aquatecture as Mitigator of Water Scarcity by Yolyanne A. García-Meléndez, B.Arch ‘23
Pontifical Catholic University of Puerto Rico | Advisor: Pedro A. Rosario-Torres
Global warming is a problem that occurs over long periods of time. It affects us little by little, but we increasingly notice the change it produces in our daily lives. With global warming, a number of problems arise that affect human lives, one of these is drought. Due to the high temperatures on the planet, the availability of water reduces while its demand increases. According to scientists, “the predictions point to a considerable increase in droughts: for every degree that the temperature increases, we will see a 4 percent reduction in rainfall, so we will suffer reductions of between 5 and 20 percent.” This affects humans, animals and the agriculture of a place. If drought extends too long, what we know as famine can occur. Drought depends on the climate and it can be caused by two different variants that affect the weather, thus causing a lack of rain. The first one is natural, either by changes in atmospheric patterns or variations in solar activity. The second is caused anthropogenically, with the main reason being global warming due to bad human practices against the environment.
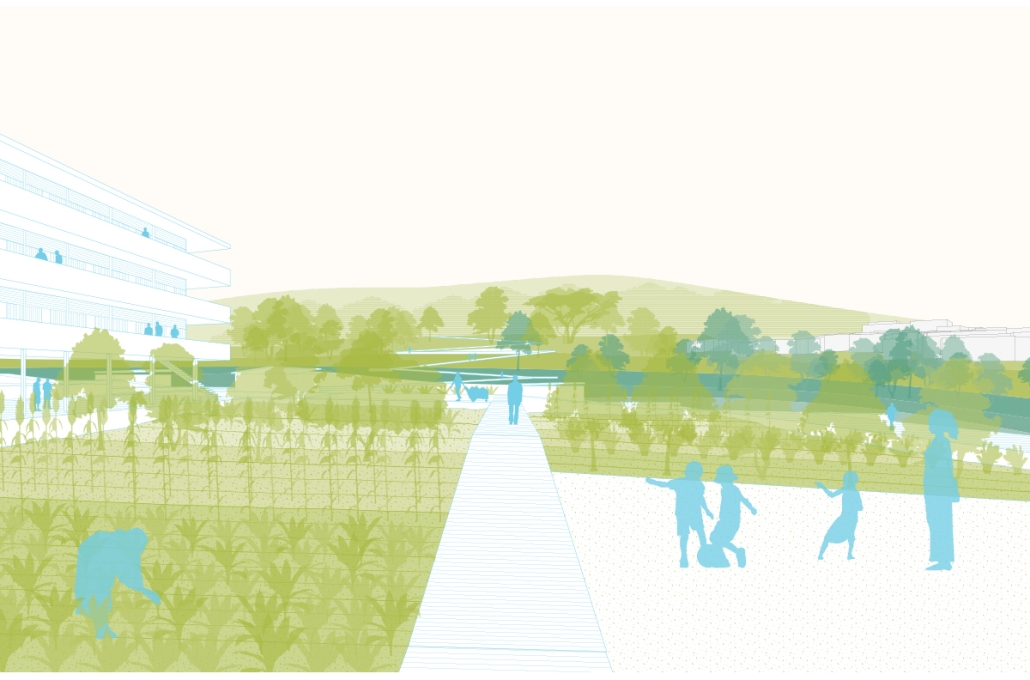
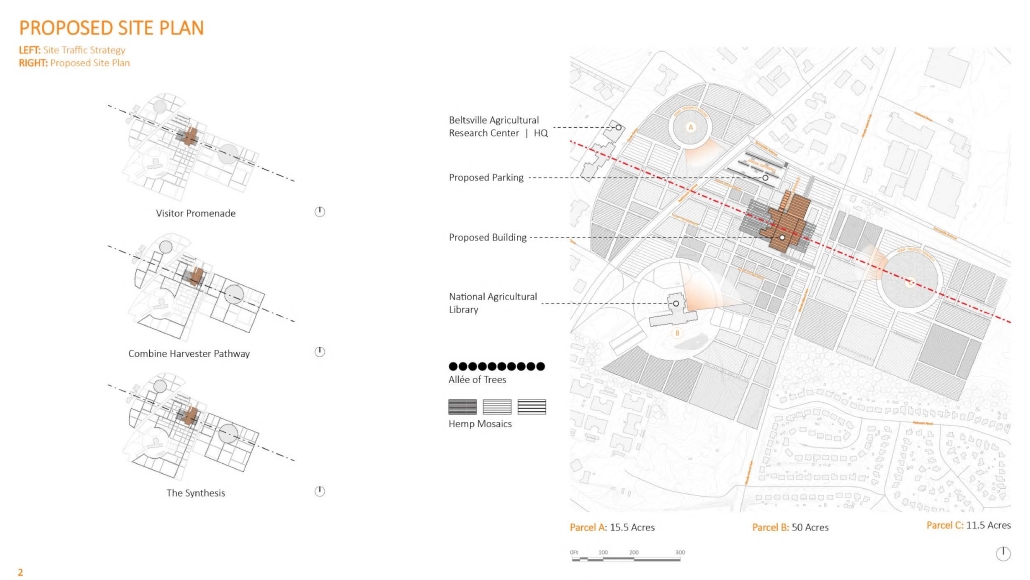
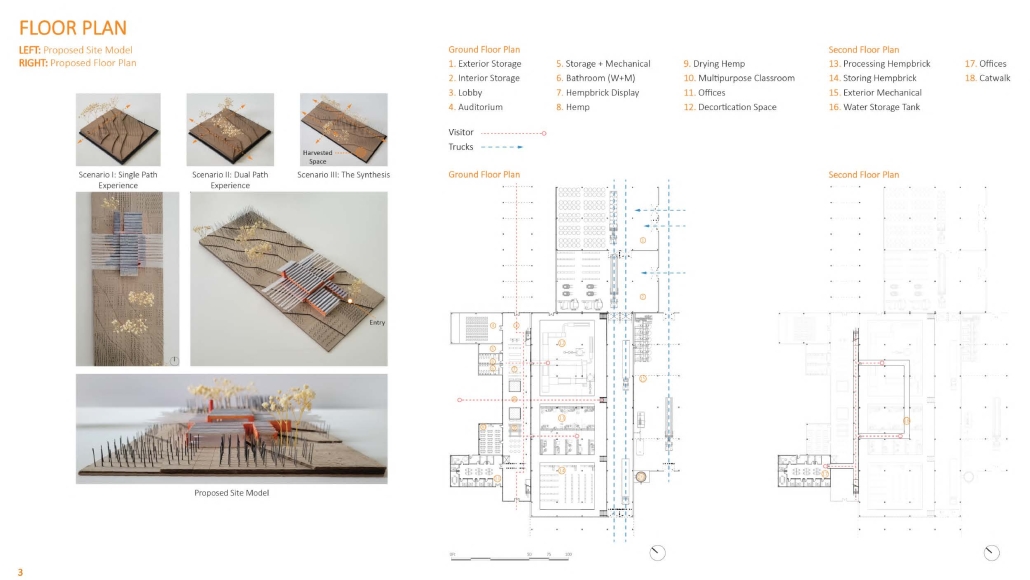
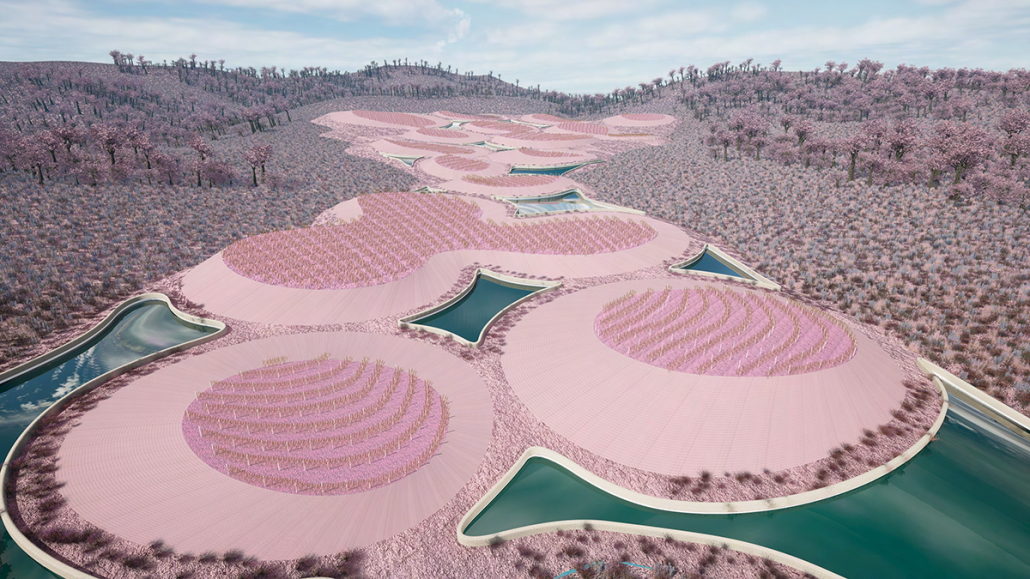
The project’s location in Copiapo, Chile, is a town located in the Atacama region and desert, and one of the driest places in South America. Chile is big on crop exportation and importation for its agriculture is very important. It is also known for its history of dry seasons and a big drought that lasted for about 10 years. The proposal seeks to collect and distribute water to the nearby crops. The idea was to create a water pump experience, using the water from underground canals that the visitors could see and learn from, while also enjoying the process of collecting water and distributing it to the crops. Spaces for restaurants, a museum and stations with important information aim to create awareness of water management and usage. The project also serves as an information center and tourist spot, with the goal of maximizing water for crops and food for the city.
Instagram: @y_anne_
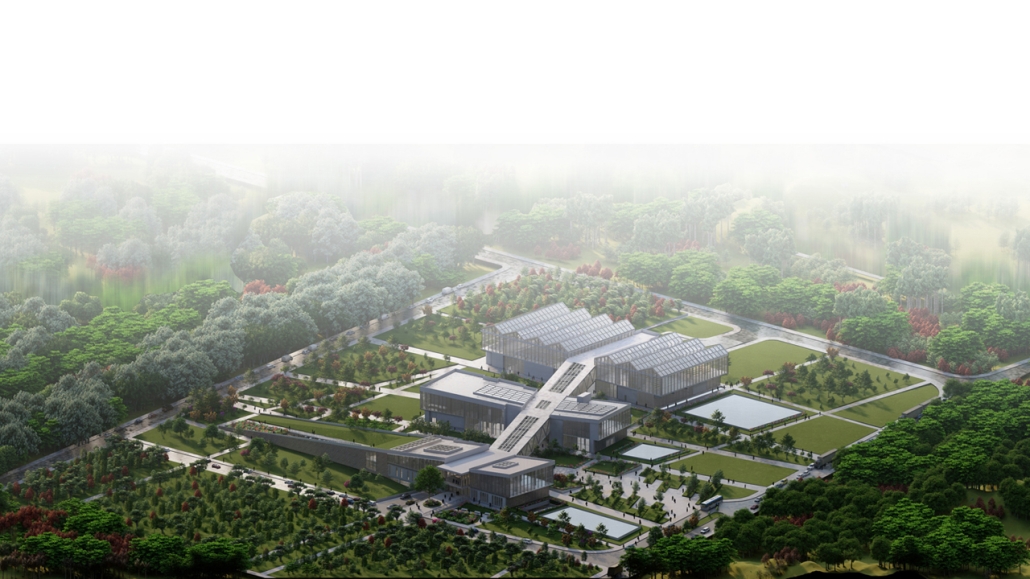
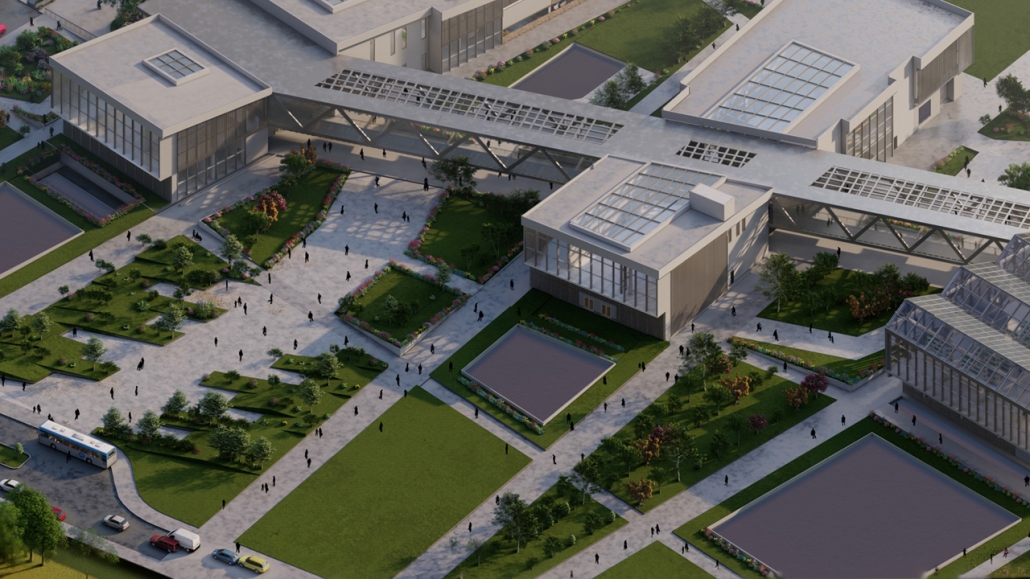
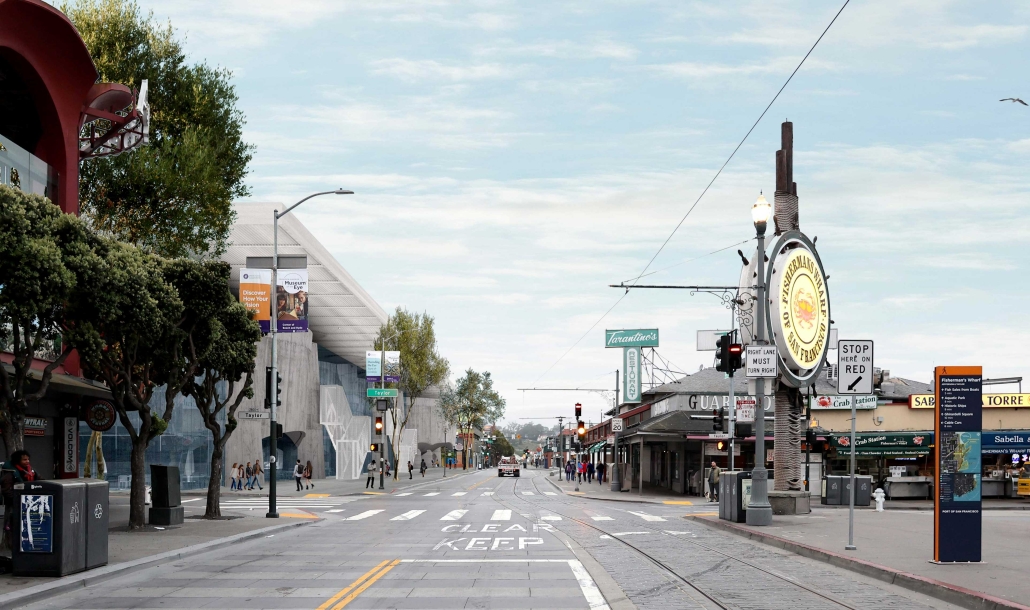
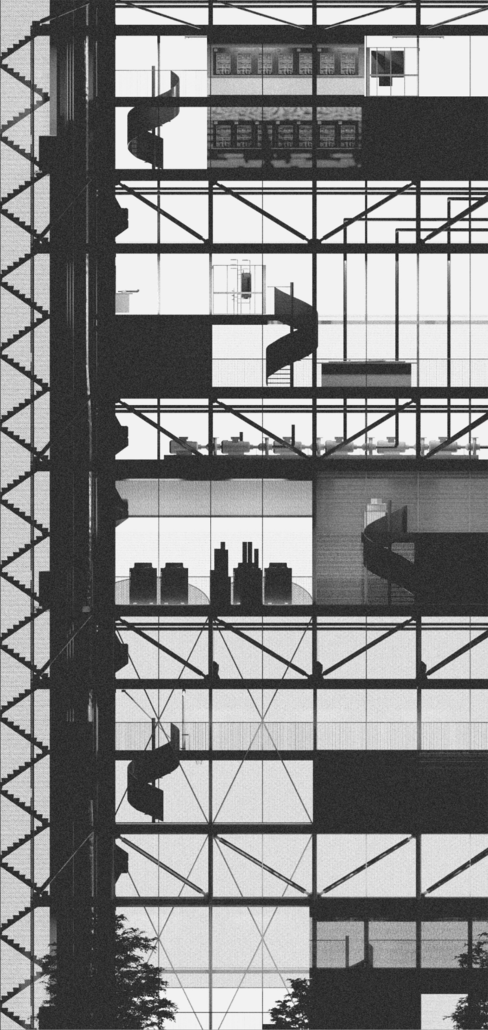
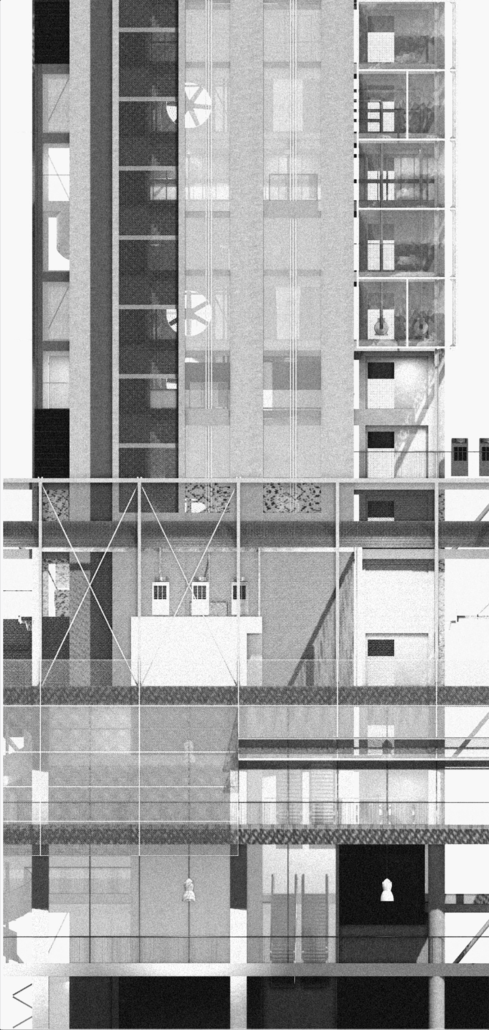
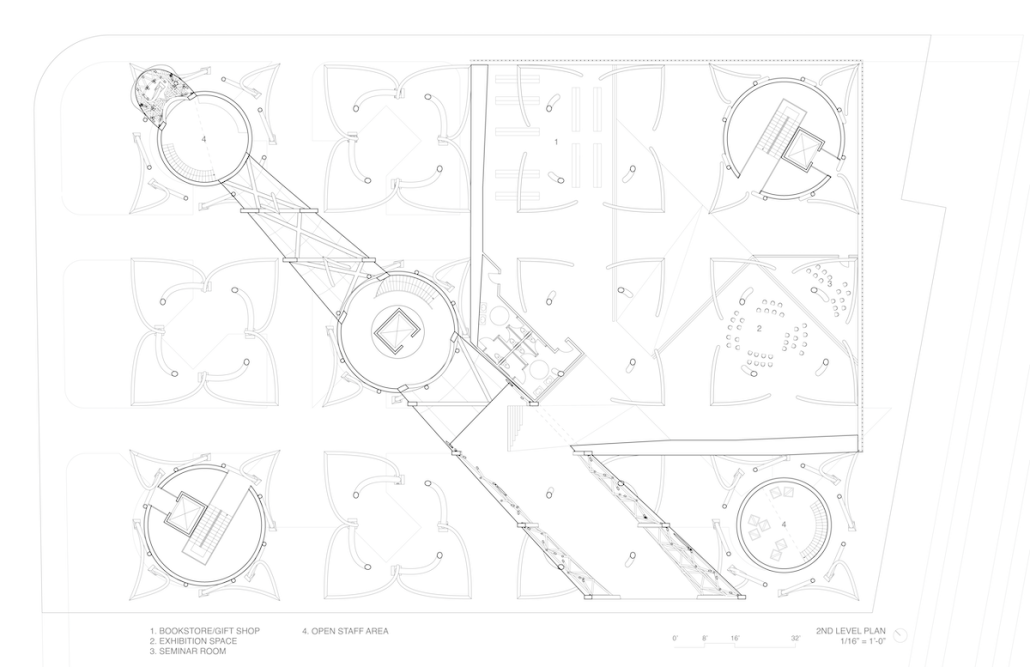
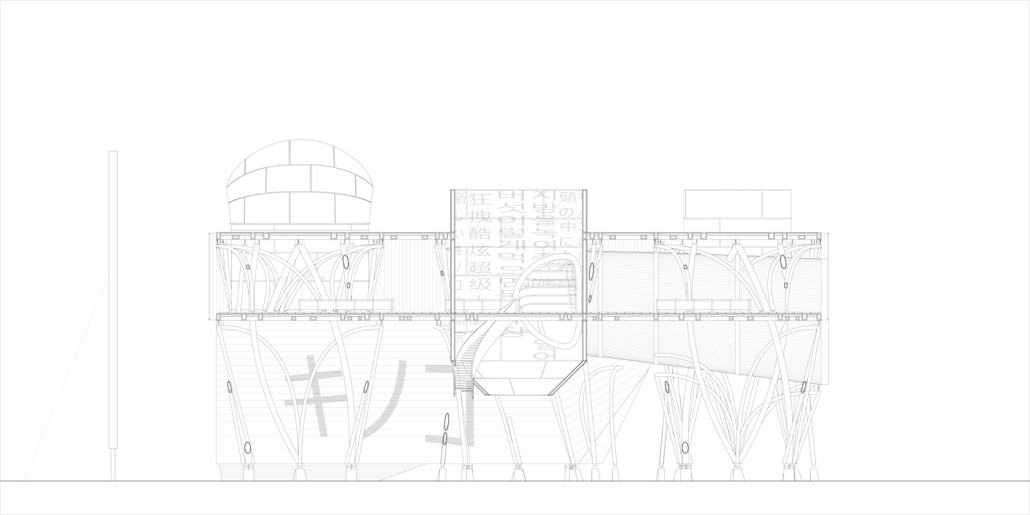
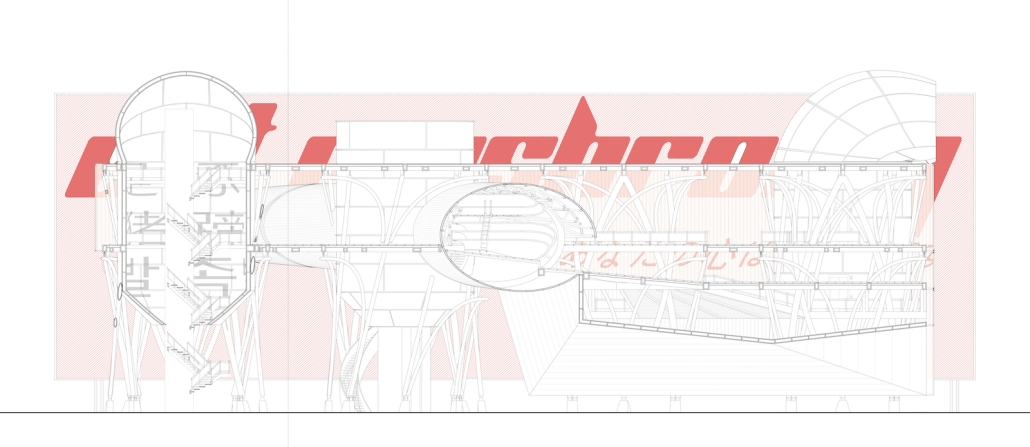
Education Point by Francesco Manninno, B.Arch ‘23
New York Institute of Technology | Advisor: Evan Shieh
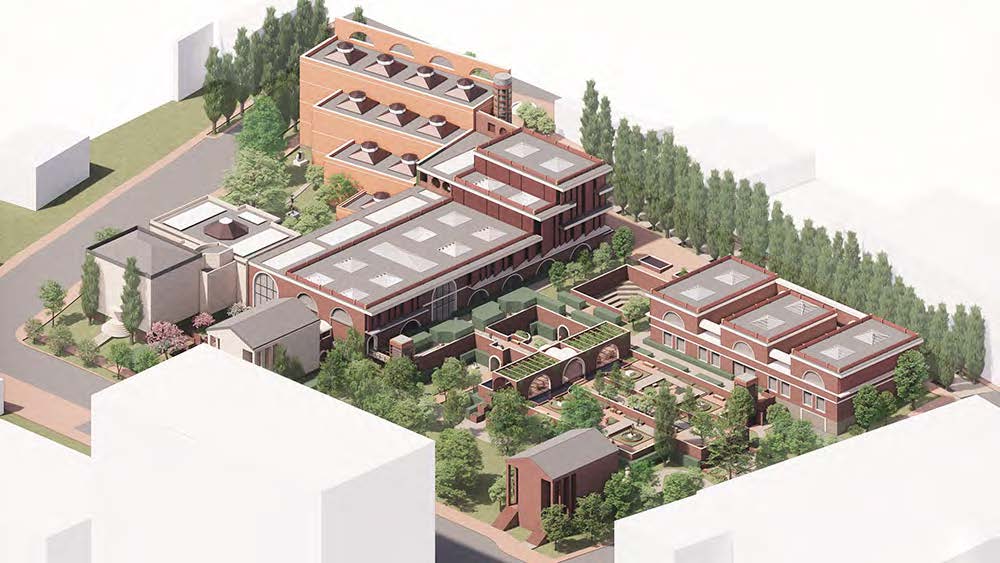
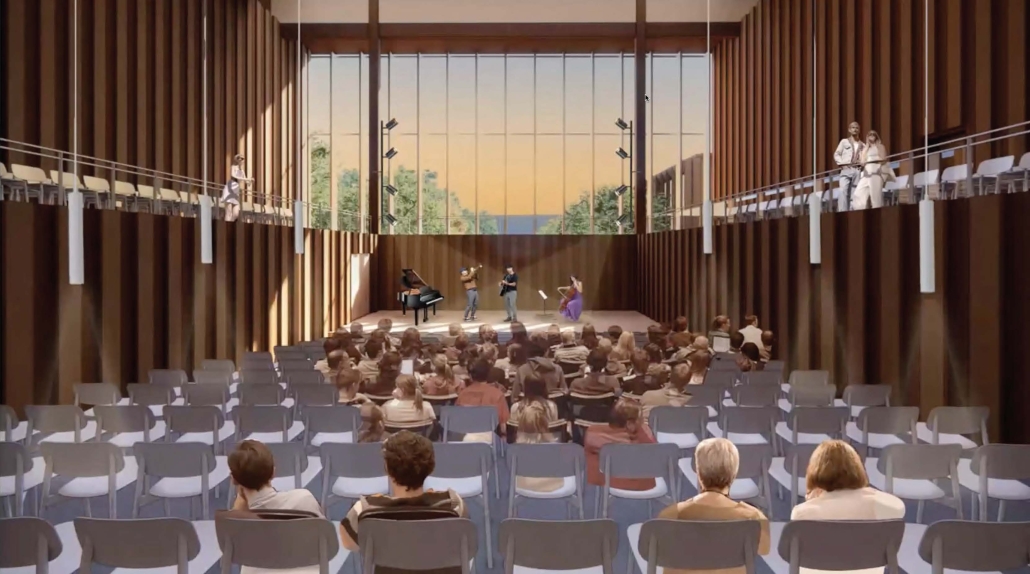
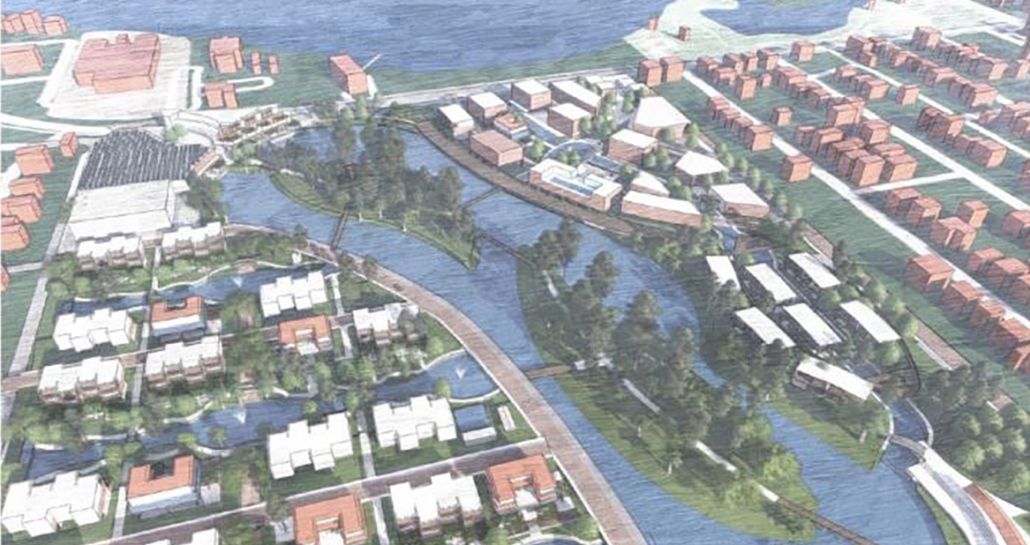
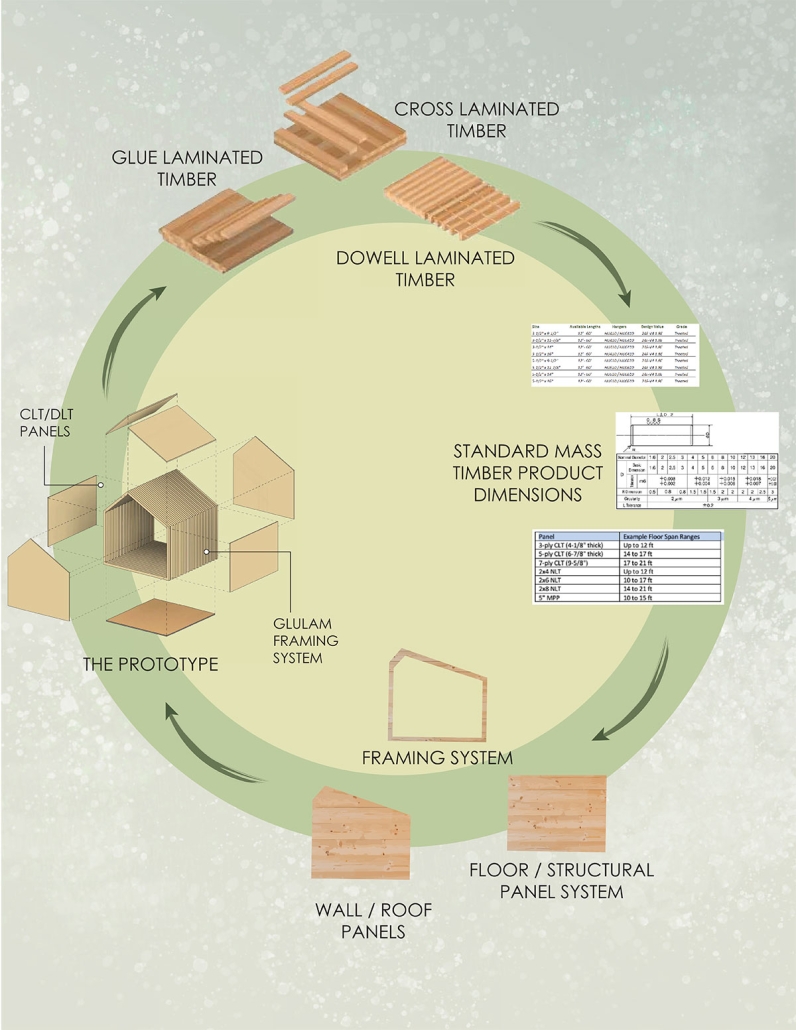
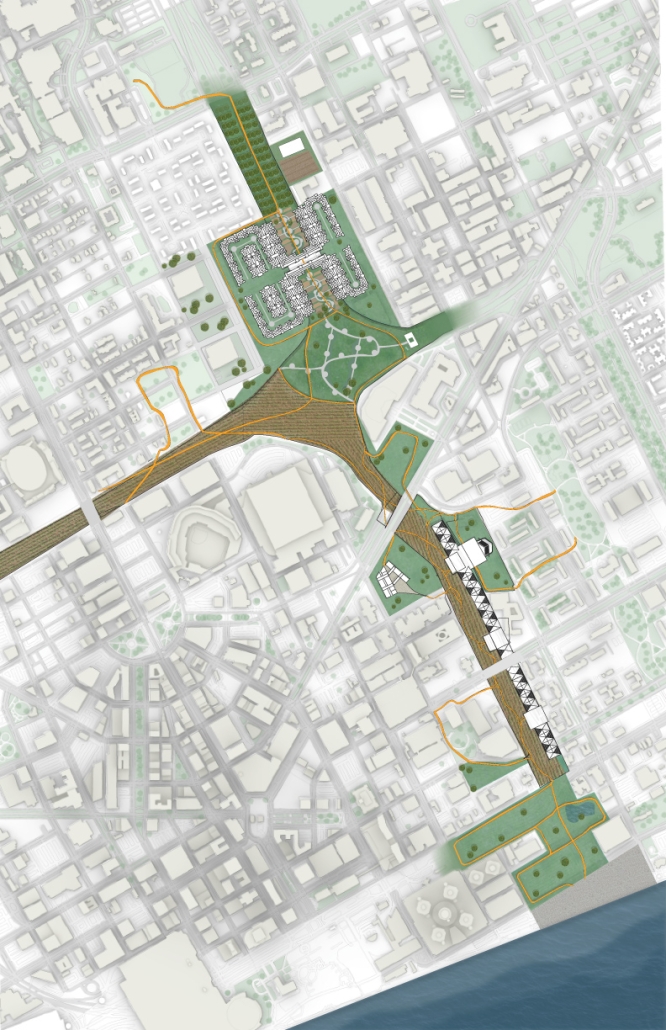
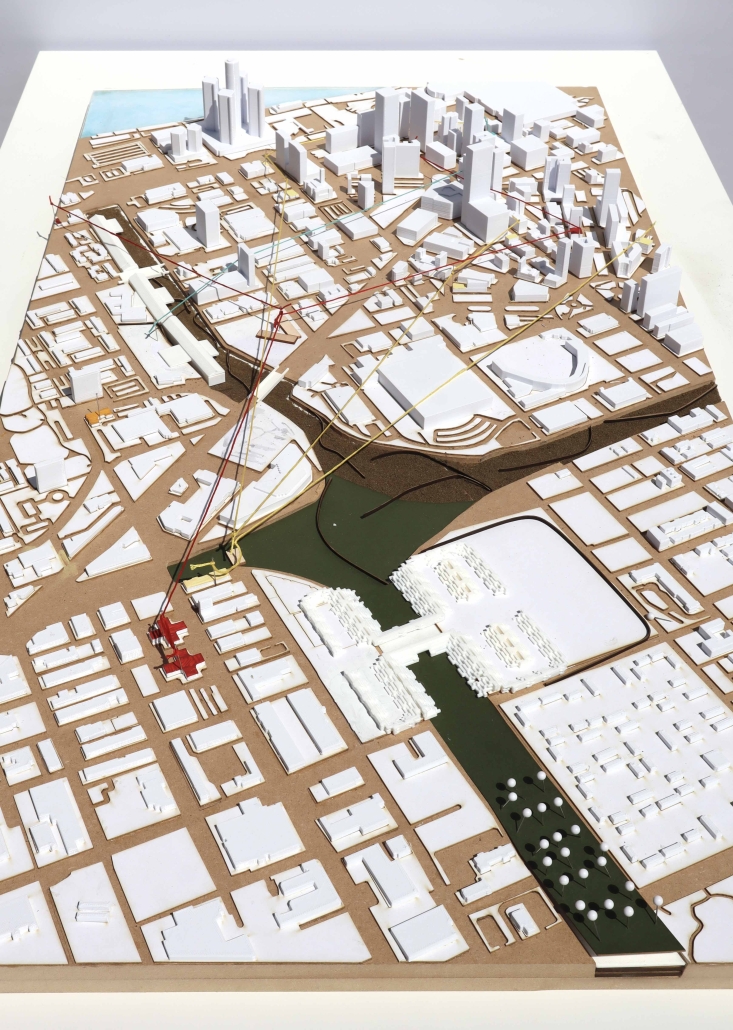
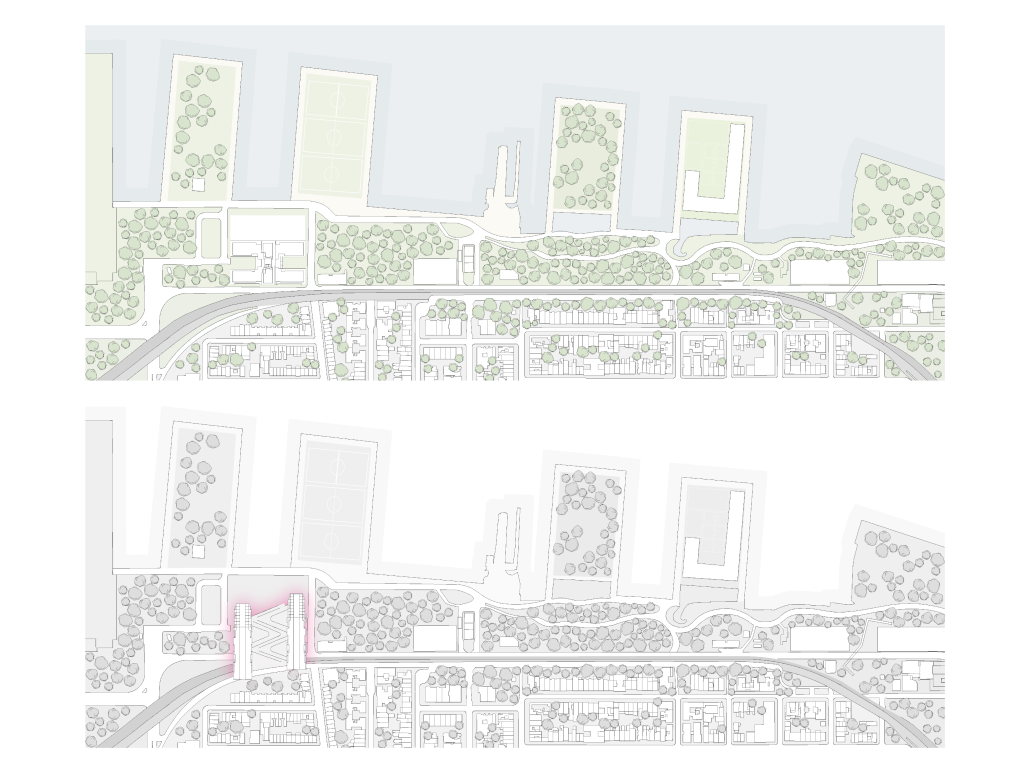
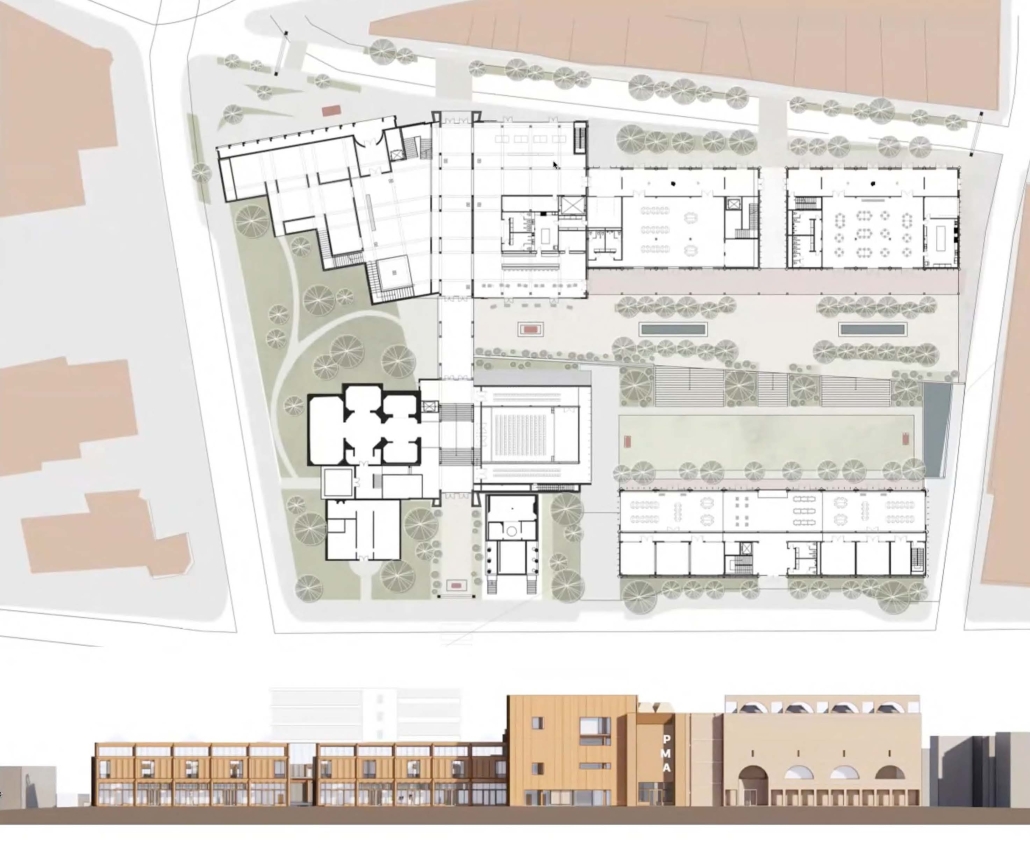
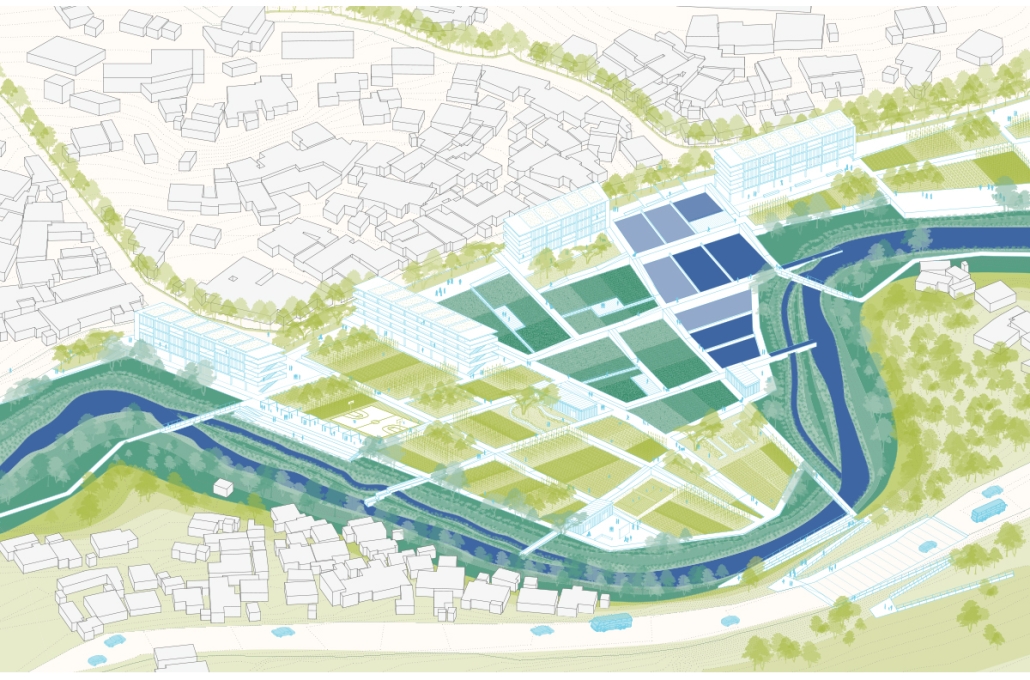
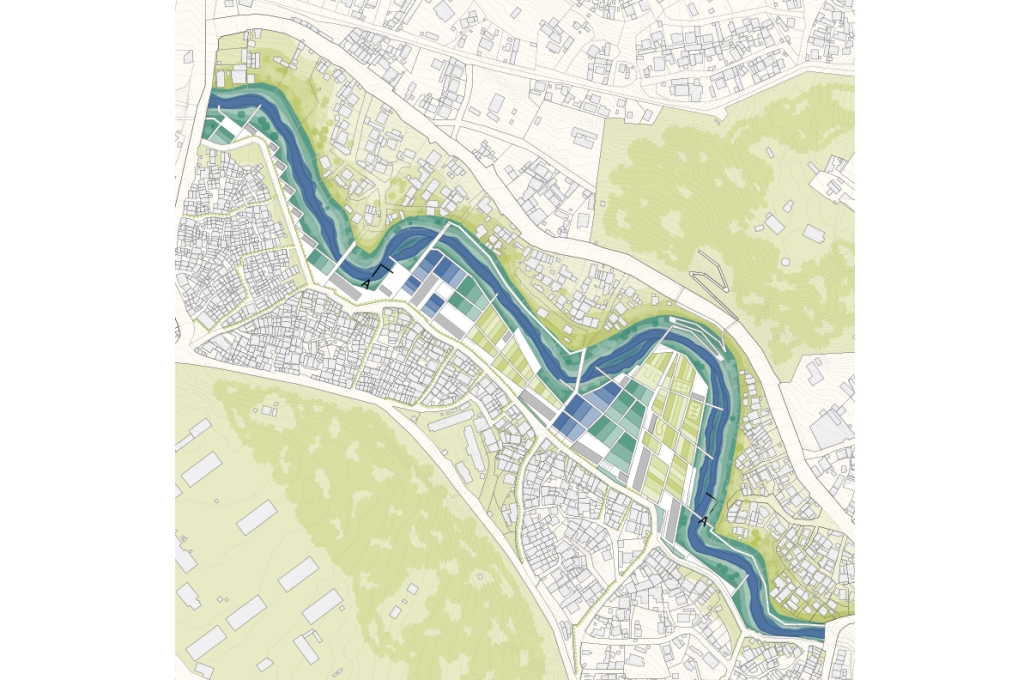
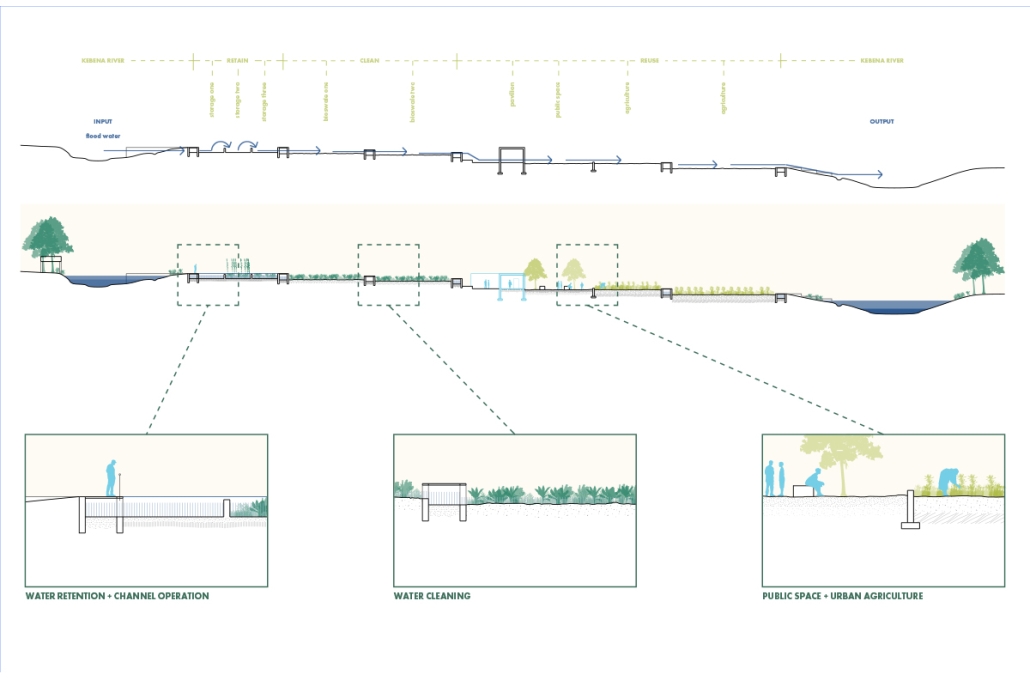
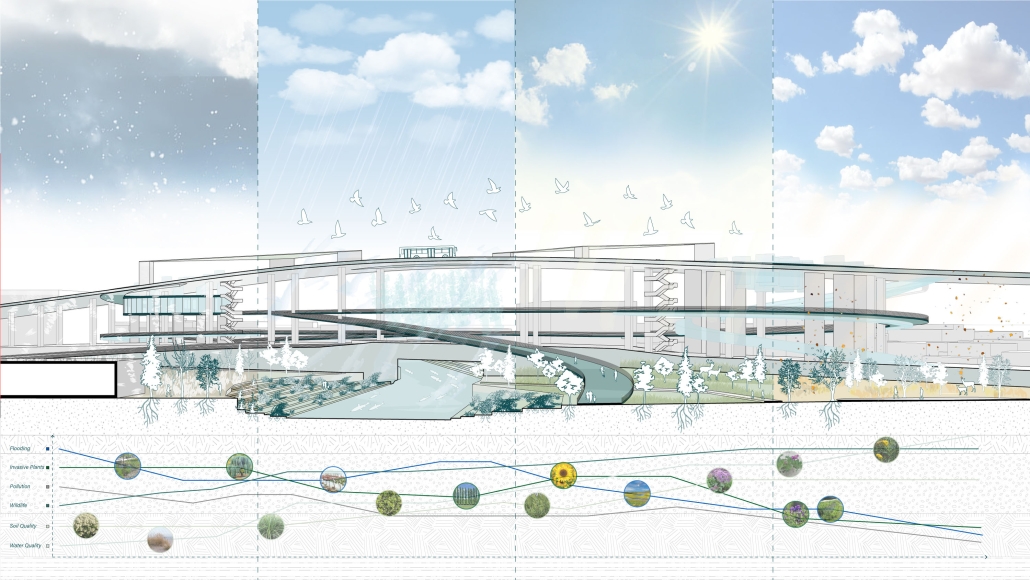
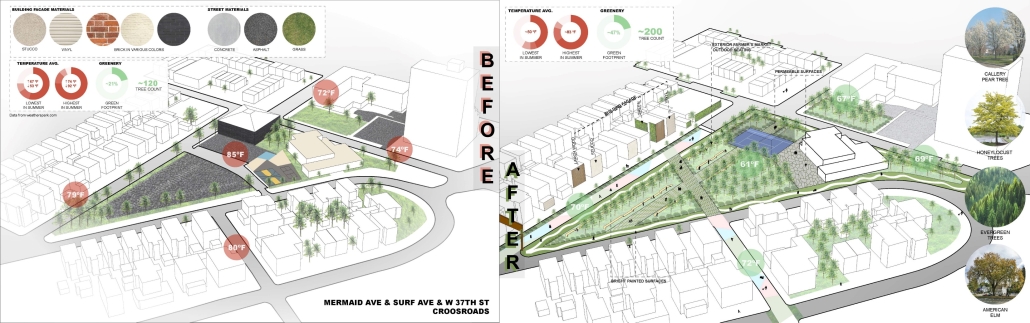
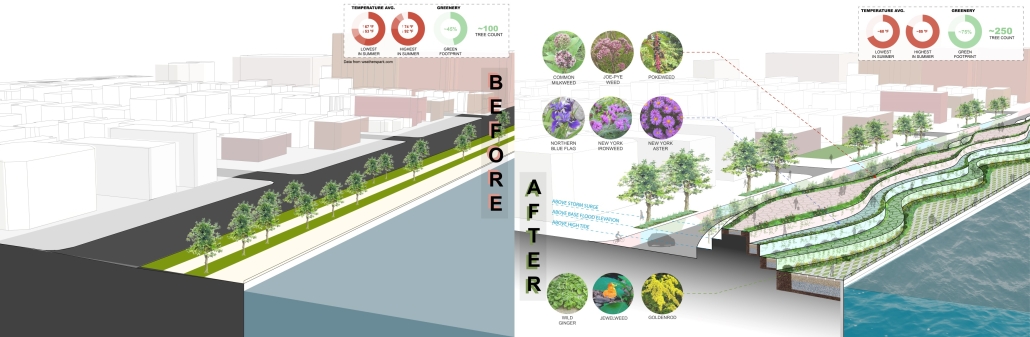
Duluth, MN, is a mid-size American city that historically relied upon declining mono-industries (like ore + timber) and mono-functional transportation modes to fuel its economic growth. Education Point is a Marine Research + Development Satellite Campus proposal that provides a blueprint to transition the city’s future towards education and tourism as more sustainable industries. Located on Duluth’s shoreline at the termination point of Interstate I-35, the project spans over and transforms an underutilized highway to reconnect the city to its shoreline while simultaneously providing a local educational hub for neighboring university institutions and the greater public.
Instagram: @studio.fs2, @ev07
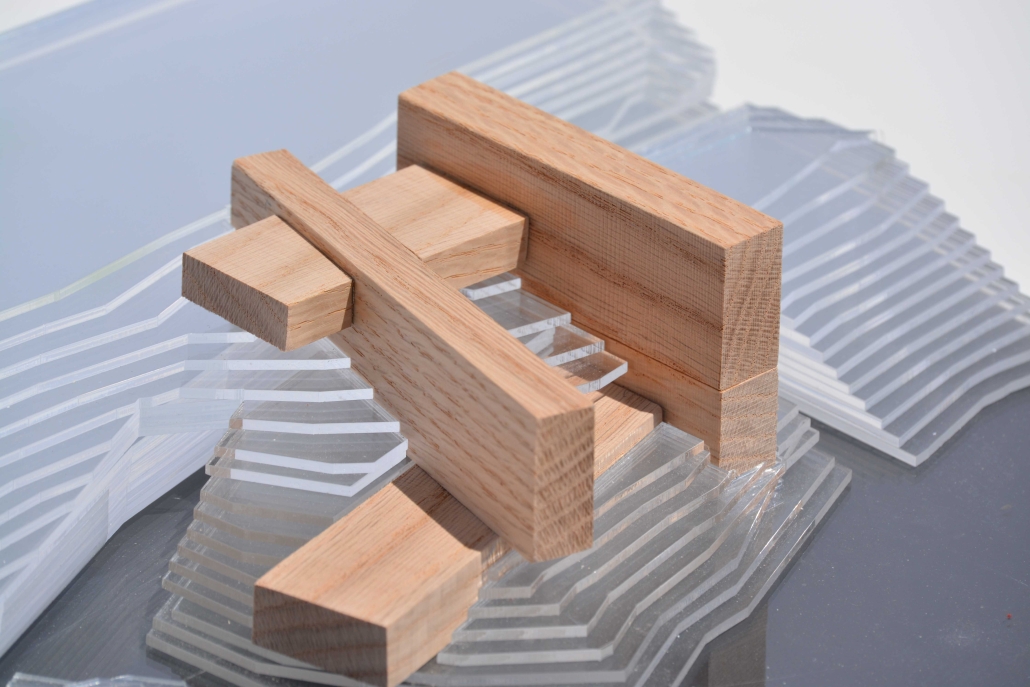
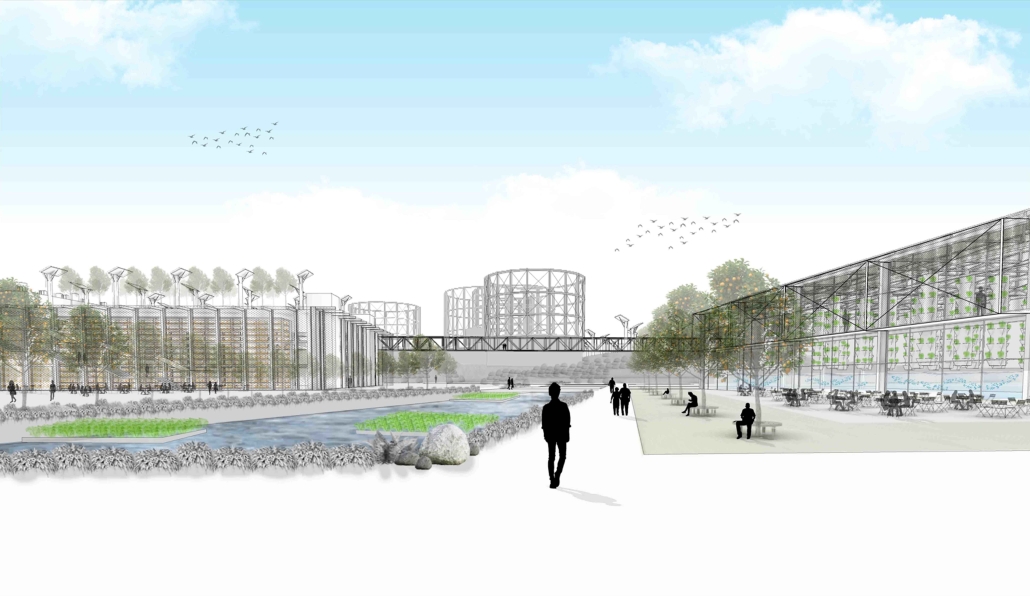
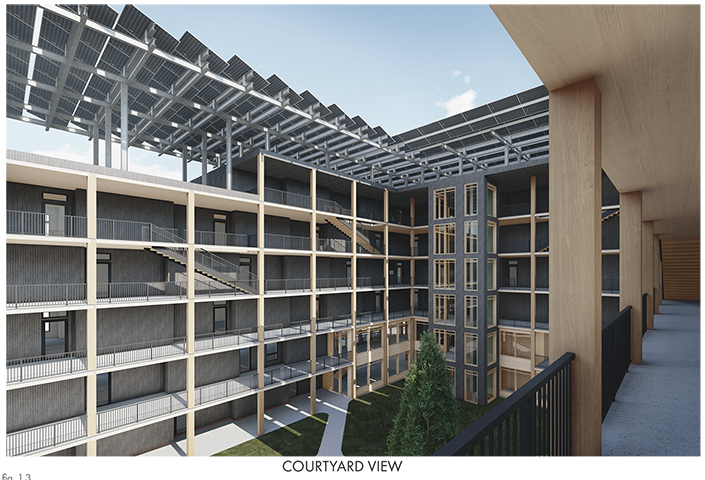
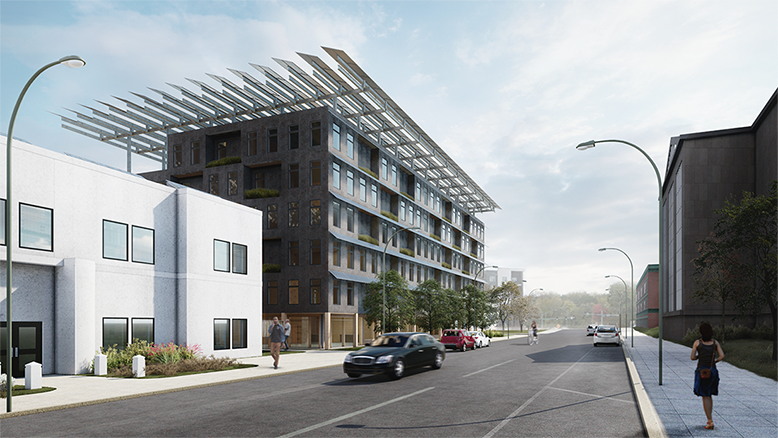
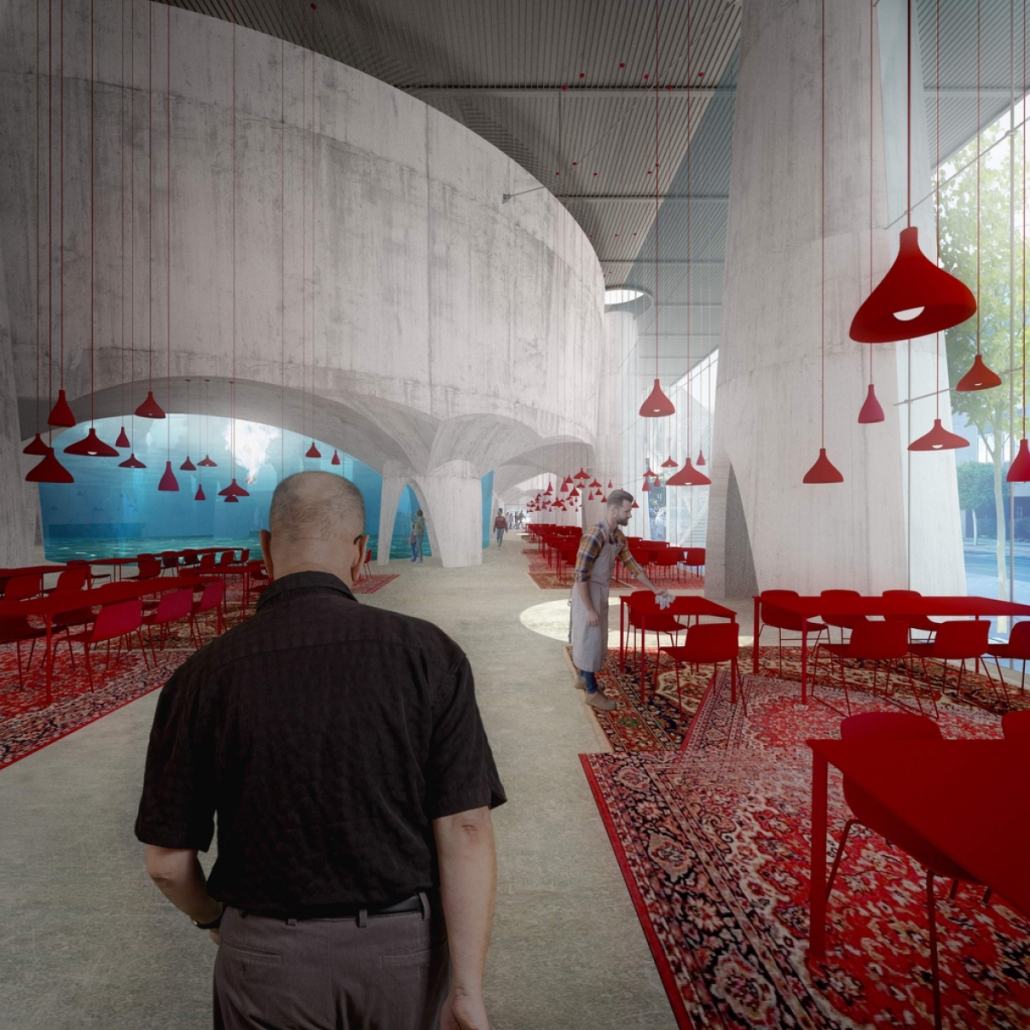
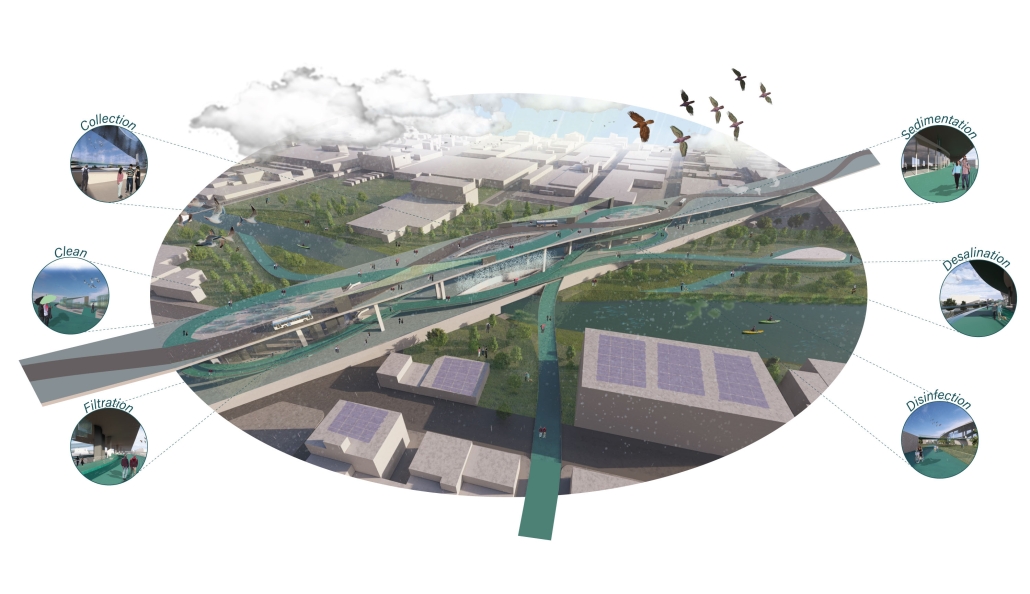
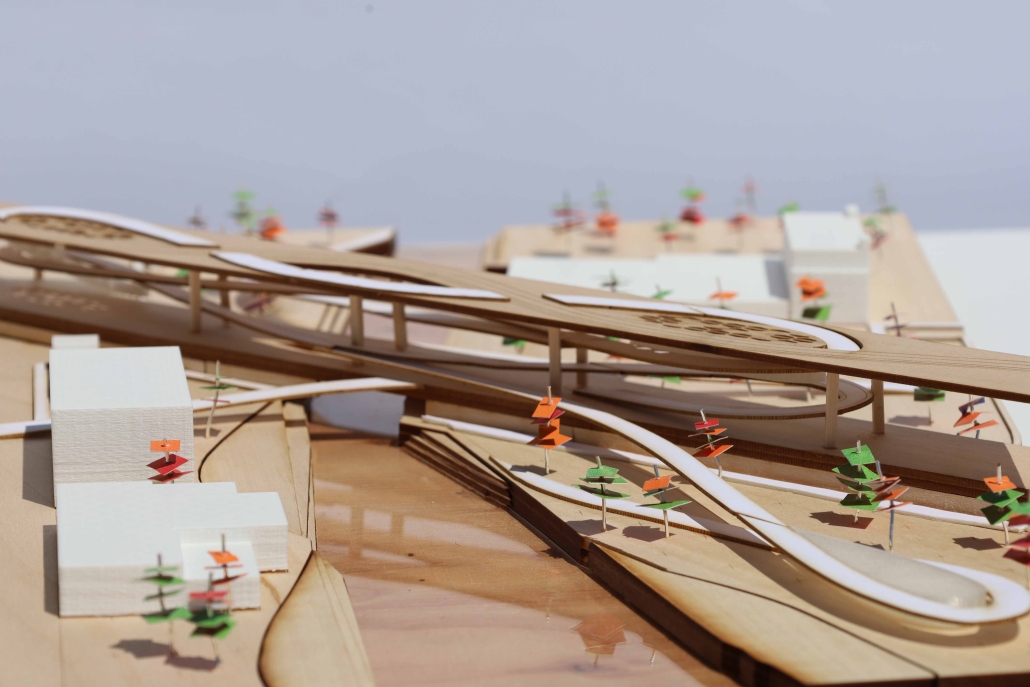
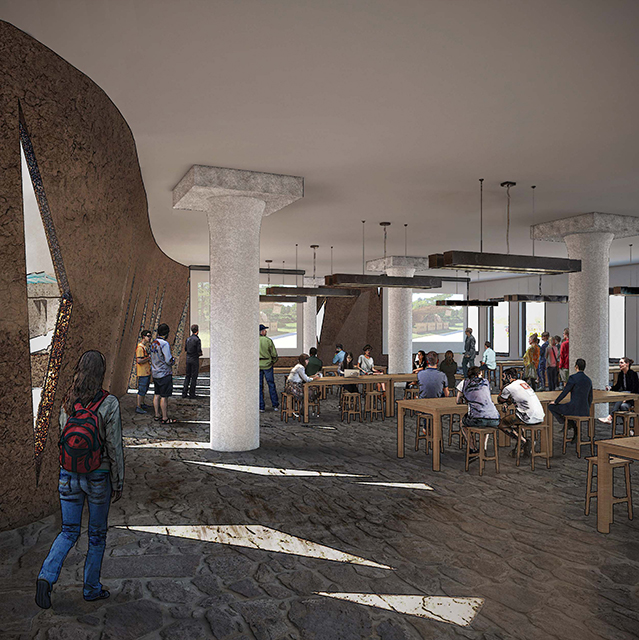
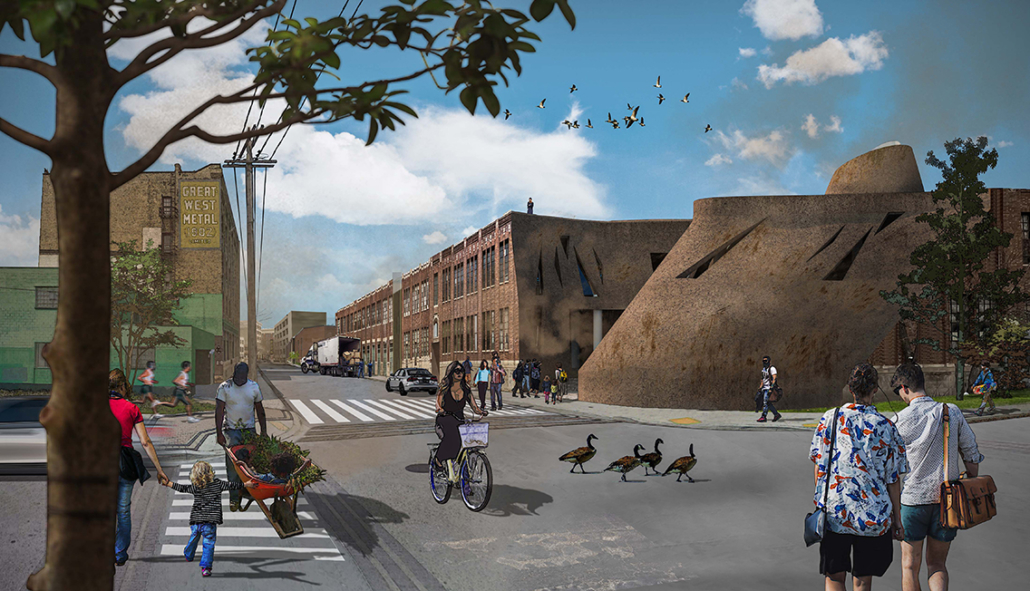
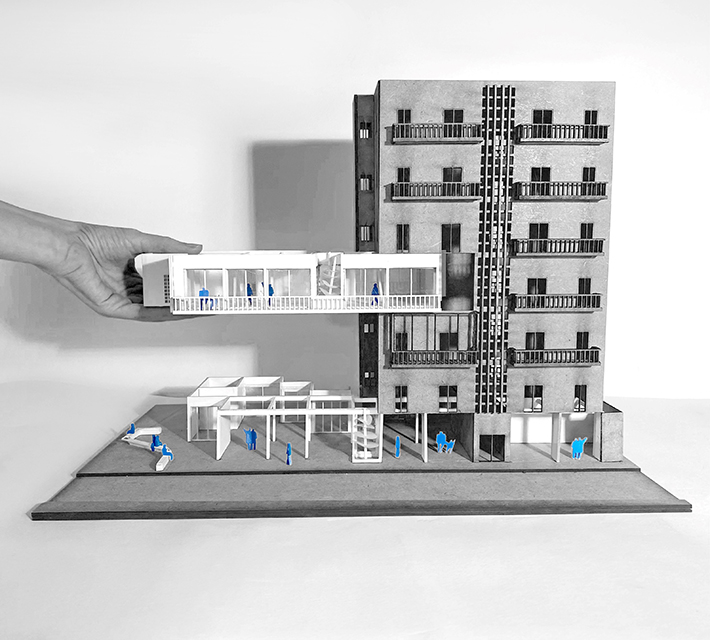
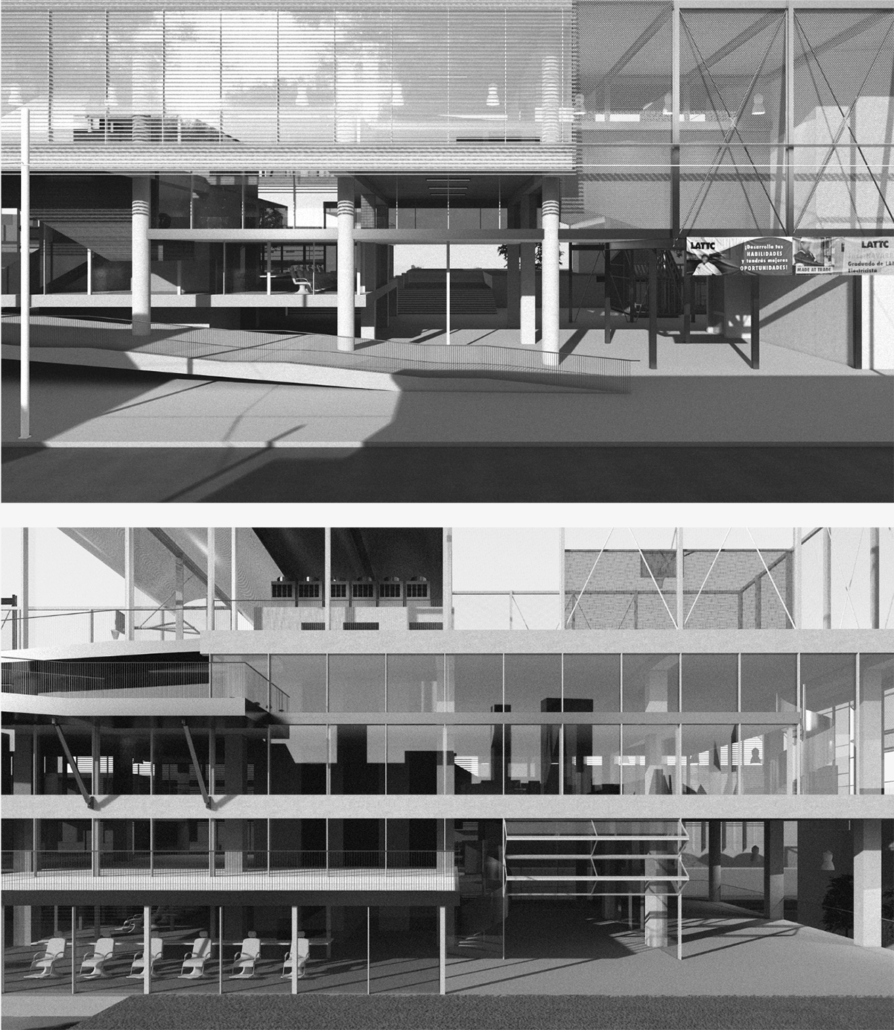
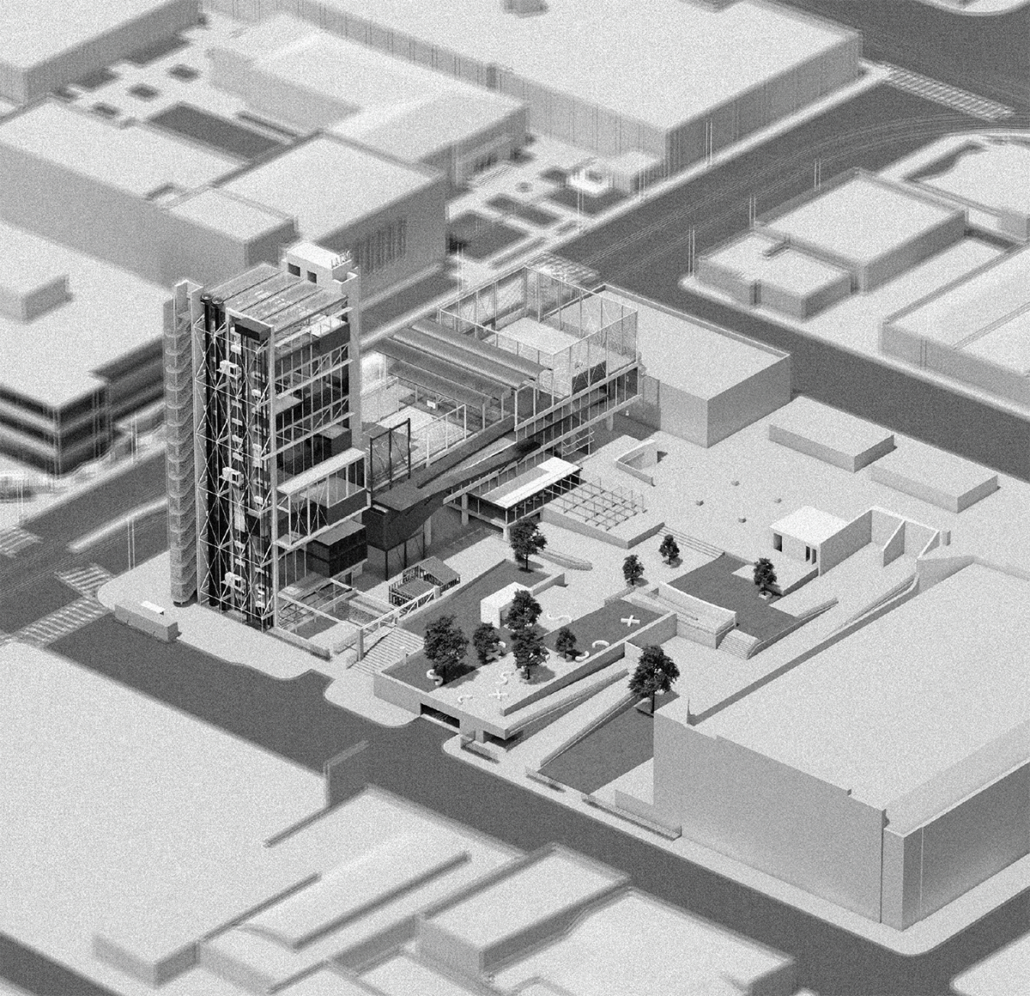
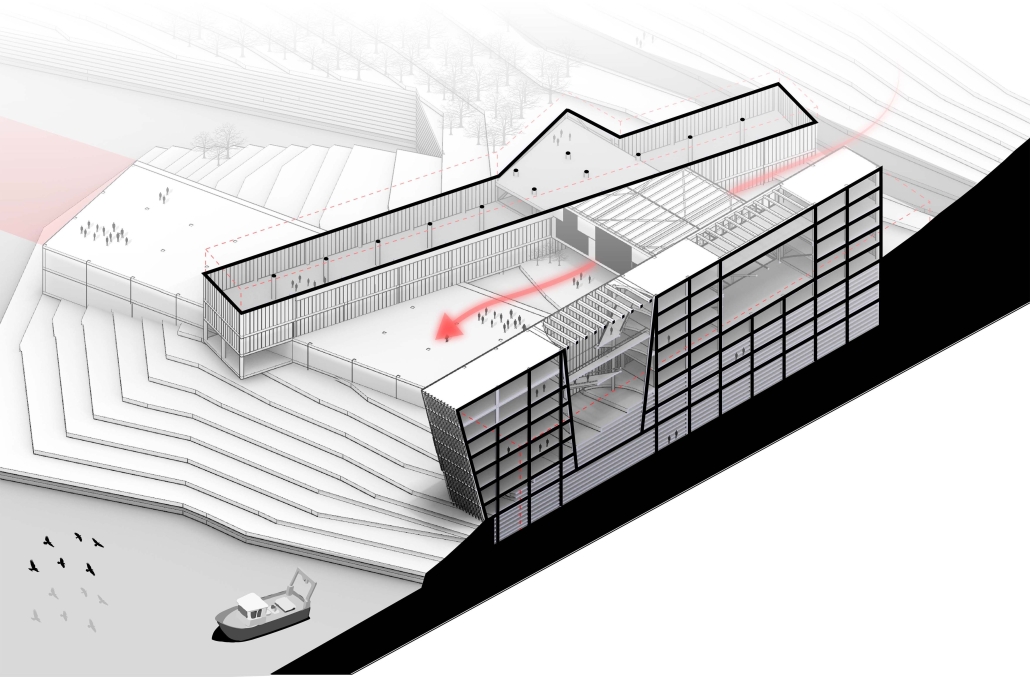
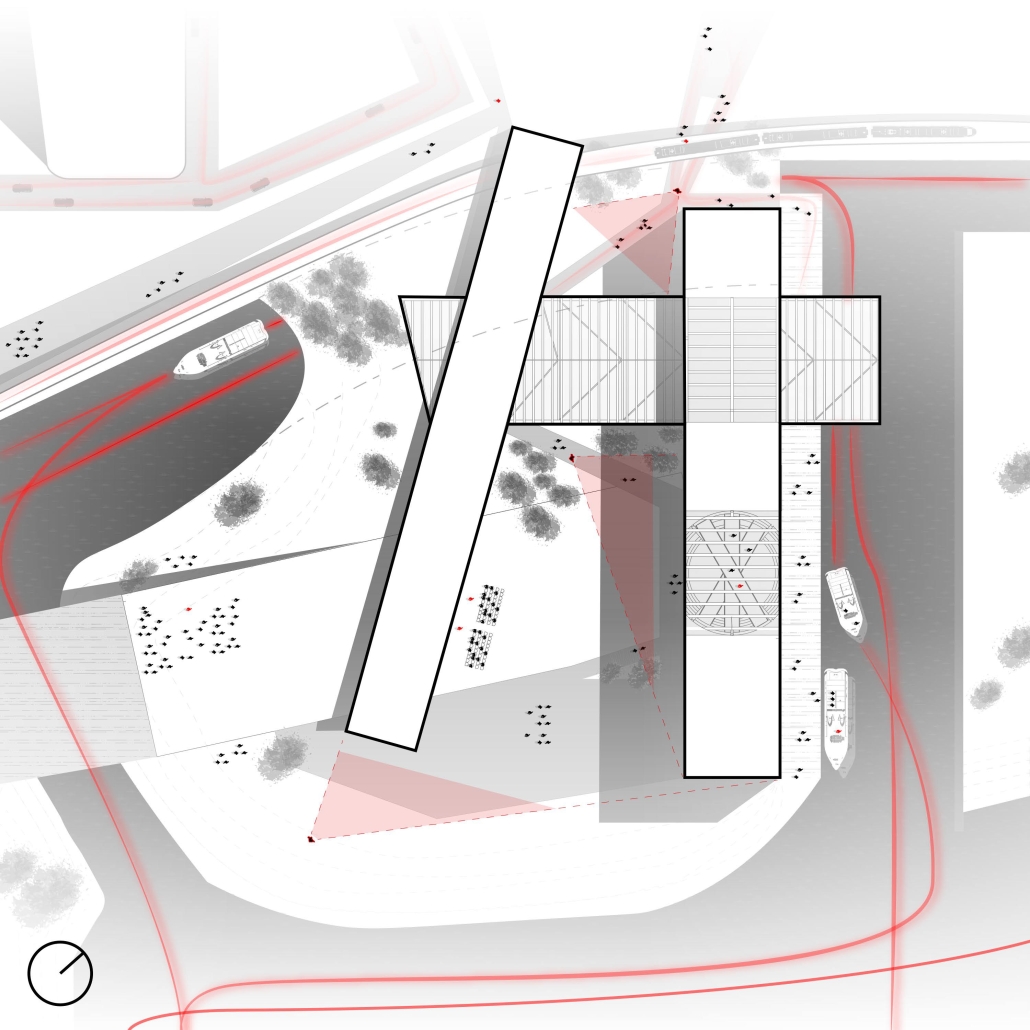
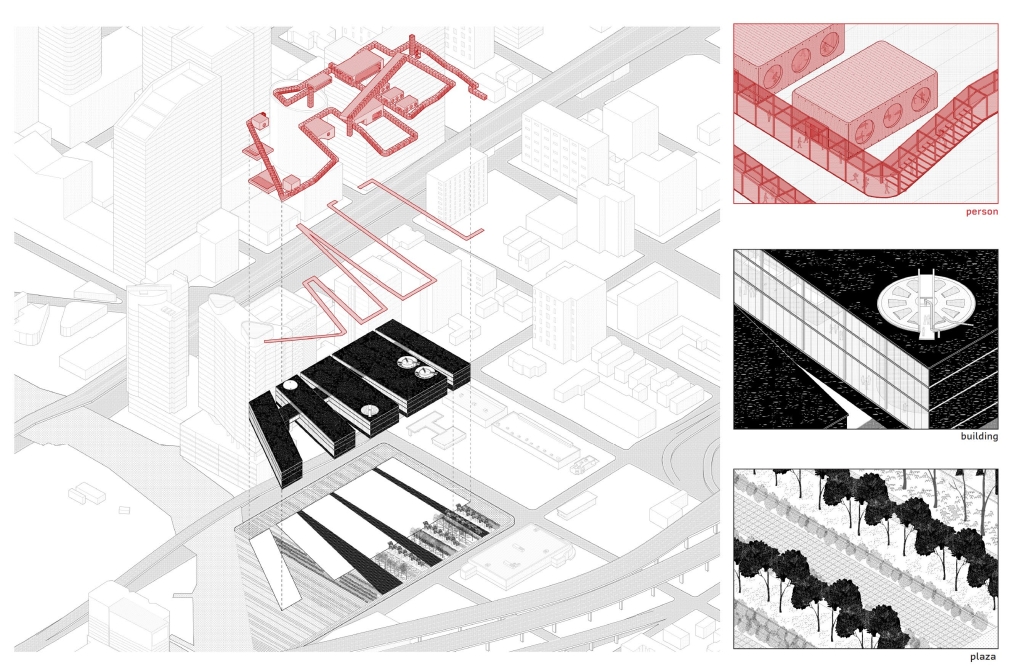
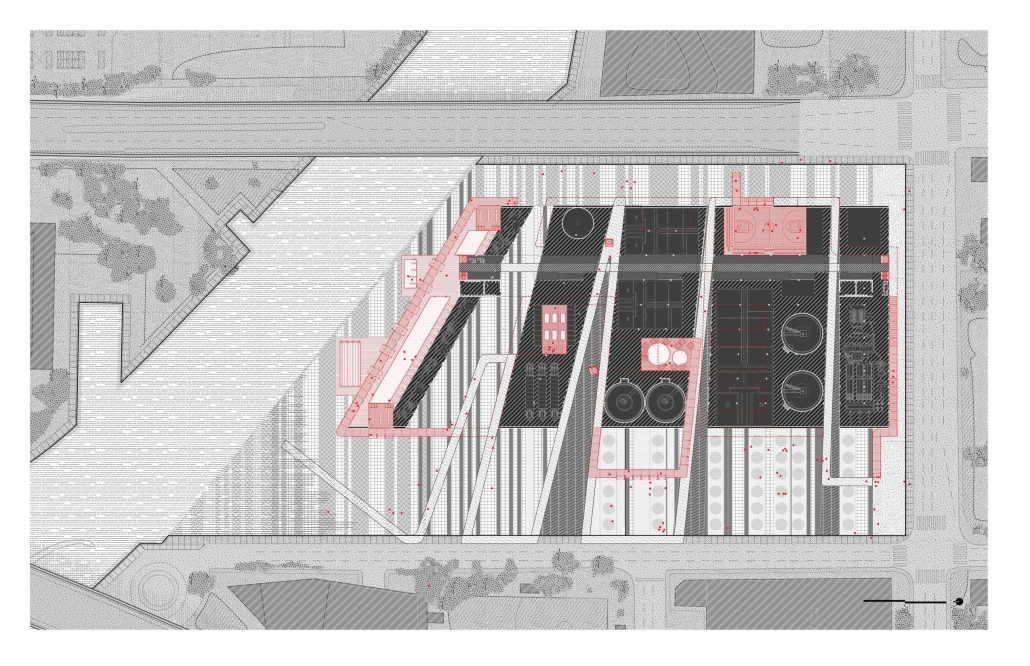
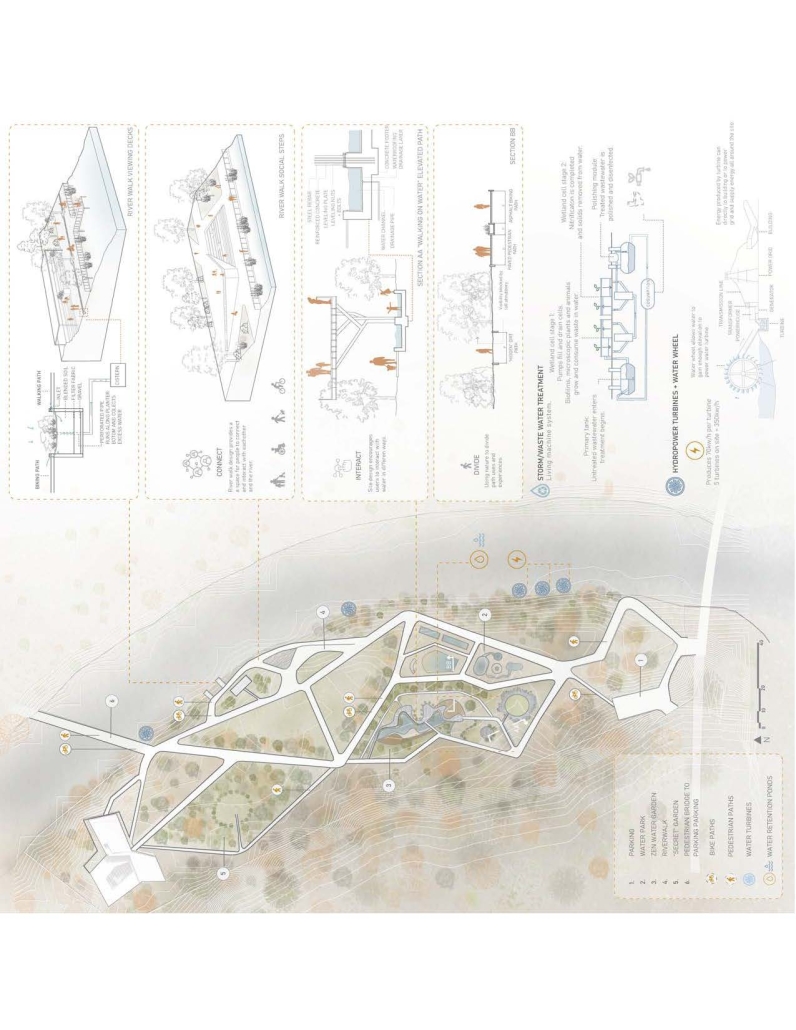
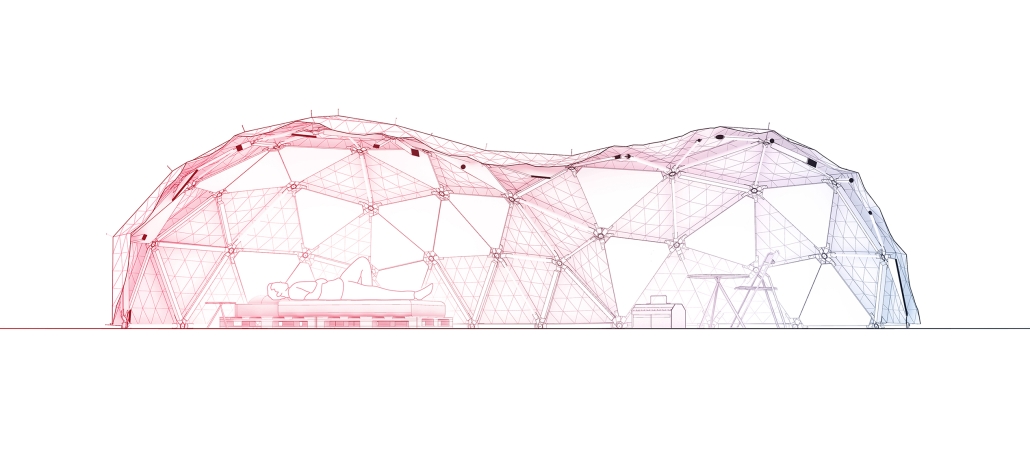
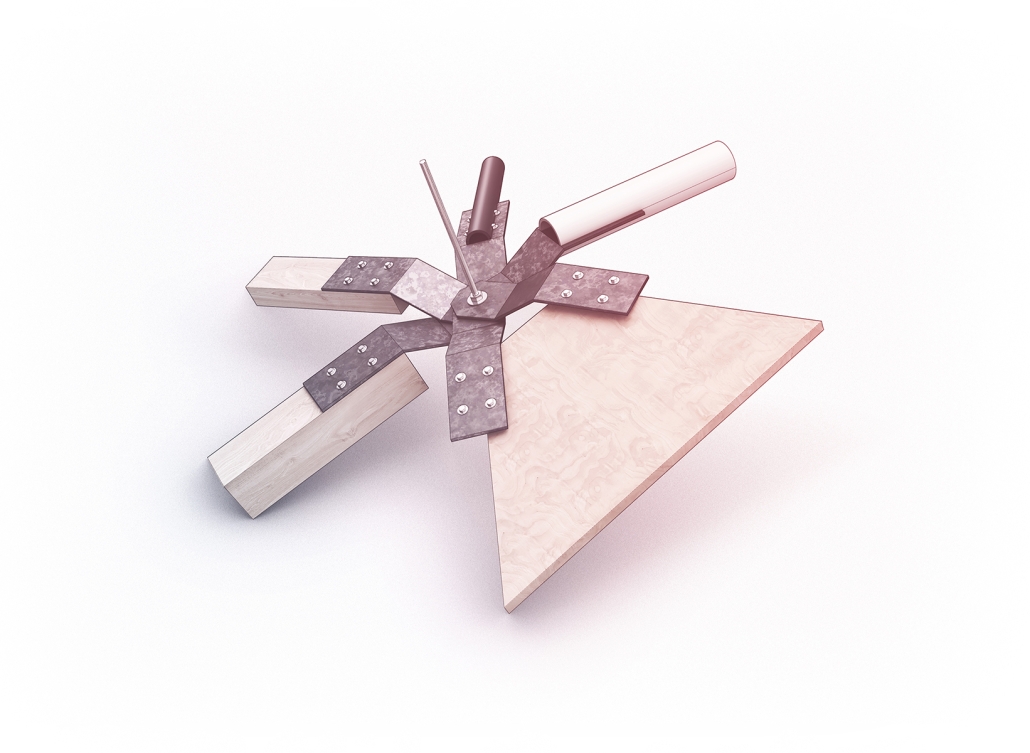
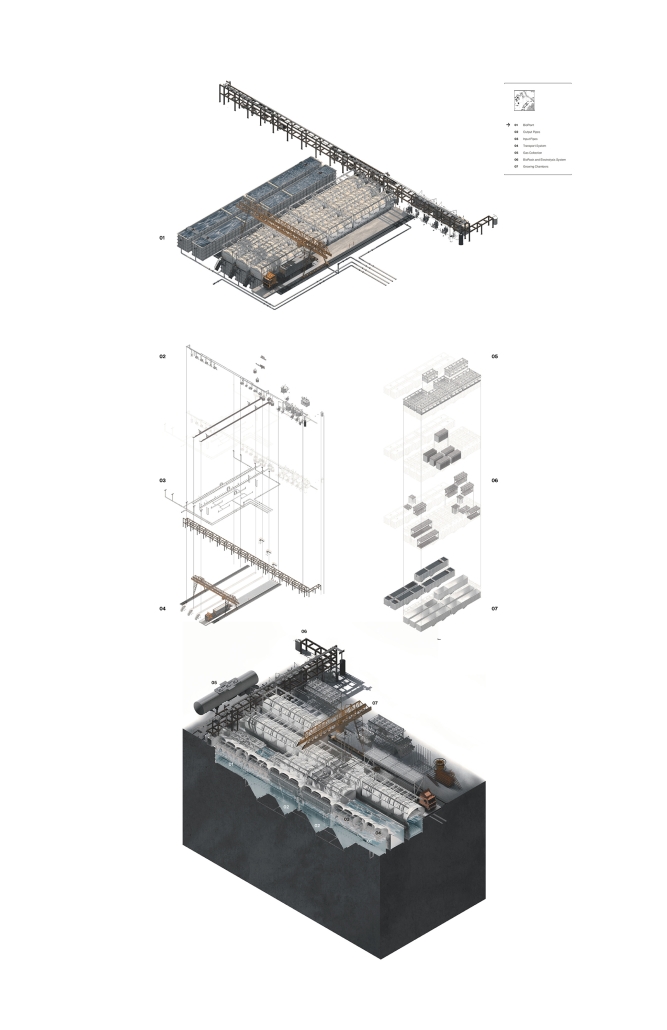
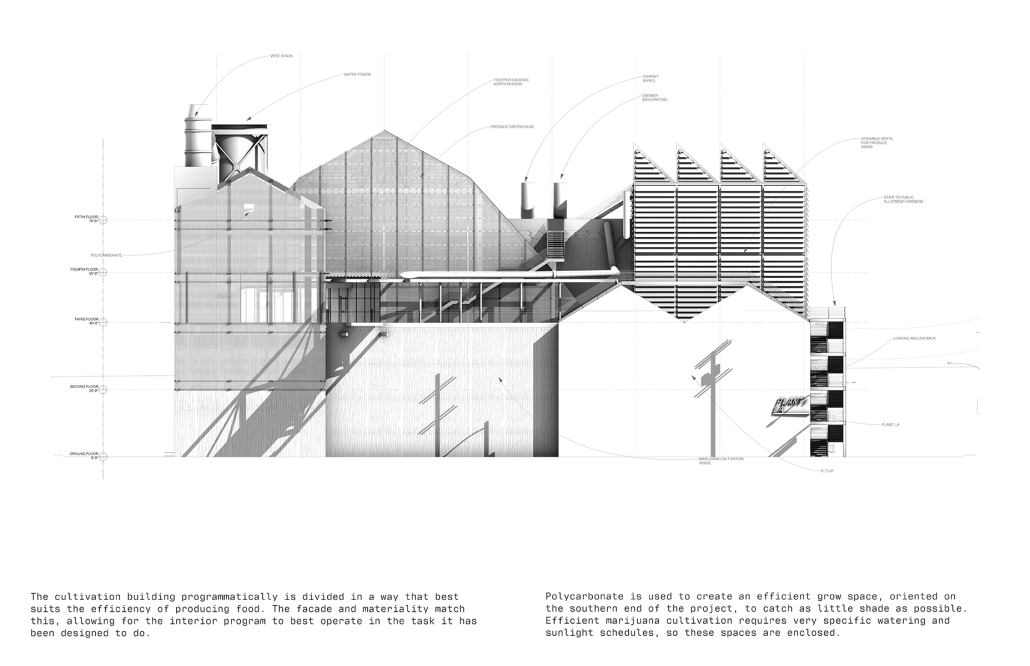
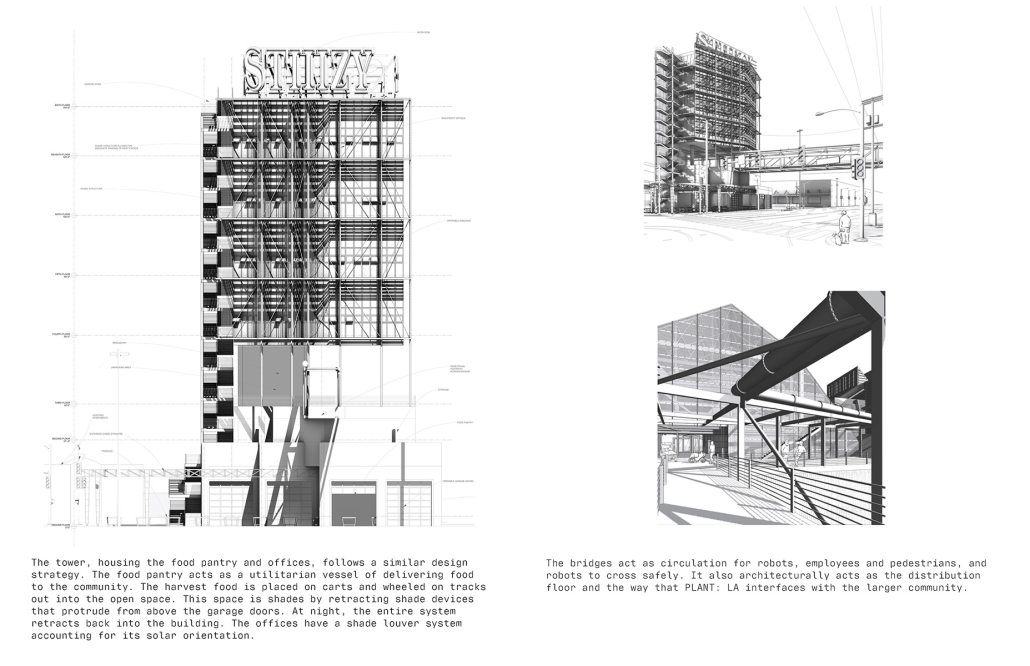
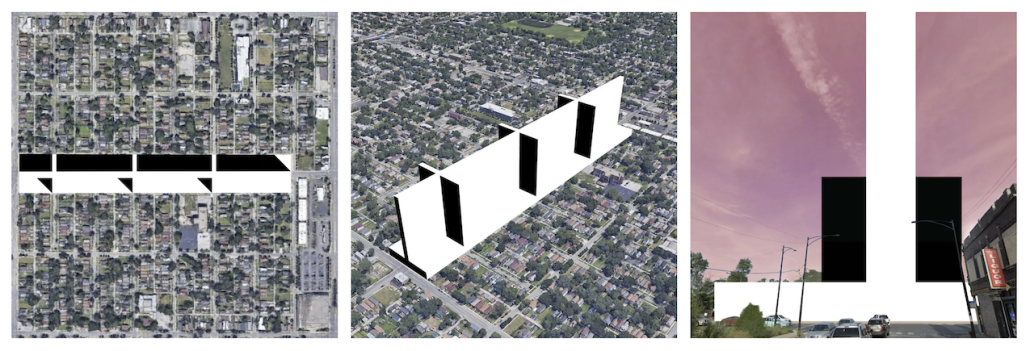
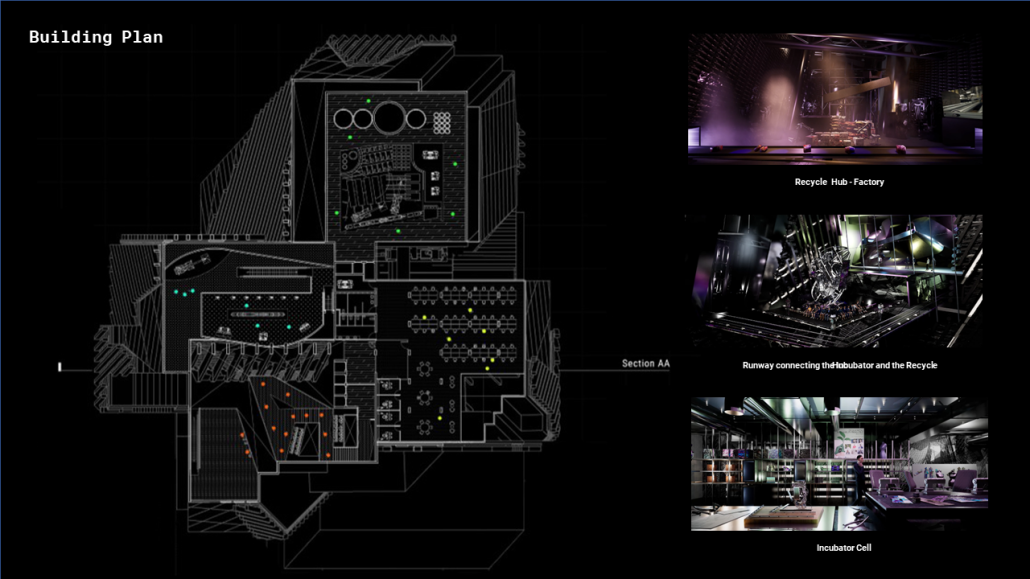
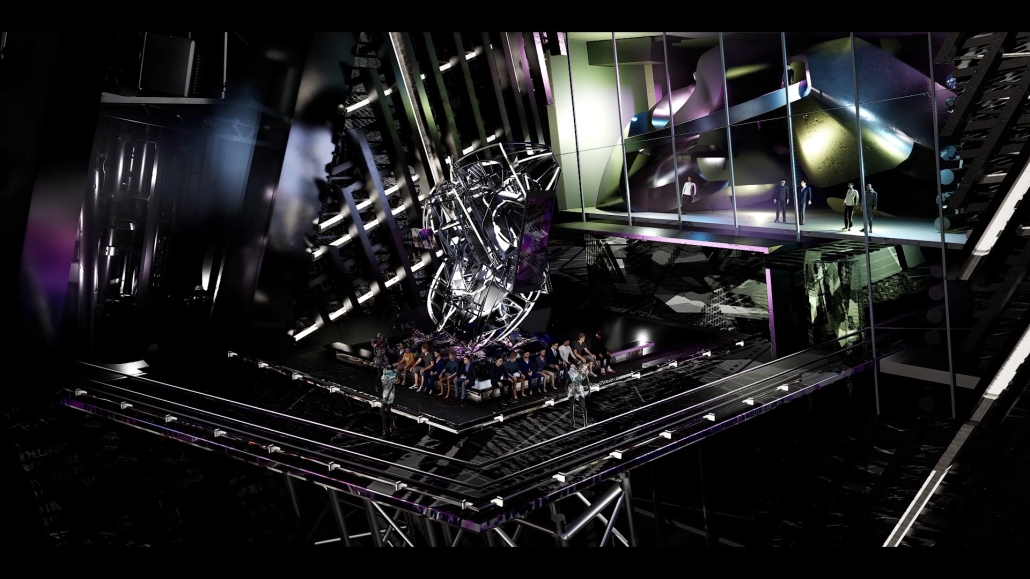
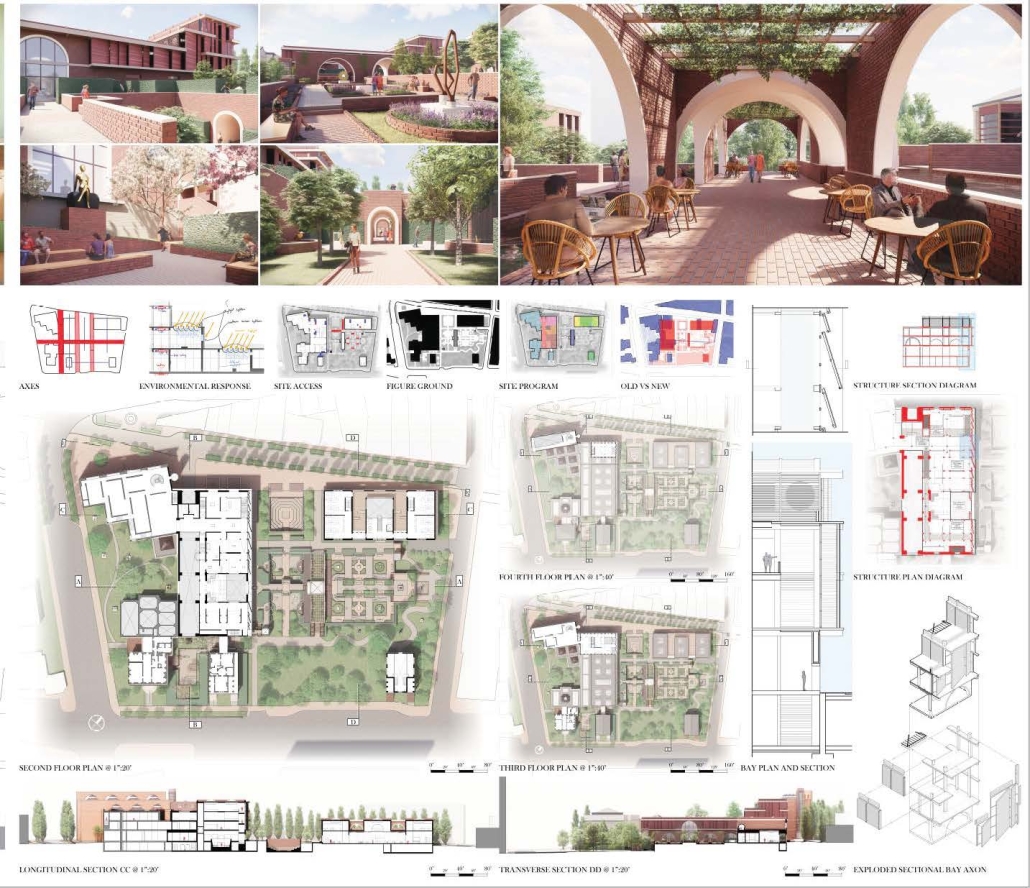
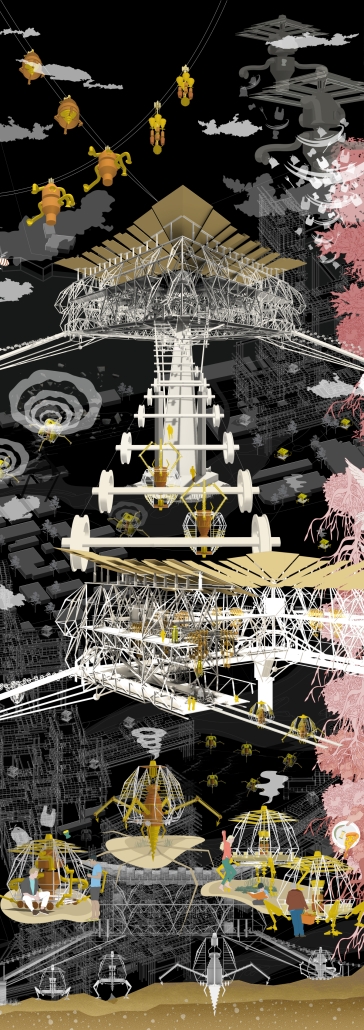
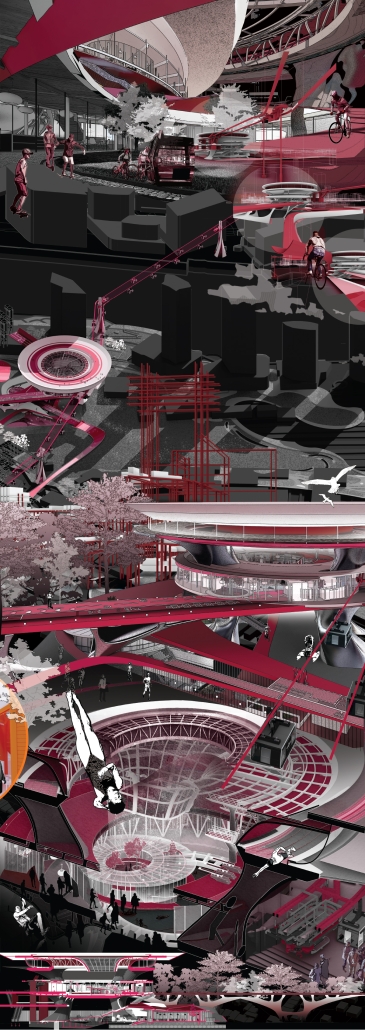
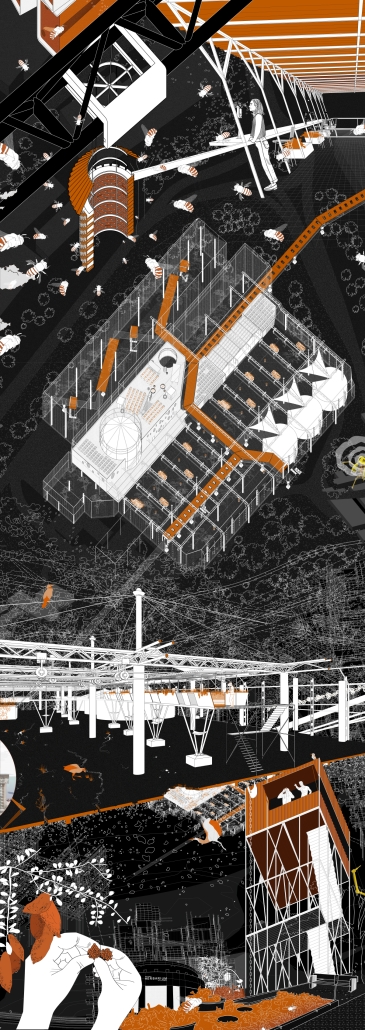
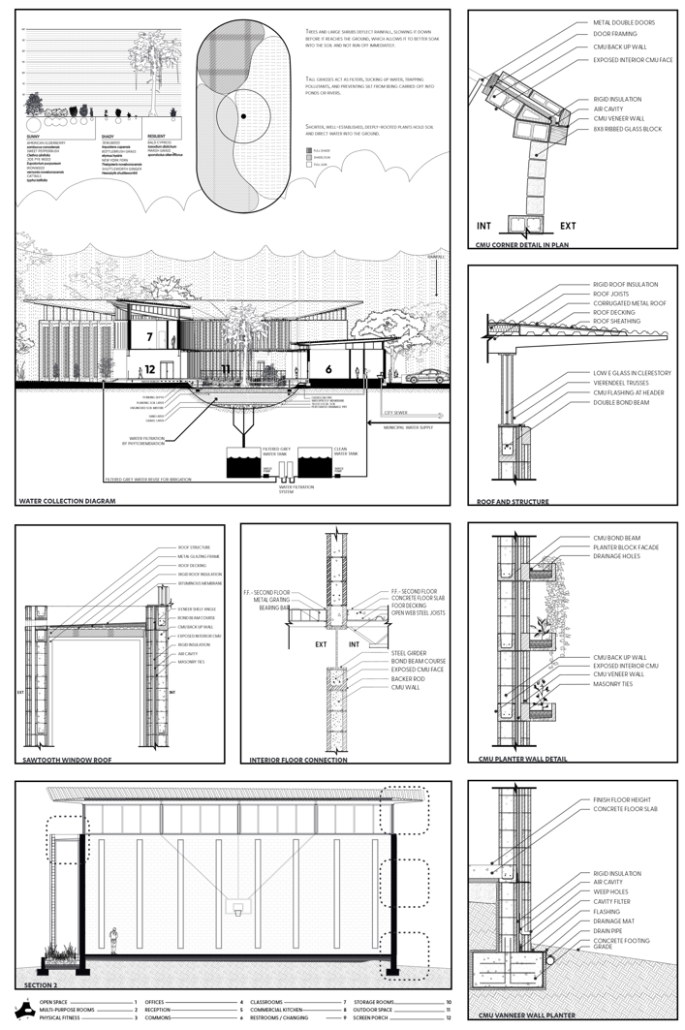
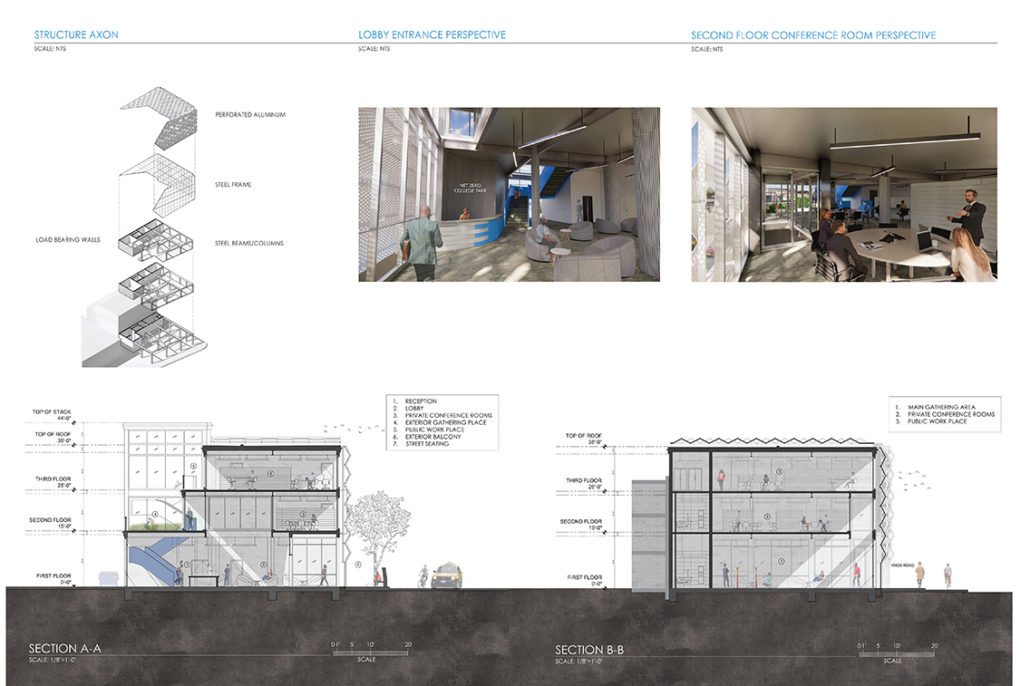
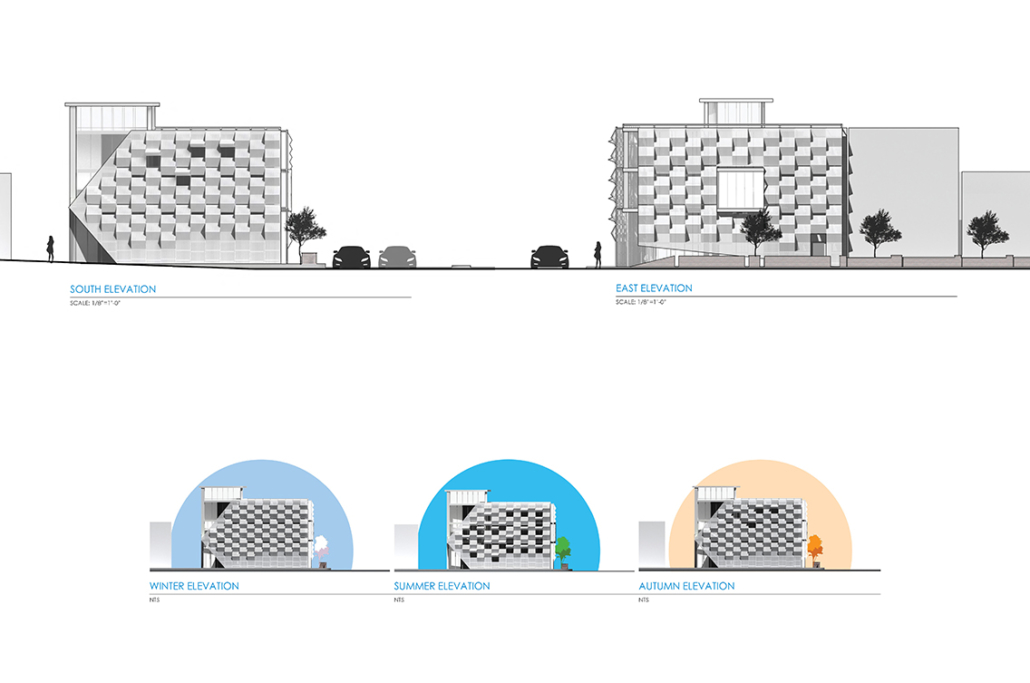
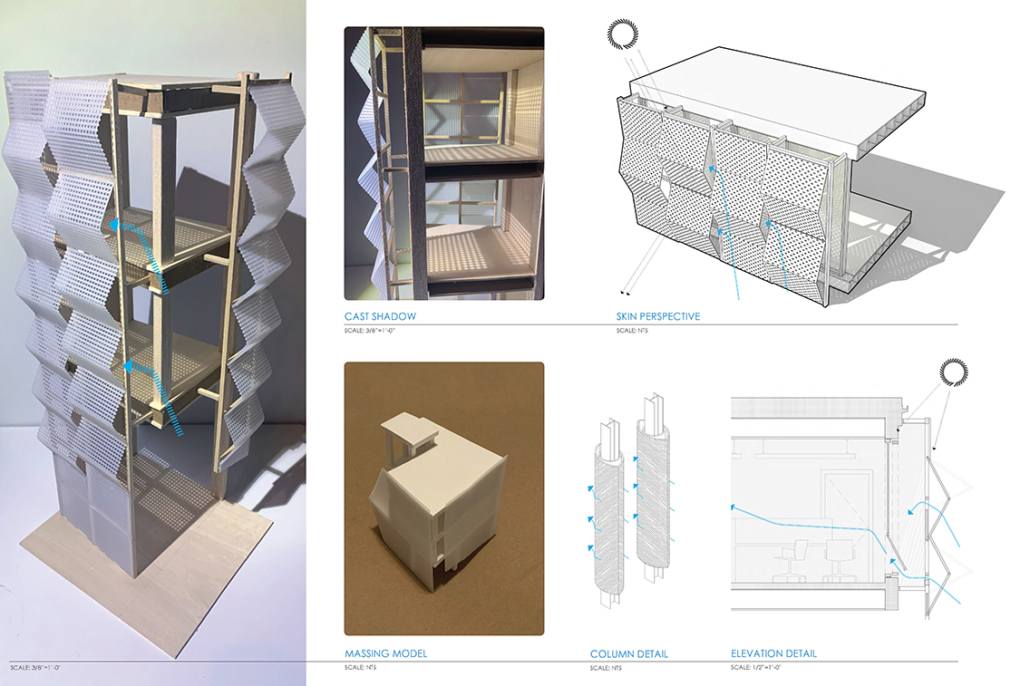
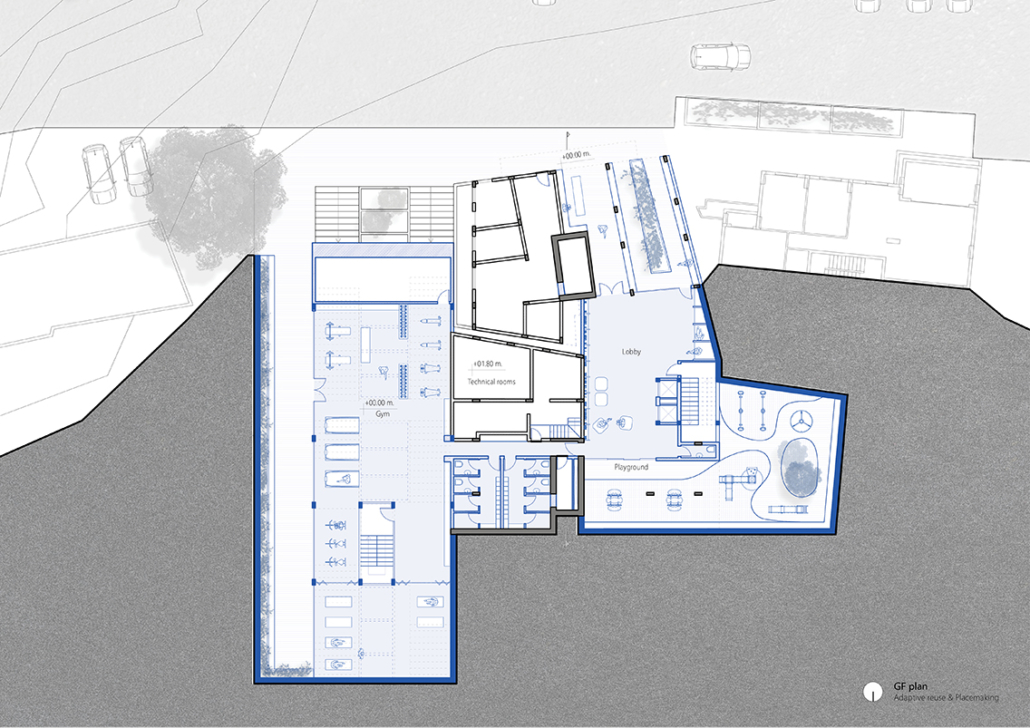
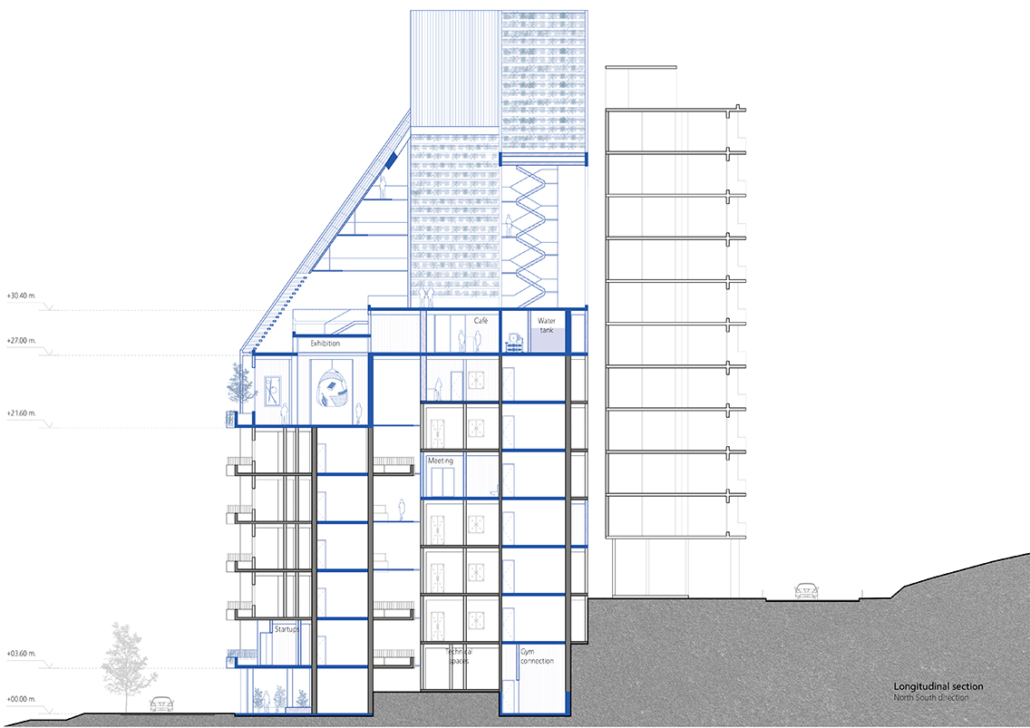
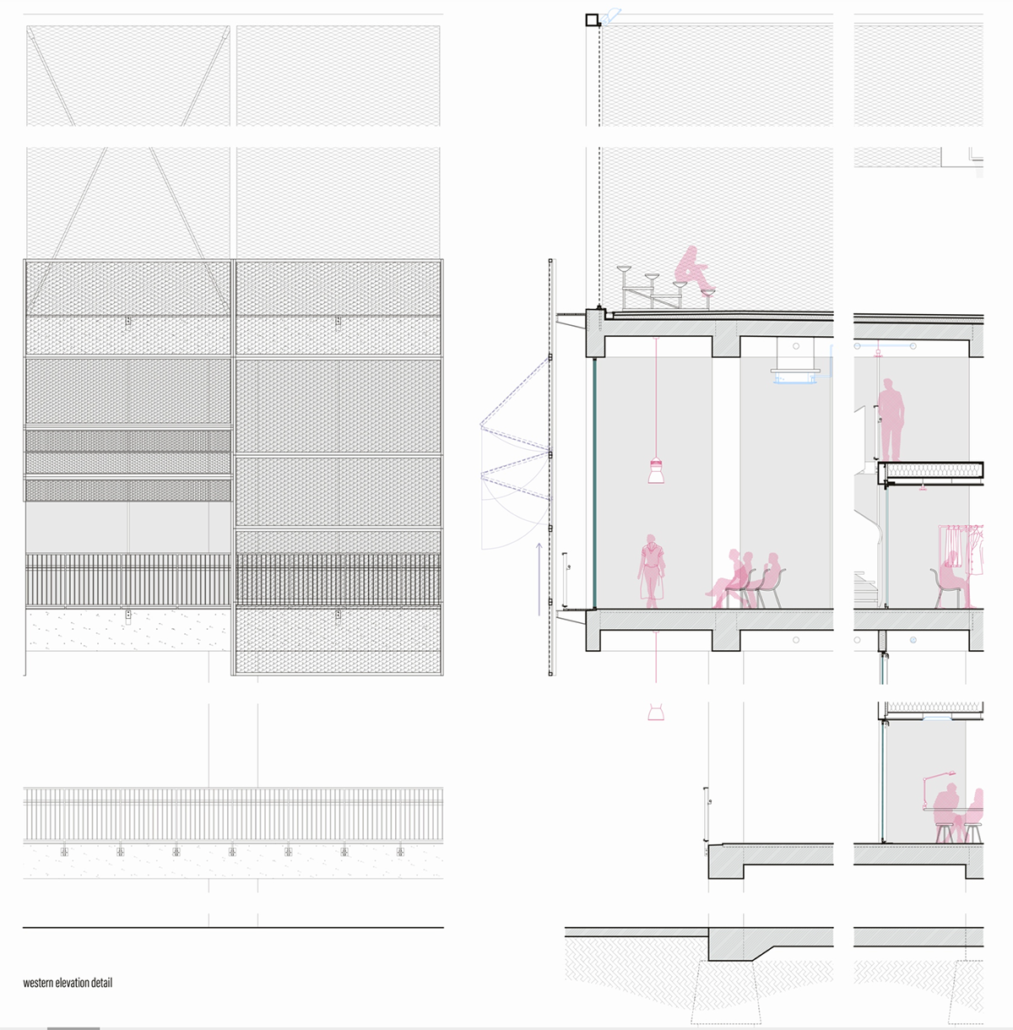
Industrial Interface: A Transparent Relationship Between Wastewater Treatment and The Human by Leah Bohatch & Camille Kreisel, B.Arch ‘23
Tulane University School of Architecture | Advisors: Cordulla Roser Gray & Ammar Eloueini
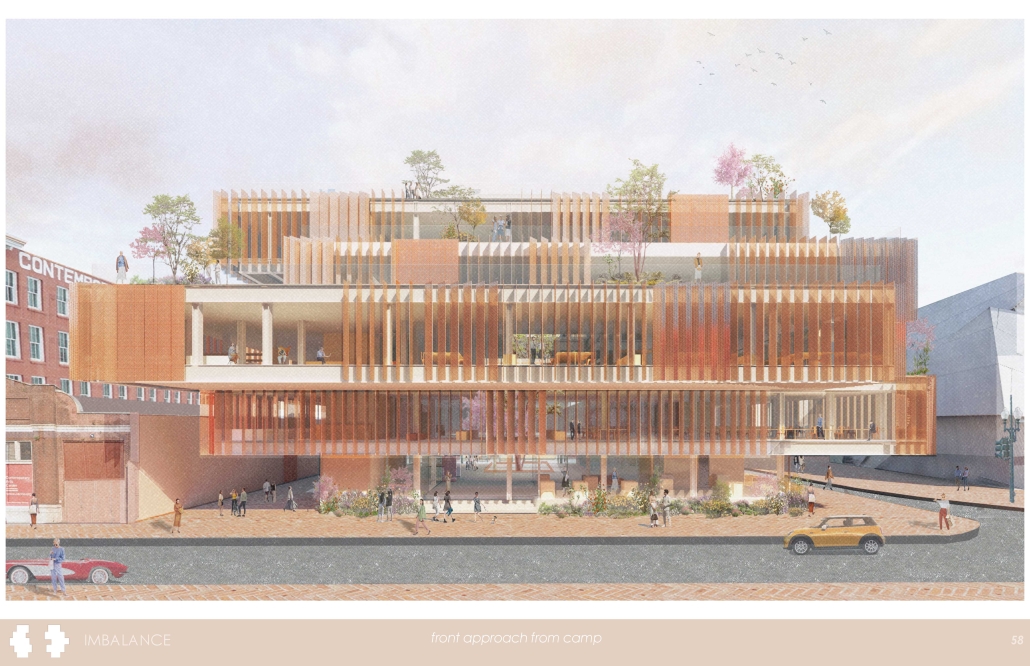
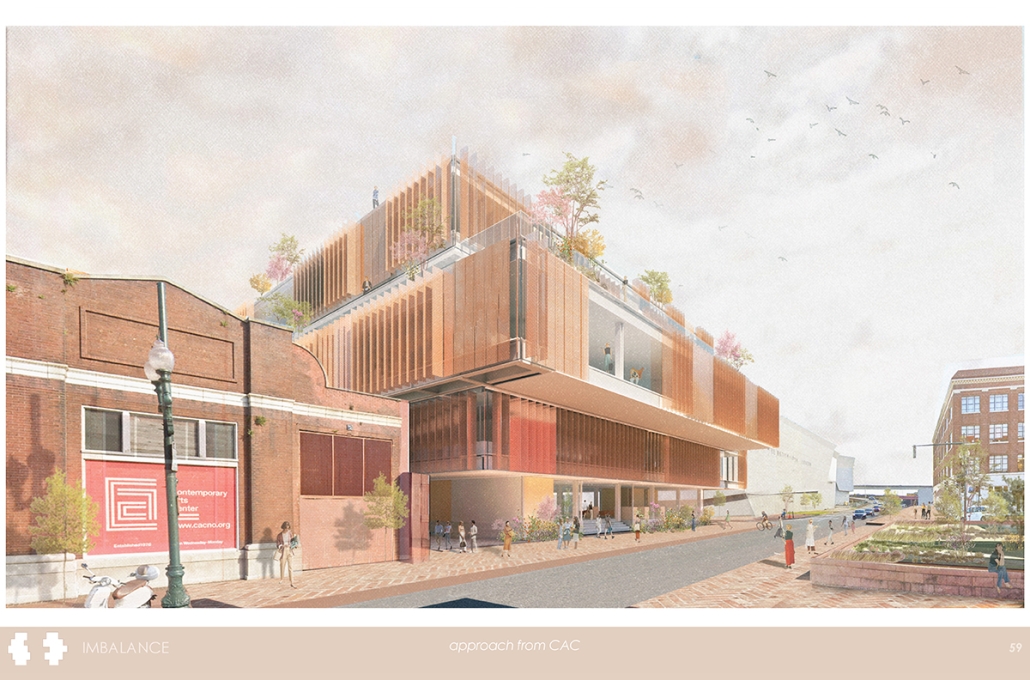
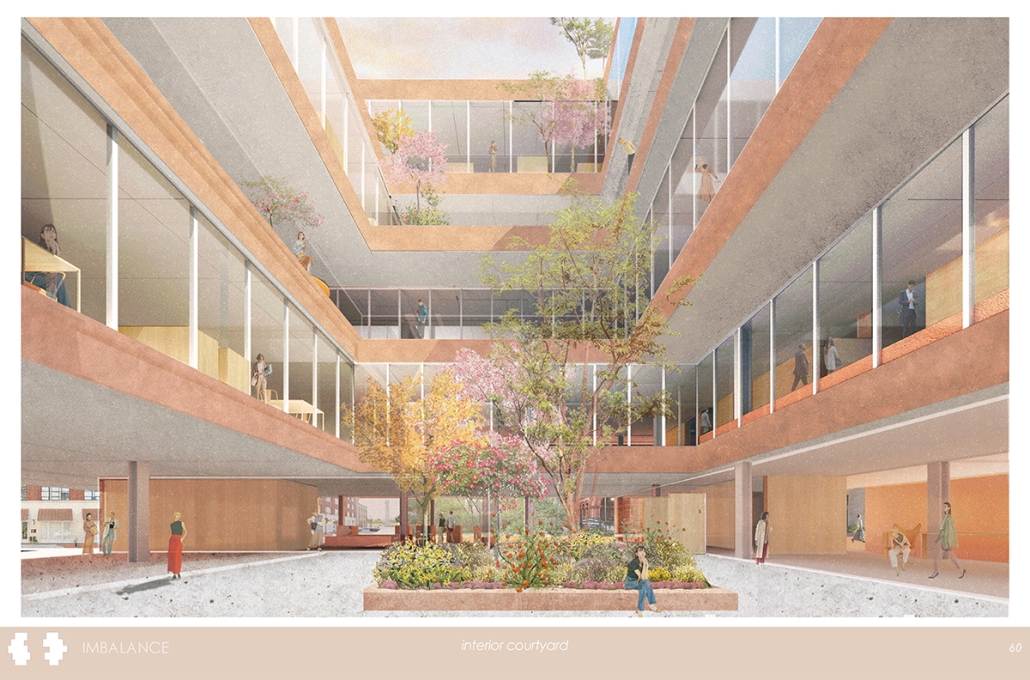
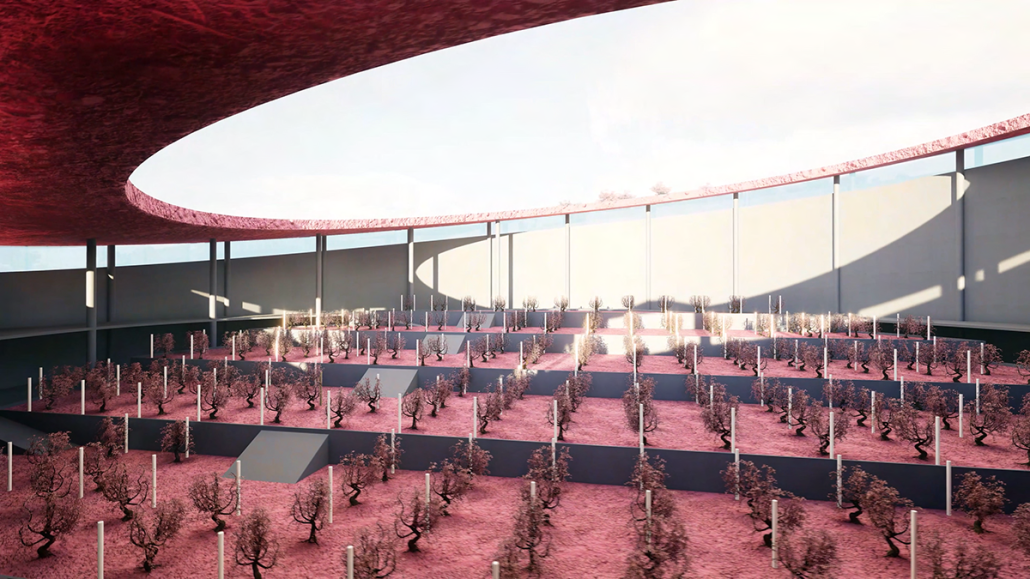
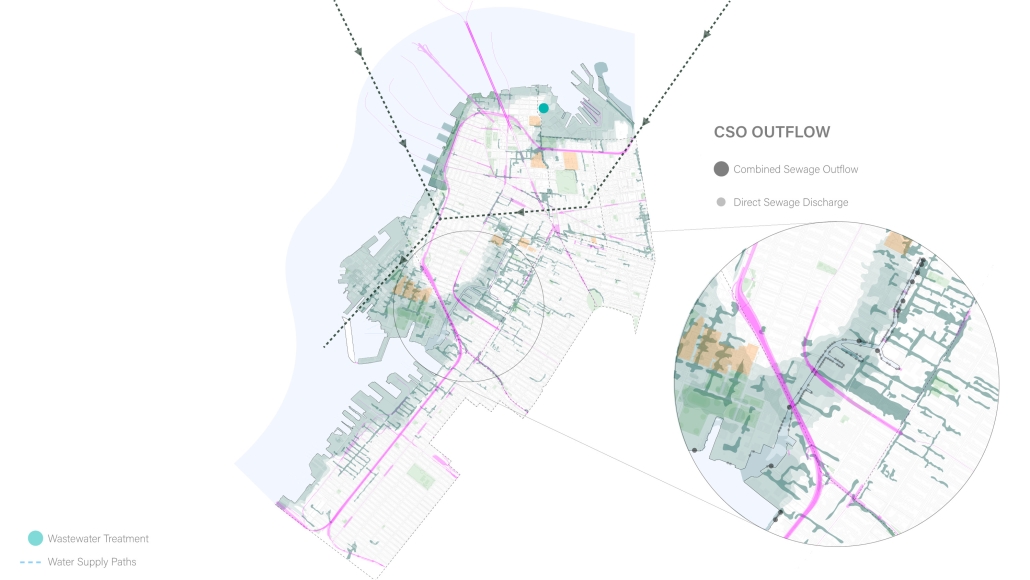
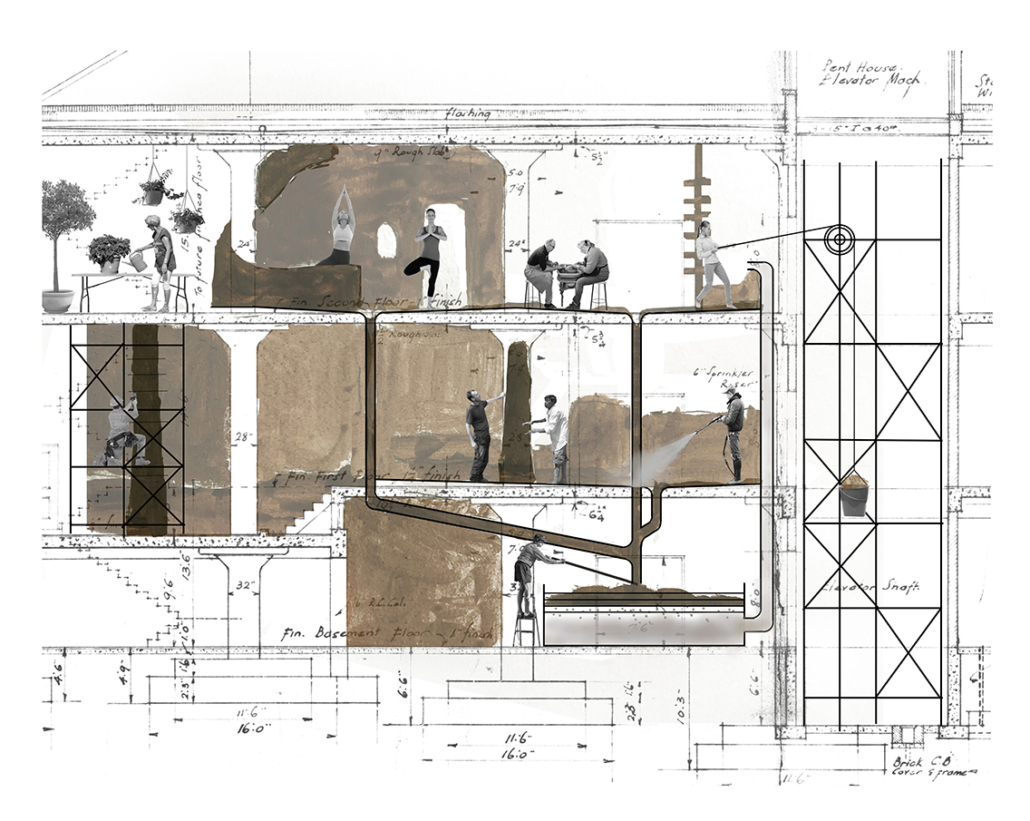
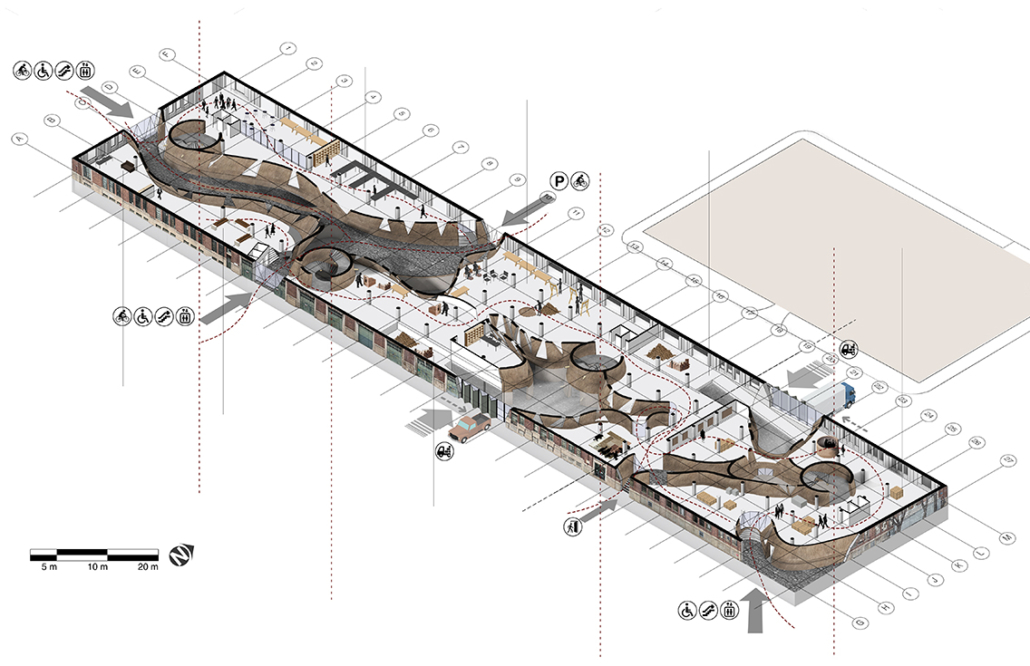
Wastewater treatment is currently an isolated system despite its importance in serving civilians, creating a linear relationship that wastes a limited resource while harming the health of its source: the body. Such isolation has further harmed the environment due to civilians’ lack of knowledge and overuse. Additionally, such physical and social separation has made citizens more unlikely to adapt to wastewater reuse methods because of misconceptions about safety standards.
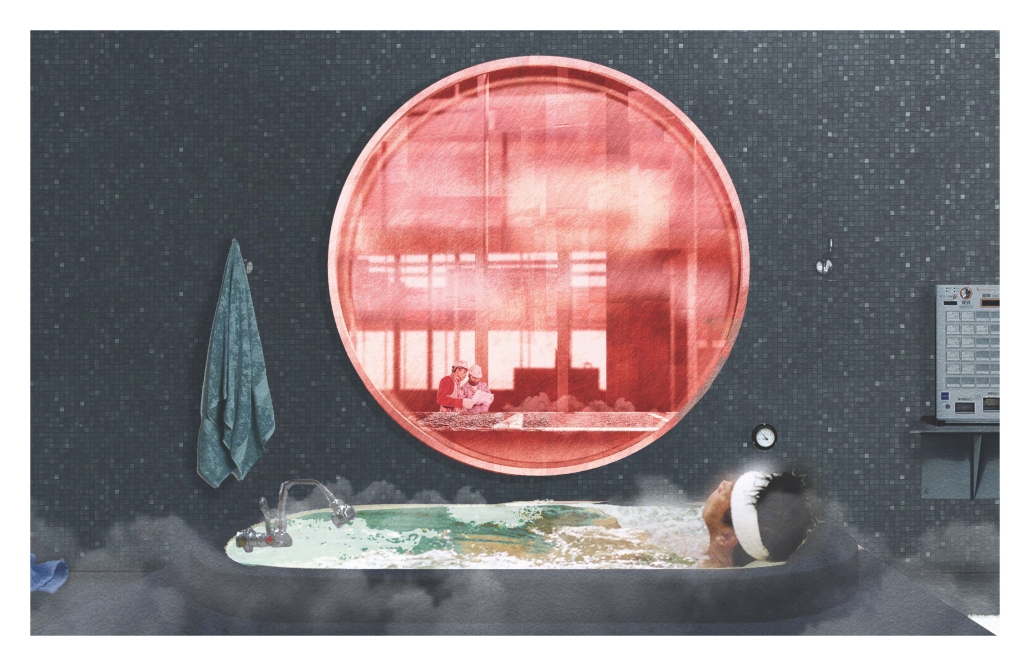
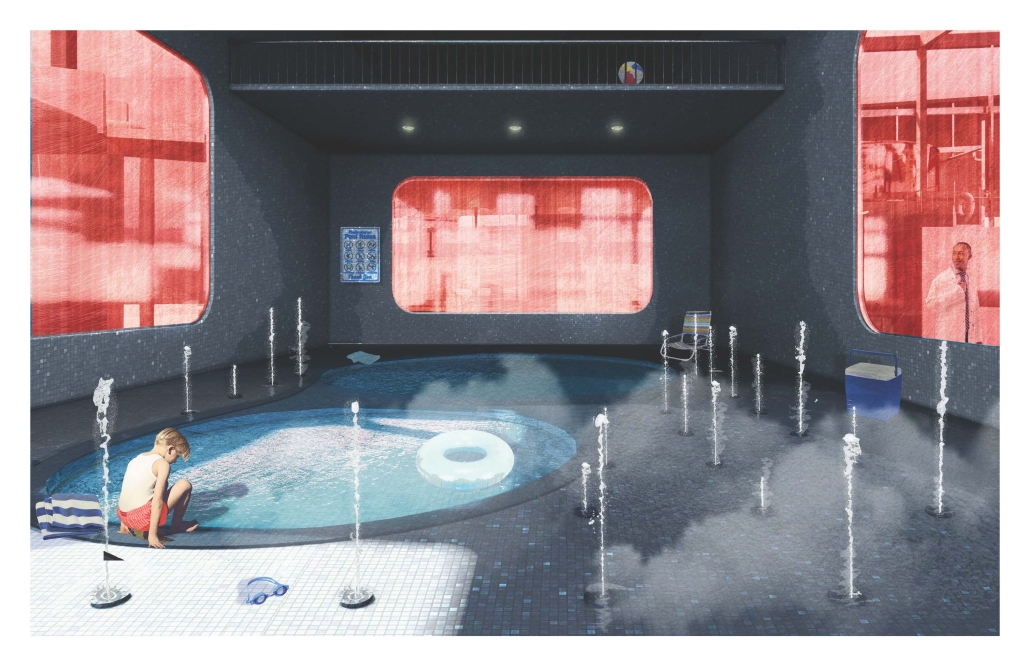
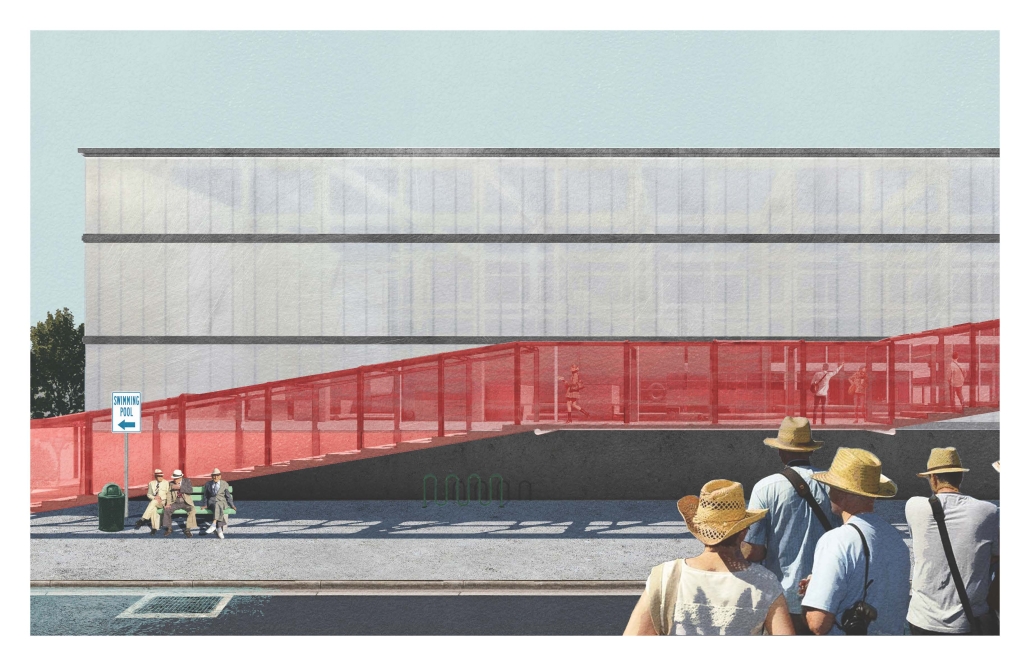
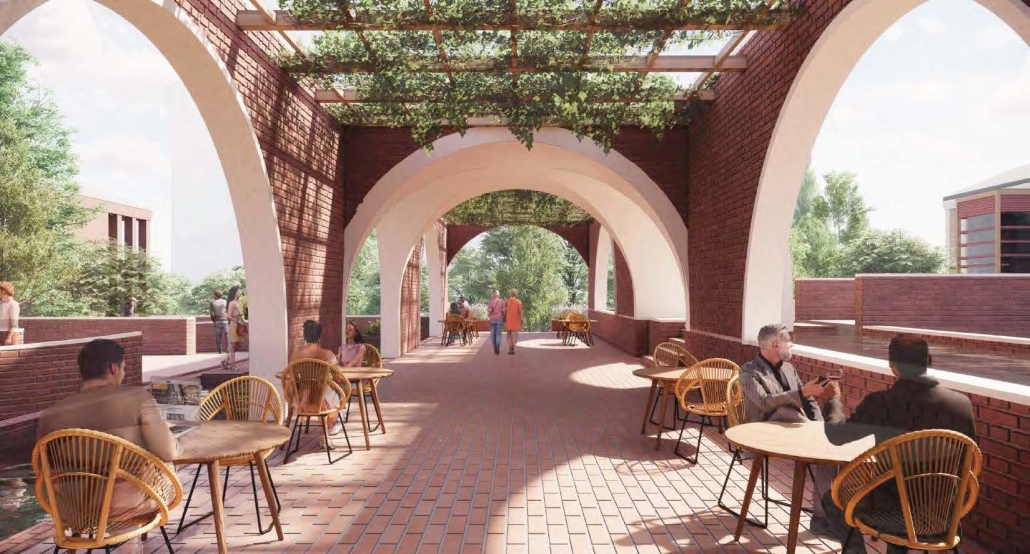
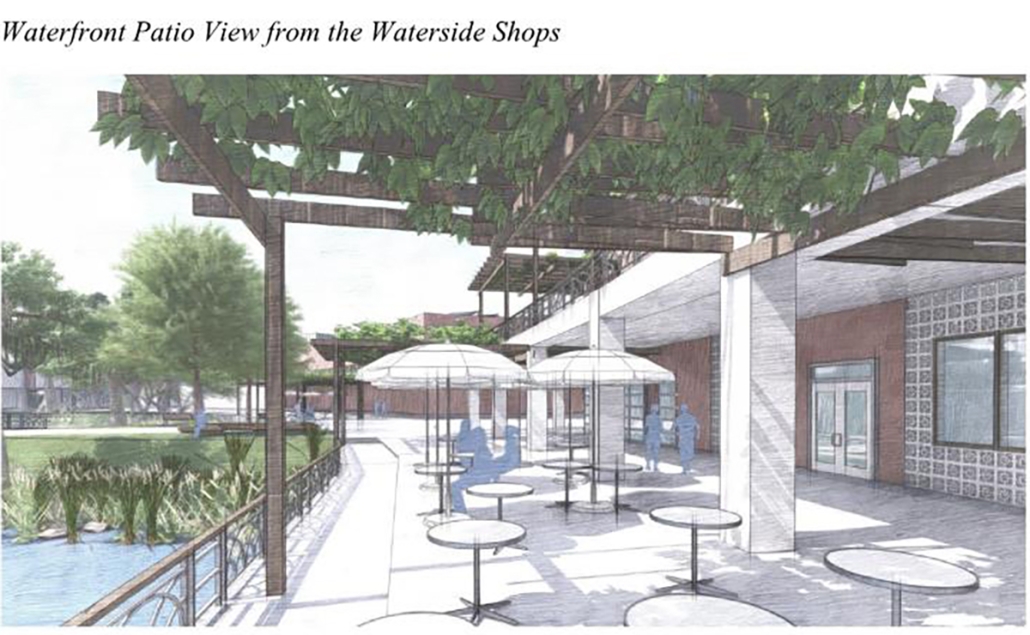
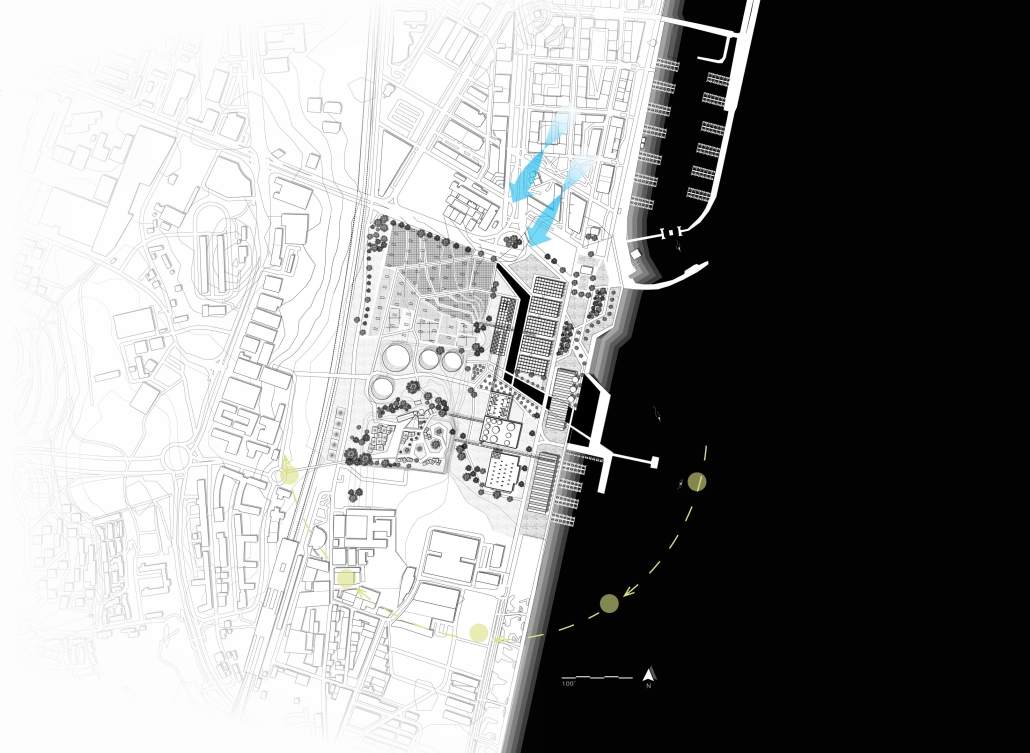
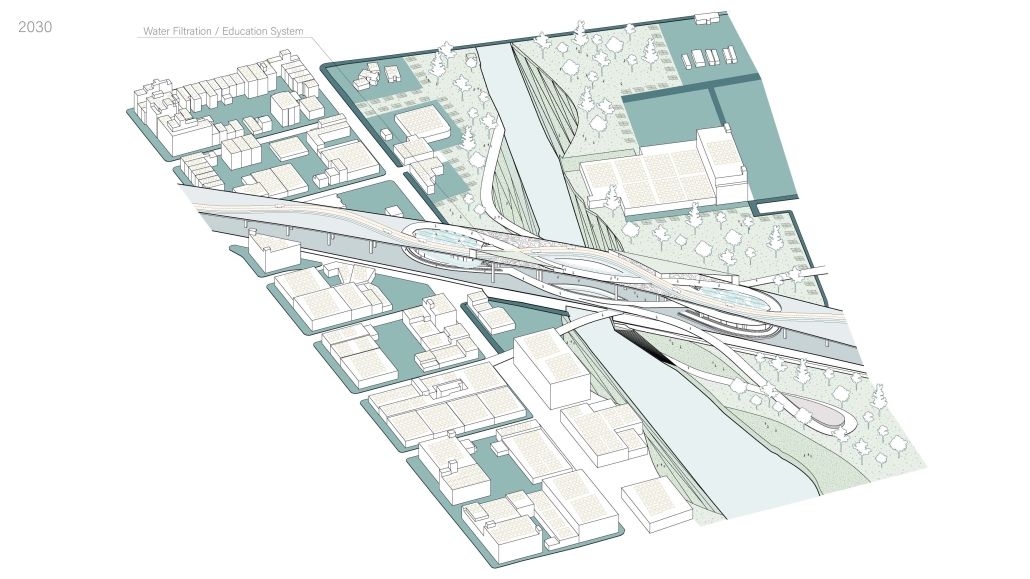
Miami’s current wastewater plant, located on the flood-threatened Virginia Key, requires an assessment and renewal of systems that should be raised, work on a network, separate different water types for efficient cleansing, reuse treated water for facility use, and invite the public into the process. A micro WWTP in Miami is proposed to run a cycle of water treatment and reclamation that supports the heat-stricken city by reprogramming a cooling aquatic center to act as an example for future plants. This redefinition of infrastructure proposes a rejuvenated future in which civilians can experience the necessity and amenity of wastewater infrastructure.
This new interface is represented in a ribboning red path of circulation that fluctuates between snaking around mechanical systems or inhabiting the mechanical space as a volume that enables the user to experience the treatment cycle. The user moves in a multisensory path of observation and inhabitation, allowing them to reflect on their own impact on the municipal water cycle, as well as experience a new relationship with treated water in which waste is no longer the end, but the beginning, of a treated community spring through a sauna, splash pool, and bathhouse. The stripped plaza allows for exterior cleansing of city runoff as a gradient strategy composed of vegetation, gravel, and enhancement ponds, merging the mechanical and landscape.
This project won the AIA Louisiana 2023 Celebrate Architecture Scholarship and the Tulane University School of Architecture Outstanding Thesis Award 2023
Instagram: @leahb_arch, @ckreisel_arch, @tulanearch
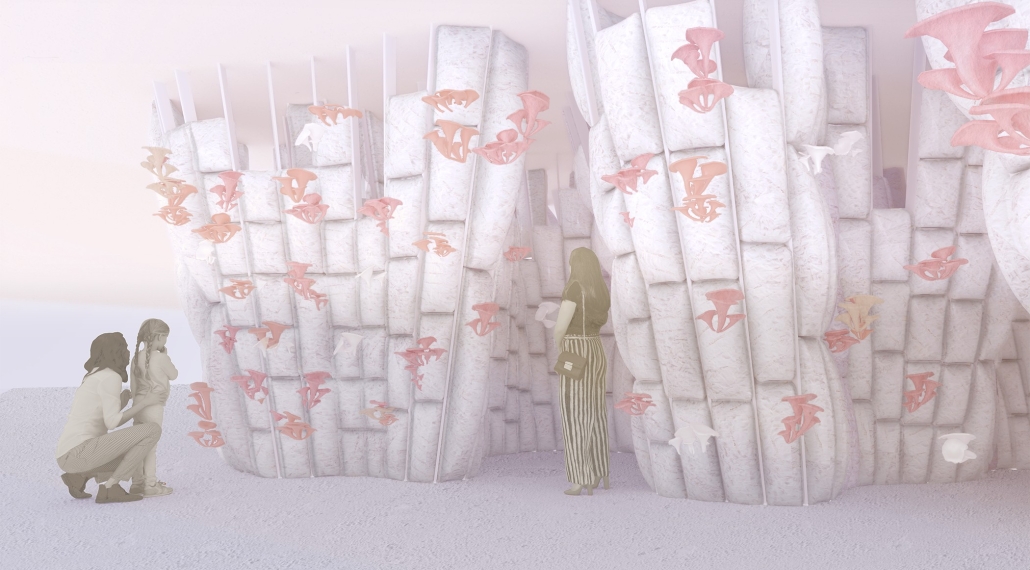
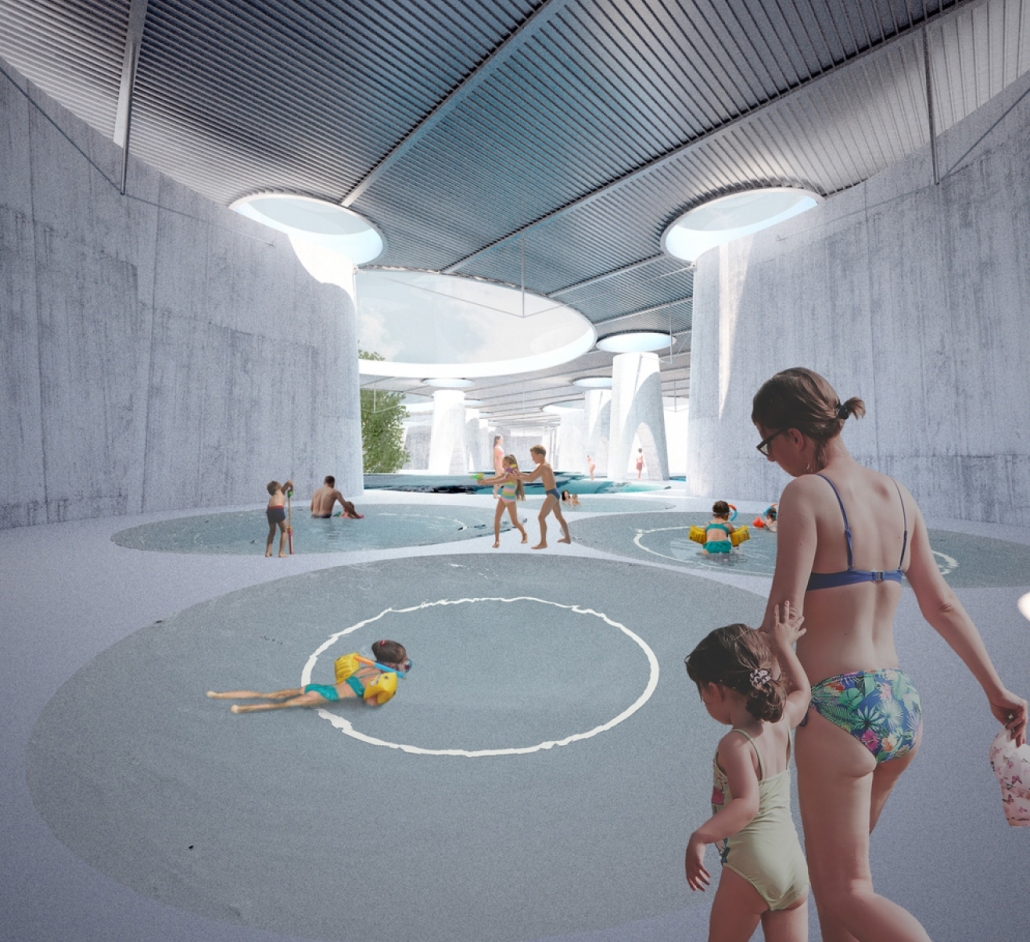
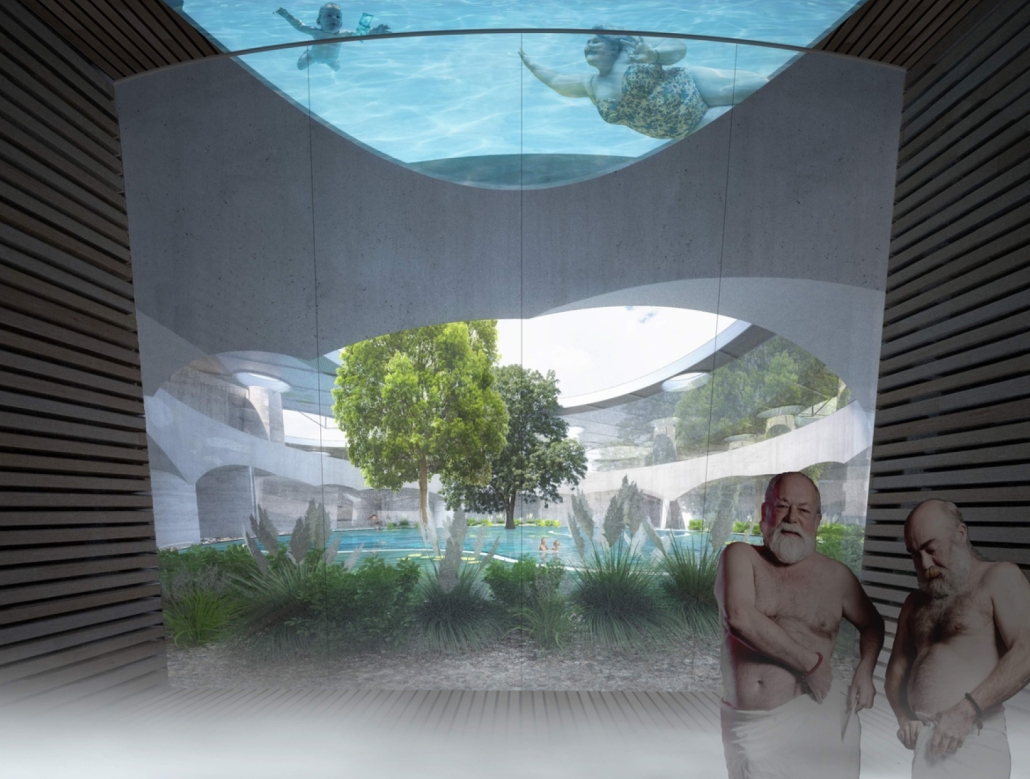
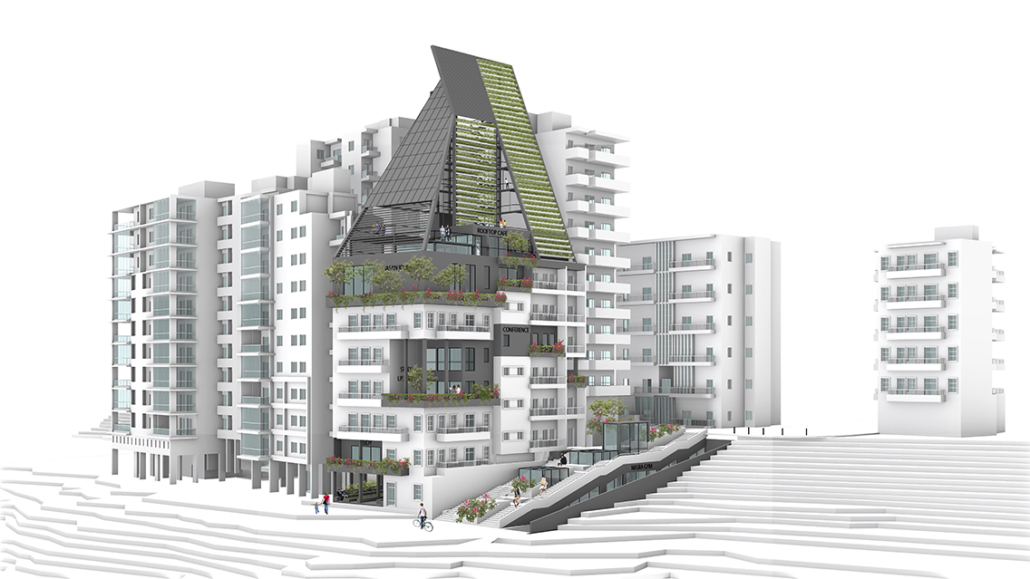
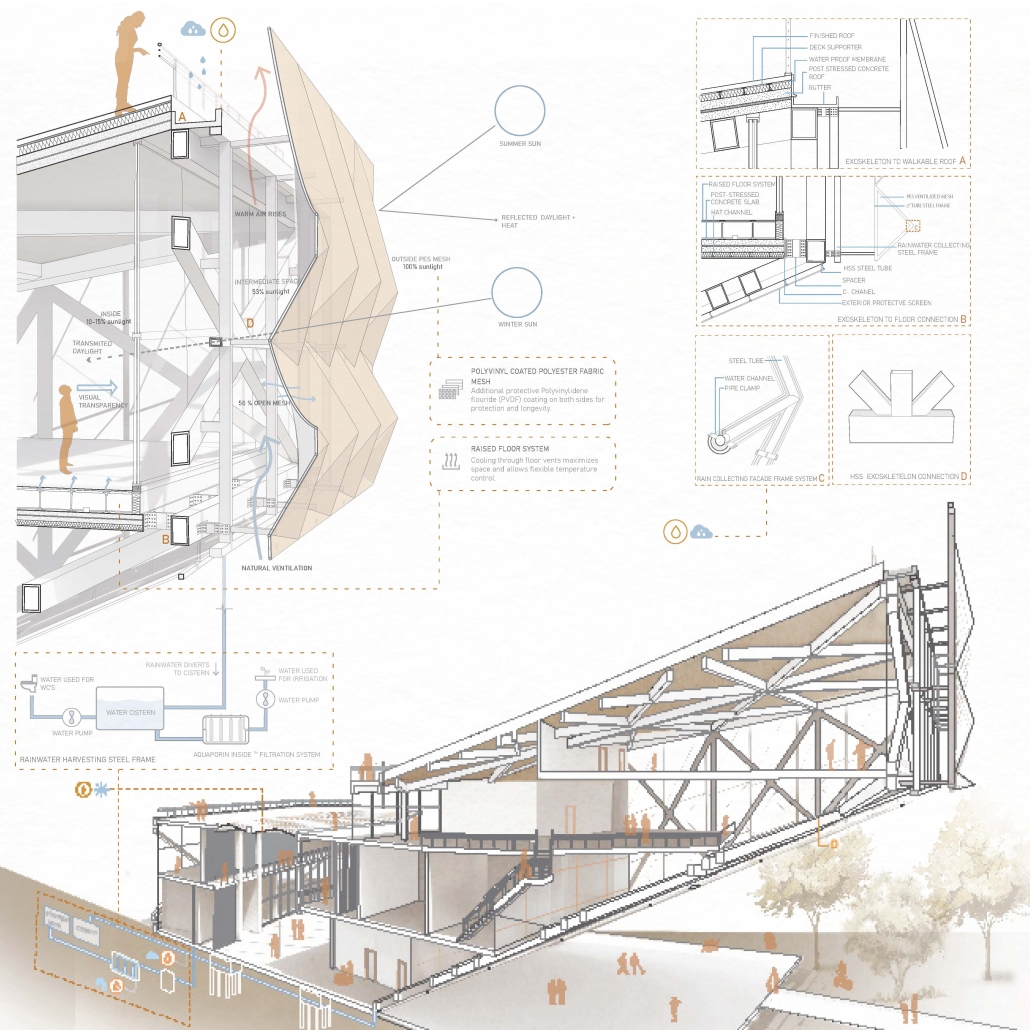
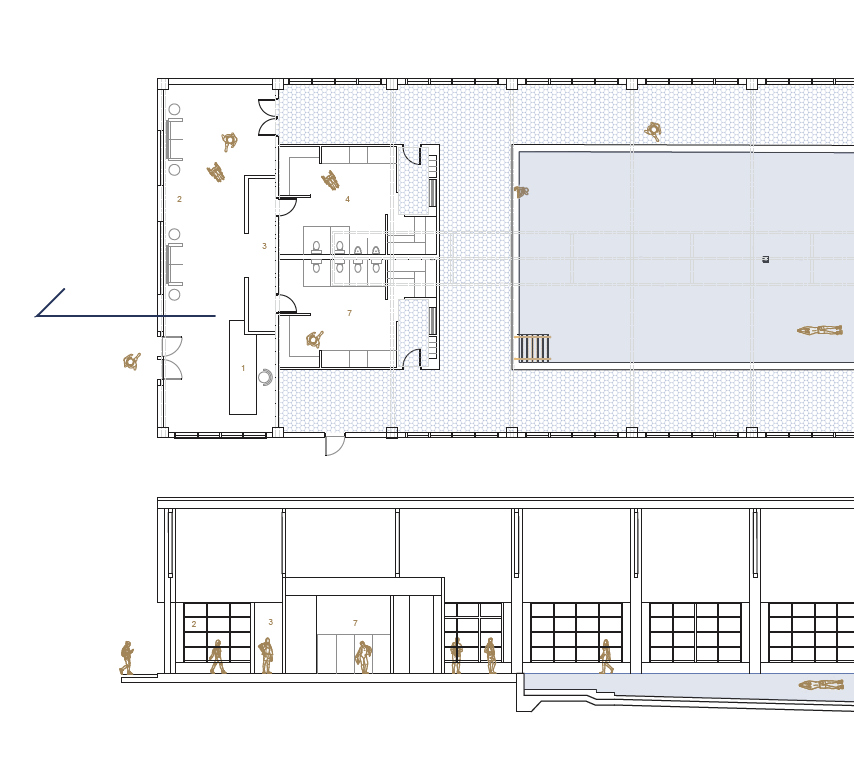
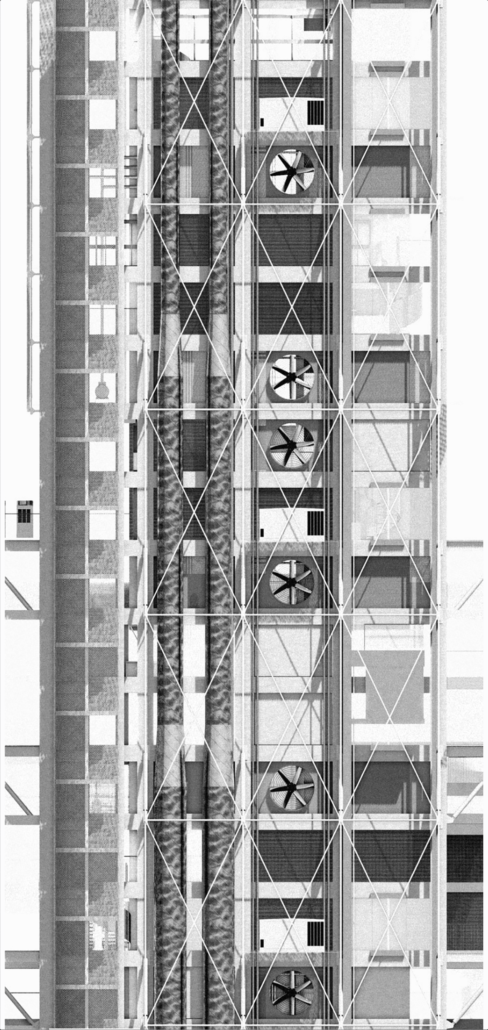
SULIS: Hydrotherapy Centre and Spa by Alanis Baez Colon, BFA Architecture ‘23
Savannah College of Art and Design | Advisor: Daniel Brown
Minerva Sulis: Celtic goddess of healing and sacred waters.
In the bustling modern world, where stress and tension have become an everyday reality, the need for holistic healing has become increasingly vital. Water has been known for its remarkable mental and physical healing properties in many cultures. Sulis Hydrotherapy Centre and Spa seeks to create a haven of tranquility, where the power of water is harnessed to promote a deeper state of well-being. The building and site design marry to create a journey for its users, where water is highlighted as a transformative element in healing the human body, mind, and spirit.
Nestled in the French Broad River Park, North Carolina, Sulis harmoniously integrates with its surroundings. Situated next to a flowing river, the building takes inspiration from the natural allure of water to create a sensory experience that fosters healing. From end to finish, the site design aims to create an immersive journey for users of all ages allowing them to engage and connect with water in diverse and captivating ways. Finally, at the end of the journey, visitors reach their final destination- Sulis Hydrotherapy Centre and Spa.
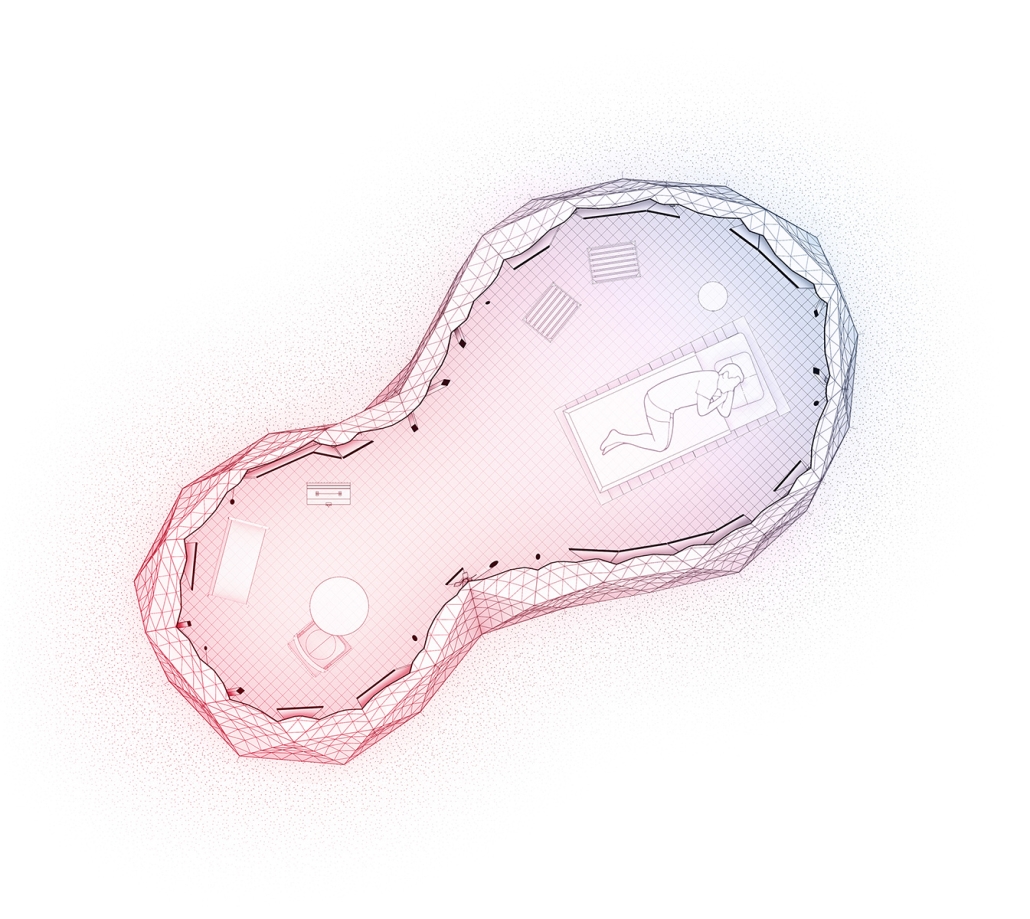
Sulis encapsulates the belief that water holds remarkable healing properties by offering a range of pools and spas, each carefully designed to cater to the different needs of the users. A large central public pool at the ground level serves as the heart of the facility, aiming to promote a community-centric space where users of all ages can immerse themselves in the soothing waters and interact with each other. On this level, we can also find the Hydrotherapy pool area where specialized treatments are available for those seeking specific physical therapies. The programmatic elements on the upper levels housed within the cantilevered wings are dedicated to creating a more intimate connection between the users and the water. Here, we can find spaces such as private baths, where users can immerse themselves in mineral waters and heal their minds through meditative therapies. These diverse offerings allow visitors to tailor their experience and find solace in a personalized healing journey.
The façade design was inspired by the fluidity and transparency of water, and its interaction with sunlight creates a captivating façade that constantly transforms throughout the day. Instead of completely concealing the robust steel exoskeleton at the core of the design, the façade celebrates it by still allowing the steel to visually shine through a composition of a lightweight and dynamic material that mimics the cascading and rippling nature of water. The steel exoskeleton acts as a framework upon which the facade elements are anchored, accentuating the fluidity and movement of the design. From night to day, the ever-changing pattern of light and shadow, embraces the dynamic qualities of water and light, offering a visually stunning experience for both occupants and passersby. It establishes a strong connection to lightness, while still expressing the strength and stability of the underlying structure, leaving an unforgettable impression on all who behold it.
This project was awarded Best Senior Project.
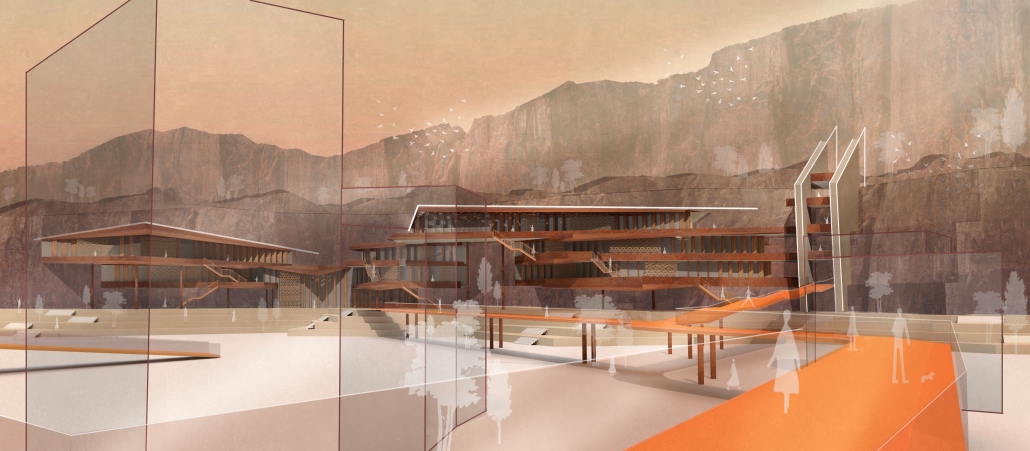
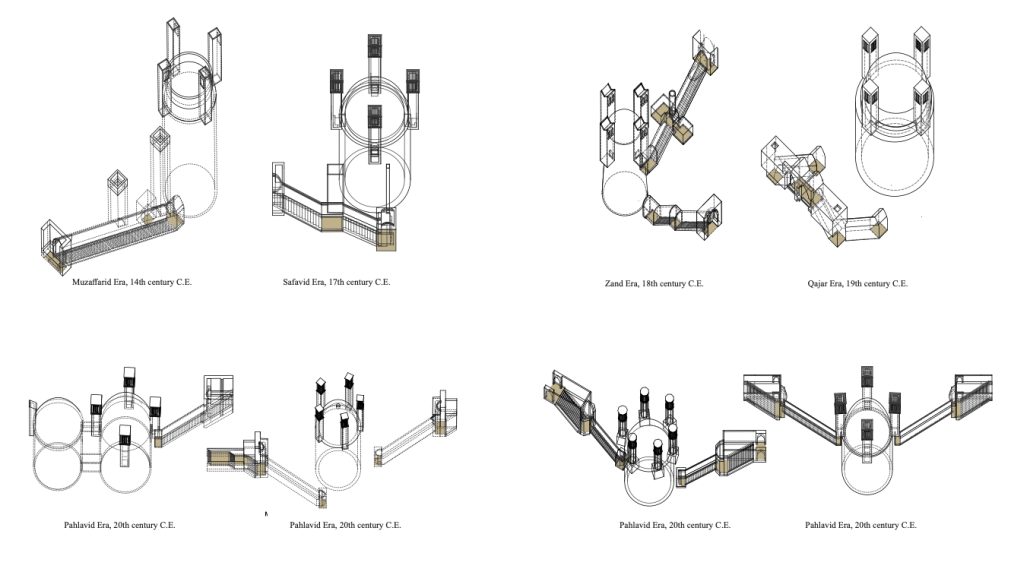
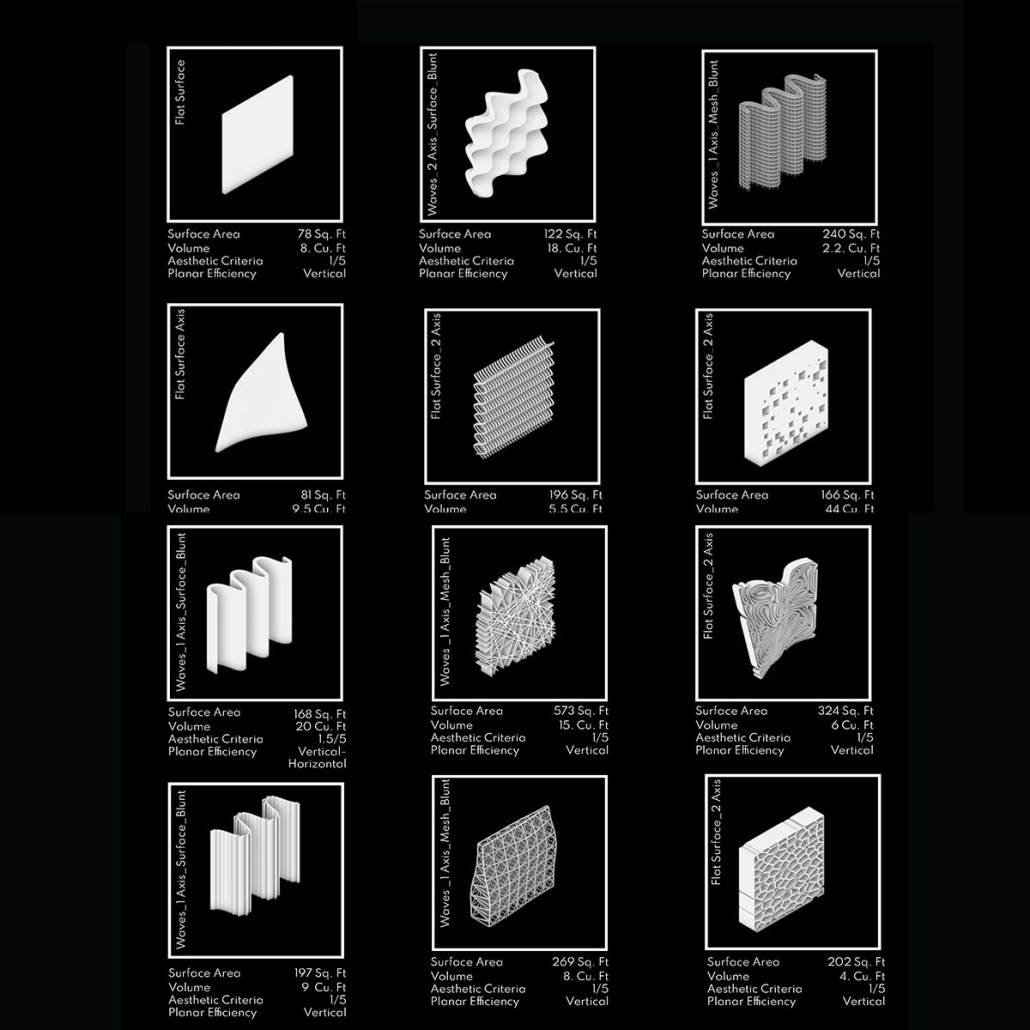
Cultural Infrastructures: Cisterns as Urban Artifacts in Yazd by Najmeh Malekpour Bahabadi, M.S. in Architecture and Historic Preservation ‘23
Texas Tech University | Advisor: David Turturo
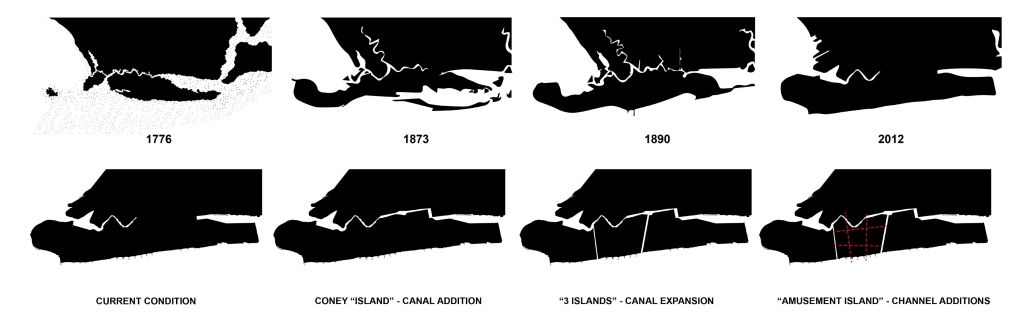
Yazd is a city in the arid central plateau of present-day Iran that arose around a water source in the protective Shirkuh mountain range. This water source established Yazd as an important stop on an ancient trade route, the secondary branch of the Silk Road. Water structures and facilities, including Ab-Anbars (cisterns for local water access), Yakhchaals (ice houses), Asiab (mills), Hammams (bathhouses), and Payaabs (underground ponds), played a significant role in shaping the city. These buildings are located on qanats, elaborate underground canals that guided the city’s development. Today, most of the qanats within the city are drained and have therefore lost their initial function. Some water structures are abandoned and others have been adapted to serve new purposes.
This research considers the contemporary water crisis of Yazd to bring attention to the forces that allowed these ancient water structures to shape the city both historically and presently, after losing their initial function. In particular, this project focuses on cisterns as an architectural typology. The implication is that cisterns comprise a generic architectural form that is bound to the public space and public buildings of the city. This project uses analytical drawings to identify the significance of a building type in forming the city. Such typologies are of particular value for discussing both a building’s singleness and shared features. In other words, this project is concerned not only with the forms of buildings in isolation but also with the external forces that shape those buildings and are shaped by them. As such, the cisterns act as a historical grammar for a city shaped by the architecture of water.
Instagram: @na.malekpour, @davidturturo
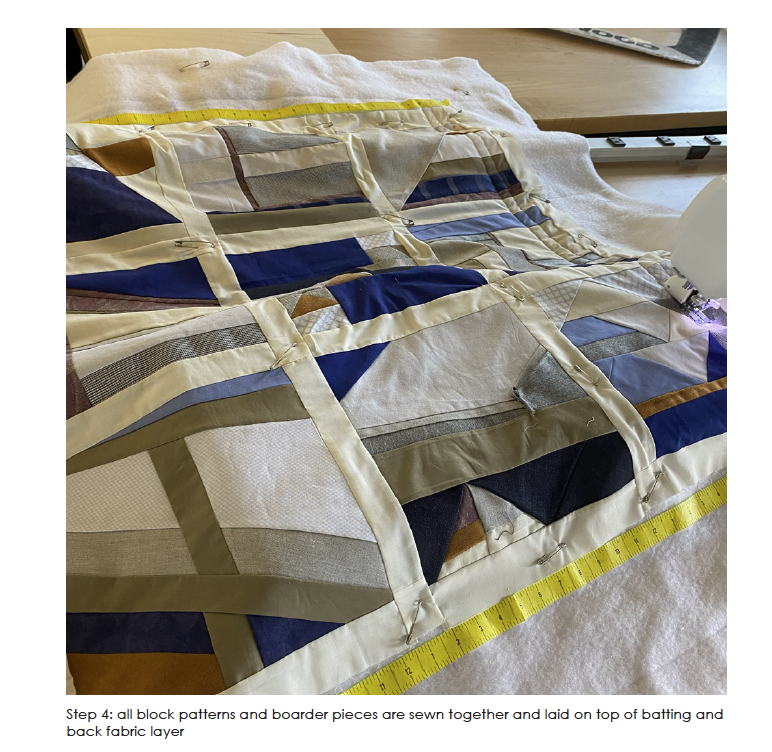
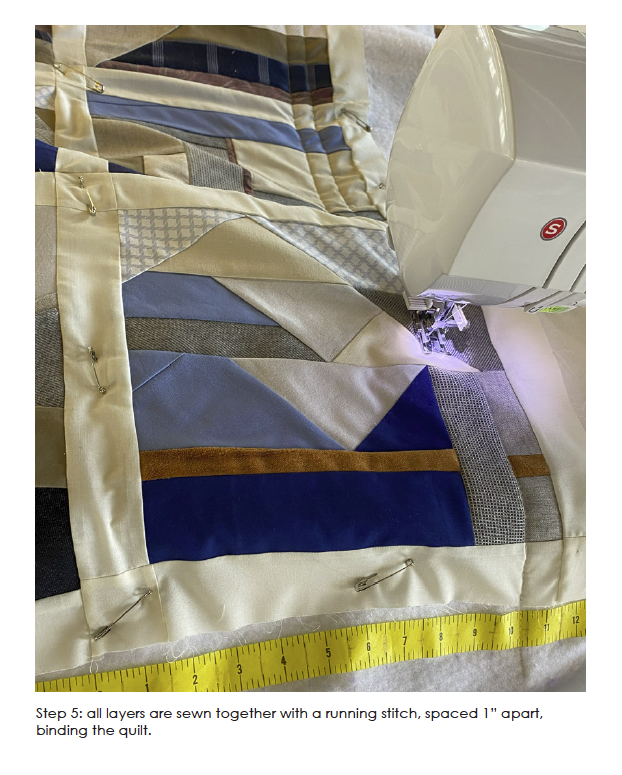
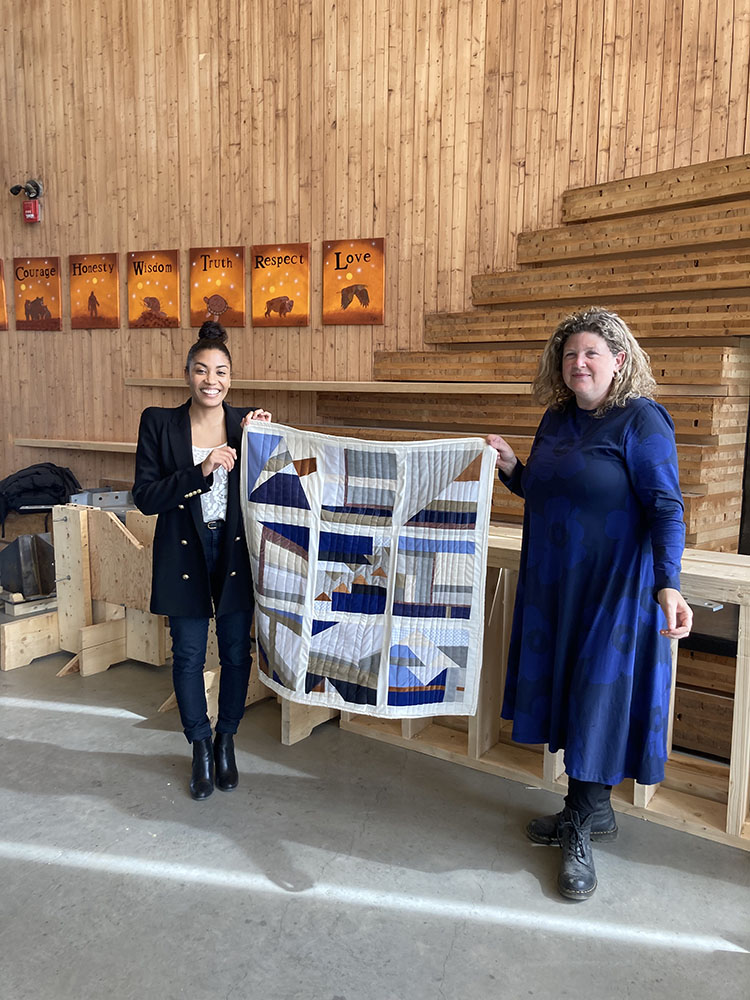
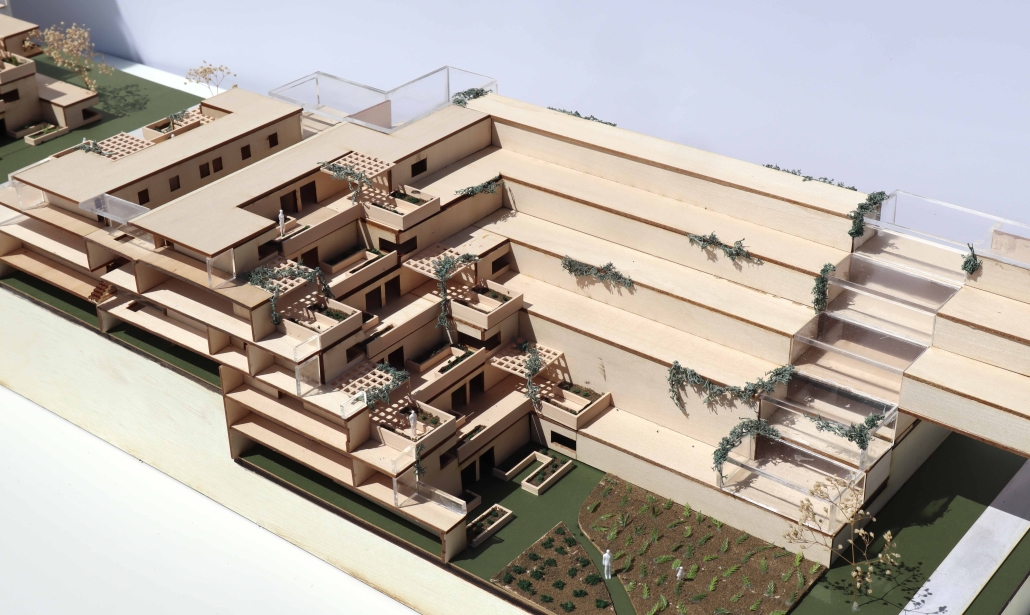
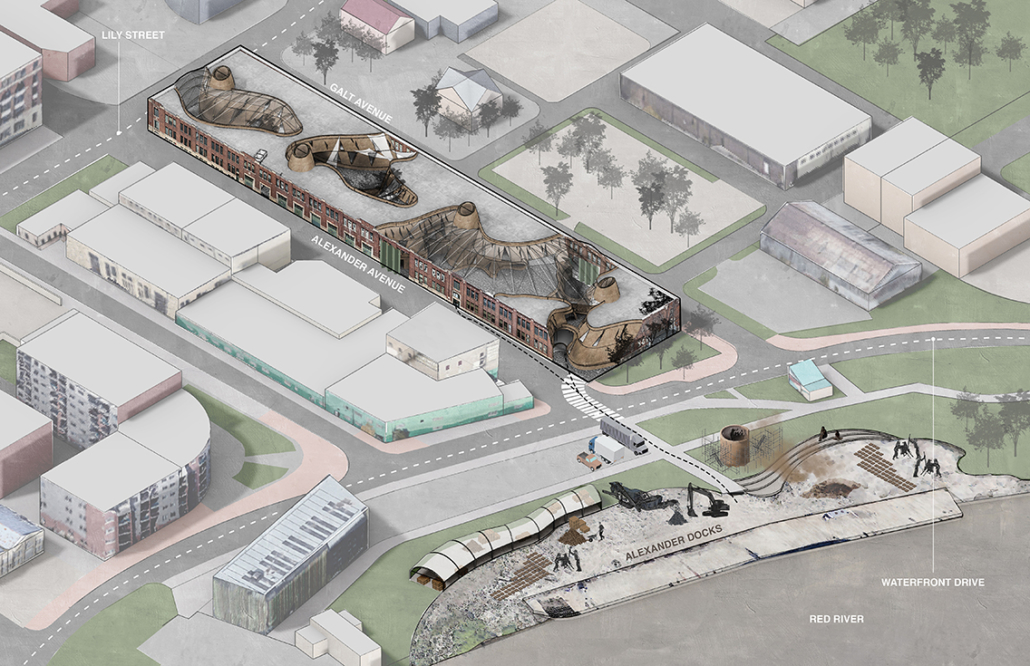
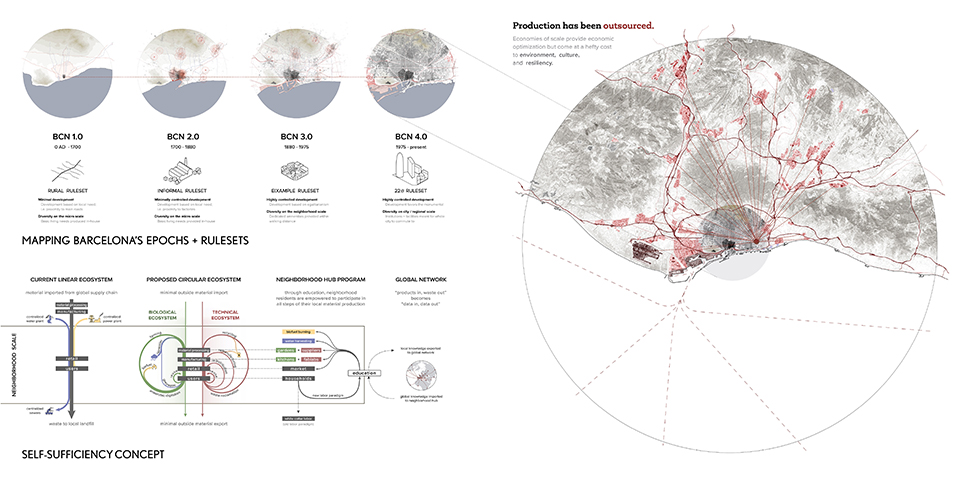
Still Waters Run Deep – Mobilizing Architecture through the Art of Quilting along the Lachine Canal, Montréal, Canada by Ashleigh Abraham, M.Arch ‘23
Laurentian University | Advisors: Shannon Bassett (Advisor), Claire Weisz (Second Reader) & Heather Braiden
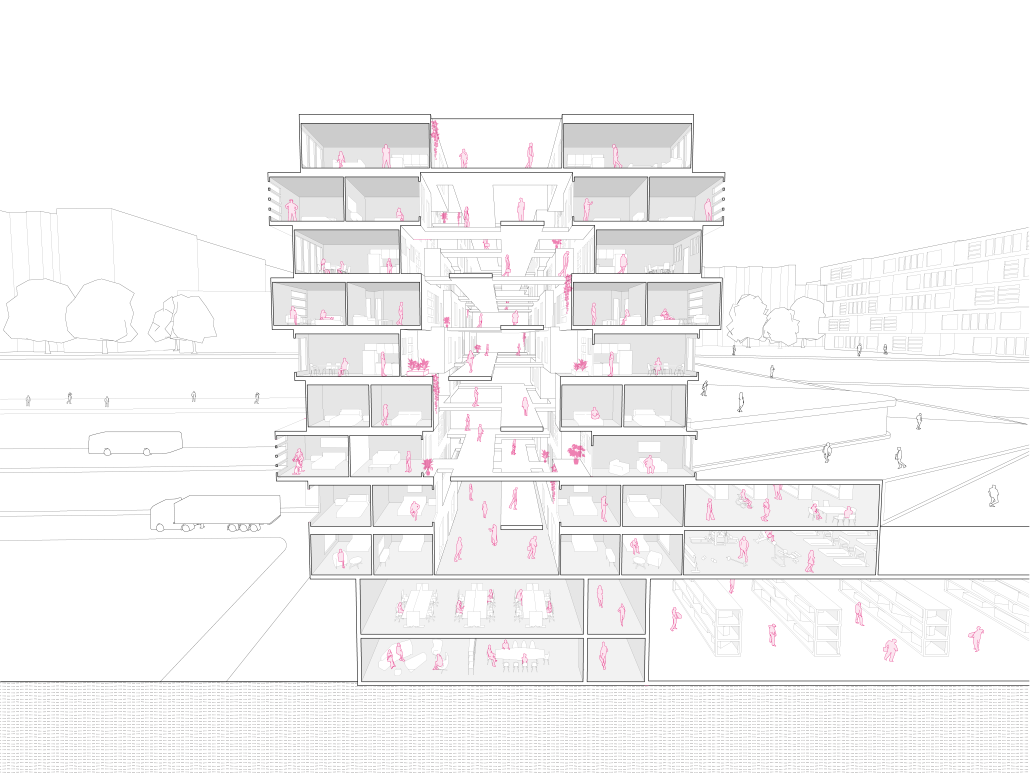
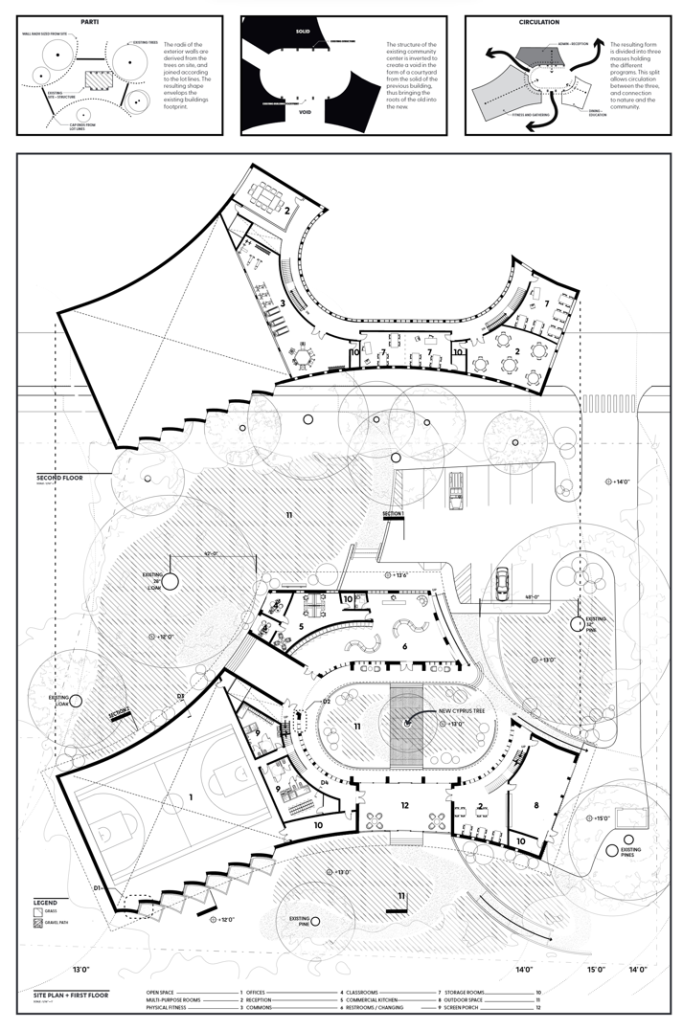
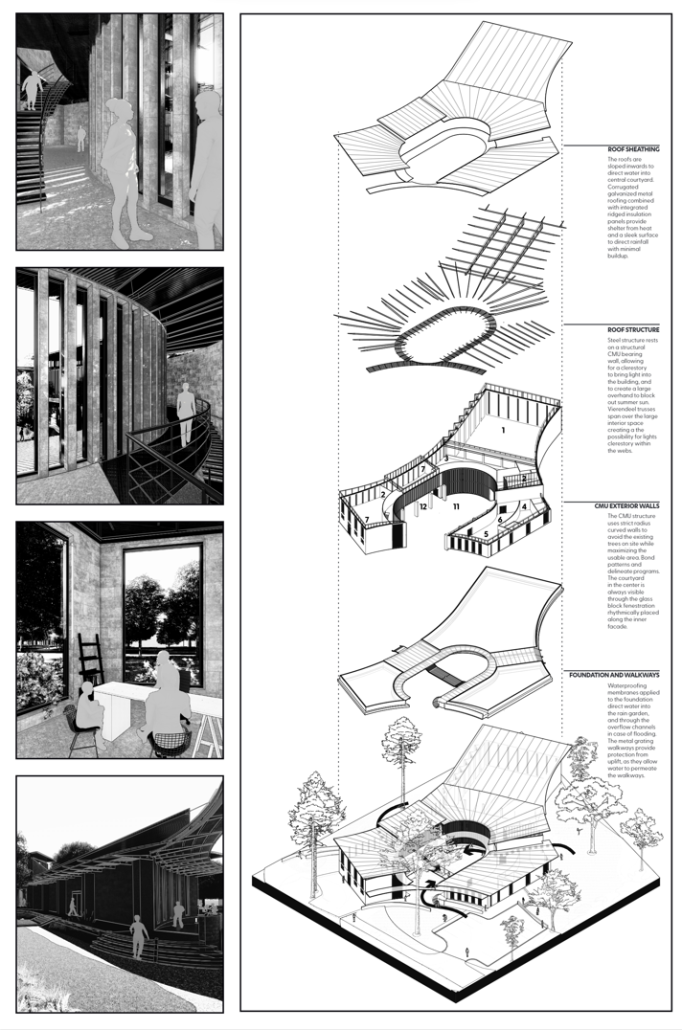
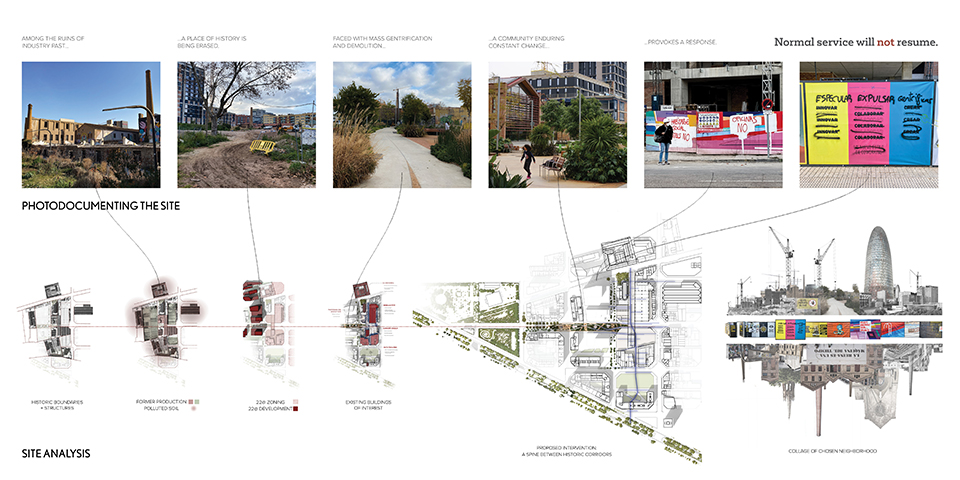
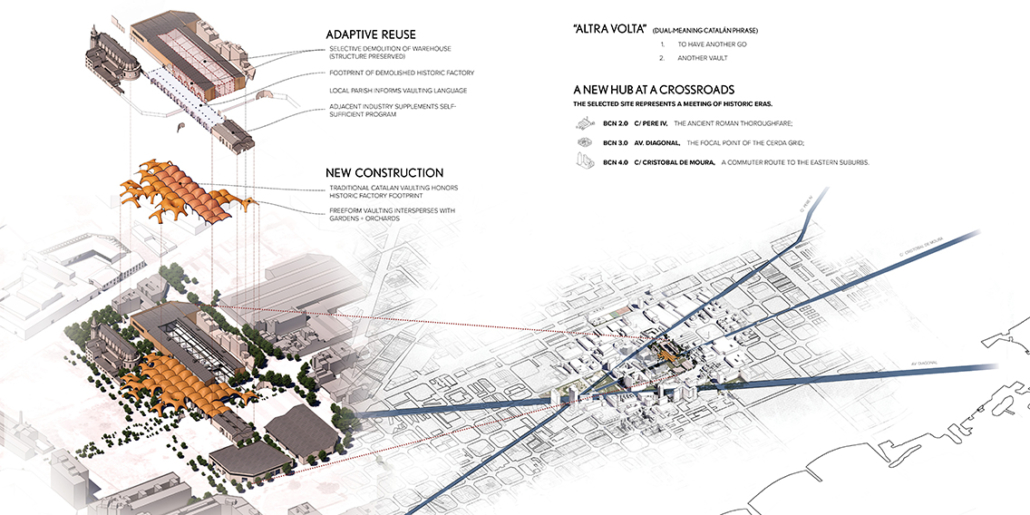
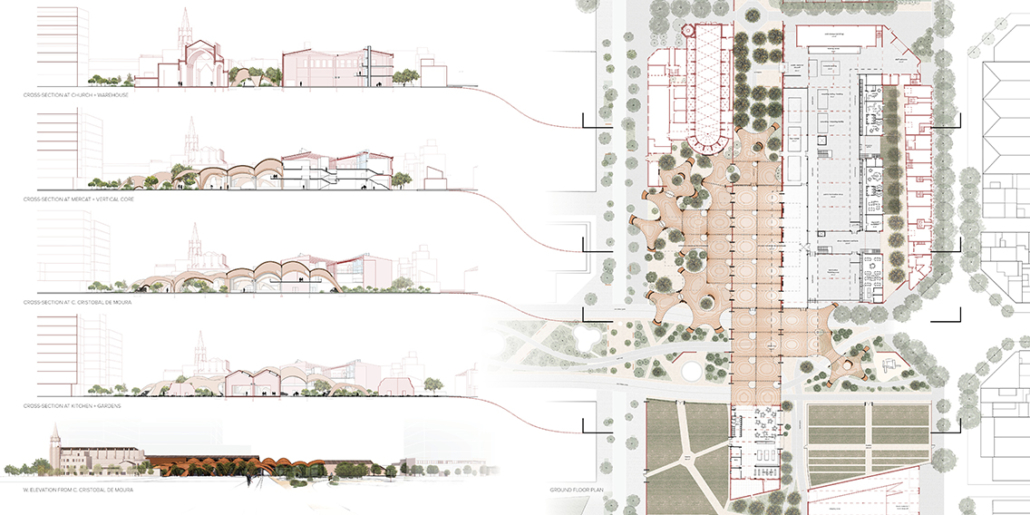
This design research and proposal gives voice to the histories of Montréal’s Black community which, until now, have largely been untold, save through oral histories. The design proposal is for a community centre for the Black communities of Montréal’s Little Burgundy and Pointe St. Charles. This includes a Community Pool and Centre for Oral Archives, located on one of the derelict post-industrial sites along Montréal’s post-industrial Lachine Canal.
Excerpted from Ashleigh’s thesis:
Keywords: water heritage, public space, deindustrialization, eco-gentrification, oral histories, spatial justice, quilting, stewardship, Montreal
“The project maps the relationship with Montréal and water. Through the proposed re-greening and anticipated gentrification of the Lachine Canal, the critical histories of residents, neighborhoods and industrial workers have been neglected. Only through oral histories their narratives have lived on, acknowledging a fraught, yet rich and diverse history of Montréal’s industrial era. Through the intersection of interdisciplinary theory and place-based investigation, this thesis explores how architecture might utilize water as an agent to challenge existing power structures to offer cultural inclusivity and stewardship. The craft of quilting is used as a methodology for employing oral histories and establishing a framework for equitable access to the Lachine Canada. The framework established is applied to one of the canal’s discarded industrial sites, addressing spatial injustices and opportunities for community engagement within the realm of public space.
This thesis was inspired by a walk along the Lachine Canal with my grandfather, during which we discussed the canal’s history and the politics that shaped its current state. My grandparents were born in Montréal to parents from the Caribbean Island of Barbados and witnessed the city’s evolution firsthand. Oral histories were essential to their everyday lives. Offering insights into the history and experiences of a community that cannot be found in conventional records. These extraordinary tales included hardship and success, happiness and sorrow, frustration and perseverance. In her later years, my grandmother never lost her sense of belonging. She frequently referred to “home” as her childhood residence on Atwater Avenue, once in the St. Antoine neighborhood. Her residence has been demolished, and her neighborhood is unrecognizable. However, her memories were as strong and vivid as when she was a child. My grandmother’s home was expropriated and demolished, forcing her family to relocate to a place that would never feel like “home.” They persevered in maintaining strong ties to the people and locations they once frequented, despite being uprooted. They may have encountered obstacles, but they were not vanquished by their situation. In spite of adversity, they became community pillars. They forged ties with a community split apart by people and structures that did not recognize their value and place within the urban fabric of the city.”
This project won the McEwen School of Architecture (MSoA) Architecture and Society Award.
Instagram: @shannonbassett
See you in the next installment of the Student Showcase!